Pixel circuit and display device
A pixel circuit and common electrode technology, which is applied in the field of display devices, can solve the problems of reducing the aperture ratio, complex peripheral drive circuits, and complex structures, and achieve the effect of reducing unevenness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
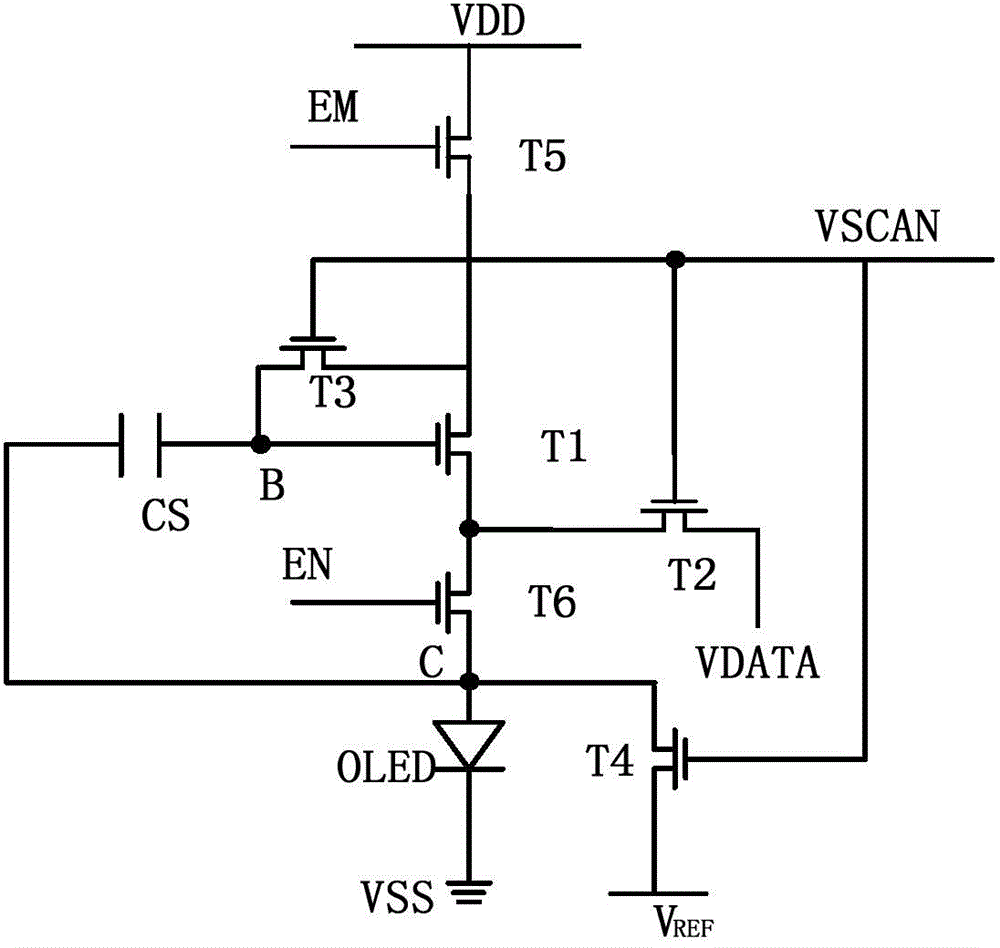
[0039] Please refer to figure 2 , figure 2 Shown is the structure of an embodiment of the pixel circuit of the present application, including: a storage capacitor CS, a third transistor T3, a second transistor T2, and a light-emitting branch for coupling between the first common electrode VDD and the second common electrode VSS road. The light emitting branch circuit includes a fifth transistor T5, a driving transistor T1, a sixth transistor T6 and a light emitting element OLED connected in series.
[0040]Wherein, the fifth transistor T5 is connected in series between the first common electrode VDD and the driving transistor T1, the sixth transistor T6 is connected in series between the second common electrode VSS and the driving transistor T1, and the control electrode (eg gate) of the fifth transistor T5 It is used to input the first control signal EM; the control pole (such as the gate) of the sixth transistor T6 is used to input the second control signal EN; the first...
Embodiment 2
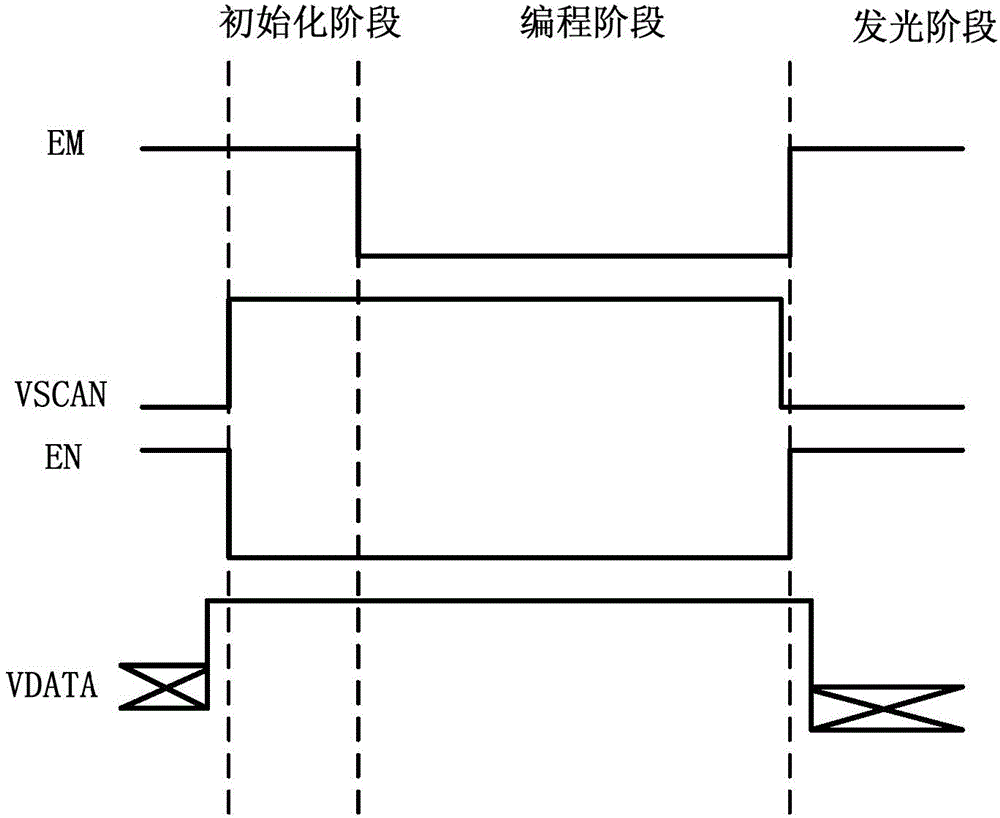
[0058] according to image 3 It can be seen that the phase of the second control signal EN is opposite to that of the scanning signal VSCAN, that is, when the second control signal EN is at a high level, the scanning signal VSCAN is at a low level; when the scanning signal VSCAN is at a high level, the second control signal EN is at a low level level. Based on this, this embodiment reduces the input of signal lines by changing the types of certain transistors. Please refer to Figure 4 , in the above embodiment, each transistor is an N-channel transistor, and in this embodiment, the sixth transistor T6 is selected as a P-channel transistor. At this time, the sixth transistor T6 and the second transistor T2 The channel types are different, and the second control signal EN is provided by the scan signal VSCAN. Please refer to Figure 5 , is the signal timing diagram of the pixel circuit in this embodiment, wherein the timing relationship between the scanning signal VSCAN and...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Please refer to Figure 6 , is the pixel circuit structure diagram of this embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and the above embodiment is that the positions of the light-emitting elements OLED in the light-emitting branch are connected in different positions, and the first end of the light-emitting element OLED in this embodiment is coupled to the first common electrode VDD, specifically:
[0063]The first terminal (such as the anode) of the light-emitting element OLED and the first pole (such as the drain) of the fourth transistor T4 are coupled to the first common electrode VDD; the second terminal (such as the cathode) of the light-emitting element OLED and the fourth transistor T4 The second pole (such as the source) is coupled to the first pole (such as the drain) of the fifth transistor T5; the control pole (such as the gate) of the fourth transistor T4 is used for input and responds to the scan signal VSCAN to switch on / off open state. Similarly...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com