Fermented red ginseng and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for red ginseng and original ginseng is applied in the field of preparation of fermented red ginseng, which can solve the problems of reducing efficiency, destroying ginseng saponin components, and low content, saving processing time and cost, preventing cross-contamination problems, and increasing soap production. The effect of angular content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
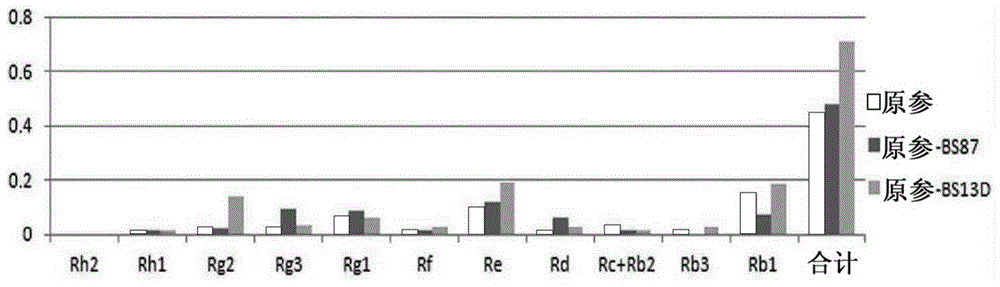
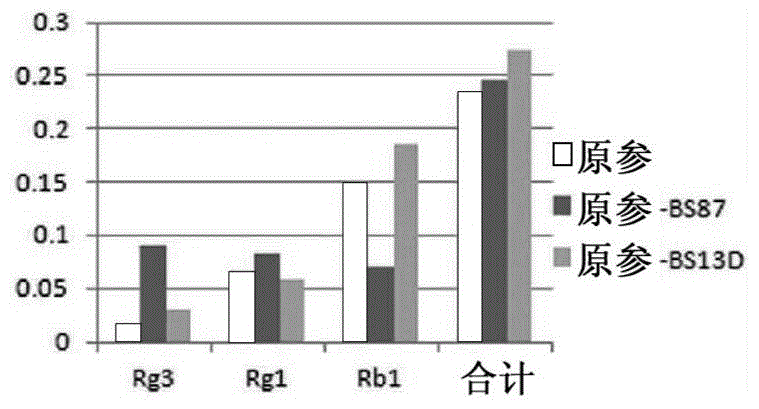
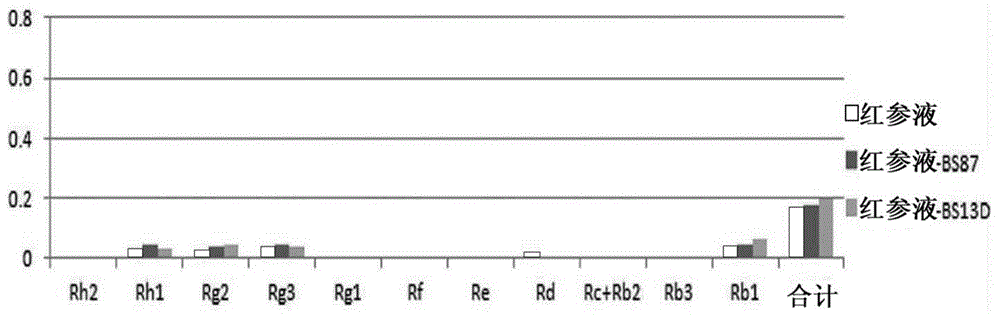
[0034] The fermented red ginseng of the present invention is prepared by obtaining and culturing the preserved antagonistic microorganism Bacillus velezensis BS87 (strain preservation number: KACC 91217P).
[0035] The preparation method of the fermented red ginseng of the present invention comprises: (a) the process of preparing red ginseng; and, (b) the process of inoculating KACC 91217P on the prepared red ginseng and carrying out fermentation.
[0036] The red ginseng can be prepared through the following steps: 1) a step of mixing raw ginseng and water, and crushing with a pulverizer; and, 2) a step of steaming at 95-125°C for 10-20 minutes. For red ginseng, raw ginseng was mixed with water, crushed with a pulverizer, and steamed at 121° C. for 15 minutes in an autoclave. In addition, regarding red ginseng, a prepared red ginseng liquid or red ginseng concentrate can also be prepared. Using raw ginseng or prepared red ginseng liquid for fermentation can save processing t...
Embodiment 1
[0050] 95 g of raw ginseng was mixed with 190 g of water, and after pulverization with a household grinder, 90 g of each was put into an Erlenmeyer flask, 10 g of water was added, and steamed in an autoclave at 121° C. for 15 minutes. The BS87 strain (Bacillus velezensis) and the BS13D strain (Bacillus sp) were smeared on the medium, cultured in a 30° C. incubator, and diluted in sterile water to prepare inoculum. Inoculate 1ml of the inoculum BS87 strain (9.5×10 5 cfu / ml), BS13D strain (6.4×10 5 cfu / ml). The sample bacteria are placed in a shaking incubator and cultured for 3 to 10 days under the conditions of 30° C. to 35° C. and 150 rpm. Red ginseng not inoculated with the above-mentioned inoculum was used as a control group.
Embodiment 2
[0052] As for the red ginseng liquid used in the experiment, 100 g of commercially available red ginseng liquid of Company A was prepared. The BS87 strain (Bacillus velezensis) and the BS13D strain (Bacillus sp) were smeared on the medium, cultured in a 30° C. incubator, and diluted in sterile water to prepare inoculum. Inoculate 1ml of the inoculum BS87 strain (9.5×10 5 cfu / ml), BS13D strain (6.4×10 5 cfu / ml). The sample bacteria are placed in a shaking incubator and cultured for 3 to 10 days under the conditions of 30° C. to 35° C. and 150 rpm. Red ginseng not inoculated with the above-mentioned inoculum was used as a control group.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com