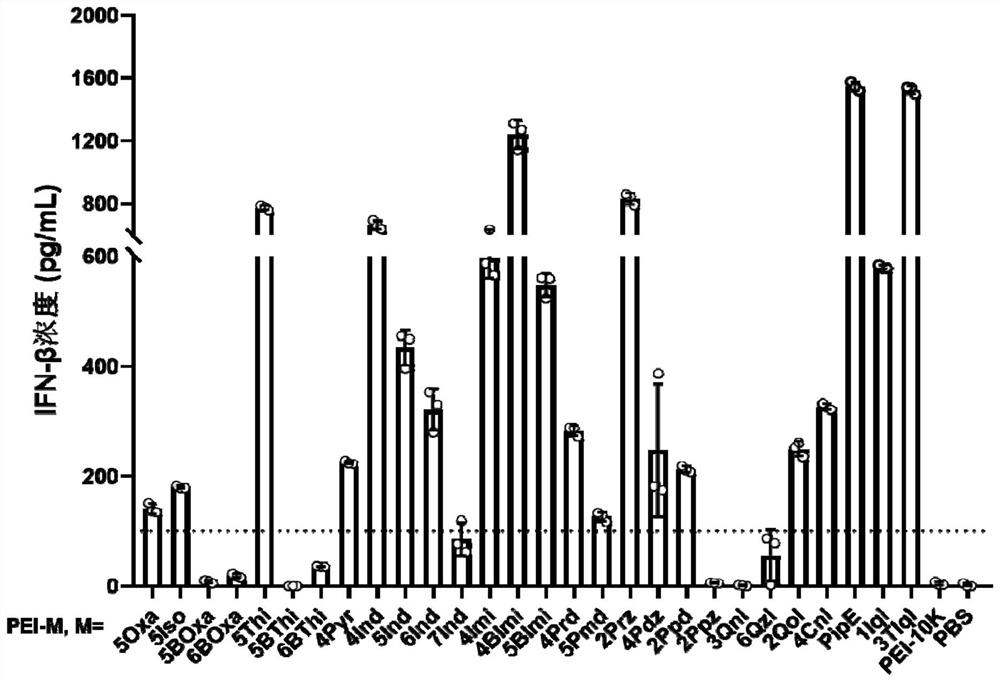
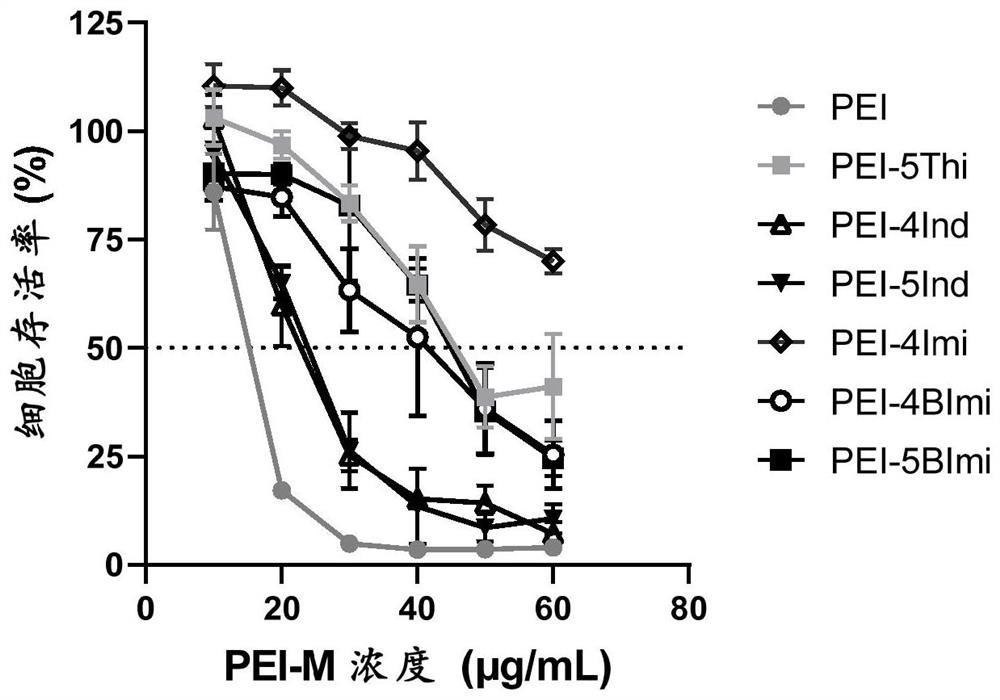
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Transfection vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
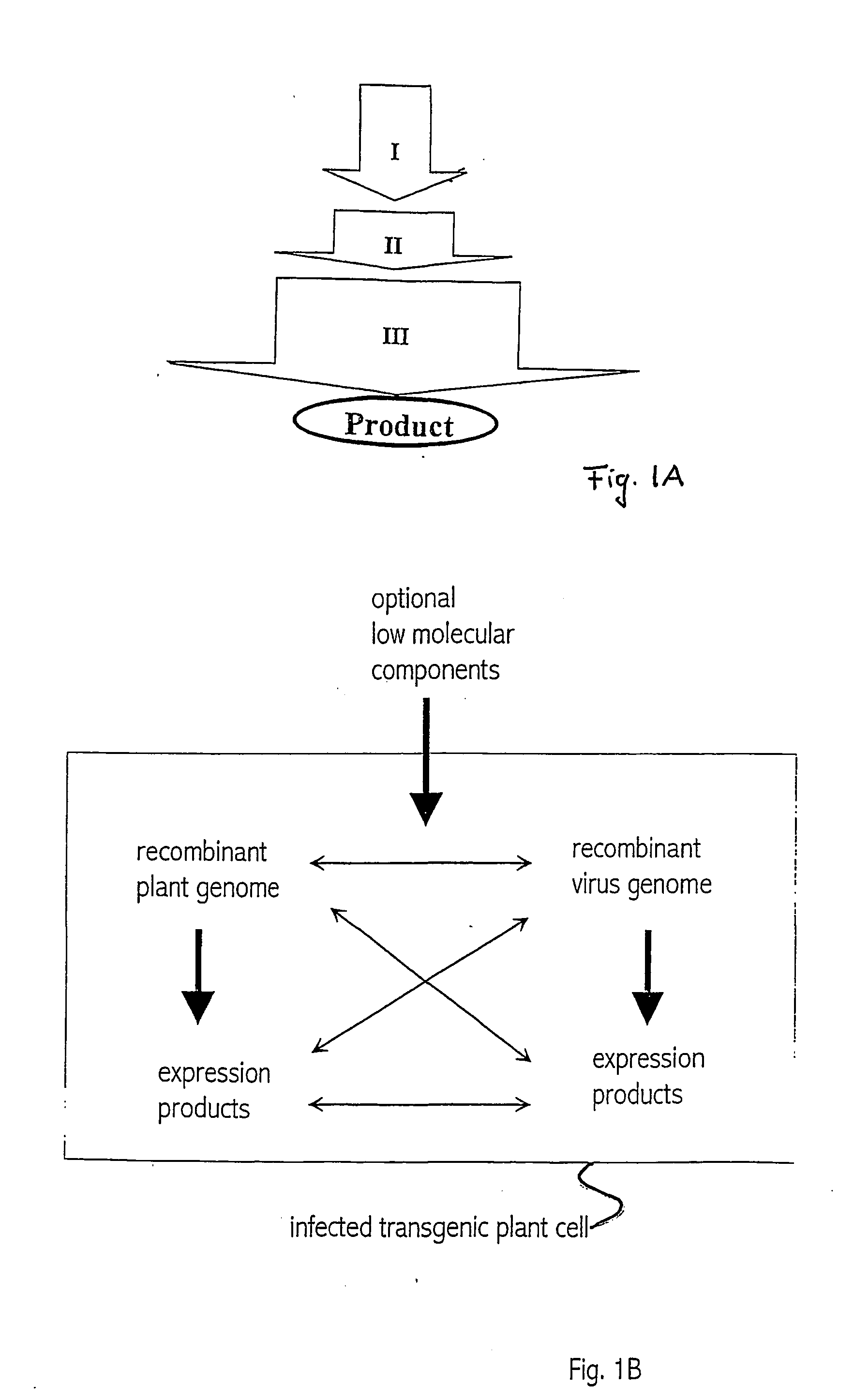
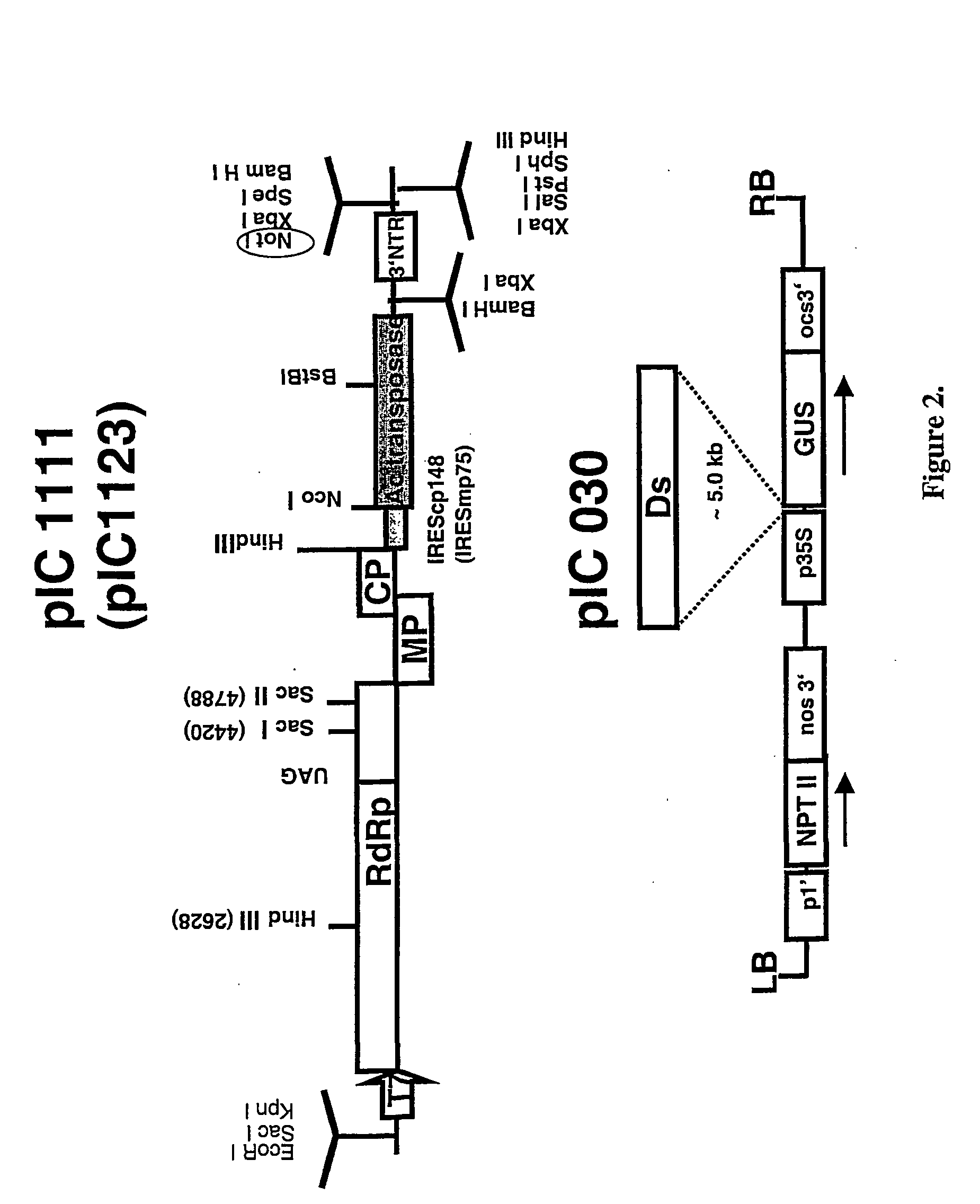
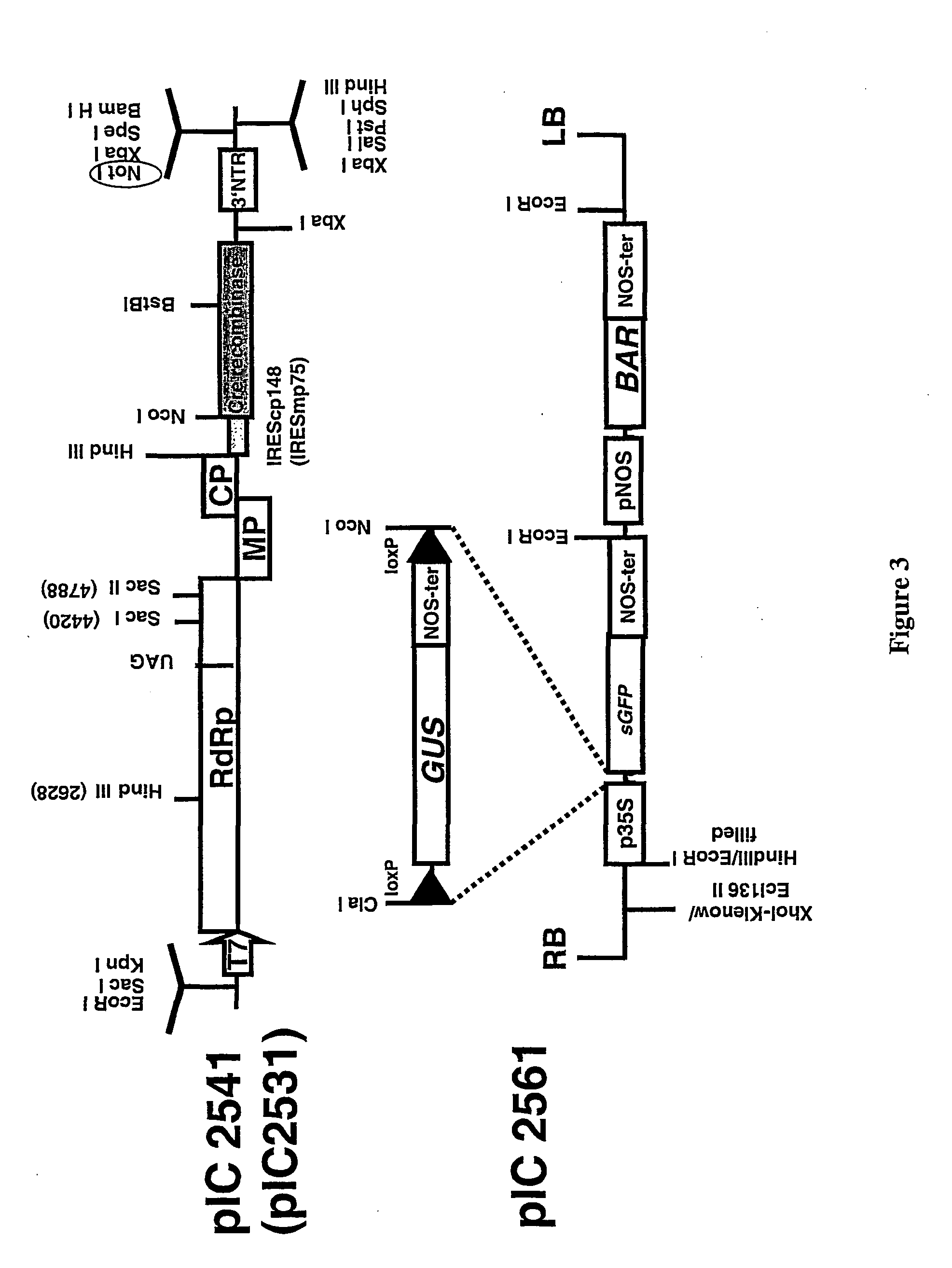
Recombinant viral switches for the control of gene expression in plants
InactiveUS20050091706A1Improve interferenceGrowth retardationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationHeterologousPlant virus
Owner:ICON GENETICS
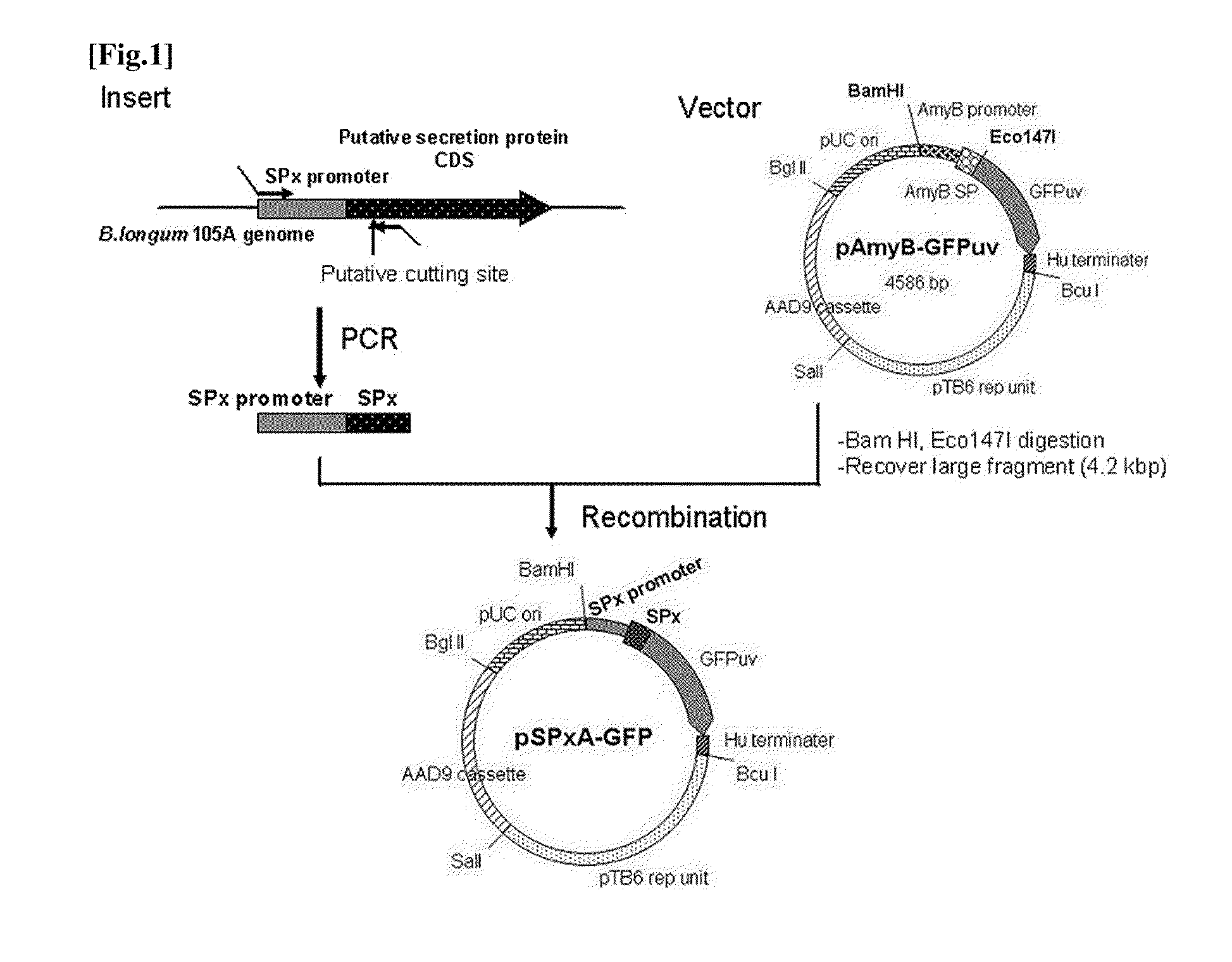
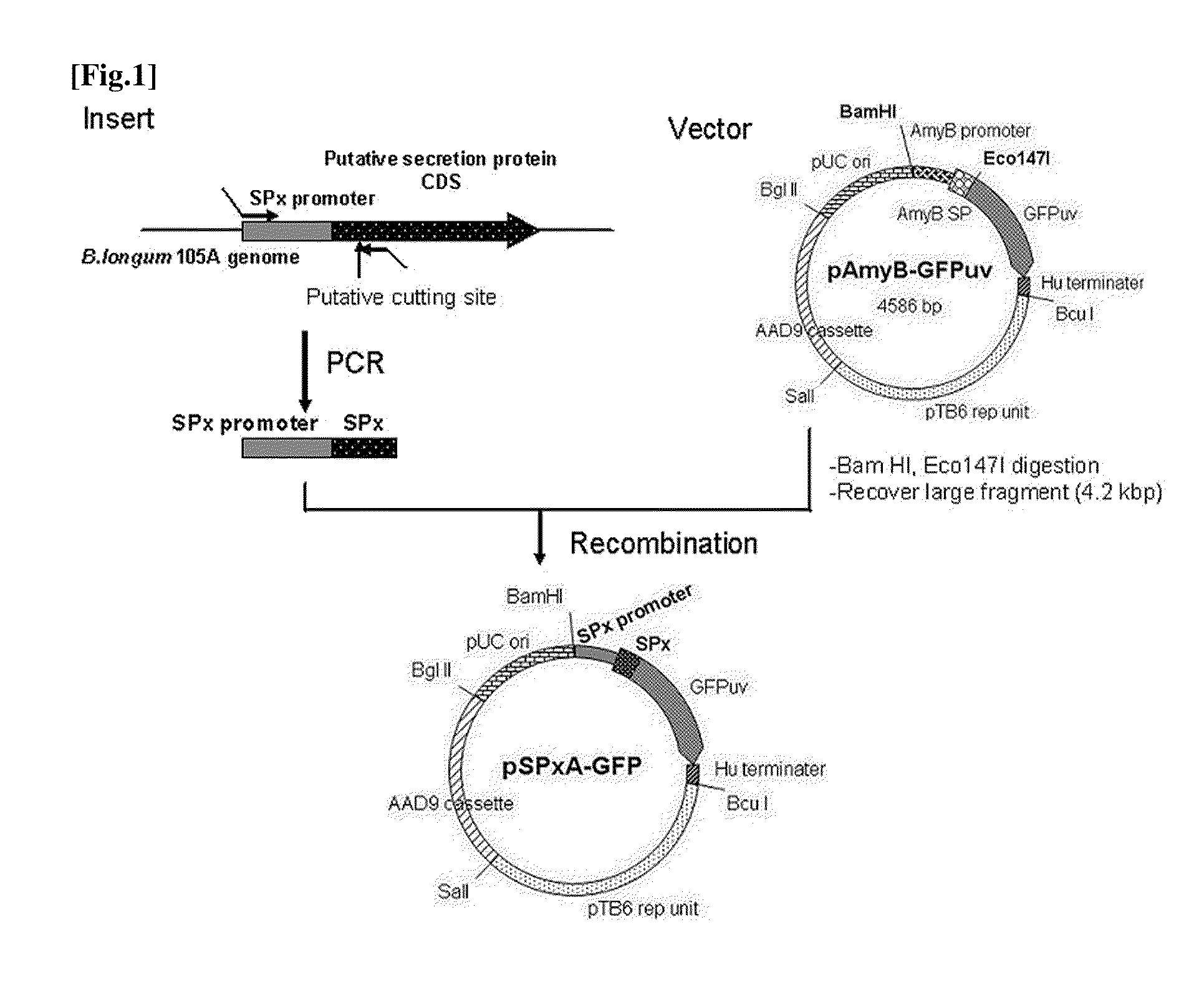
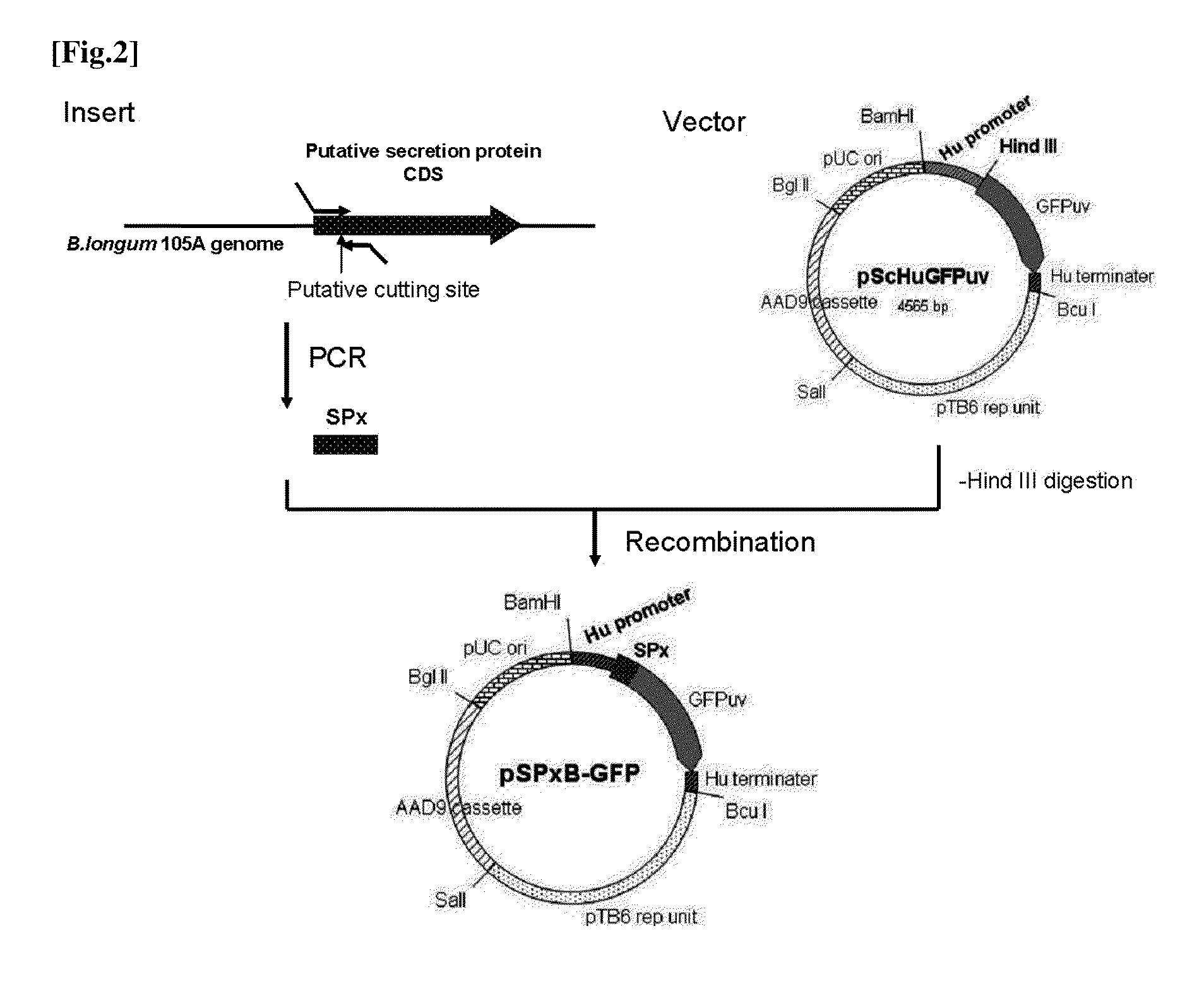
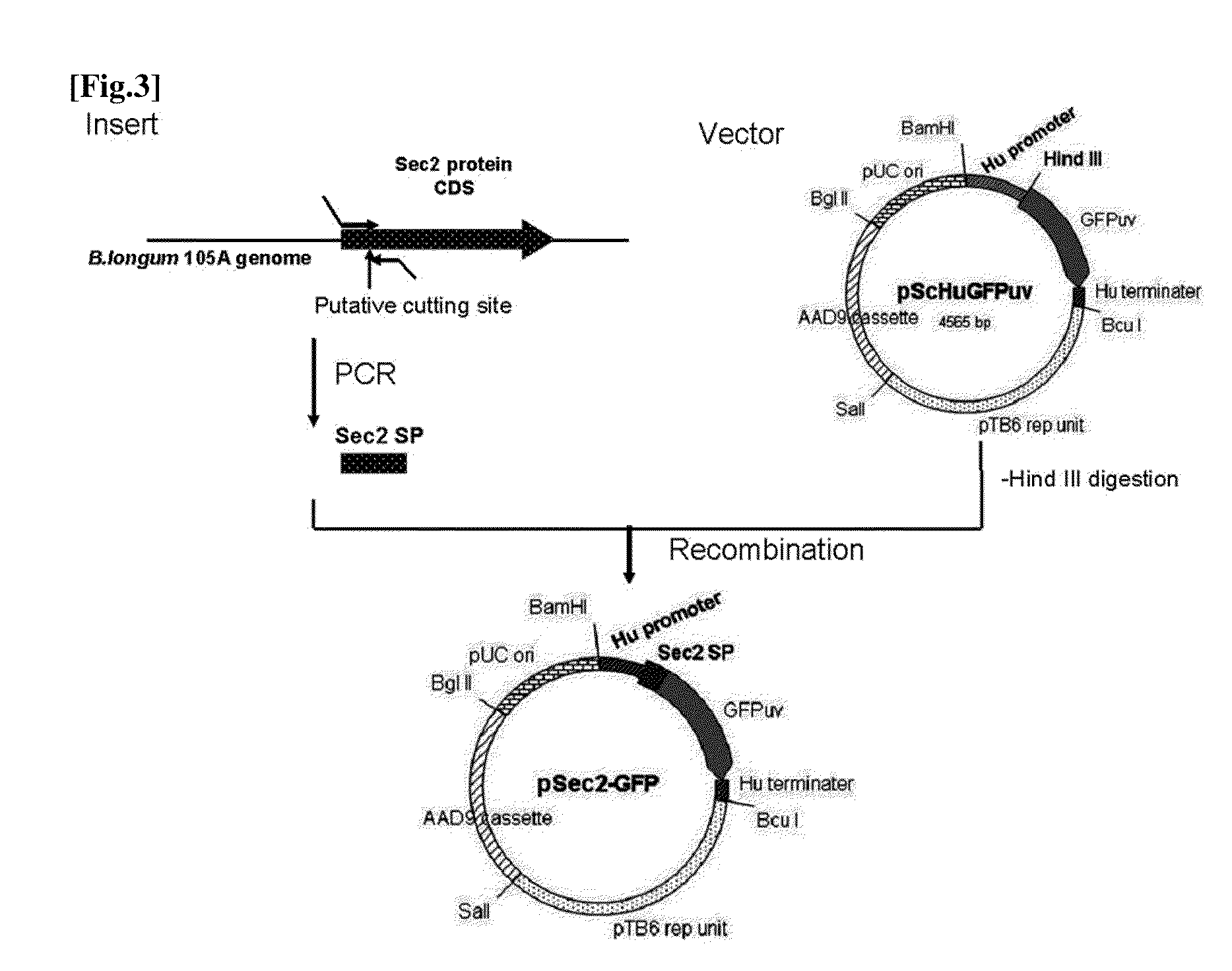
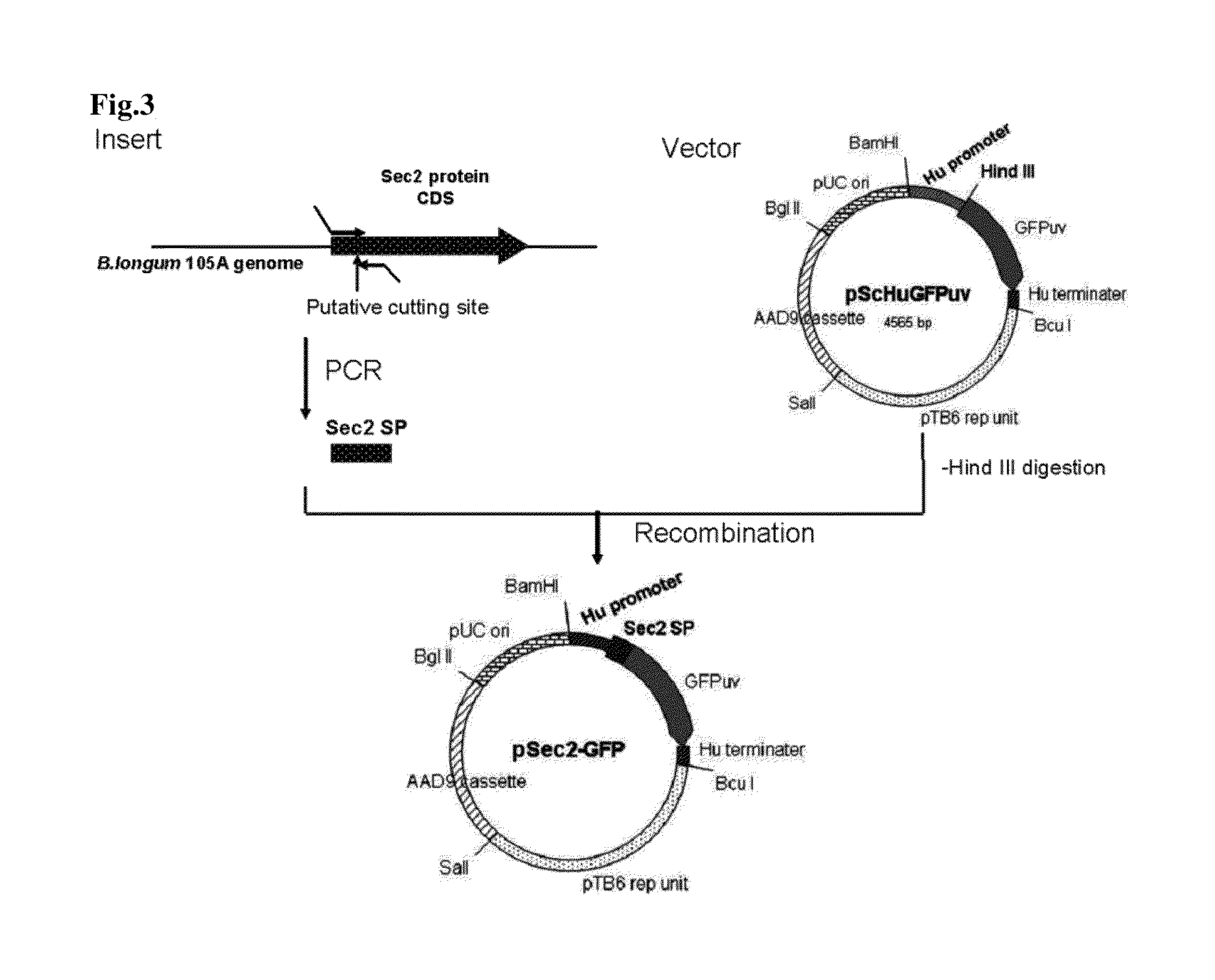
Transfection vector
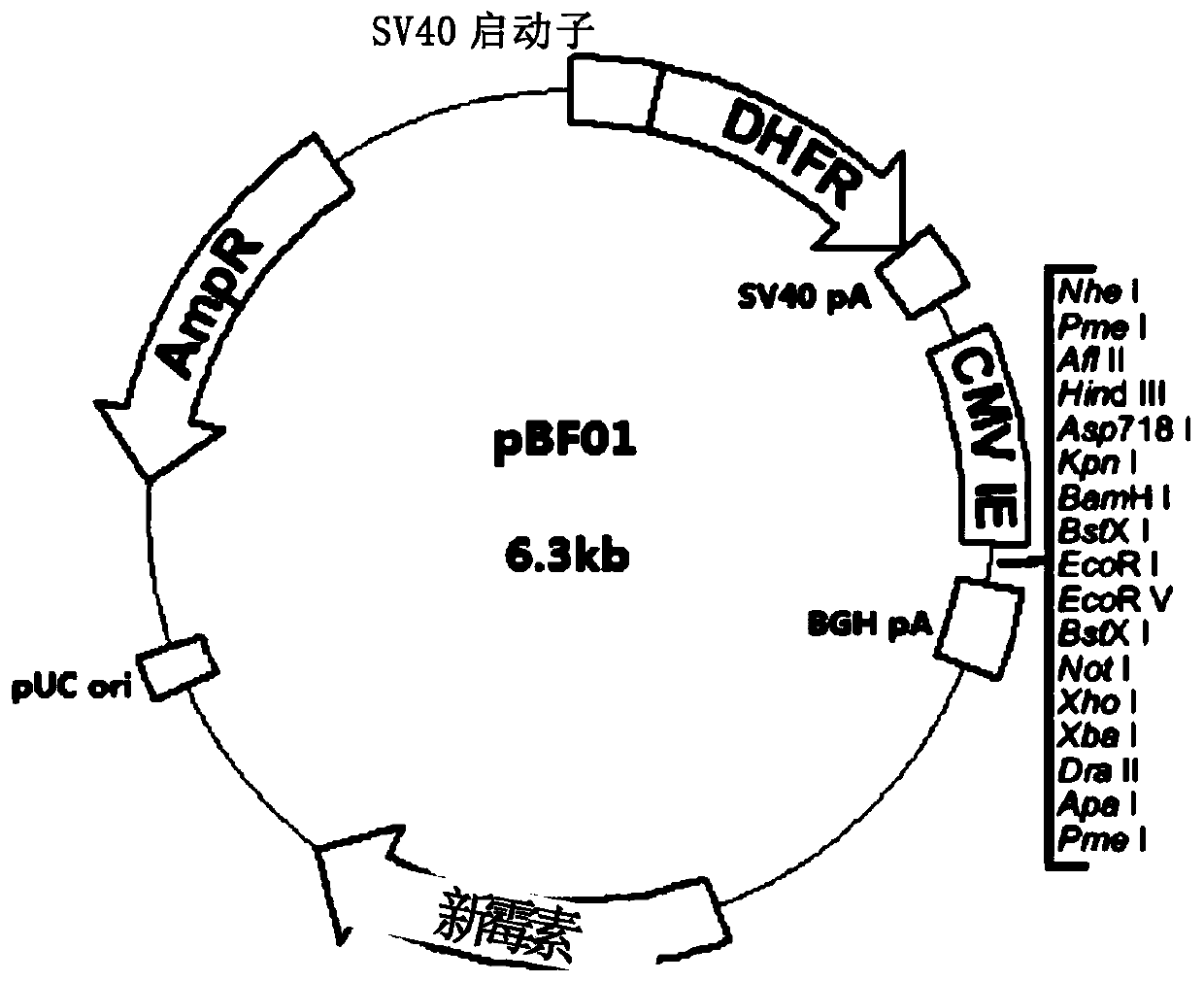
ActiveUS20110189757A1Process safetyQuality improvementBacteriaNon-active genetic ingredientsGene transferPlasmid
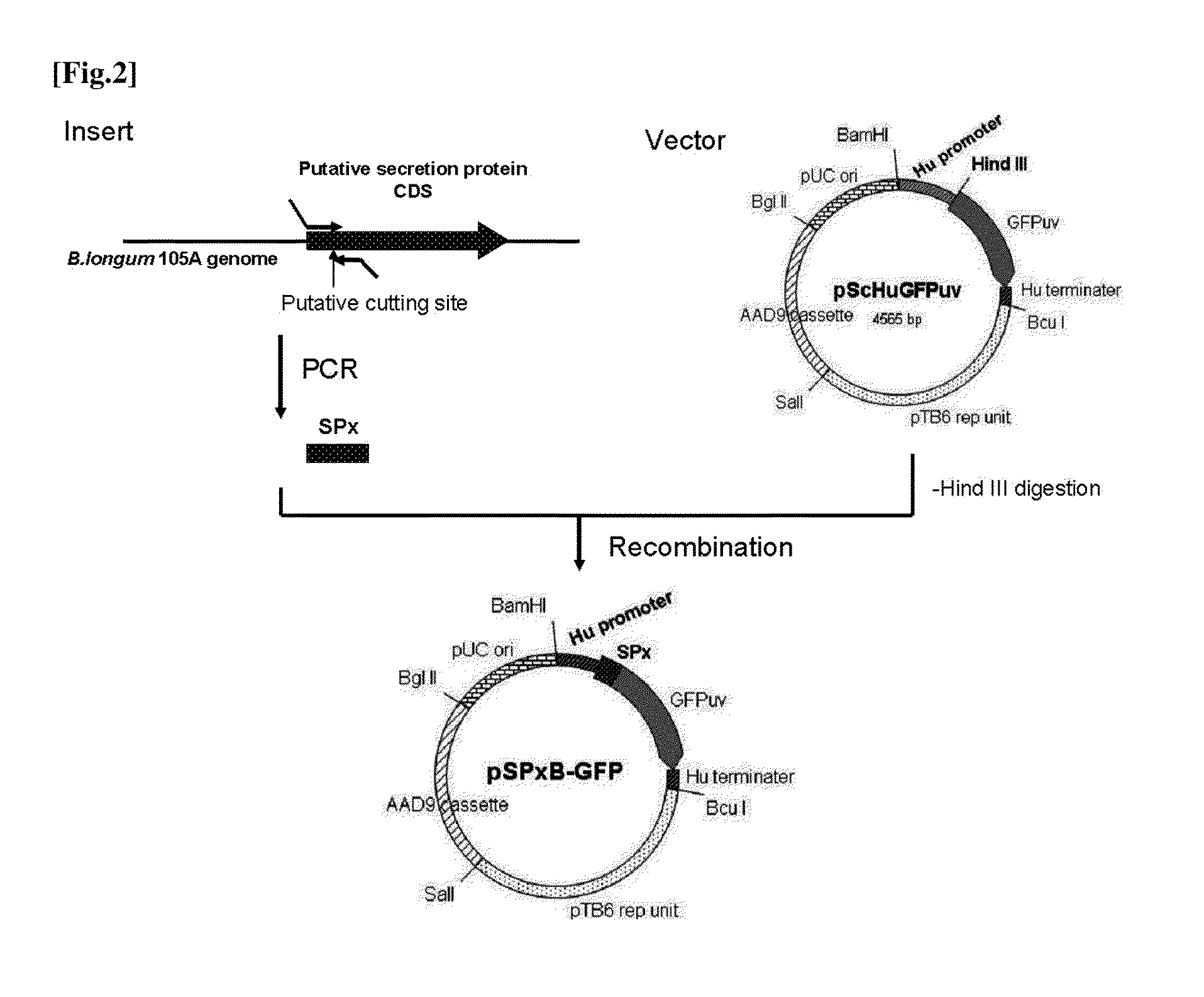
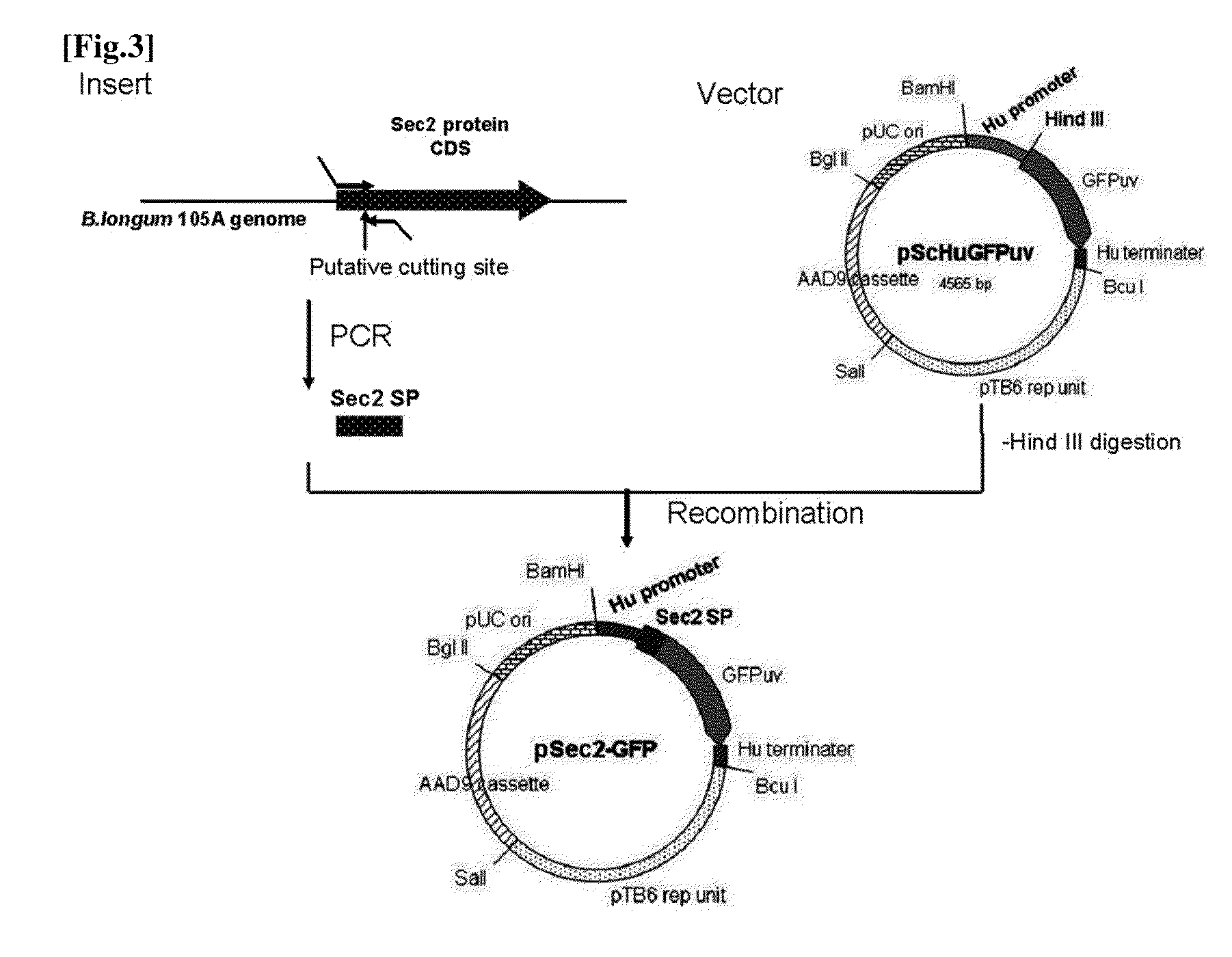
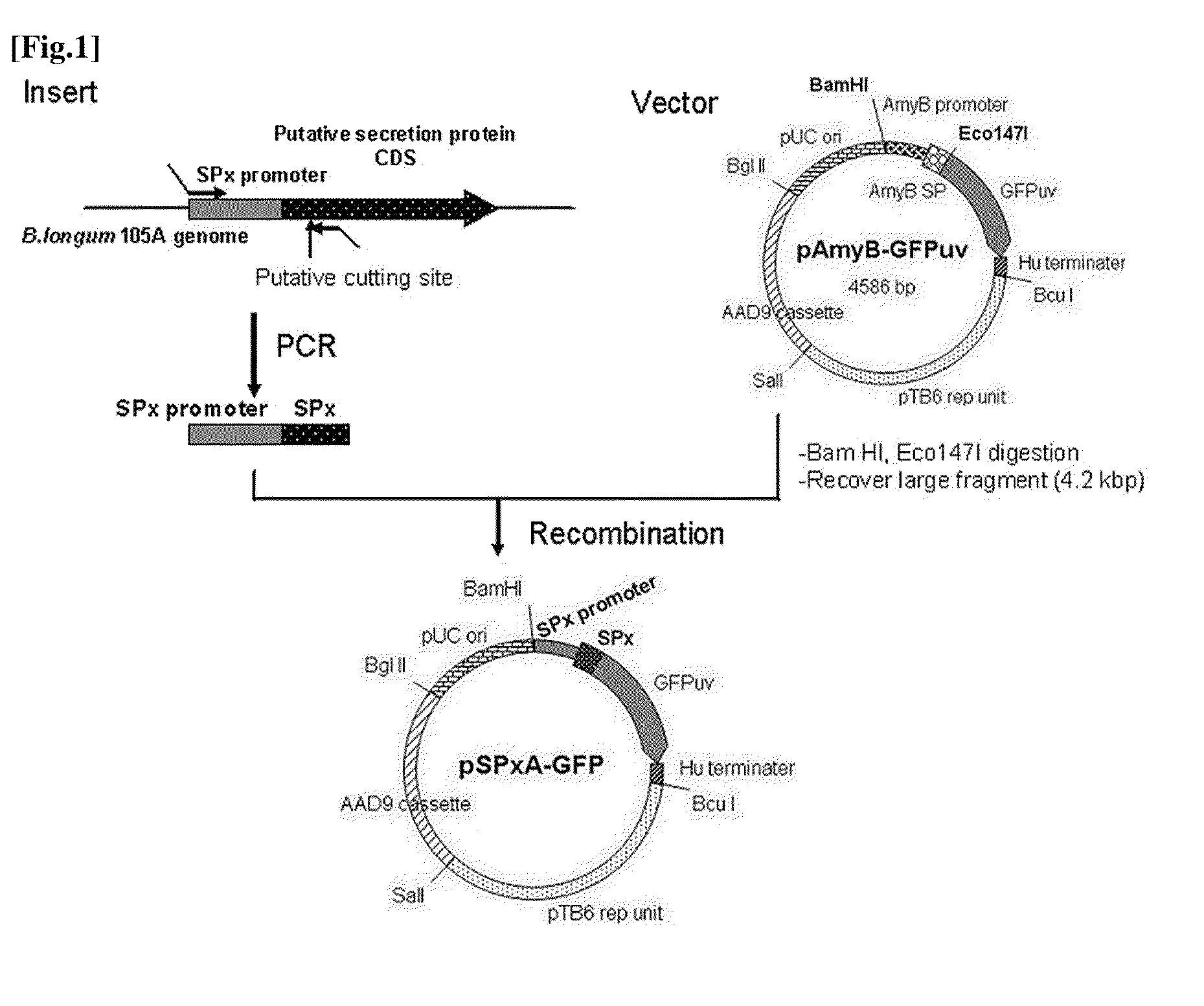
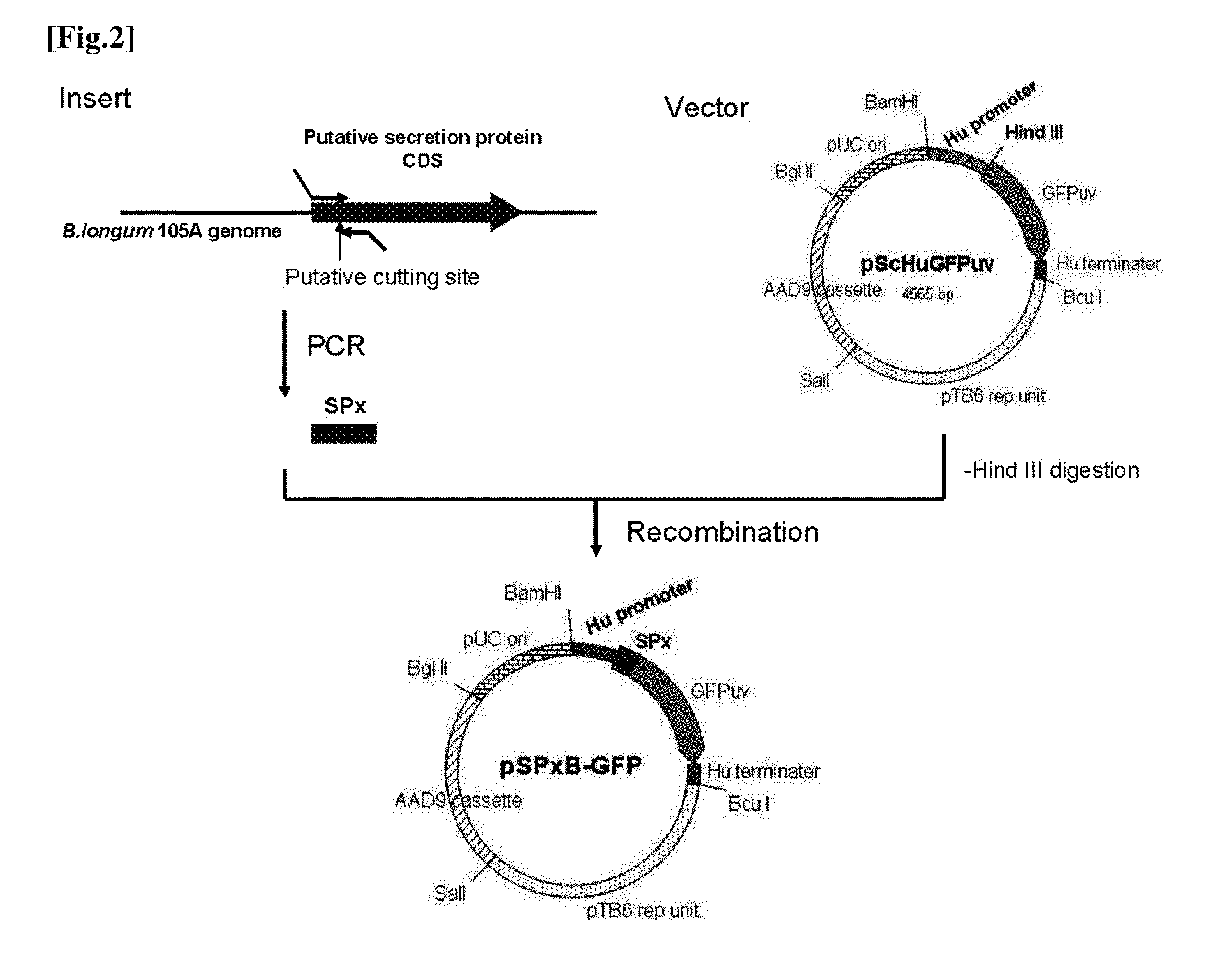
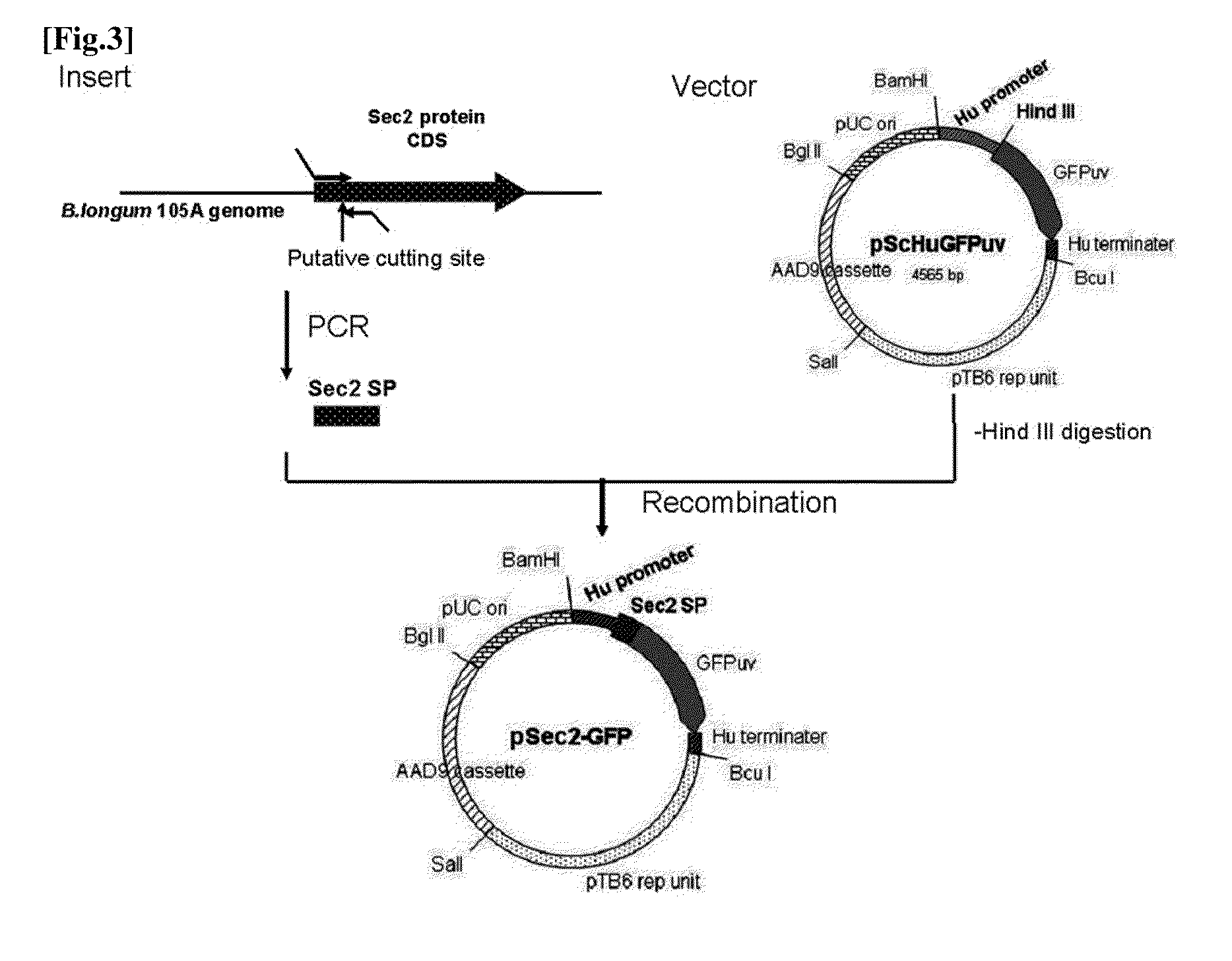
The present invention relates to a novel secretory signal, a novel plasmid containing the secretory signal, a transformed anaerobic bacterium transformed with said plasmid, a gene transfer carrier consisting of said anaerobic bacterium, and a pharmaceutical composition containing said carrier.
Owner:AZUSAPHARMA SCI INC
Application of hydroxyl-containing crosslinked polymer guanidinated product in gene transfer
InactiveCN103193979AEfficient transfectionHighly effective topical drug deliveryGenetic material ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesGene deliveryActive agent
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a hydroxyl-containing crosslinked polymer and guanidinated product thereof used for delivering nucleic acid and other bioactive agents. The method comprises the specific steps that: linear or branched polyethyleneimine with a molecular weight of 100-30000Da or various multi-amine compounds are subjected to a compounding reaction with one or more crosslinking agents with a molecular weight of 100-5000Da and containing two or more epoxy groups, such that the hydroxyl-containing crosslinked polymer is prepared. The invention also provides a synthesizing method of a novel guanidination reagent 3-guanidino propanol acrylate or 5-guanidino amyl acrylate. With the guanidination reagent, the hydroxyl-containing crosslinked polymer or other polymers can be guanidinated, such that gene transfection efficiency thereof can be substantially improved, and cytotoxicity can be reduced. The excellent-performance polymers screened by the invention have gene transfection efficiencies in various cell lines such as A549, B16F10, 3T3, and U87 substantially higher than conventional commercialized gene transfection reagents. The polymers are low-toxic high-efficiency non-virus gene transfection vectors. With the vectors provided by the invention, in-vitro high-efficiency and low-toxicity transfection of various cells can be realized, and in-vivo high-efficiency and low-toxicity local administration can be realized. The application has wide application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Non-viral gene transfection vector material based on cationic helical peptide
ActiveCN106589355ALow cytotoxicityHigh transfection efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsPeptidesSide chainPolypropylene
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical macromolecular materials and discloses a non-viral gene transfection vector material based on cationic helical peptide, and a preparation method and application thereof. The structure of the vector material is shown by general formulas (1) to (6) in the description, wherein R1 is C1-6 alkyl, benzyl, methoxypolyethylene glycol, polyethylene glycol or polypropylene oxide, R2 is C1-3 alkyl, benzyl or phenethyl, R3 is methyl or ethyl, R4 is hydroxy, and A is H, C1-3 alkyl, alkoxy, halogen or nitryl; in the general formulas (1) to (4), x represents polymerization degree of polypeptide and is not less than 5; in the general formulas (5) and (6), x represents the ratio of side chain repeating units, with 0<x<1. The cationic helical polypeptide main chain is of Alpha-helical conformation and effectively forms complex micelles with DNA and siRNA, and the material has good transfection efficiency, low cell toxicity and applicable to the transfer of pDNA and siRNA.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Transfection vector
ActiveUS20110190472A1Process safetyQuality improvementSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsGene transferPlasmid
The present invention relates to a novel secretory signal, a novel plasmid containing the secretory signal, a transformed anaerobic bacterium transformed with said plasmid, a gene transfer carrier consisting of said anaerobic bacterium, and a pharmaceutical composition containing said carrier.
Owner:AZUSAPHARMA SCI INC
Method for manufacturing linear polyethylenimine (pei) for transfection purpose and linear pei obtained with such method
InactiveCN101821317AImprove efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesFiltrationEvaporation
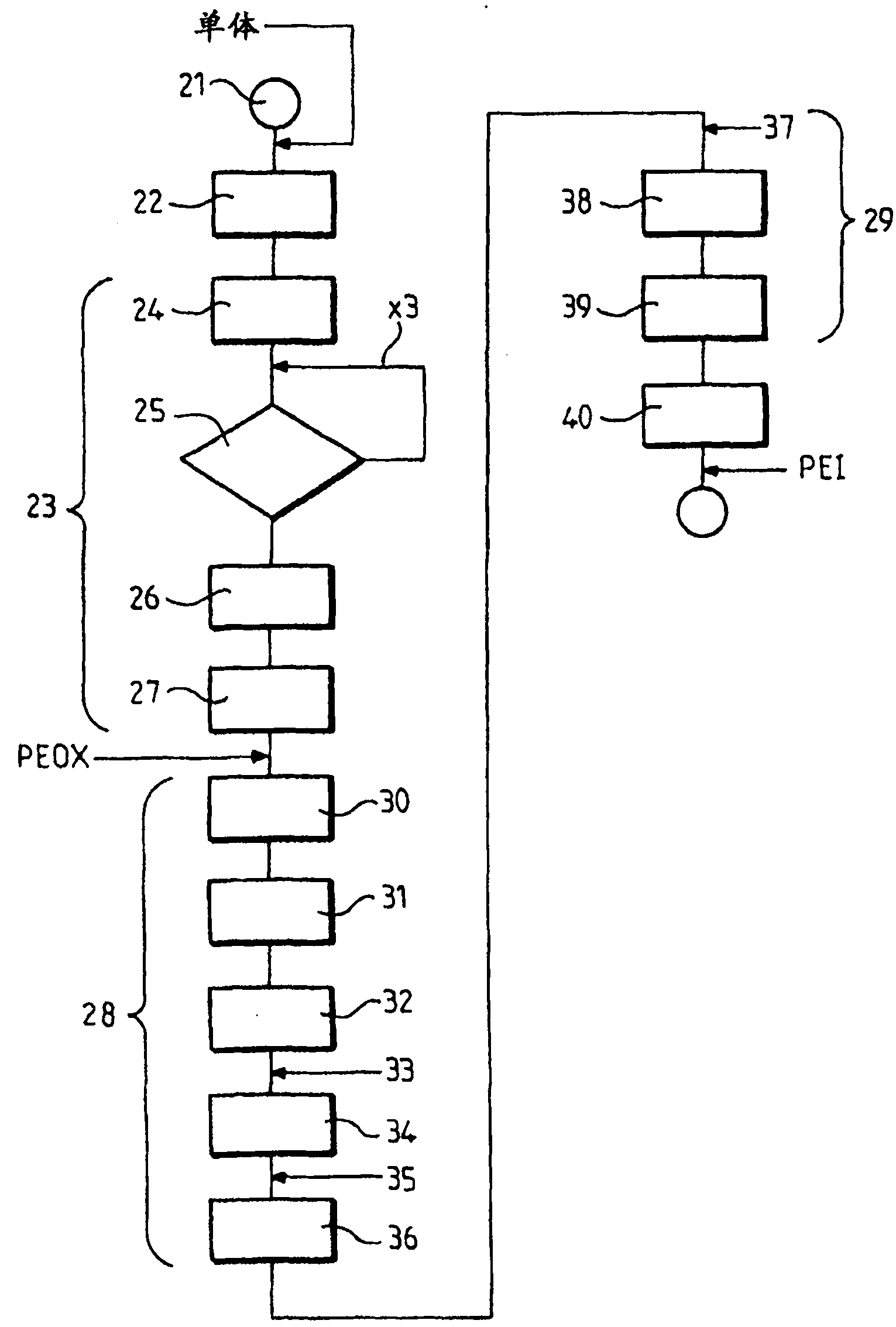
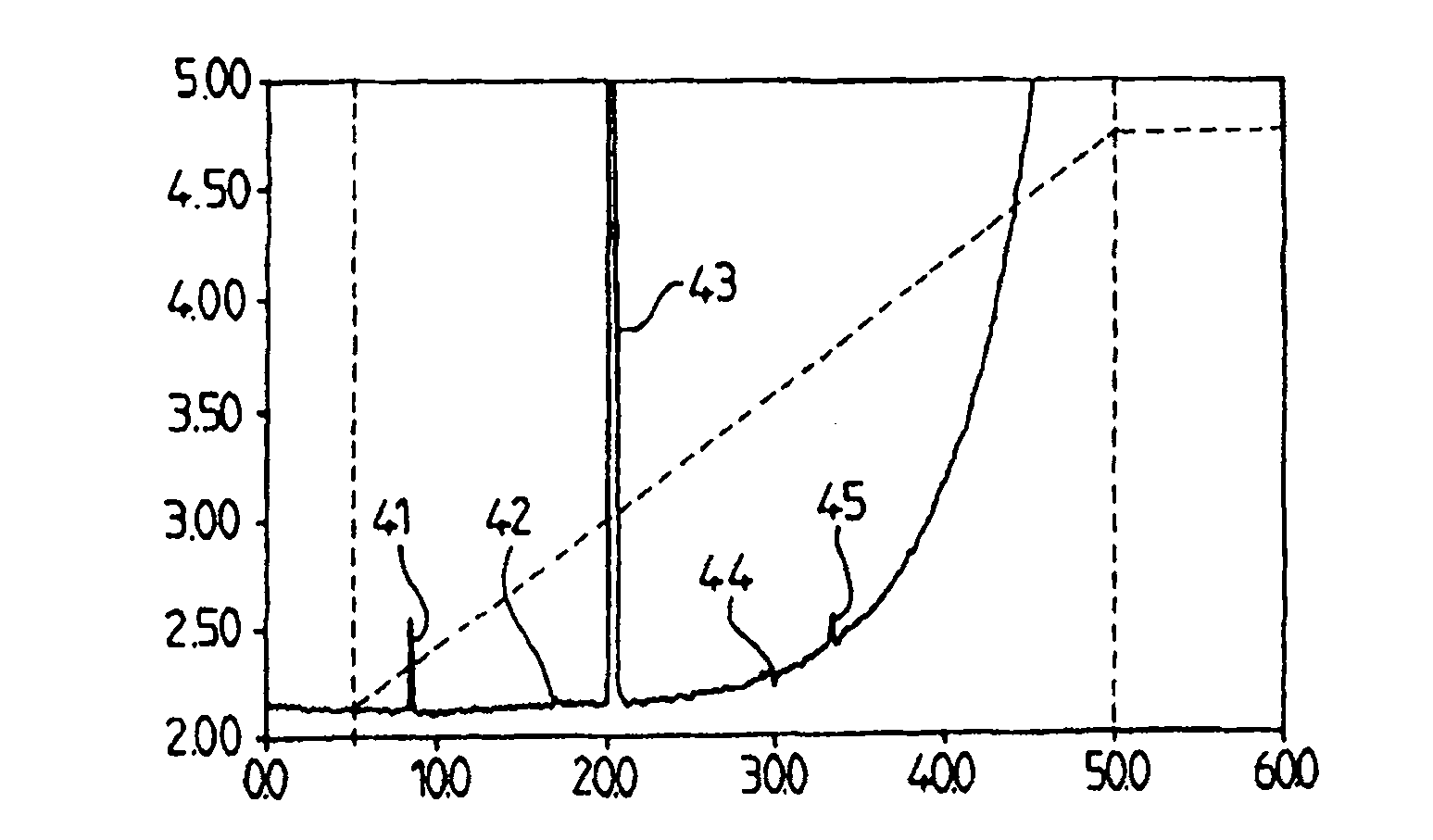
The invention concerns a method of synthesising and preparing linear polyethylenimine (PEI) for use as a transfection vector, and the product obtained with such a method. It comprises drying a monomer 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline and polymerising said monomer for obtaining poly (2- ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEOX) by : using acetonitrile as solvent, adding a dried initiator of the reaction of polymerisation, and mixing them altogether, purifying said obtained PEOX by evaporation, while performing at least three times successive washing / precipitation steps with methanol and diethyl ether and corresponding filtrations, in order to obtain (i), by performing 1H-NMR tests, correct identification of said PEOX polymer, confirmation of absence of monomer to a level <1.0% and confirmation of absence of solvent to a level <5.0% and (ii), by performing Gel Permeation Chromatography, a mean of molecular weight (Mw) >23,000 Da and polydispersity (Mw / Mn) of said PEOX < 1.5, hydrolysing said PEOX.
Owner:POLYPLUS TRANSFECTION SA
Transfection vector
ActiveUS8535939B2Safe vectorUseful in therapyBacteriaNon-active genetic ingredientsGene transferBiology
The present invention relates to a secretory signal, a plasmid containing the secretory signal, a transformed anaerobic bacterium transformed with said plasmid, a gene transfer carrier consisting of said anaerobic bacterium, and a pharmaceutical composition containing said carrier.
Owner:AZUSAPHARMA SCI INC
Modified polyethyleneimine and application thereof in the preparation of gene transfection vector reagent
ActiveCN104974343ALow toxicityHigh gene transfection capacityOther foreign material introduction processesCell membraneComposite nanoparticles
The invention relates to the field of polymer modification, and in particular to a modified polyethyleneimine and application thereof in the preparation of a gene transfection vector reagent. According to the present invention, hydrophobic rosin acid or dehydroabietic acid is grafted onto polyethyleneimine to obtain the modified polyethyleneimine. The hydrophobic group of the modified polyethyleneimine forms a dense hydrophobic core with strong hydrophobicity due to the intermolecular forces in water, hydrophilic polyethyleneimine forms hydrophilic shell, thereby forming a nano micelles with shell-core structure, and nanoparticles with small particle size formed after DNA binding. The composite nanoparticles in smaller size gains tighter structure, so that composite nanoparticles are easier to pass through the cell membrane structure of a lipid bilayer, and the efficiency of transfection is improved. The modified polyethyleneimine can be applied to the preparation of gene transfection vectors and has the characteristics of high biological safety, high transfection efficiency, and low cost.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Transfection vector
InactiveUS20110189758A1Process safetyQuality improvementBacteriaNon-active genetic ingredientsGene transferPlasmid
The present invention relates to a novel secretory signal, a novel plasmid containing the secretory signal, a transformed anaerobic bacterium transformed with said plasmid, a gene transfer carrier consisting of said anaerobic bacterium, and a pharmaceutical composition containing said carrier.
Owner:ANAEROPHARMA SCI
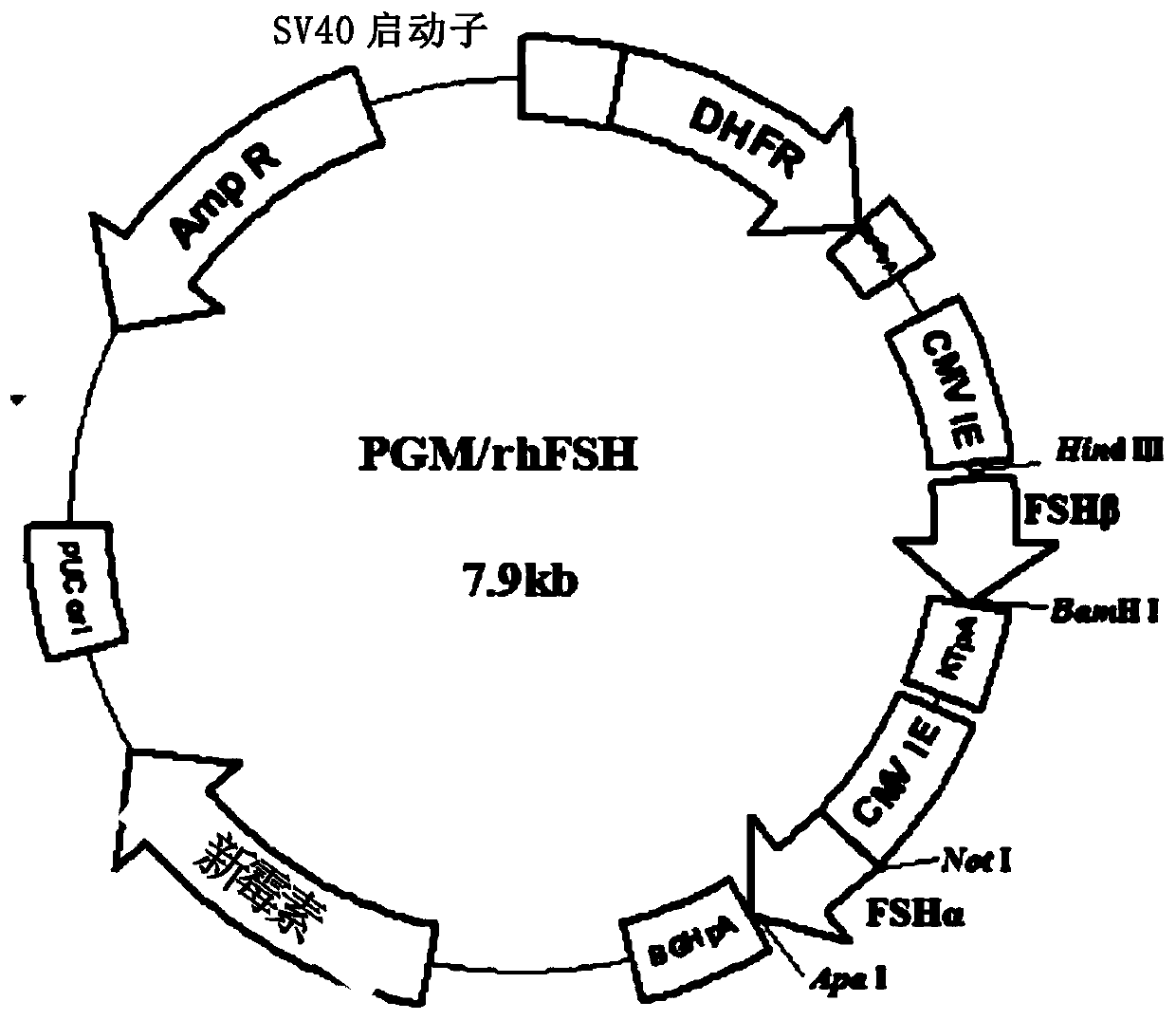
Recombinant human fallicle-stimulating hormone and preparation method thereof
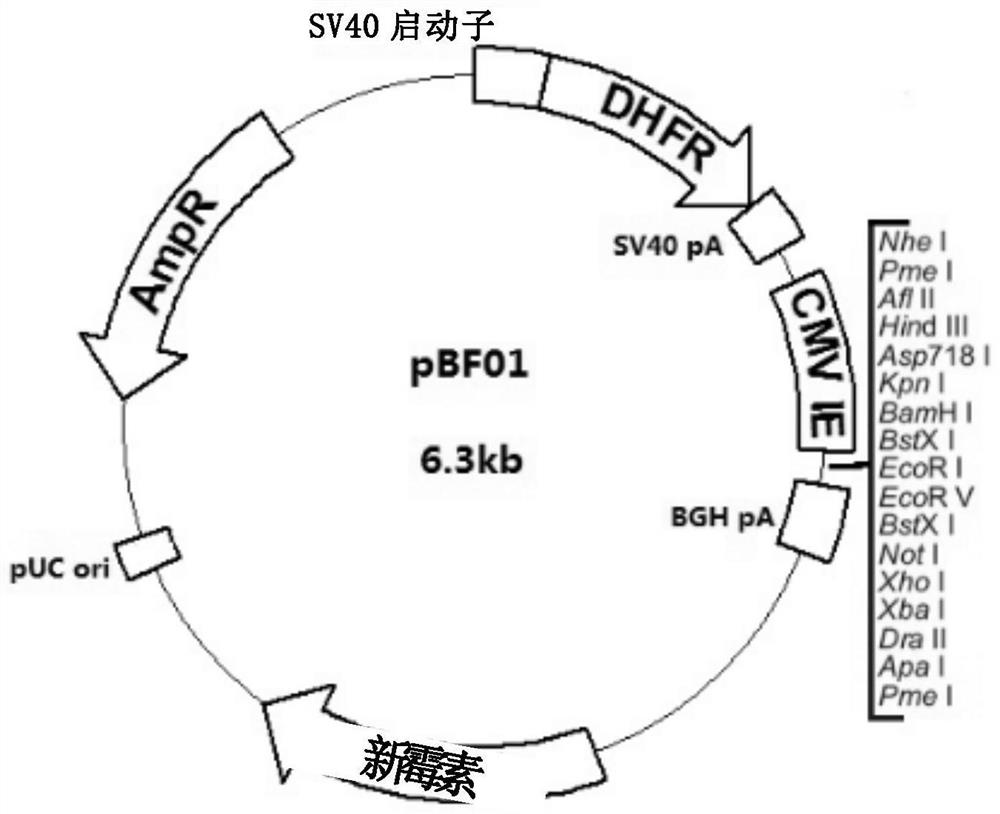
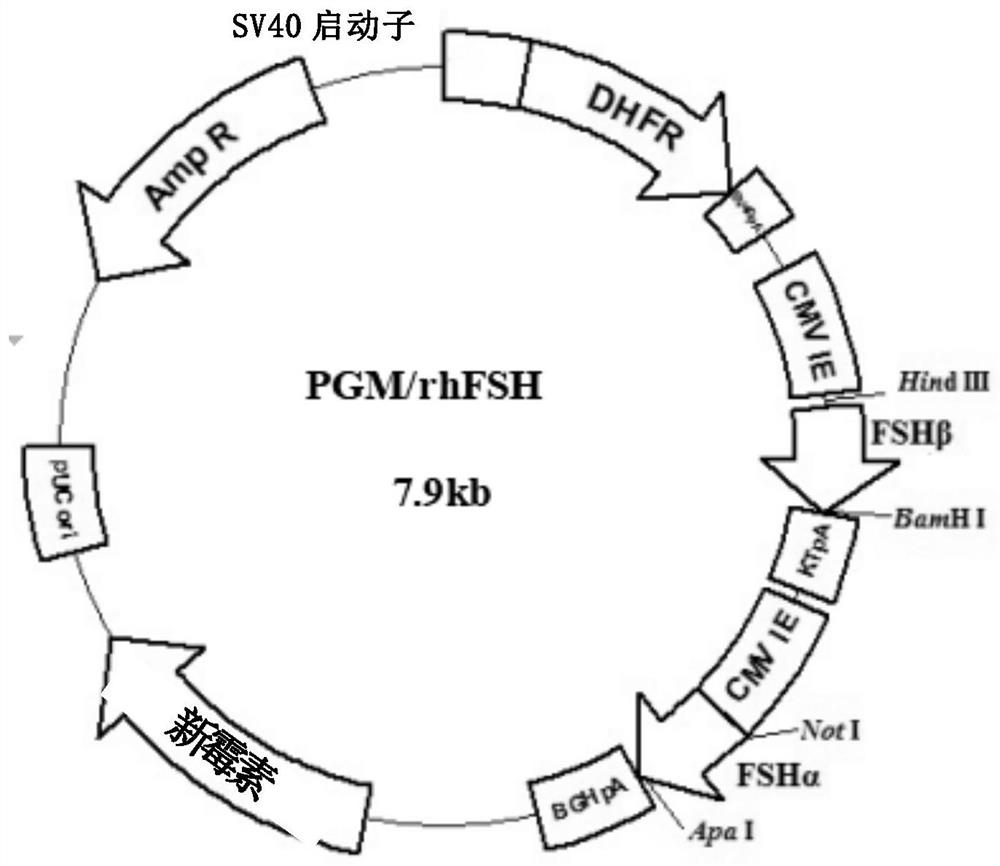
The invention provides a recombinant human fallicle-stimulating hormone and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method specifically comprises the steps of (1) operably inserting a first expression box for expressing an FSH alpha subunit and a second expression box for expressing an FSH beta subunit in a eukaryotic expression vector so as to obtain a transfection vector which can expressFSH alpha subunit protein and FSH beta subunit protein; (2) transferring the transfection vector into an eukaryotic cell so as to obtain a transformed eukaryotic cell which integrates the first expression box and the second expression box in a chromosome; (3) under the condition suitable for expression, culturing the transformed eukaryotic cell, and expressing the FSH alpha subunit and the FSH beta unit so as to obtain a fermentation product containing a recombinant fallicle-stimulating hormone; and (4) performing separation and purification on the fermentation product so as to obtain the recombinant fallicle-stimulating hormone. The method disclosed by the invention can replace a conventional human FSH use method and a conventional human FSH preparation method, and rhFSH of which the activity and the purity are notably improved is obtained.
Owner:JINGZE PHARMA (HEFEI) CO LTD +2
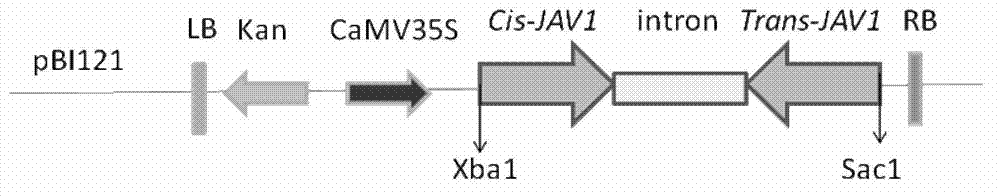
Applications of arabidopis thaliana JAV1 protein and coding gene of arabidopsis thaliana JAV1 protein in regulation of plant disease resistance and insect resistance
The invention discloses applications of arabidopsis thaliana JAV1 protein and a coding gene of arabidopsis thaliana JAV1 protein in regulation of plant disease resistance and insect resistance. The invention also provides a method used for improving plant disease resistance and insect resistance, short hairpin RNA capable of reducing JAV1 gene expression material content, small interfering RNA, an interference vector, and interference segments. It is confirmed by experiments that, compared with wild type and null-transfection vector control groups, relative expression level of T3 generation pBI121-JAV1-RNAi transfected arabidopsis thaliana is reduced significantly, leaf infected area is 0.25 to 0.27cm<2> after inoculation by botrytis cinerea, and is obviously smaller than that of wild type and null-transfection vector control groups; the weight of beet armyworm larvae which are fed with leaves of 5 weeks for 6 days increases 1.58 to 2.03mg, and is obviously lower than that of wild type and null-transfection vector control groups; and plants are capable of growing normally in 12 days when bradysia odoriphaga larvae are put into soil with the plants of 18 days. According to the applications of arabidopsis thaliana JAV1 protein and the coding gene of arabidopsis thaliana JAV1 protein, a novel approach is provided for cultivation of disease-resistant and insect-resistant plants, and in the field of agricultural production, application range is wide, and market prospect is promising.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Nano-particles capable of improving gene transfection efficiency and preparation method of gene transfection reagent based on particles
InactiveCN103865942AOvercoming the deficiency of low transfection rateHigh transfection rateVector-based foreign material introductionCytotoxicityDna load
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological medicines and aims at improving the gene transfection efficiency by adopting nano-particles NoNPs released through cells. The nano-particles exist extensively in a biosystem and an extracellular circulatory system, such as bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, body fluid, blood, saliva, cow milk or urine. A non-virus gene transfection vector is doped with the nano-particles so that the DNA (Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) carrying capacity of the gene transfection vector can be improved remarkably without increase of cytotoxicity. Experimental results indicate that the NONPs, which are extracted from the cow milk and added to the PEI gene transfection vector, are capable of remarkably improving the gene transfection efficiency under the circumstance of hardly increasing the cytotoxicity. The major use of the nano-particles is to serve as the gene transfection reagent which can be used for cell biology research, gene transfection preparation production, gene therapy and the like.
Owner:常州碳宇纳米科技有限公司
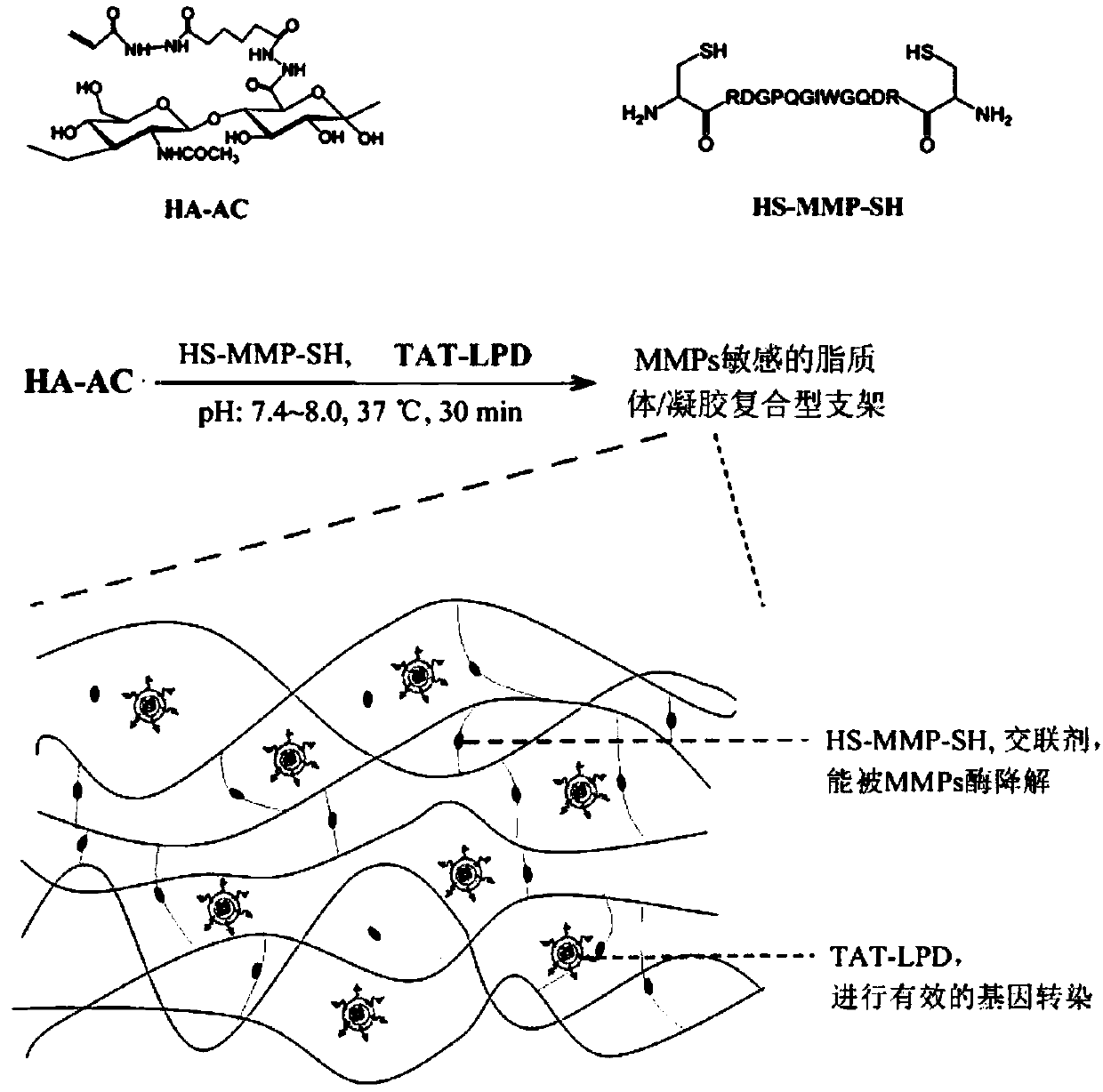
Method for preparing lipidosome/gel composite gene activation scaffold
ActiveCN107815470AHas sensitive degradation abilityEfficient and sensitive degradation abilityMicroencapsulation basedCross-linkTissue repair
The invention relates to a method for preparing a lipidosome / gel composite gene activation scaffold, belonging to the technical field of biomedicine. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: taking TAT modified liposome as a high-efficiency gene transfection vector, entrapping the vector into MMPs sensitive peptide cross-linked hyaluronic acid gel, and constructing theMMPs-sensitive gene activation scaffold in which the lipidosome is entrapped. The MMPs can be secreted by cells in the migration and proliferation process, so that the gel is degraded. On the one hand, a space is created for migration and proliferation of the cells, and a meshed structure of the gel is prevented from becoming a physical barrier of cell migration and proliferation; on the other hand, the TAT-liposome is released, and peripheral cells are subjected to high-efficiency in-situ transfection, so that growth factors are expressed and secreted, and tissue repair and regeneration can be promoted.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Fluorine-nitrogen doped carbon quantum dot as well as preparation method and application thereof
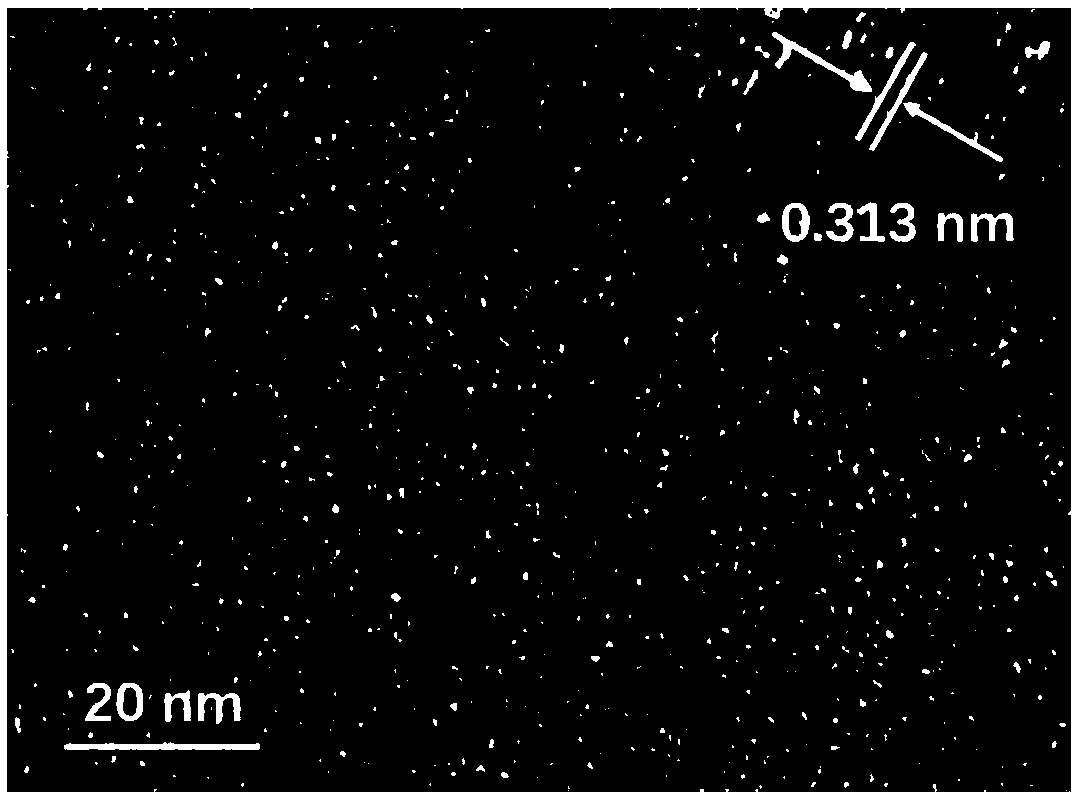
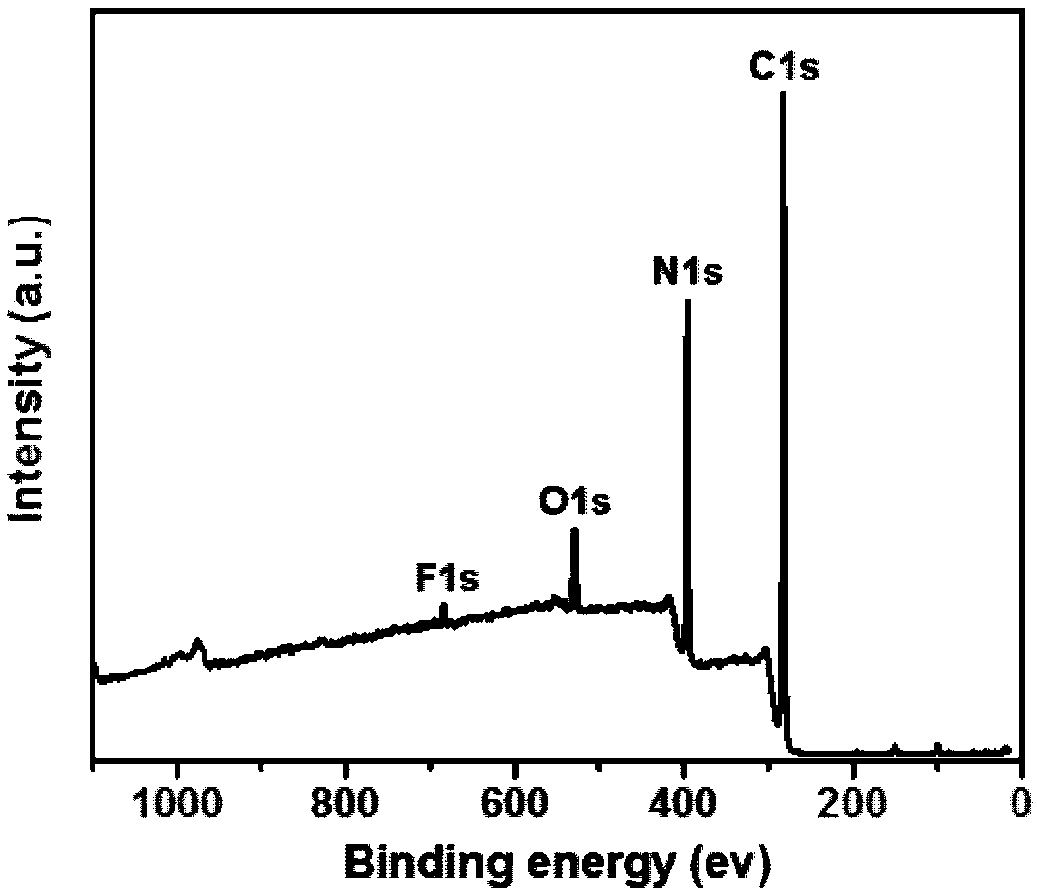
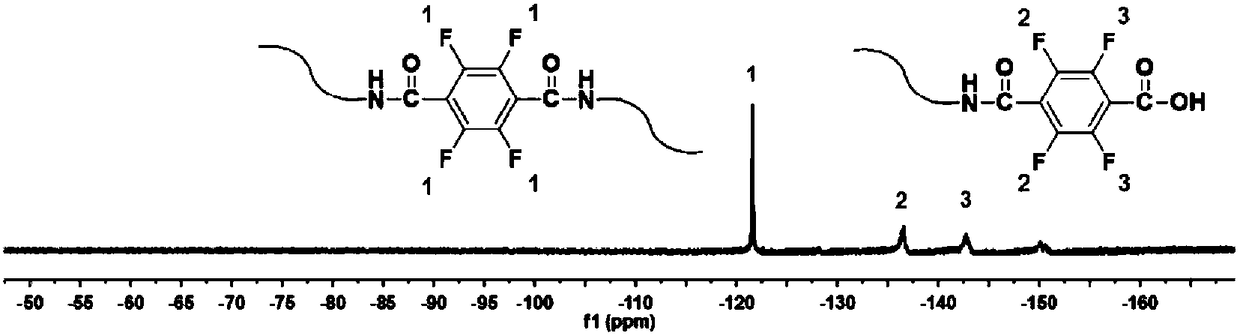
ActiveCN108502867AHigh transfection efficiencyGood biocompatibilityOther foreign material introduction processesNano-carbonGene deliverySolvent
The invention provides a fluorine-nitrogen doped carbon quantum dot prepared from a fluorine-containing aromatic compound and a cationic polymer. The fluorine-containing aromatic compound is linked tothe cationic polymer through a covalent bond; and the cationic polymer is linear polyethyleneimine or branched polyethyleneimine. The invention also provides a preparation method of the fluorine-nitrogen doped carbon quantum dot and application of the fluorine-nitrogen doped carbon quantum dot as a gene delivery vector. The preparation method provided by the invention adopts a hot solvent to prepare the fluorine-nitrogen doped carbon quantum dot with a one-pot method, is simple in reaction, low in preparation cost, available in raw material and high in yield, can reach the efficient transfection effect in the cell transfection process, is relatively small in toxicity produced to cells in the transfection process, can effectively and safely deliver gene molecules into the cells and is a gene transfection vector which has the advantages of high efficiency, low toxicity, low cost, simpleness and easiness in synthesis and the like.
Owner:NANJING WISEGEN BIOTECH
Gene editing system for preparing allotransplantable T cells
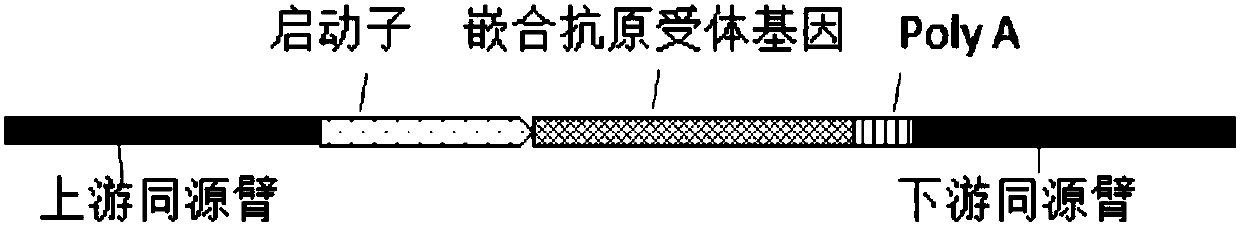
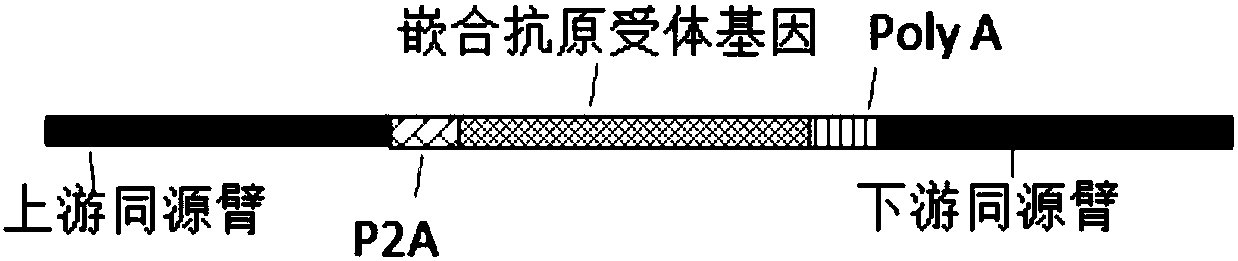
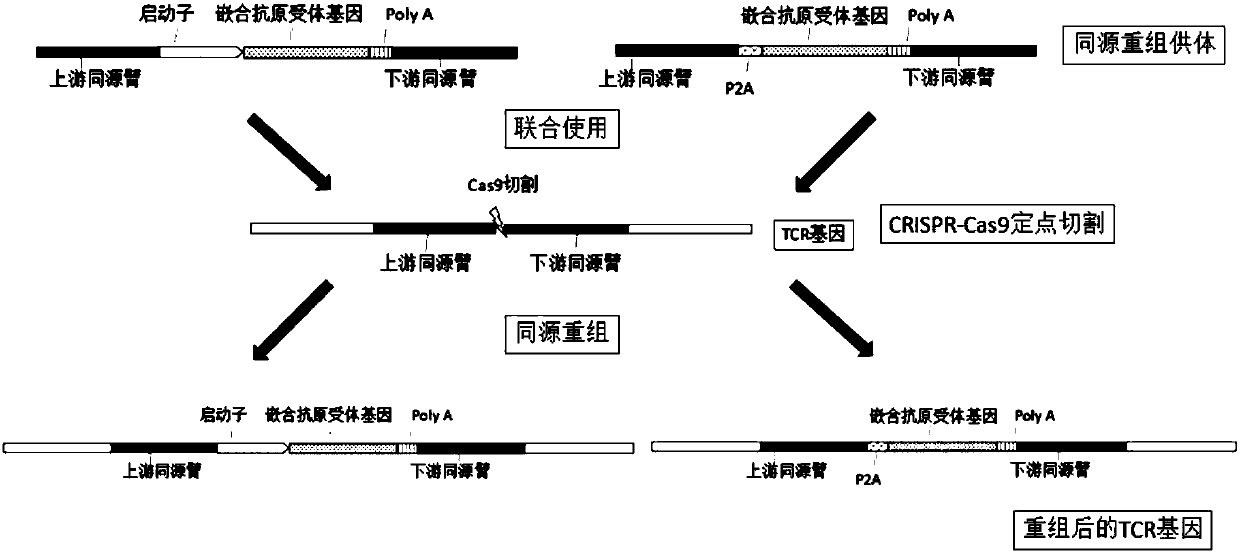
ActiveCN109628493AImprove functional activityAvoid interferenceHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAAntigenGenome editing
The invention provides a gene editing system for preparing allotransplantable T cells. The system is characterized by comprising sgRNA, wherein the sgRNA in a CRISPR / Cas9 specific knockout human TCR gene is used for specifically targeting a TCR gene. The target sequence of the sgRNA on the TCR gene conforms to a sequence arrangement rule of 5'-G(21N)NNGRRT-3 or 5'-ARRCNN(21N)C-3', the target sequence of the targeted knockout TCR gene takes virus as a transfection vector, and a chimeric antigen receptor gene with TCR gene homologous arms at the 5' end and the 3' end can transfect cells togetherwith the virus containing the target sequence of the TCR gene by using the virus as a vector when in use, or packs the target sequence of the TCR gene, Cas9 and the chimeric antigen receptor gene with the TCR gene homologous arms at the 5' end and the 3' end together in baculovirus and transfects cells with the baculovirus as a vector.
Owner:广东赤萌医疗科技有限公司
Dopamine functionalized poly(beta-amino ester) as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112876677AImprove stabilityHigh transfection efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesAmino estersCytotoxicity
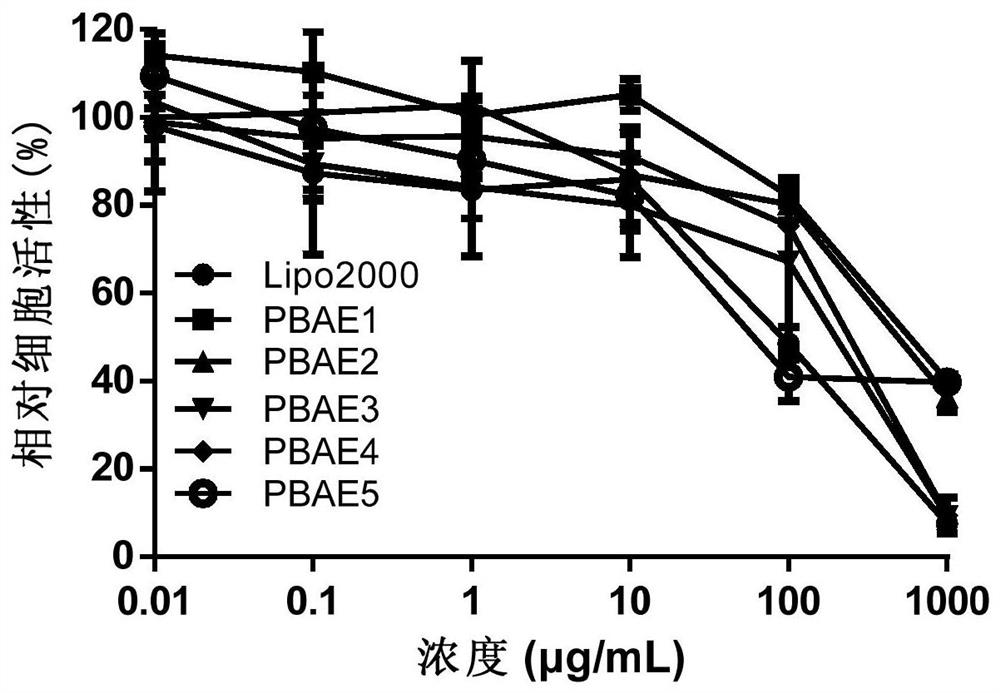
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and discloses dopamine functionalized poly(beta-amino ester) as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the poly(beta-amino ester) is shown in the specification, and the preparation method of the poly(beta-amino ester) comprises the steps: carrying out a polymerization reaction on 1,4-butanediol diacrylate and an amino-containing monomer; carrying out end capping on the polymer by adopting small molecular amine; and finally, carrying out deprotection on the phenolic hydroxyl group of dopamine to obtain the dopamine functionalized poly(beta-amino ester). Dopamine is introduced into PBAE, and ferric ions are complexed with the PBAE to form an encapsulated nanoparticle structure, so that the stability of a compound is improved, and a gene transfection vector with high transfection efficiency and low cytotoxicity is obtained, so that the gene transfection vector has potential clinical application value in the aspect of non-viral gene vectors.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV HANGZHOU GLOBAL SCI & TECH INNOVATION CENT
Recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone and its preparation method
The invention provides a recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone and a preparation method thereof. Specifically, steps are included: (1) the first expression cassette for expressing FSH α subunit and the second expression cassette for expressing FSH β subunit are operatively inserted into the eukaryotic expression vector to obtain the protein capable of expressing FSH α subunit and the transfection vector of FSH beta subunit protein; (2) transforming the transfection vector into eukaryotic cells, thereby obtaining the transformed eukaryotic cells integrated with the first expression cassette and the second expression cassette in the chromosome; (3) Under conditions suitable for expression, the transformed eukaryotic cells are cultivated to express the FSHα subunit and the FSHβ subunit, thereby obtaining a fermentation product containing recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone; (4) to the described The fermentation product is separated and purified to obtain the recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone. The method of the invention can replace the use and preparation method of the existing human FSH, and obtain rhFSH with significantly improved activity and purity.
Owner:JINGZE PHARMA (HEFEI) CO LTD +2
Lipids and complexes for the delivery of biologically-active material to cells
ActiveCN108779063AHigh transfection efficiencyEfficient releaseOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsViral GenesDelivery system
A lipid comprising a tri-chain cation of formula (la) having a cationic head group and three C12-24 hydrocarbyl groups for use in non-viral gene delivery systems, for example in the formation of lipopolyplex transfection vectors. Exceptionally good nucleic acid transfection is observed when nucleic acid and targeting peptides are formulated with the lipid of the invention (or lipid formulated witha co-lipid) into a LPD complex.
Owner:RYBOQUIN COMPANY
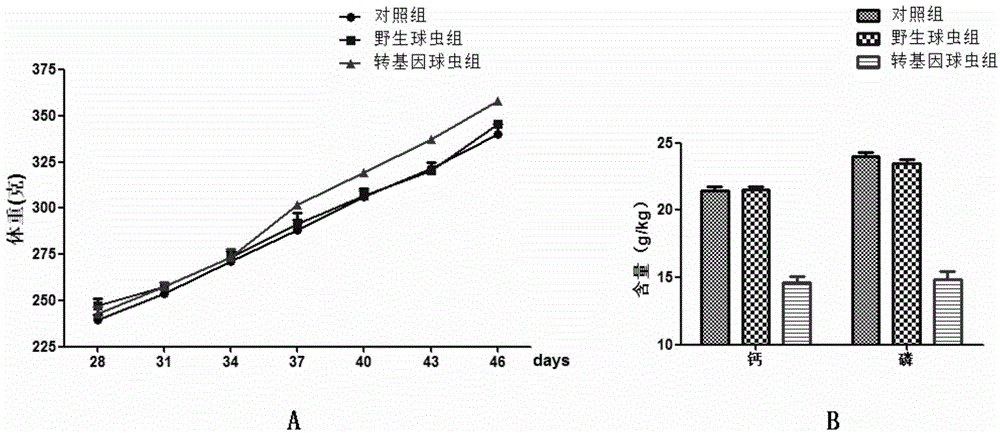
Method for improving calcium and phosphorus utilization ratio of livestock and poultry
InactiveCN104673830ANo productiveEquipment that does not require purificationHydrolasesAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyPhytic acid
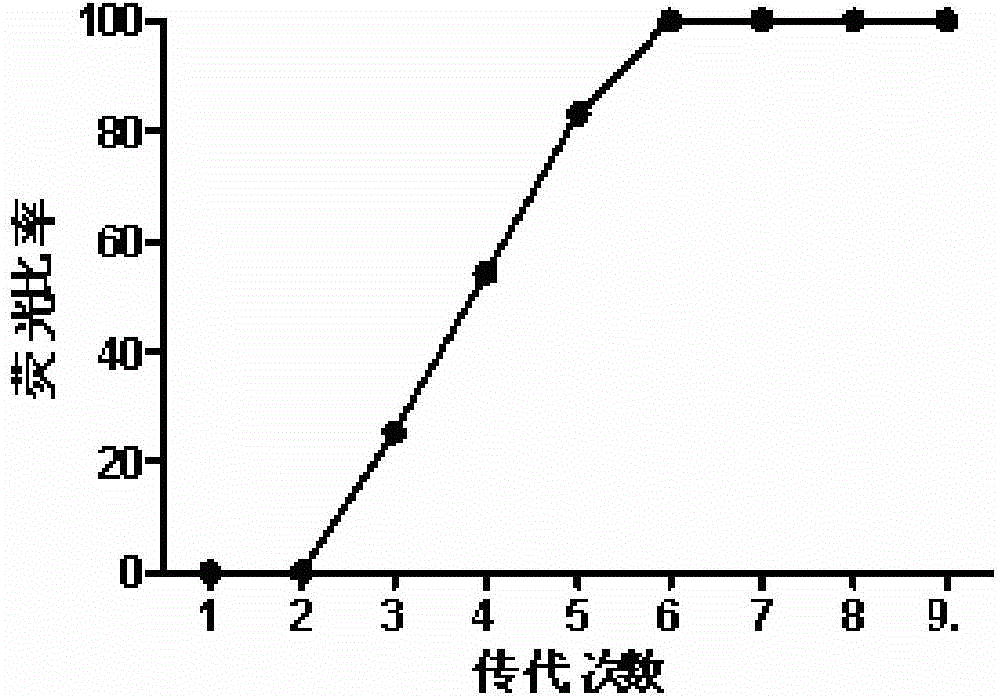
The invention provides a method for improving the calcium and phosphorus utilization ratio of livestock and poultry. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining full-length DNA of a phytase gene; (2) preparing a coccidium transfection vector pMDEA-phytase; (3) performing transfection on the vector and screening transgenic coccidia; and (4) inoculating the transgenic coccidia for expressing phytase into bodies of the livestock and poultry in an oral administration manner to ensure that the coccidia express and release phytase while developing in intestinal tracts, and degrading phytic acid. By adopting the method provided by the invention, phytase genes with different sources are expressed in the coccidia for the first time, so that a recombinant micro biological reactor is obtained and can generate phytase directly applied to the livestock and poultry, and equipment for production and purification and related operations are not needed.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
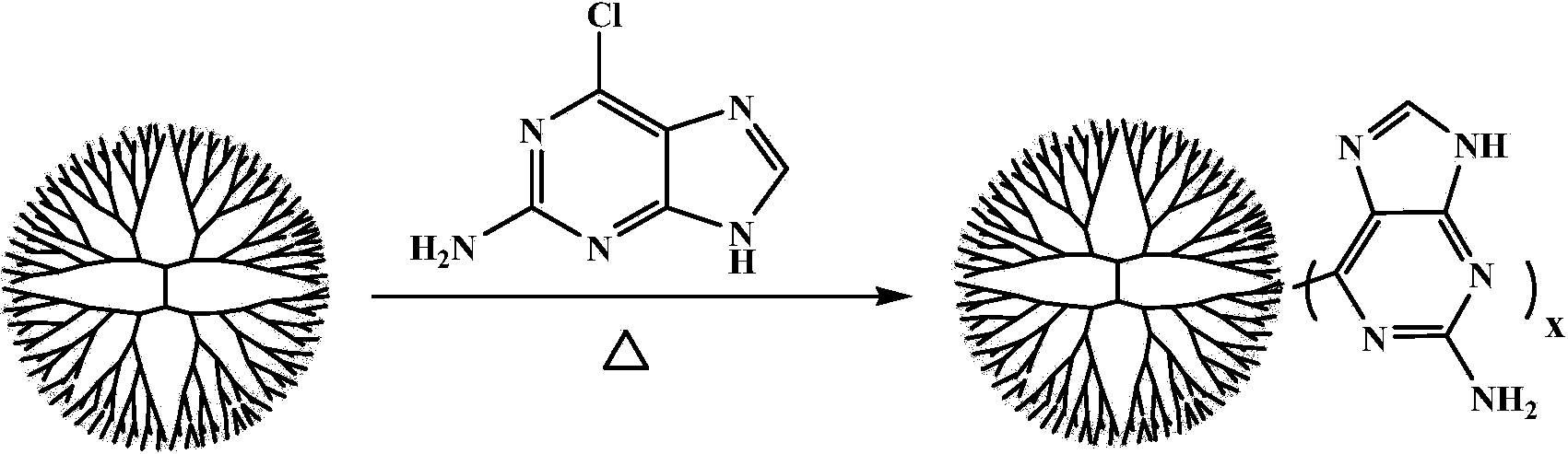
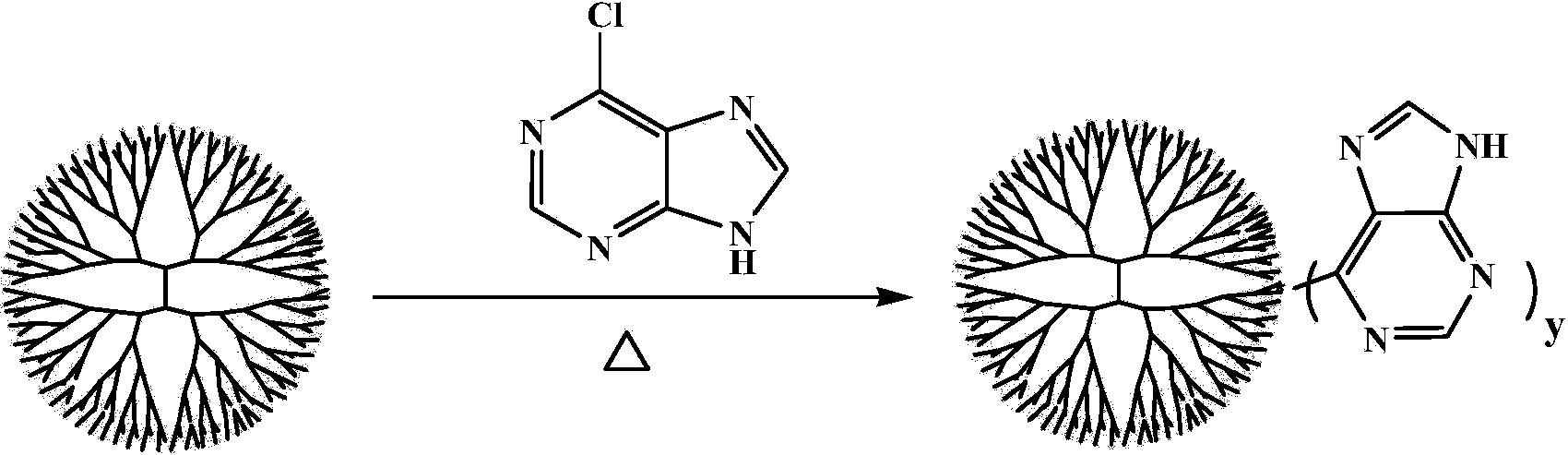
Polymer gene transfection vector based on nucleic acid base derivative and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103804694AHigh transfection efficiencyEasy to synthesizeOther foreign material introduction processesDendrimerGene
The invention provides a gene transfection vector based on a dendrimer skeleton and a nucleic acid basic group as shown in a formula (1). The gene transfection vector comprises a dendrimer and a nucleic acid base derivative, wherein the nucleic acid base derivative is in covalent linkage with the surface of the dendrimer. The invention also provides a preparation method of the gene transfection vector shown in the formula (1) and application as a nucleic acid molecule delivery vector. The gene transfection vector provided by the invention is low in synthesis cost and small in cell toxicity, can effectively and safely convey genetic molecules into cells, can be used as the gene transfection vector with the advantages of high efficiency, low toxicity, low cost and the like, and has good application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Alicyclic compound modified high-molecular material and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides an alicyclic compound modified high-molecular material. The alicyclic compound modified high-molecular material comprises an alicyclic compound gene and a cationic high-molecular skeleton, wherein the alicyclic compound gene is covalently connected with the surface of the cationic high-molecular skeleton, the cationic high-molecular skeleton comprises polyamidoamine dendrimers, polypropyleneimine dendrimers, polylysine dendrimers, branched polyethyleneimine cationic polymers and linear polyethyleneimine cationic polymers. The invention further provides a preparation method of the high-molecular material and application as a biological macromolecular transfection vector. The synthesis cost of the high-molecular material provided by the invention is low, the cytotoxicity is low, the biocompatibility is high, gene molecules can be effectively and safely delivered into cells, the high-molecular material can be used as the gene transfection vector having the advantages of high efficiency, low toxicity, low cost and the like, and the application prospect is good.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Transfection system for perkinsus species
A Perkinsus heterologous expression system that is useful to produce recombinant proteins, e.g., from related parasites of medical and veterinary relevance. This expression system increases the number of genes that can be targeted for protein structure / function studies, production of antigens, and in vitro drug screening. Also described is a transfection system for Perkinsus species, including a transfection vector expressing heterologous DNA encoding one or more Apicomplexa proteins.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BIOTECH INST
Polyethyleneimine derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN113603886ALow cytotoxicityHigh transfection efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsAntigenImmune Stimulation
The invention provides a polyethyleneimine derivative. The polyethyleneimine derivative is obtained by bonding PEI and nitrogen heterocyclic ring micromolecules. Compared with PEI, a PEI derivative material provided by the invention can reduce the toxicity of PEI and has the function of stimulating inherent immune response. The PEI derivative material provided by the invention can be used for loading protein or mRNA antigen through simple mixing to prepare a novel vaccine, and since a vector has an immune stimulation function, the design of the vaccine can be simplified and the response rate of the vaccine can be improved; and the PEI derivative provided by the invention can also be used for transfection vectors of mRNA and DNA, and can realize better cell transfection efficiency on the premise of reducing the toxicity of PEI.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Non-genetically modified light control bidirectional regulation method for human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell proliferation
ActiveCN108624554AObviously positiveThe effect of obvious negative regulationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentUmbilical cordMedical treatment
The invention relates to a non-genetically modified light control bidirectional regulation method for human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell proliferation. The method includes the steps: irradiating human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells at 95-105mm positions under a collimating mirror for 85-95min through the collimating mirror by the aid of blue light under the conditions of the light wavelength of 400-480nm and the light intensity of 95-105 micro-w / cm<2>, and performing negative regulation; or irradiating the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells at the 95-105mm positions under the collimating mirror for 115-125min through the collimating mirror by the aid of blue light, and performing positive regulation. According to the method, the multiplication speed of the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells is firstly and bi-directionally regulated only through blue light irradiation under setting of special parameters, foreign genes transferred into the stem cells areomitted, virus transfection vectors are omitted, any other substances are omitted, and the method more meets clinical application requirements of 'noninvasive light therapy' and has a wide clinical application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Carbon nano-tube as siRNA carrier and transfection method thereof
InactiveCN101220369ALow cytotoxicityOther foreign material introduction processesVector-based foreign material introductionCulture cellCytotoxicity
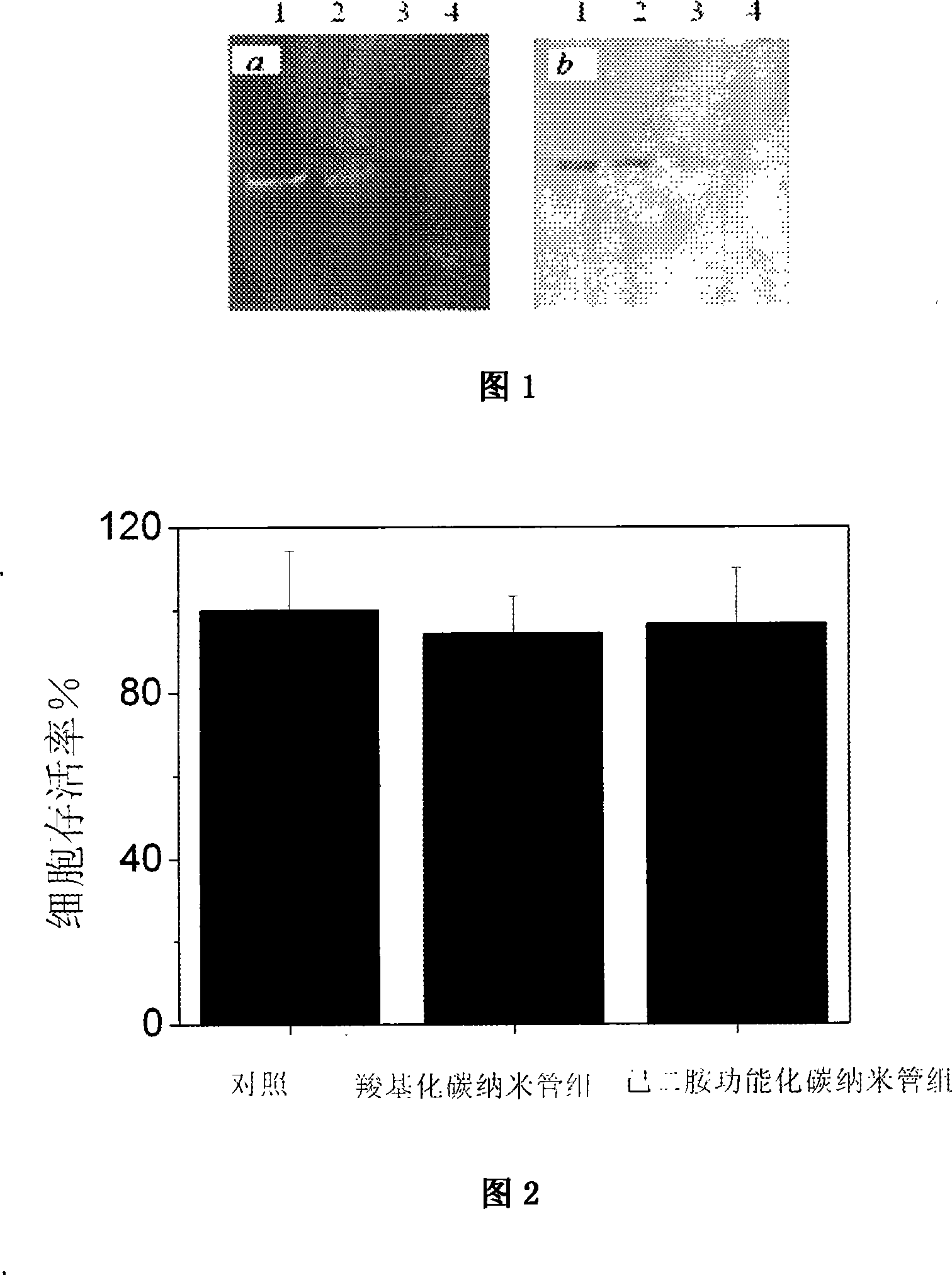
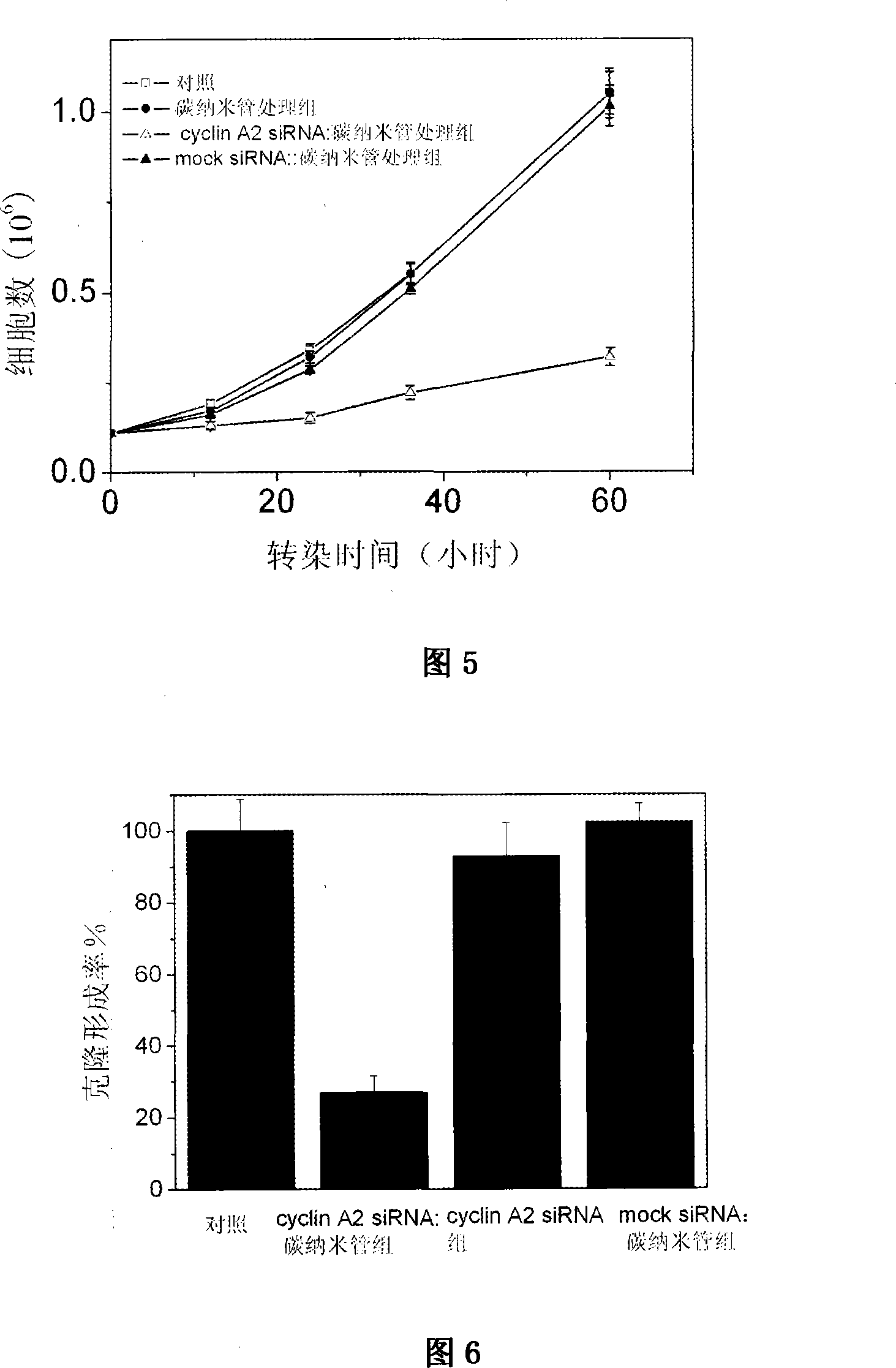
The invention relates to a method for utilizing a carbon nano-tube as a siRNA vector and the transfection. The invention utilizes the carbon nano-tube as the siRNA transfection vector, the vector has very low cytotoxicity and can effectively transfect the siRNA into a cell for leading the siRNA to play biological function. The transfection proposal is that: (1) the siRNA is prepared by a conventional method; (2) the carbon nano-tube and the siRNA are mixed evenly and placed for a period of time at the room temperature; (3) the treated mixture of the carbon nano-tube and the siRNA is utilized for culturing cells. The method for utilizing a carbon nano-tube as the siRNA vector and the transfection of the invention has the advantages of low cytotoxicity, high transfection efficiency and so on. The siRNA takes the hexamethylene diamine-functionized carbon nano-tube as the vector, and the mRNA expression level of the human cyclin A2 of K562 cell is reduced by 60 to 95 percent via the transfection.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Construction method of fusarium graminearum single-stranded circular DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) virus FgGMTV1/HB58 infectious cloning
ActiveCN109810997ASimplified cloningSimplify the transfection stepVector-based foreign material introductionSingle strandFusarium
The invention discloses a construction method of fusarium graminearum single-stranded circular DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) virus FgGMTV1 / HB58 infectious cloning. A virus genome contains two single-stranded circular DNA molecules including DNA-A and DNA-B, and genome sequences of the DNA-A and the DNA-B are shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 to 2; the virus genome does not contain a single-stranded circular DNAmolecule DNA-C and the genome sequence of the DNA-C is shown as SED ID NO: 3. The construction method comprises the following steps: constructing DNA-A infectious cloning, constructing DNA-B infectious cloning and constructing DNA-C infectious cloning. When the infectious cloning is constructed, only one bacterium cloning vector pBluescript II SK(+) is needed and fungi can be cloned and transfected successfully; cloning and transfection steps are simplified and a plurality of times of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) cloning are not needed; a plurality of cloning vectors and transfection vectors are not needed, and the transfection can be finished, without the need of cloning the fungi to a binary expression vector.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
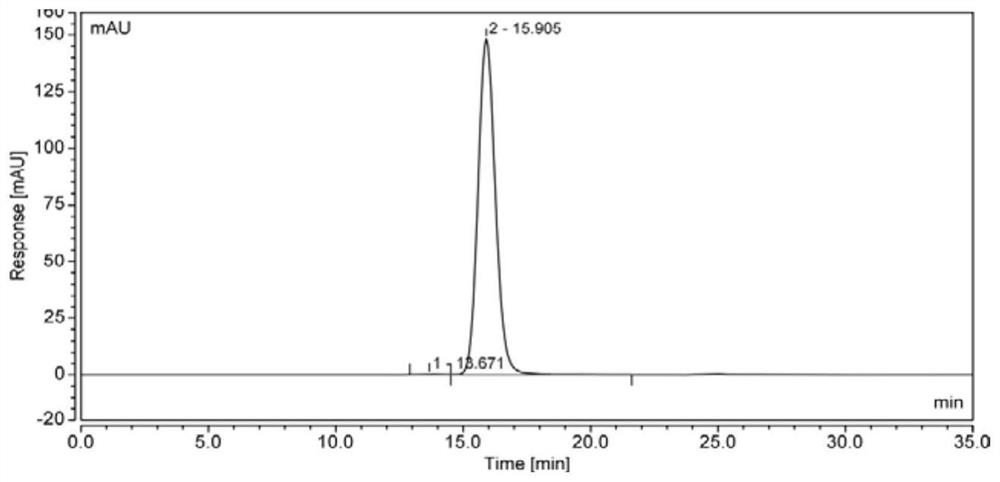
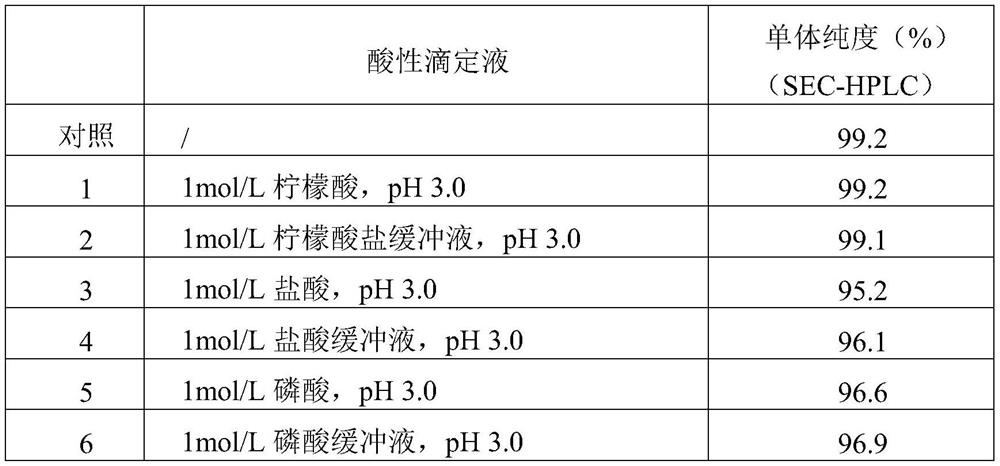
Preparation method for recombinant human antibody fusion protein
The invention provides a purification method for a recombinant human antibody fusion protein. The method comprises the following steps: (a) providing a transfection vector for expressing a gene of therecombinant human antibody fusion protein; (b) transfecting the transfection vector into a mammalian cell and performing culturing to obtain a raw material solution containing the recombinant human antibody fusion protein and impurities; (c) carrying out affinity chromatography on the raw material solution to obtain an affinity chromatography solution; and (d) carrying out low-pH incubation and deep filtration on the affinity chromatography solution to prepare a first purified solution, namely the purified recombinant human antibody fusion protein, wherein the pH value of the low-pH incubation is 3-4, and citric acid or salt thereof is utilized to adjust the pH value. The method disclosed by the invention not only can remove the impurities efficiently, but also keeps the activity of the target protein-the recombinant human antibody fusion protein, so that the high-purity and high-concentration recombinant human antibody fusion protein is prepared so as to be used for treating ocular neovascularization diseases of mammals.
Owner:SHANGHAI JINGZE PHARMA CO LTD +1
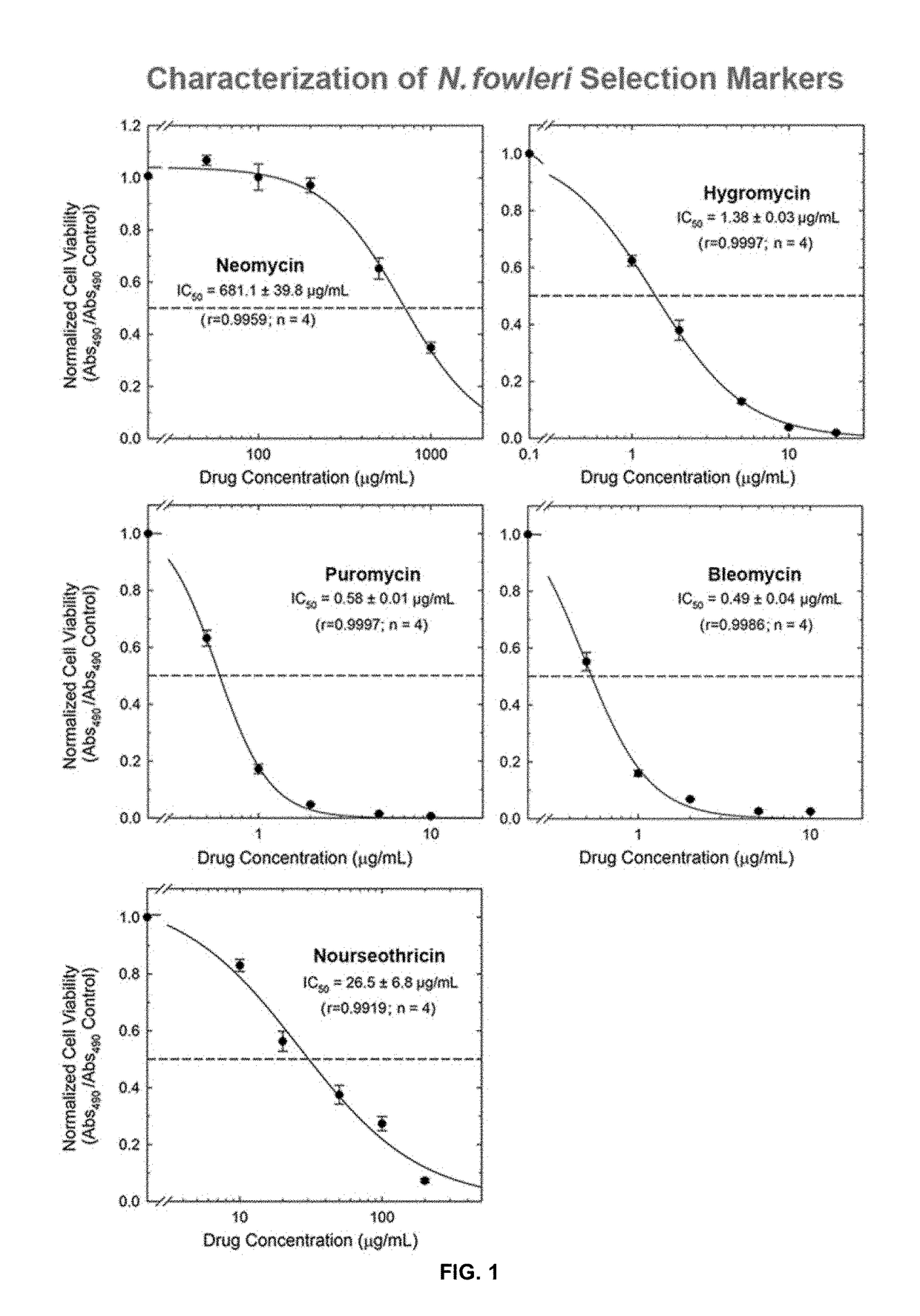
Transfection vector for pathogenic amoebae and uses thereof
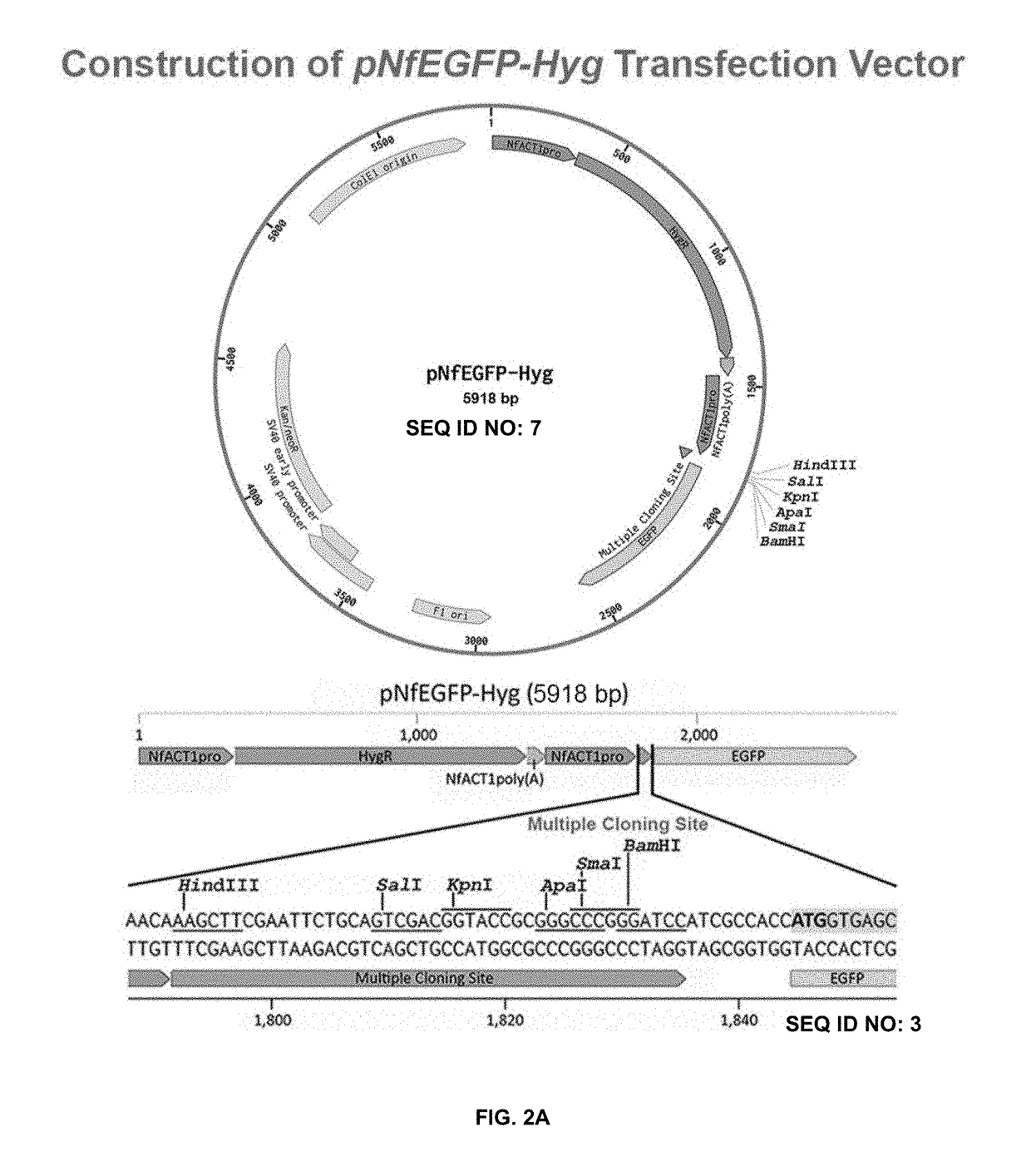
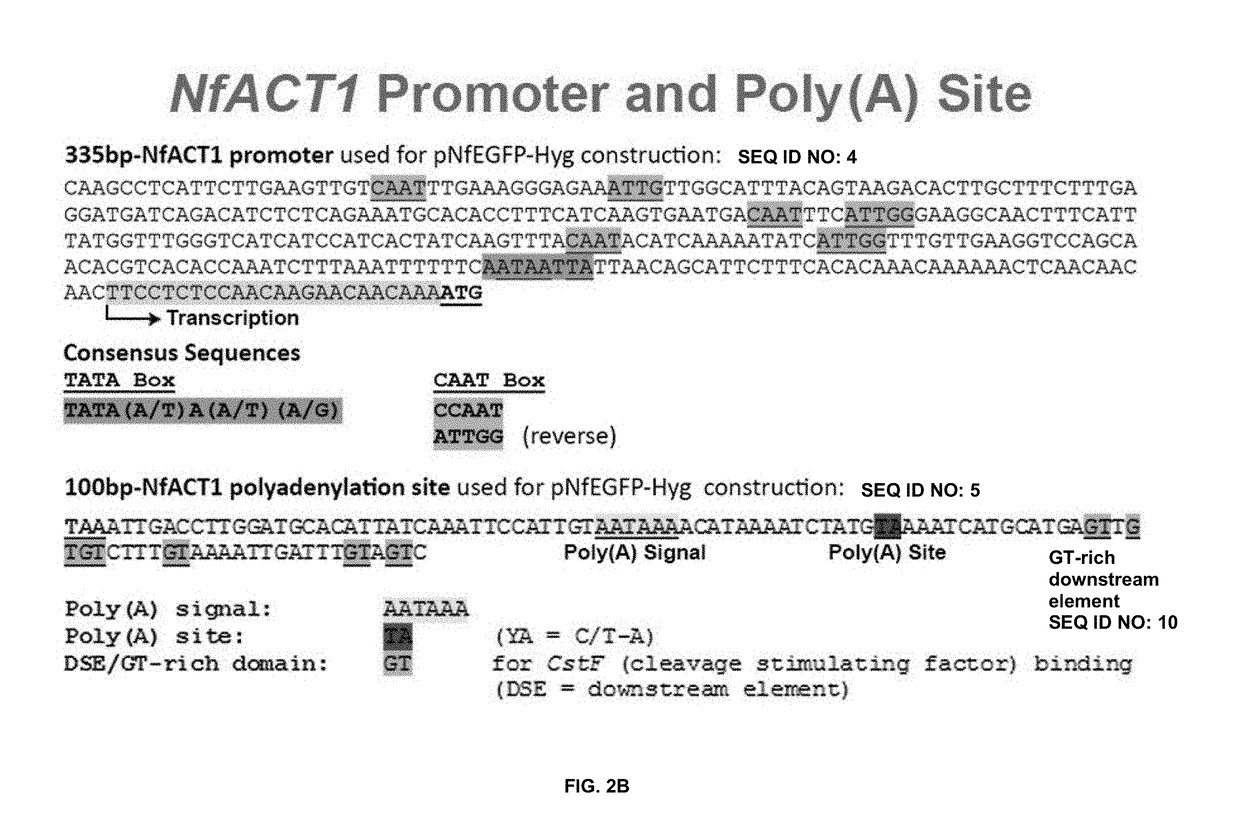
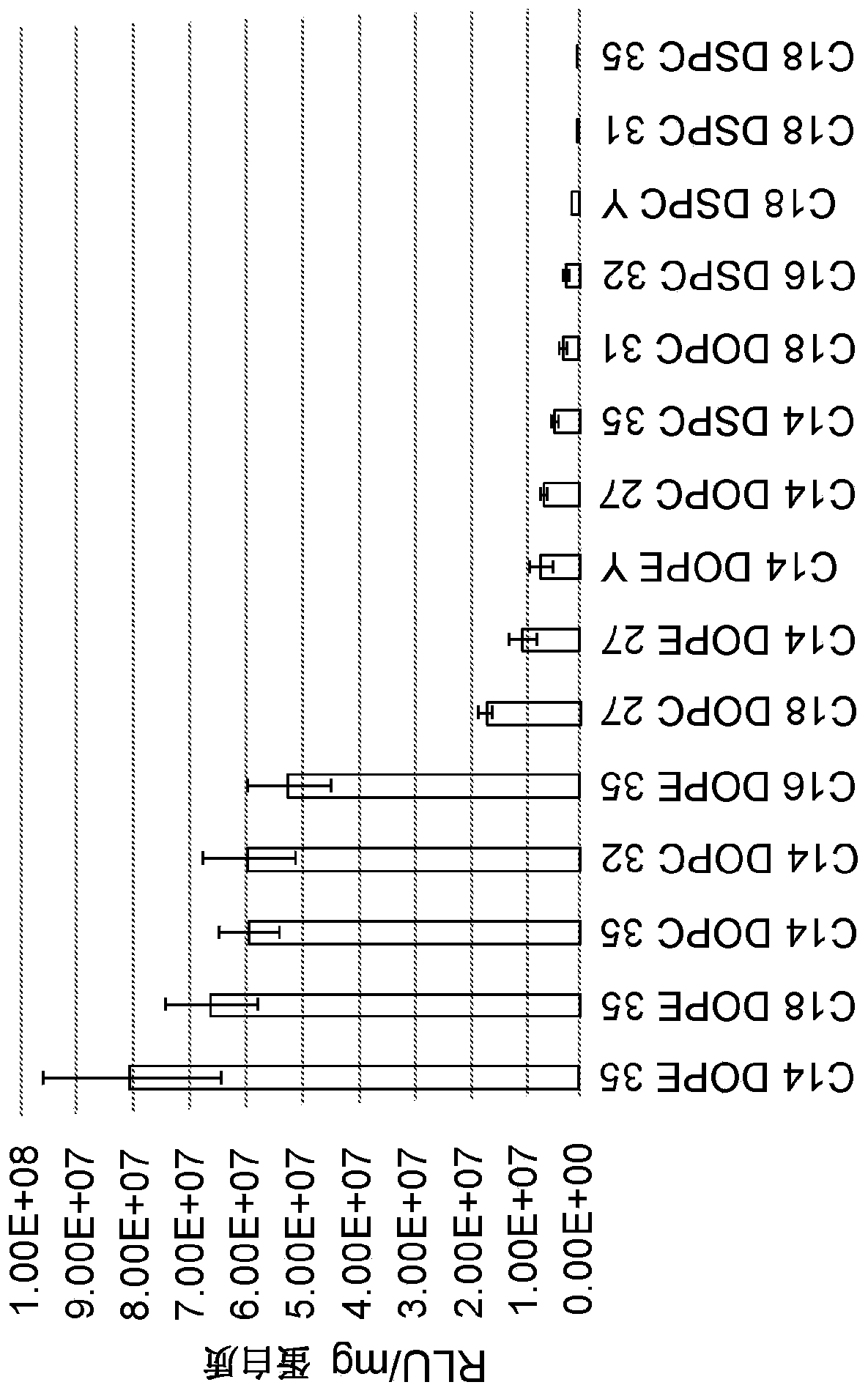
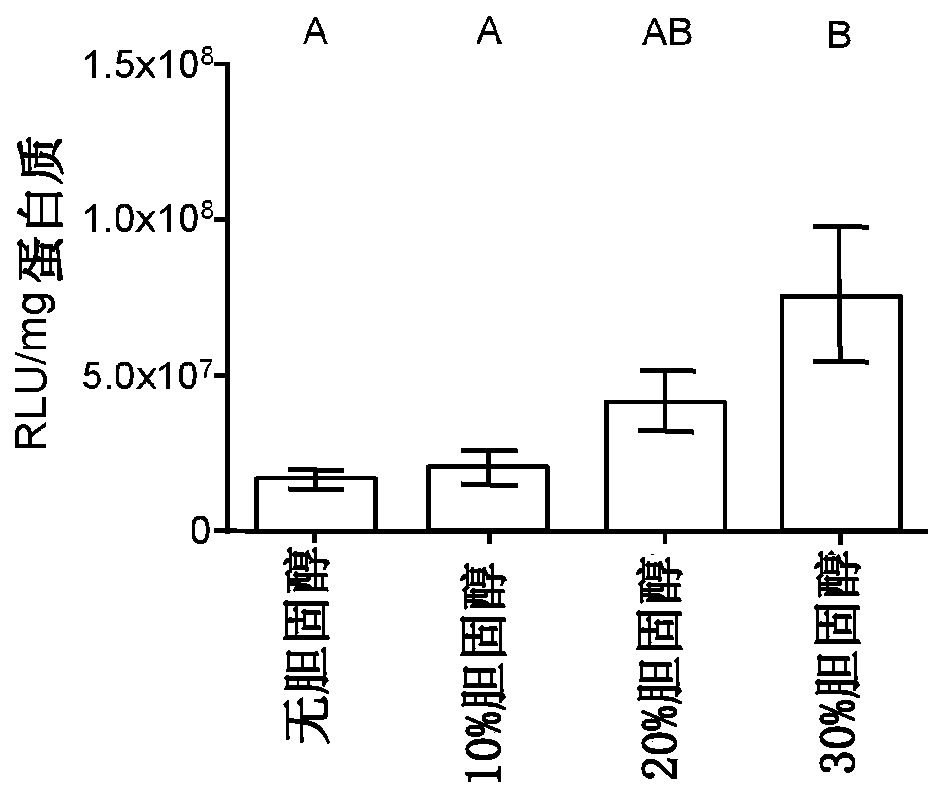
Disclosed herein are expression vectors suitable for transfection in amoebas. The vectors may include a promoter from a protein-encoding gene from an amoeba, a selection marker, and a polynucleotide sequence encoding a polypeptide of interest, operably linked to the promoter. The promoter may be from the ACT1 gene from Naegleria fowleri.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Improved lipid-peptide nanocomplex formulation for mRNA delivery to cells
A liposome comprising a cationic lipid, a phospholipid and a peptide and optionally consisting of from 20 to 50% by molarity cholesterol, based on the total amount of lipids,for use in non-viral genedelivery systems, for example,in the formation of lipopolyplex transfection vectors for the delivery of mRNA to cells.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Dendrimer transgene carrier modified with bone-targeting peptide and naphthalimide, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108753829BEasy to purifyLow toxicityOther foreign material introduction processesDendrimerTarget peptide
The present invention provides a dendrimer transgene carrier modified with bone-targeting peptide and naphthalimide, which includes a dendrimer skeleton, a bone-targeting peptide group, and a functional group containing naphthalimide. The targeting peptide group and the naphthalimide functional group are covalently bonded on the surface of the dendrimer; the dendrimer is a polyamide-amine dendrimer. The invention also provides the preparation method of the gene transfection carrier and the application of the dendrimer transgene carrier as a nucleic acid molecule delivery carrier. The invention adopts a brand-new modification method and a functional group to modify the dendrimer, the reaction is simple and efficient, the yield is high, the efficient transfection effect is achieved in the cell transfection process, and the bone targeting performance is better. The production of materials is simple and low in cost, the cytotoxicity of the transfection process is low, and gene molecules can be effectively and safely transported into cells. The dendrimer transgene carrier of the present invention has the advantages of high efficiency, low toxicity, low price, and simple synthesis .
Owner:西安九清医疗科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com