A total knee replacement prosthesis
A technology for total knee replacement and prosthesis, applied in the directions of knee joint, elbow joint, joint implant, etc., can solve the problem of unstable combination of tibial tray and joint pad, short service life of knee joint replacement prosthesis, tibia To ease the problems of sinking and rotation, to achieve the effect of being beneficial to metabolism, improving biocompatibility, and improving long-term use stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
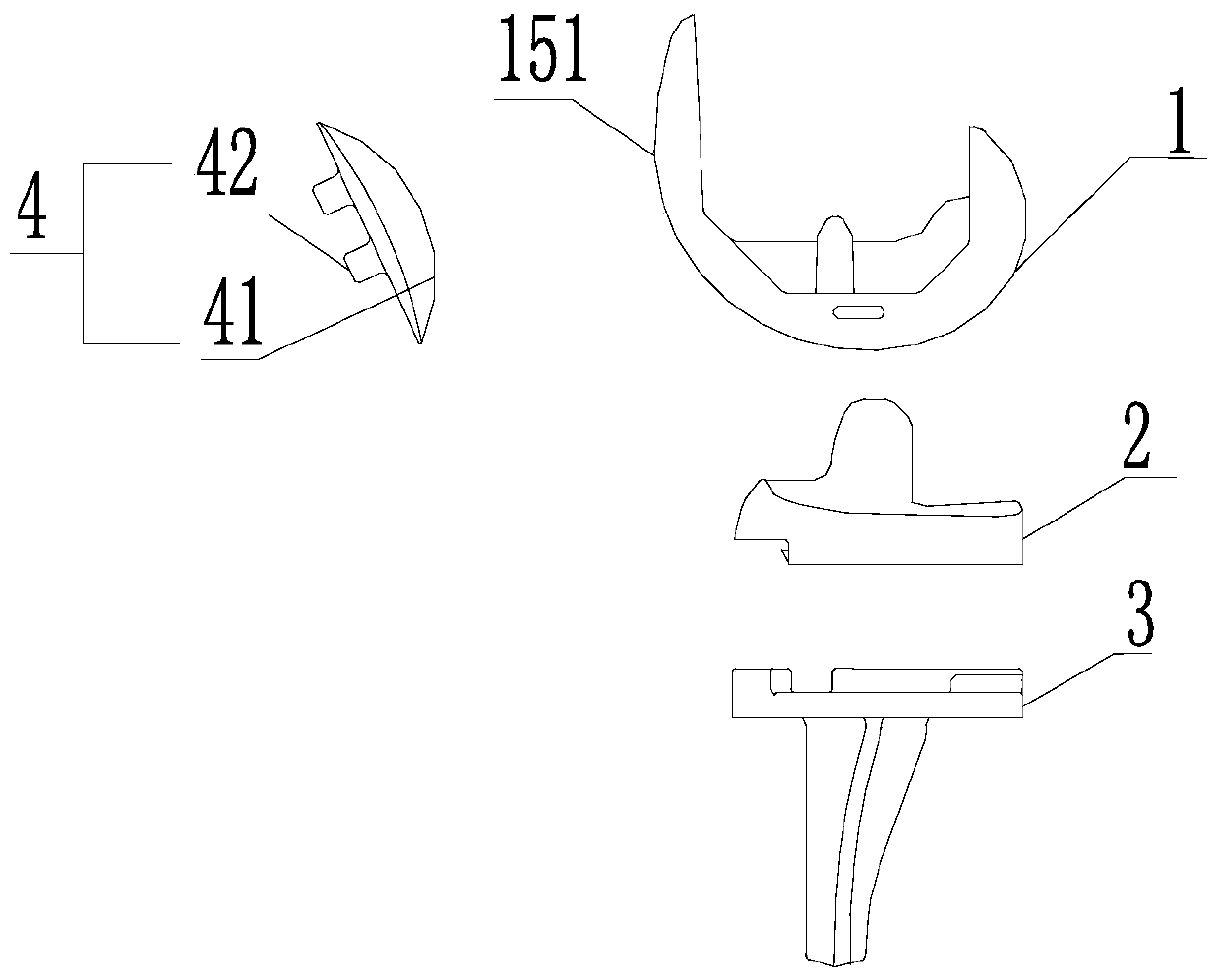
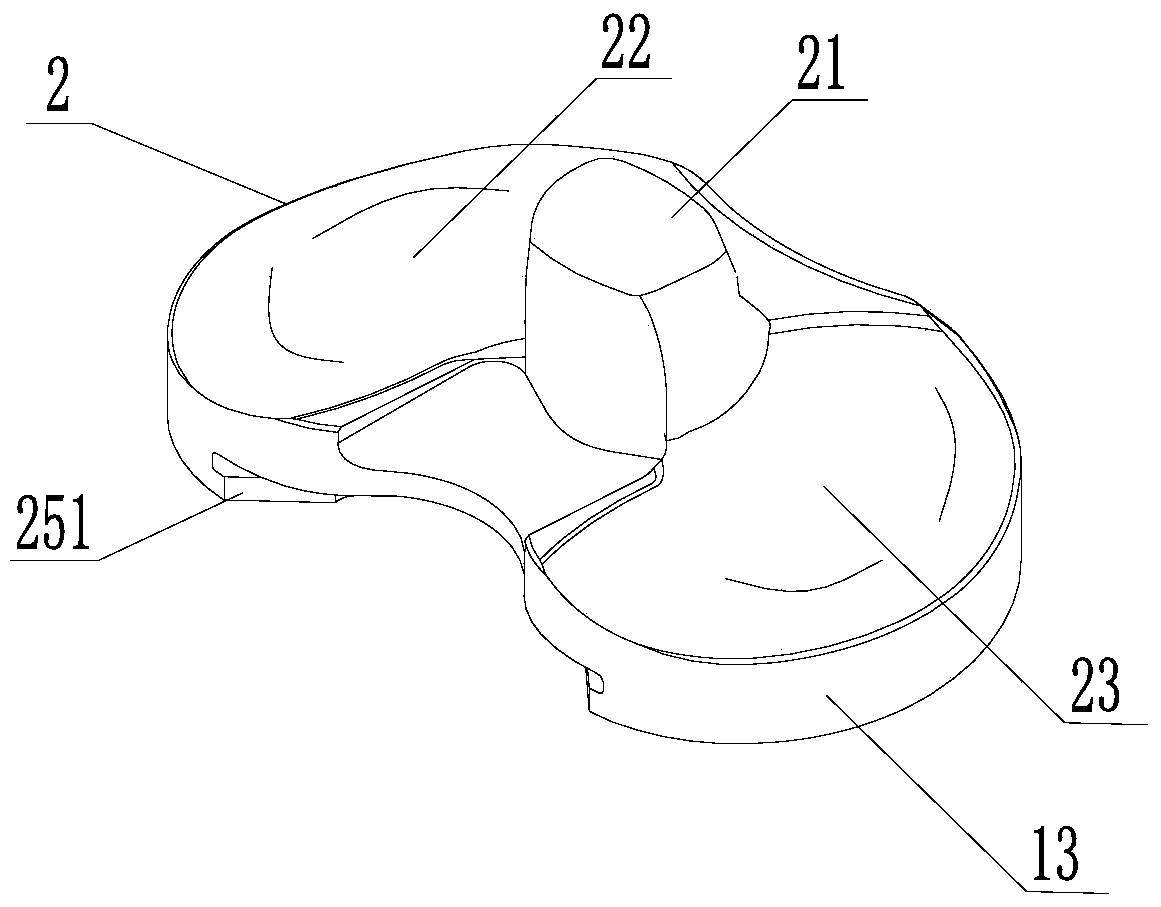
[0037] The present invention provides a total knee replacement prosthesis, such as Figure 1 to Figure 6 As shown, the total knee replacement prosthesis includes a femoral condyle 1, a tibial pad 2, a tibial tray 3, and a patella 4, and the tibial pad 2 is high cross-linked polyethylene, wherein,
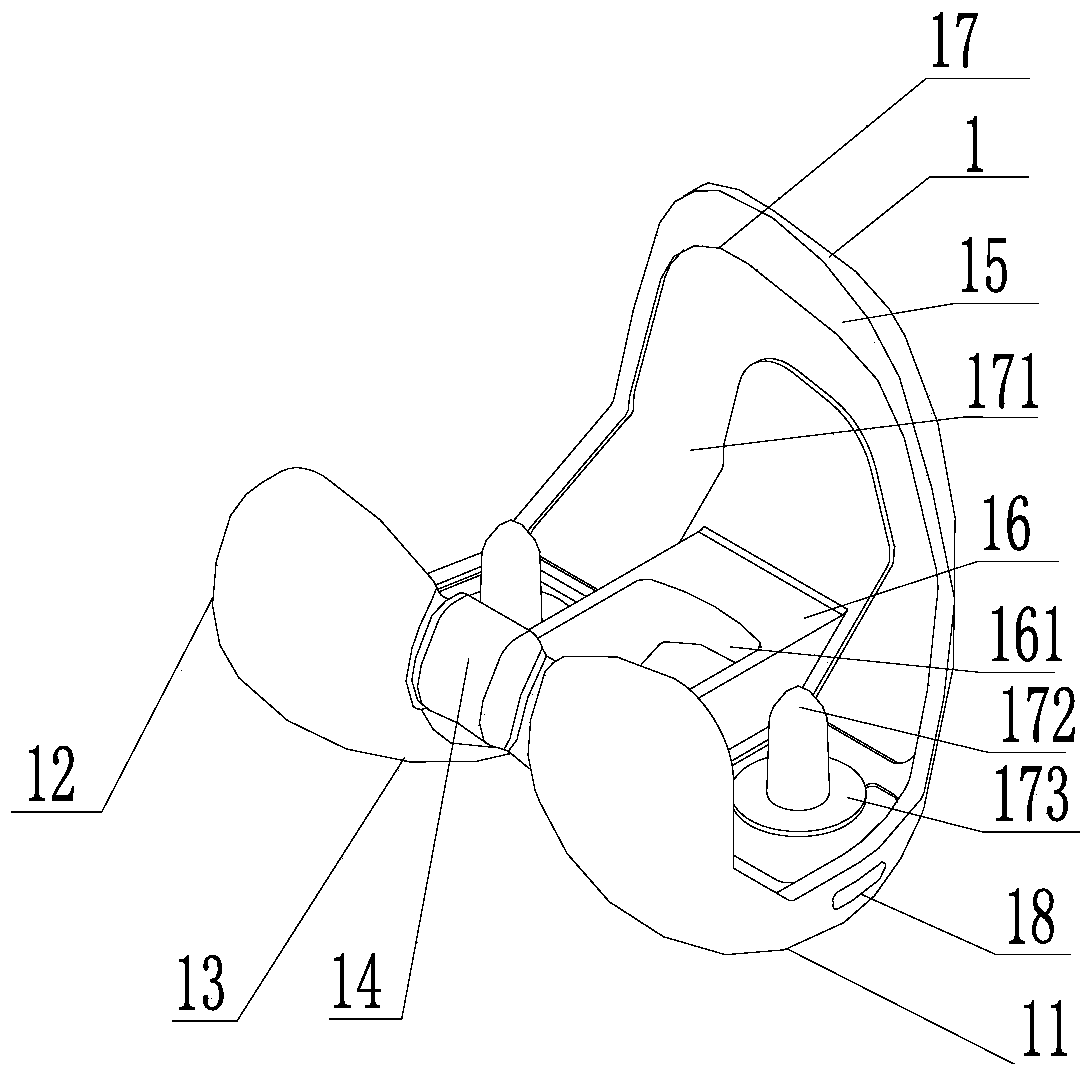
[0038] The femoral condyle 1 includes the medial condyle 11, the lateral condyle 12, the articular surface 13 defined jointly by the distal ends of the medial condyle 11 and the lateral condyle 12, an intercondylar box 16 located between the medial condyle 11 and the lateral condyle 12, and an intercondylar box located between the medial condyle 11 and the lateral condyle 12. The condyles on both sides of 16 join the inner surface 17; the distal ends of the medial condyle 11 and the lateral condyle 12 are connected by a stopper 14, and after the proximal ends meet, they extend to form a femoral trochlea 15, and the lower end surface of the femoral trochlea 15 forms a patellar trochle...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The present invention provides a total knee replacement prosthesis, which is different from Example 1 in that, as Figure 7 As shown, the limiting column 21 and the fixing keel 32 are arranged on the same straight line perpendicular to the support plate 31 , and the straight line passes through the end point of the second column 35 closest to the first column 34 . In this way, the longitudinal force on the tibial pad is more reasonable, transmitted to the tibial tray and dispersed through the fixed keel at the lower part of the tibial tray, and at the same time minimizes the lateral force on the support plate caused by the uneven force exerted by the femoral condyle on the tibial pad Torsion effect, which increases the lifespan of total knee replacement prostheses.
Embodiment 3
[0049] The present invention provides a total knee replacement prosthesis, such as Figure 8 As shown, the difference between this total knee replacement prosthesis and embodiment 1 is that the structure of the tibial support 3 is as follows Figure 7 As shown, the tibial interface 36 includes a second cement pocket 362 defined by a protrusion 361 formed in a peripheral portion. Wherein, both the second bone cement tank 362 and the first bone cement tank 151 are filled with bone cement. The bone cement consists of the following raw materials in mass percentage: magnesium oxide 15%-30%, titanium chloride 15%-25%, hydroxyethyl methylcellulose 2%-4.5%, polyvinylpyrrolidone 10%-15% %, collagen 10%-15%, chitin 0.5%-1%, polyvinyl alcohol 1.1%-2%, and deionized water 20%-30%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com