Method for knocking out HPV (human papilloma virus) E6E7 oncogene by use of TALEN (transcription activator-like effector nuclease)
A human papillomavirus, E6E7 technology, applied in the field of knocking out high-risk human papillomavirus E6E7 oncogene, can solve the problems of frame shift mutation, gene insertion or deletion, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0036] Example 1. Construction of TALEN-512 expression vector
[0037] The full-length sequence information of the E6E7 oncogene of HPV16 was obtained from the NCBI website, and the sequence was copied to the TALEN RVD sequence online design tool (https: / / tale-nt.cac.cornell.edu / node / add / talen / ) to complete the design. The TALENs pair targeting the 512th base of the HPV16E7 gene (counting from the first base of the E6E7 gene) was selected and named TALEN-512. The targeted DNA sequence is:
[0038] TALEN-512: ATGTTAGATTTGCAACCAGAGACAACTgatctctactgttatgagcAATTAAATGACAGCTCAGAGGAGG
[0039] Among them, the capital letter is the recognition and binding region of TALE, and the lowercase letter part is the Spacer region, that is, the FokI enzyme cleavage region in TALEN. specifically,
[0040] TALEN-512L: ATGTTAGATTTGCAACCAGAGACAACT
[0041] TALEN-512R: CCTCCTCTGAGCTGTCATTTTAATT
[0042] The preferred RVD sequence corresponding to the recognition module TALEN-512L:
[0043] N...
example 2
[0048] Example 2. TALEN-512 induces apoptosis
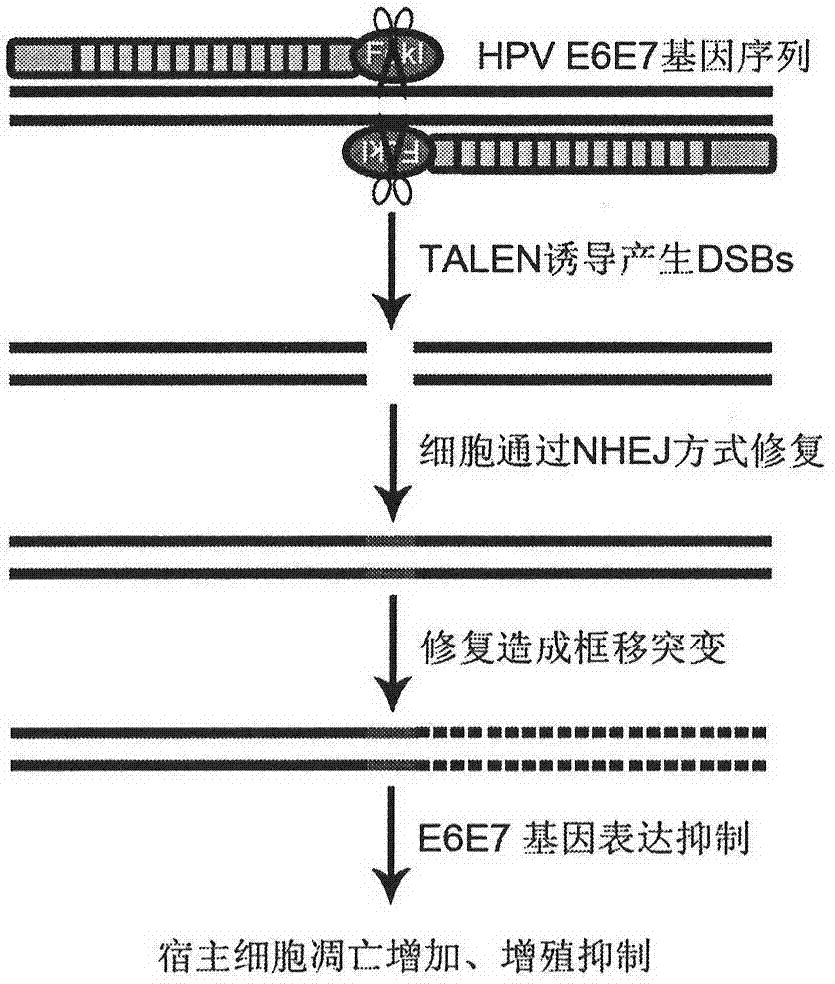
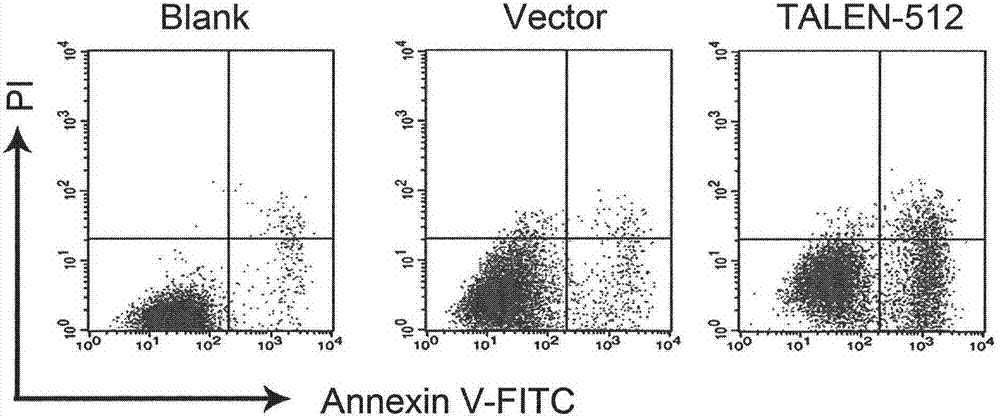
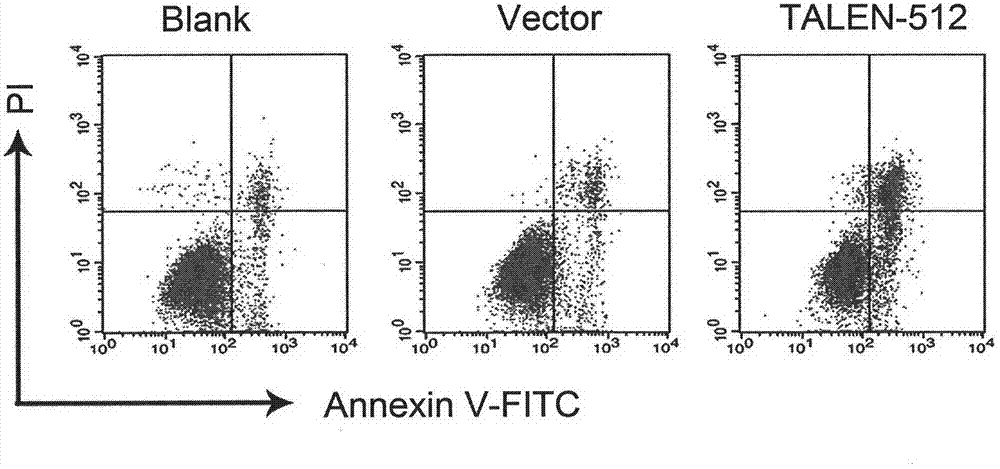
[0049] The TALENs expressed after transfection of TALEN-512 targeting HPV16E6E7 into cells can quickly recognize and bind to the target sequence, and the FokI endonucleases expressed on the two monomers are spatially close and dimerize cleavage of the target sequence, forming a double-strand DNA break (DSB), which initiates the cell's self-repair. Because cells preferentially use the error-prone NHEJ method for repair, it is easy to cause base insertion or deletion during repair, resulting in frame-shift mutation of codons, which eventually inhibits the expression of HPV16E6E7 protein. The expression of E6E7 protein is the prerequisite for the immortalization of HPV-infected cells. Therefore, after the expression of E6E7 protein is inhibited, the proliferation ability of HPV-infected cells decreases and the apoptosis ability increases.
[0050] The specific operation method is:
[0051] (1) Cell culture
[0052] Cervical cance...
example 3
[0058] Example 3. Verification of cutting efficiency of TALEN-512
[0059] The DSBs formed by cutting TALEN after functioning in cells can rapidly induce cells to repair themselves. In eukaryotic cells, in order to avoid the impact of DNA degradation caused by DNA breaks on cell survival, most cells use NHEJ to directly connect the two ends, but this error-prone repair method is very easy to introduce small DNA fragments at the break point. The gene insertion or deletion of the fragment causes the frame shift mutation of the codon, which finally hinders the expression of the target gene. At this time, if the nucleotide sequence that has been cleaved by TALEN and repaired by the cell is mixed with the untreated normal (wild-type) nucleotide sequence and then annealed and extended, a cleavage site can be formed. A specific hybrid duplex where there is a mismatch (corresponding to a repaired base insertion or deletion). This hybrid duplex can be recognized by T7 Endonuclease I ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com