Modified polyethyleneimine and application thereof in the preparation of gene transfection vector reagent
A polyethyleneimine modification technology, applied in the field of modified polyethyleneimine and its application in the preparation of gene transfection carrier reagents, can solve the problems of high toxicity, achieve reduced toxicity, high biological safety, The effect of high biosecurity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
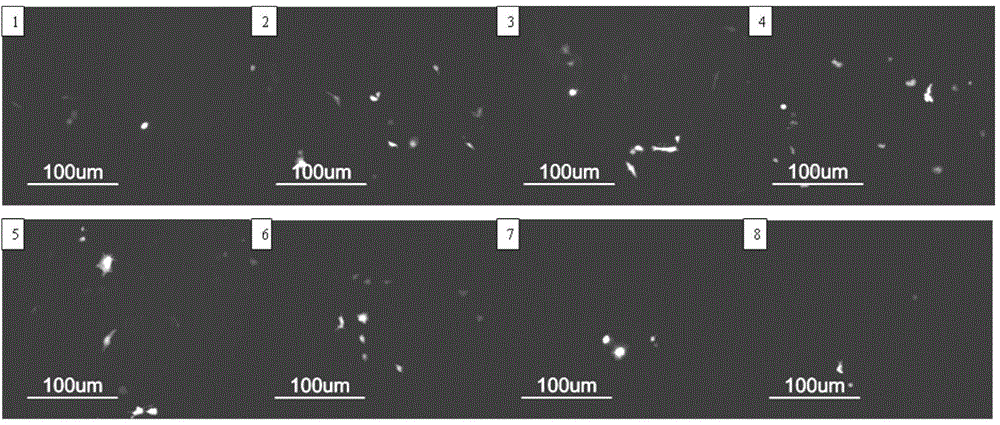
Embodiment 1
[0045] (1) 0.24g of N-hydroxysuccinimide and 0.60g of dehydroabietic acid were mixed and fully dissolved in 50mL of tetrahydrofuran, and reacted at 25°C for 6h;
[0046] (2) After fully dissolving 10g polyethyleneimine (molecular weight: 10000) in 200mL of tetrahydrofuran, drop the solution prepared in step (1) into the polyethyleneimine solution, add 0.84g O-benzotriazole -N,N,N',N'-tetramethylurea tetrafluoroboric acid and 0.28g N,N-diisopropylethylamine, and nitrogen protection, reacted at 25°C for 16h; after the reaction was completed, lyophilized , dialyzed and then freeze-dried to obtain modified polyethyleneimine (the degree of substitution of the substituent R is 0.1%, and the molecular weight is 6000);
[0047] The particle size of the modified polyethyleneimine detected by laser scattering in the aqueous solution is 46nm.
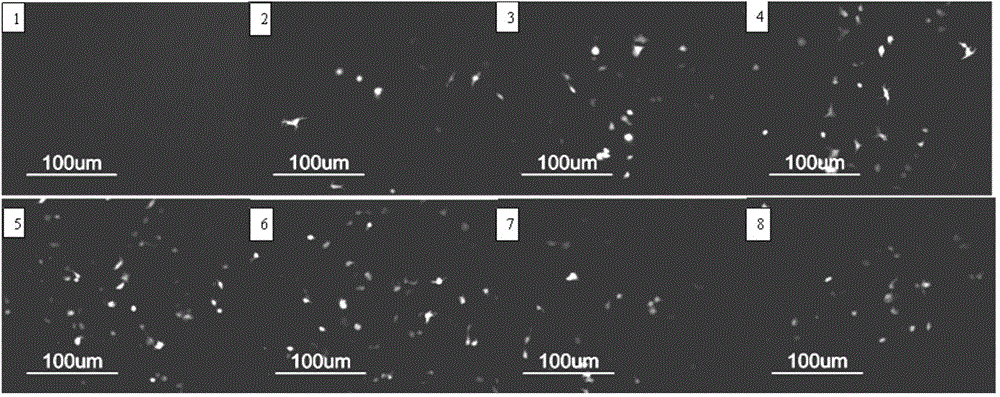
Embodiment 2
[0049] (1) 0.36g of N-hydroxysuccinimide and 0.90g of dehydroabietic acid were mixed and fully dissolved in 50mL of tetrahydrofuran, and reacted at 15°C for 12h;
[0050] (2) After fully dissolving 10g polyethyleneimine (molecular weight: 6000) in 200mL of tetrahydrofuran, drop the solution prepared in step (1) into the polyethyleneimine solution, add 1.26g O-benzotriazole -N,N,N',N'-tetramethylurea tetrafluoroboric acid and 0.42g N,N-diisopropylethylamine, and nitrogen protection, reacted at 25°C for 8h; after the reaction was completed, lyophilized , dialyzed and then freeze-dried to obtain modified polyethyleneimine (the degree of substitution of the substituent R is 3%, and the molecular weight is 11000);
[0051] The particle size of the modified polyethyleneimine detected by laser scattering in aqueous solution is 58nm.
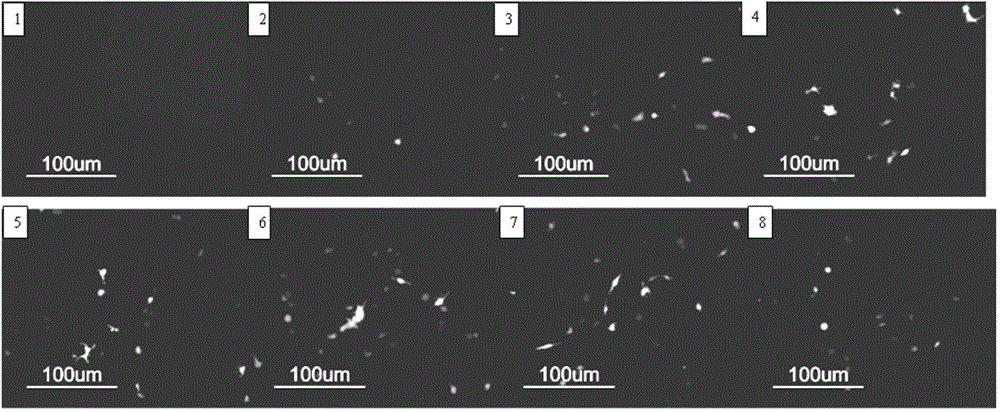
Embodiment 3
[0053] (1) 0.48g of N-hydroxysuccinimide and 1.2g of dehydroabietic acid were mixed and fully dissolved in 50mL of tetrahydrofuran, and reacted at 0°C for 24h;
[0054] (2) After fully dissolving 10g of polyethyleneimine (molecular weight: 40,000) in 200mL of tetrahydrofuran, drop the solution prepared in step (1) into the polyethyleneimine solution, and add 1.68g of O-benzotriazepam Azole-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroboric acid and 0.56g N,N-diisopropylethylamine, under nitrogen protection, reacted at 25°C for 24h; after the reaction was completed, freeze Dry, dialyze and then freeze-dry to obtain modified polyethyleneimine (the degree of substitution of the substituent R is 12%, and the molecular weight is 19000);
[0055] The particle size of the modified polyethyleneimine detected by laser scattering in the aqueous solution is 76nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com