Molecular marker closely linked with cabbage type rape seed coat color and application of molecular marker
A Brassica napus and molecular marker technology, applied in the field of plant molecular genetics, can solve problems such as the lack of versatility of linkage markers, the lack of a clear genetic model, and the complex genetic mechanism of yellow seed traits in Brassica napus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1 Construction and Character Measurement of Brassica napus Recombinant Inbred Line Mapping Population
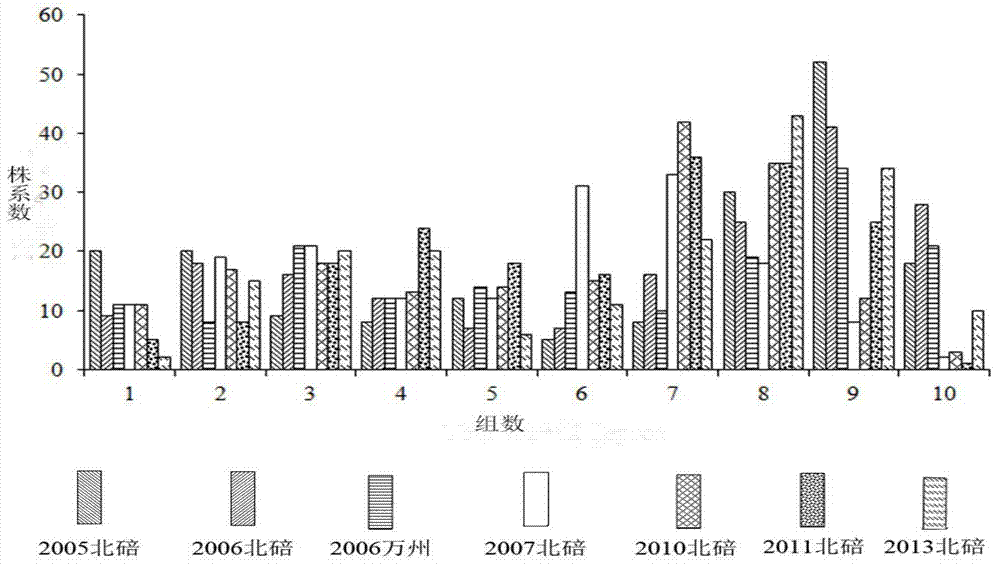
[0034] The mapping population used in this example is a recombinant inbred line population constructed by continuous selfing of the brassica napus yellow seed line GH06 and black seed line ZY821 by continuous selfing. The phenotypic data of seven different environments of this group were obtained by using a near-infrared analyzer, and the analysis of the data by the analysis software SPSS 13.0 showed that the color of the testa in different environments showed a continuous approximately normal distribution, with a wide range of variation. It is proved that the seed coat color of Brassica napus is a typical quantitative trait ( figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2 Extracting Genomic DNA
[0036] According to the CTAB method of Doyle (1990) et al., the CTAB method was slightly improved, and the genomic DNA of the leaves of the two parents of Brassica napus GH06 and ZY821 and the recombinant inbred line population were extracted. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0037] A) Put about 0.1g of fresh leaves into a 2ml centrifuge tube, and put 4 steel balls to crush the leaf tissue.
[0038] B) To prevent oxidation during pulverization, 100 μL of 2×CTAB extraction buffer containing 2% β-ME (mercaptoethanol) was added.
[0039] C) Put the 2ml centrifuge tube filled with materials into SPEX GENO 2010 in the United States A high-throughput tissue grinder pulverizes leaf tissue at a speed of 1250 rpm for 55 s.
[0040] D) After the pulverization is completed, add 700 μL of CTAB extraction buffer preheated at 65° C., shake vigorously to make it mix quickly, and then keep it at 65° C. for 45 minutes, shaking 3-4 time...
Embodiment 3
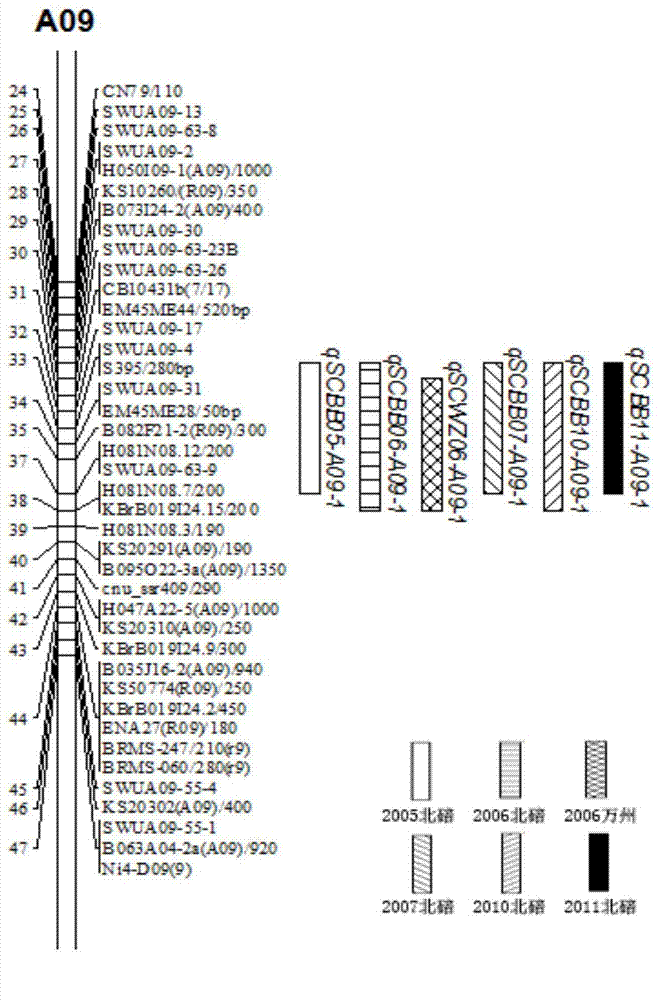
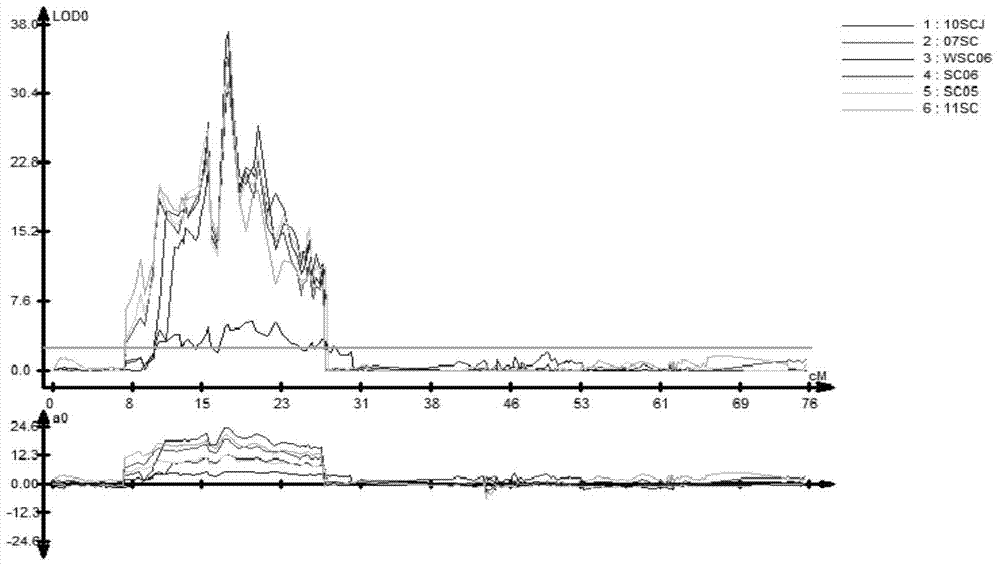
[0045] Example 3 Construction of Molecular Marker-Linked Genetic Map of Brassica napus and Mapping of QTL for Seed Coat Color
[0046] Four different markers, SSR, SRAP, RAPD and IBP, were used to construct the genetic linkage map of molecular markers in Brassica napus. The SSR markers mainly include: Na-, Ol- published by BrassicaDB (http: / / www.ukcrop.net) , Ra-, Ni-primers, a total of 284 pairs of primers; Piquemal et al. (2005) published a total of 157 pairs of CB-, BRAS-, MR- and MD primers; a total of BRMS-primed 130 pairs (Fu et al., 2007); 97 pairs of FITO-primers published by Osborn Laboratory; 109 pairs of sR, sN, sO, nga-, BN-primers published by NAFF in Canada; Dr. Beom-Seok Park of Korea A total of 240 pairs of KS-, H-, B- and S-primers donated by Dr. Soo-Jin Kwon (http: / / brassicadb.org / brad); BnGMS-primers published by Cheng et al. (2009) 135 pairs; a total of 124 pairs of EJU, ENA, GOL, niab- and cnu-primers published by Choi et al. (2007); and SWU-specific prim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com