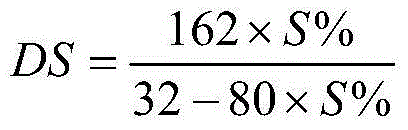Sulphating method for improving water solubility of yeast beta-D-glucan
A technology of sulfate esterification and glucan, applied in the field of food processing, can solve the problems of low degree of substitution and uneven distribution, and achieve the effects of wide application range, reduction of operational risk, increase of utilization rate and added value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
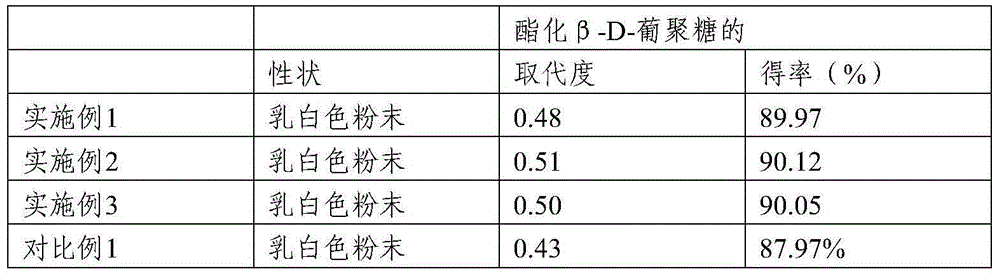
[0044] Example 1, the sulfation method for improving the water solubility of yeast β-D-glucan
[0045] 1) Dissolve 100 g of yeast β-D-glucan in 2 L of DMSO (containing 5 M urea), stir and dissolve to obtain solution a.
[0046] 2) Place solution a in an ice bath, and perform ultrasonic treatment at a working frequency of 20KHz with a power of 400W. The treatment time per cycle is 20s, and the intermittent time is 5s. Cycle 10 times, and the ultrasonicated solution is placed in an ice bath. While stirring, slowly dropwise add 5% H 2 SO 4 DMSO 2L (solution a with 5% H2 SO 4 The volume ratio of DMSO is 1:1, the same below), to obtain solution b.
[0047] 3) Put solution b in an oil bath constant temperature oscillator at 100°C, and carry out esterification reaction at a speed of 100rpm. After reacting for 2 hours, quickly cool the reaction solution to room temperature, add deionized water to 80L, and pass through 0.8μm Polyester membrane microfiltration to remove unreacted ye...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2, the sulfation method for improving the water solubility of yeast β-D-glucan
[0049] 1) Dissolve 500 g of yeast β-D-glucan in 12.5 L of DMSO (containing 5 M urea), stir and dissolve to obtain solution a.
[0050] 2) Place solution a in an ice bath, and perform ultrasonic treatment at a working frequency of 18KHz with a power of 400W. The treatment time per cycle is 20s, the intermittent time is 5s, and the cycle is 12 times. The ultrasonicated solution is placed in an ice bath. While stirring, slowly dropwise add 5% H 2 SO 4 12.5 L of DMSO to obtain solution b.
[0051] 3) Put solution b in an oil bath constant temperature oscillator at 100°C, and carry out esterification reaction at a speed of 100rpm. After 3 hours of reaction, quickly cool the reaction solution to room temperature, add deionized water to 250L, and pass through 0.8μm Polyester membrane microfiltration to remove unreacted yeast β-D-glucan particles. The filtered sulfated yeast β-D-glucan ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3, the sulfation method for improving the water solubility of yeast β-D-glucan
[0053] 1) Dissolve 800 g of yeast β-D-glucan in 18 L of DMSO (containing 5 M urea), stir and dissolve to obtain solution a.
[0054] 2) Place solution a in an ice bath, and perform ultrasonic treatment at a working frequency of 15KHz with a power of 400W. The treatment time per cycle is 20s, and the intermittent time is 5s. Cycle 11 times, and place the ultrasonicated solution in an ice bath. While stirring, slowly dropwise add 5% H 2 SO 4 18L of DMSO to obtain solution b.
[0055] 3) Put solution b in an oil bath constant temperature oscillator at 100°C, and carry out esterification reaction at a speed of 100 rpm. After 2.5 hours of reaction, quickly cool the reaction solution to room temperature, add deionized water to 480 L, and pass through 0.8 μm polyester membrane microfiltration to remove unreacted yeast β-D-glucan particles. The filtered sulfated yeast β-D-glucan is subj...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com