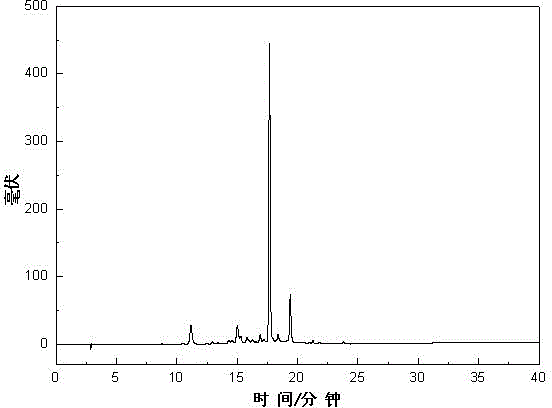
Pretreatment method of phenolic components in three mountainous sage plants
A technology of alpine sage and phenolic acids, applied to plant/algae/fungi/moss components, drug combinations, plant raw materials, etc., to achieve the effect of low resin price, stable and controllable quality, and easy implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1 The pretreatment method of phenolic acid components in three kinds of Alpine Salvia plants, comprising the following steps:
[0029] ⑴ Extraction:
[0030] 1.0 kg of the whole herb of Salvia villosa was dried in the shade and pulverized to obtain pulverized sage plants, and an ethanol solution with a volume fraction of 75% was added to the pulverized sage plants according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1kg:4L, After extracting at 60°C for 3 h, filter, repeat 3 times, and combine to obtain the filtrate; the filtrate was dried under reduced pressure to a paste, and the deep red extract was obtained.
[0031] Wherein: the conditions of decompression drying refer to a vacuum degree of 0.09 MPa and a temperature of 40°C.
[0032] ⑵Resin column chromatography enrichment:
[0033] Add 10 times of its mass to the deep red extract in a methanol solution with a volume fraction of 10% to dissolve, and after separation by a resin column, add an aqueous solution, a m...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 The pretreatment method of phenolic acid components in three kinds of Alpine Salvia plants, comprising the following steps:
[0042] ⑴ Extraction:
[0043] 5.0 kg of the whole sage herb was dried in the shade and crushed to obtain the crushed sage plant, which was added with an ethanol solution with a volume fraction of 95% according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1kg:8L, After extracting at 95°C for 1 h, filter, repeat once, and combine to obtain the filtrate; the filtrate was dried under reduced pressure to a paste, and the deep red extract was obtained.
[0044] Wherein: the conditions of decompression drying refer to a vacuum degree of 0.04 MPa and a temperature of 65°C.
[0045] ⑵Resin column chromatography enrichment:
[0046] Add 5 times its mass to the deep red extract in a methanol solution with a volume fraction of 30% to dissolve, and after separation by a resin column, use an aqueous solution, a methanol solution with a volume fraction of 50%...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 The pretreatment method of phenolic acid components in three kinds of Alpine Salvia plants, comprising the following steps:
[0055] ⑴ Extraction:
[0056] Dry 2.0 kg of the whole sage herb of Kangding in the shade and crush it to obtain the crushed sage plant. Add an ethanol solution with a volume fraction of 80% to the crushed sage plant according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1kg:6L, After extracting at 80°C for 2 h, filter, repeat twice, and combine to obtain the filtrate; the filtrate was dried under reduced pressure until it became a paste, and the deep red extract was obtained.
[0057] Wherein: the conditions of decompression drying refer to a vacuum degree of 0.06 MPa and a temperature of 50°C.
[0058] ⑵Resin column chromatography enrichment:
[0059] Add 8 times of its mass to the deep red extract in a methanol solution with a volume fraction of 20% to dissolve it, and separate it with a resin column, then use an aqueous solution, a methanol ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com