Method for improving plant adverse resistance and application thereof
A plant stress resistance, plant technology, applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, applications, etc., can solve problems such as improving plant stress resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The acquisition of embodiment 1GmAKT1
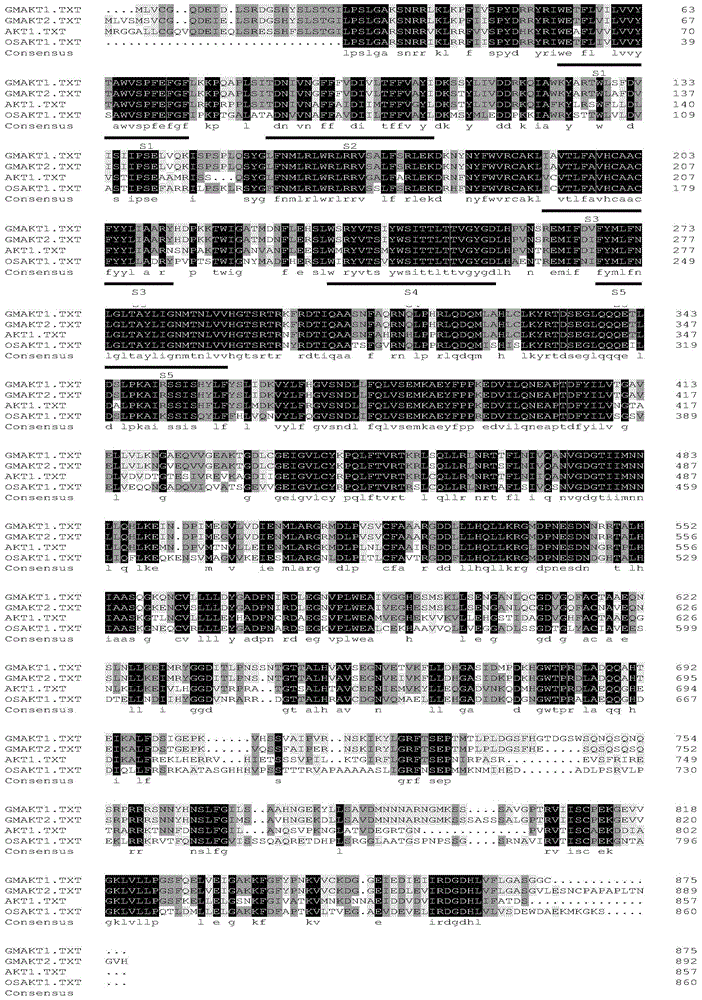
[0039] 1. Cloning and bioinformatics analysis of GmAKT1
[0040] The homologous gene of Arabidopsis thaliana AKT1 was obtained from the Phytozome database, and the two gene copies with the highest homology were obtained from Dongnong 50 by homologous cloning method, which were located on chromosome 17 and chromosome 5 respectively, and the amino acid homology rate 69.41% and 68.00%, respectively, named GmAKT1, GmAKT2. The cloned GmAKT1 of the present invention contains an open reading frame with a length of 2628 bp, encoding 875 amino acids.
[0041] Soybean (Glycine max) extracted with Trizol reagent (Dongnong 50, Wu Tianlong, Yang Qingkai, Ma Zhanfeng, Wu Zongpu, Zhao Shuwen, Gao Fenglan, Li Wenbin, Zhang Guodong, Yang Qi, Meng Qingxi, Wang Jinling. Dongnong Xiaodoudou No. 1 new soybean variety selection Report, [J]. Northeast Agricultural University Journal, 1994, (25) 1:104; the public can obtain from Northeast Agricultural ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2 Construction of GmAKT1 gene plant expression vector and cultivation of GmAKT1 gene Arabidopsis
[0051] 1. Construction of plant expression vector pCXSN-GmAKT1
[0052] The pCXSN vector is a plant expression vector for TA cloning. The pCXSN vector fragment with a T-terminal was obtained by single-digestion with XcmⅠ, and the GmAKT1 fragment with an A-terminal was inserted into the pCXSN plant expression vector. After Hind III identified the positive connection, it was transformed into a TOP10 sensor After the positive colonies were identified, they were transformed into Agrobacterium to obtain the pCXSN-GmAKT1 plant expression vector.
[0053] 2. Cultivation of Transgenic GmAKT1 Arabidopsis
[0054] 1. Obtaining of transgenic GmAKT1 Arabidopsis
[0055] 1) The plant expression vector pCXSN-GmAKT1 obtained above was transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105 by freeze-thaw method and sent for sequencing. As a result, the Agrobacterium with plasmid p...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3 Transgenic T4 generation function analysis of GmAKT1 Arabidopsis
[0067] 1. Phenotype analysis of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana
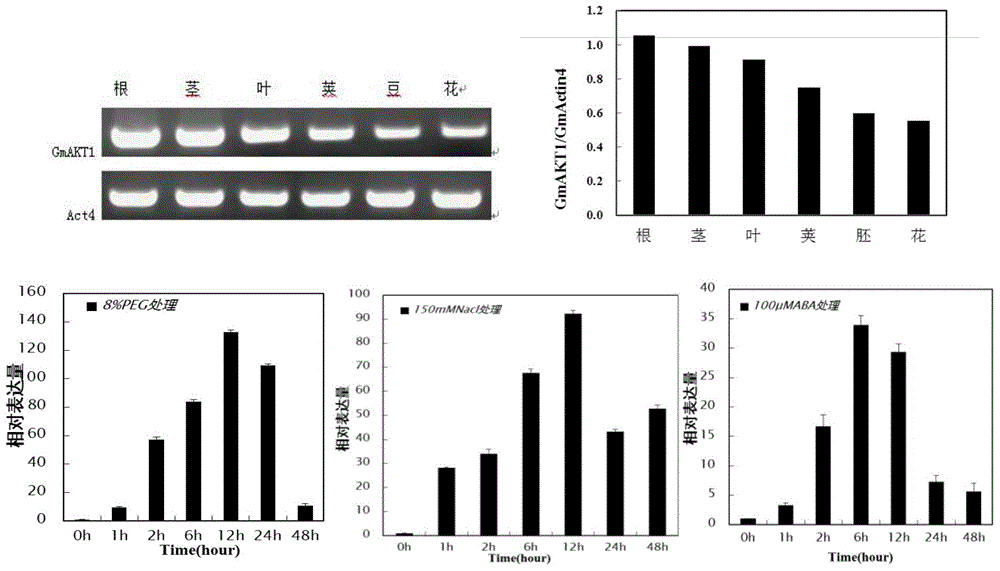
[0068] Seeds of wild type, GmAKT1-transformed wild-type Arabidopsis, AKT1 mutant, and GmAKT1-transferred AKT1 mutant Arabidopsis were planted on MS medium, and moved to soil after 1 week to observe their growth and development process and count the plant height , rosette leaf number, flowering days, pod number, calculate the average value, the results are shown in Table 1 and Figure 4 shown.
[0069] Table 1 The growth conditions of four kinds of Arabidopsis
[0070]
[0071] The plant height of GmAKT1-transformed wild-type Arabidopsis was significantly higher than that of wild-type, mutant and GmAKT1-transformed mutants. It had fewer rosette leaves, earlier flowering days, and more pods in the growth cycle.
[0072] 2. ABA treatment of transgenic Arabidopsis
[0073] Seeds of wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana, AKT1 mutant, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com