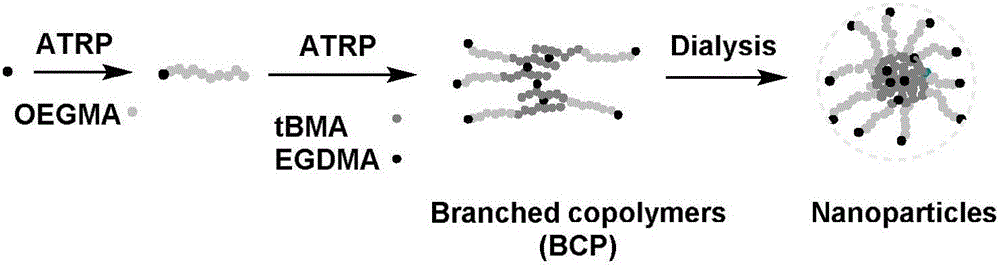
Ultra-mild crosslinking hyperbranched structure polymer nanometer slow-release material and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of nano slow-release materials and structural polymers, applied in the direction of botany equipment and methods, applications, biocides, etc., can solve the problems of ecological system structure and function damage, low use efficiency, low efficiency, etc., and achieve special structure , Nano size controllable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Example 1: P(OEGMA 50 / tBMA 27 )
[0055] 1. Preparation of hyperbranched polymer
[0056] Ethyl isobromobutyrate (65mg, 0.33mmol), cuprous bromide (47.8mg, 0.33mmol), polyethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate (OEGMA, 5g, 16.67mmol), anisole (10ml) It was placed in a dry 50ml Schlenk flask, vacuumized after liquid nitrogen freezing - nitrogen filling was repeated three times to remove oxygen, then pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (114.2mg, 0.66mmol) was added with a micro syringe, and then the Schlenk flask was placed Put into the oil bath of 70 ℃ to react, take the sample during the reaction for NMR to determine the monomer conversion rate, when the OEGMA conversion rate reaches 90%, add tert-butyl methacrylate (1.42g, 10mmol ), the reaction continues, and the sample is taken during the reaction for NMR to determine the monomer conversion rate. When the PEGMA conversion rate reaches 90%, the polymerization is terminated. After the reaction solution is passed throug...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Embodiment 2: P(OEGMA 50 / tBMA 45 )
[0061] 1. Preparation of hyperbranched polymer
[0062] Ethyl isobromobutyrate (65mg, 0.33mmol), cuprous bromide (47.8mg, 0.33mmol), polyethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate (OEGMA, 5g, 16.67mmol), anisole (10ml) Placed in a dry 50ml Schlenk flask, evacuated after liquid nitrogen freezing-nitrogen was repeated three times to remove oxygen, then added pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (114.2mg, 0.66mmol) with a micro syringe, then the Schlenk flask was placed Put it into an oil bath at 70°C for reaction, and take a sample during the reaction for NMR to determine the monomer conversion rate. When the OEGMA conversion rate reaches 90%, add tert-butyl methacrylate (2.37, 16.67 mmol), the reaction continues, and the sample is taken during the reaction for NMR to determine the monomer conversion rate. When the PEGMA conversion rate reaches 90%, the polymerization is terminated. After the reaction solution is passed through the neutral...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Embodiment 3: P(OEGMA 50 / tBMA 63 )
[0075] 1. Preparation of hyperbranched polymer
[0076] Ethyl isobromobutyrate (65mg, 0.33mmol), cuprous bromide (47.8mg, 0.33mmol), polyethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate (OEGMA, 5g, 16.67mmol), anisole (10ml) It was placed in a dry 50ml Schlenk flask, vacuumized after liquid nitrogen freezing - nitrogen filling was repeated three times to remove oxygen, then pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (114.2mg, 0.66mmol) was added with a micro syringe, and then the Schlenk flask was placed Put into the oil bath of 70 ℃ to react, take a sample during the reaction for NMR to determine the monomer conversion rate, when the OEGMA conversion rate reaches 90%, add tert-butyl methacrylate (3.31g, 23.34mmol), the reaction continues, take a sample during the reaction and do NMR to determine the monomer conversion rate, when the PEGMA conversion rate reaches 90%, the polymerization is terminated, after the reaction solution is passed through th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com