Method for expressing proteins by using plant petal cell protoplast
A technology of protoplasts and plant petals, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of no specificity of tissues and organs, not as good as the real state of petal cells, etc., and achieve the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
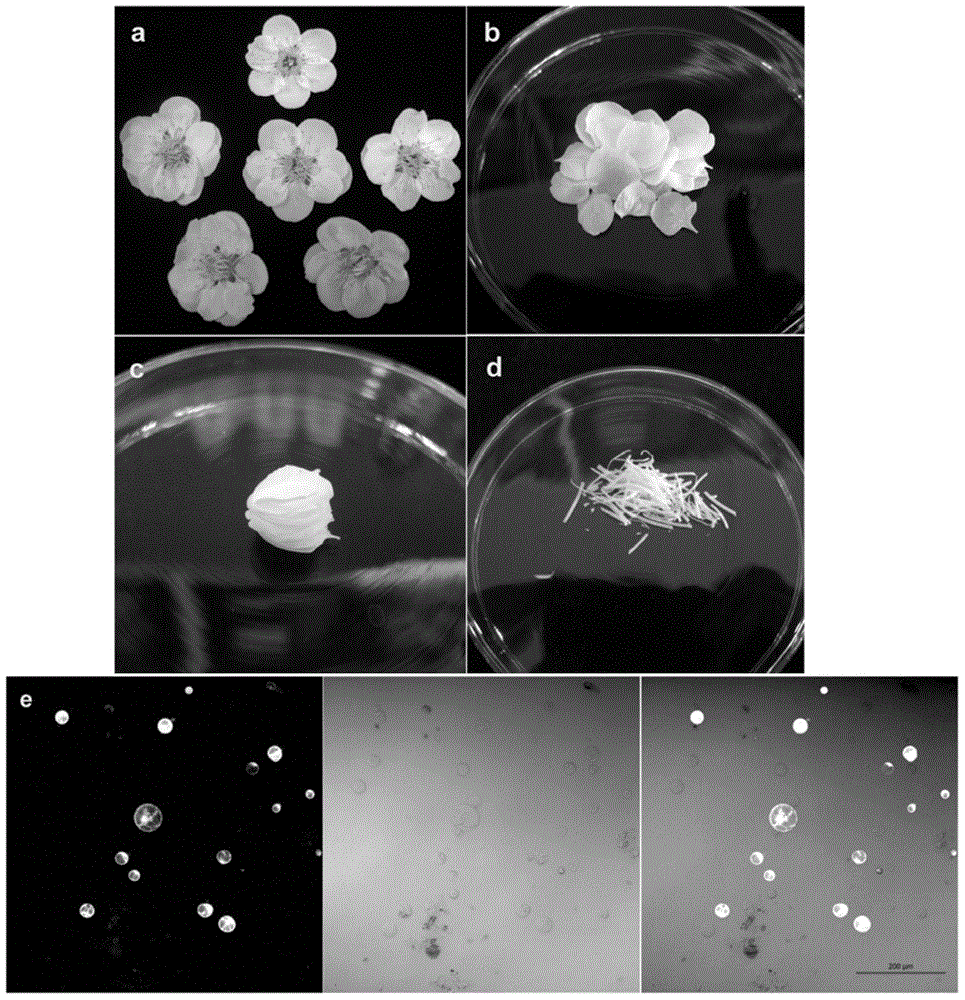
[0039] In the following, the petals of the plum blossom variety "Green Calyx with long stamens" are used as materials, and the vector pSuper1300-GFP encoding green fluorescent protein driven by the pSuper promoter is used as the exogenous target gene to be transformed, and the present invention will be further described in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0040] Tissue processing: select six newly bloomed plum blossoms (such as figure 1 a), remove the petals (such as figure 1 b), stack 10-20 petals together (such as figure 1 c), use a blade to cut the petals into filaments (1-1.5cm in length and 0.3-0.8mm in width such as figure 1 d), the finer the cut, the more conducive to enzymatic hydrolysis;
[0041] Enzymolysis: Prepared enzymolysis solution 20mL (2% (m / v) Cellulase R-10, 2% (m / v) Resolase R-10, 0.4M Mannitol, 20mM KCl, 10mM CaCl 2, 20mM MES with a pH of 5.7, 0.1% (m / v) BSA and 5mM β-mercaptoethanol) were added to a glass petri dish with a radius of 90mm,...
Embodiment 2
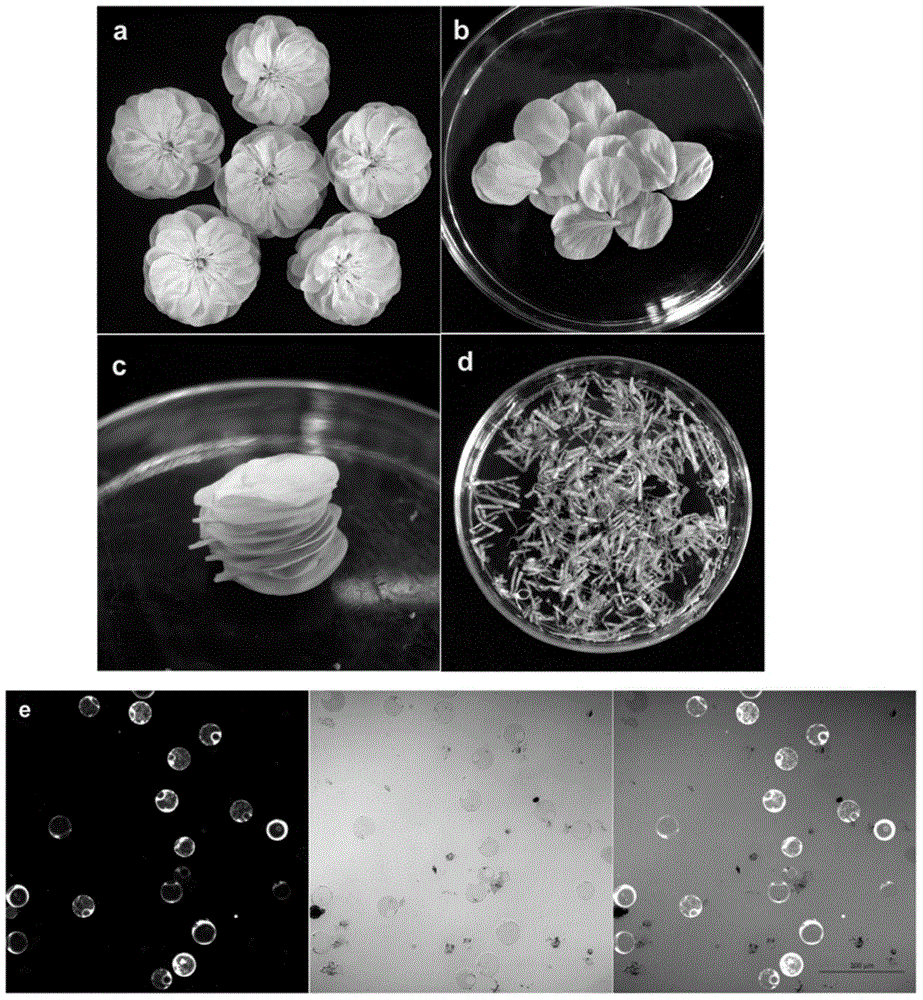
[0051] This example is used to illustrate the preparation of green peach petal protoplasts and the expression of exogenous green fluorescent protein GFP. Method is identical with the preparation of the plum flower petal protoplast of embodiment 1 and exogenous gene transformation (see figure 2 ).
[0052] like figure 2 Shown in e is the morphology of peach petal protoplasts and the expression of green fluorescent protein GFP observed under a 20× laser confocal microscope, and the scale bar is 200 μm. From left to right: the images obtained under 484nm excitation light, under bright field, and after synthesis. According to statistics, the transformation efficiency is about 85%, so this method is also very suitable for the preparation of Peach petal protoplasts and the expression of exogenous target genes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com