A kind of hole-protecting drying method of porous material
A porous material and drying method technology, applied in the field of porous materials, can solve the problems of large loss of entrainer, high cost, high equipment cost, etc., and achieve the effect of mild operating conditions, easy recycling, and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: The operation steps are: a certain amount of silica gel is placed in a heated kettle with stirring; ethyl acetate is selected as the displacing agent, n-butanol is the pore protectant, and the volume ratio is 5:0.1:1 ( Displacer: pore protectant: water content in the gel) add solvent; heat the heating kettle to boiling (about 71℃), reflux for 2h, this process replaces most of the water in the silica gel; continue heating to reduce Press distillation to obtain dry silica powder.
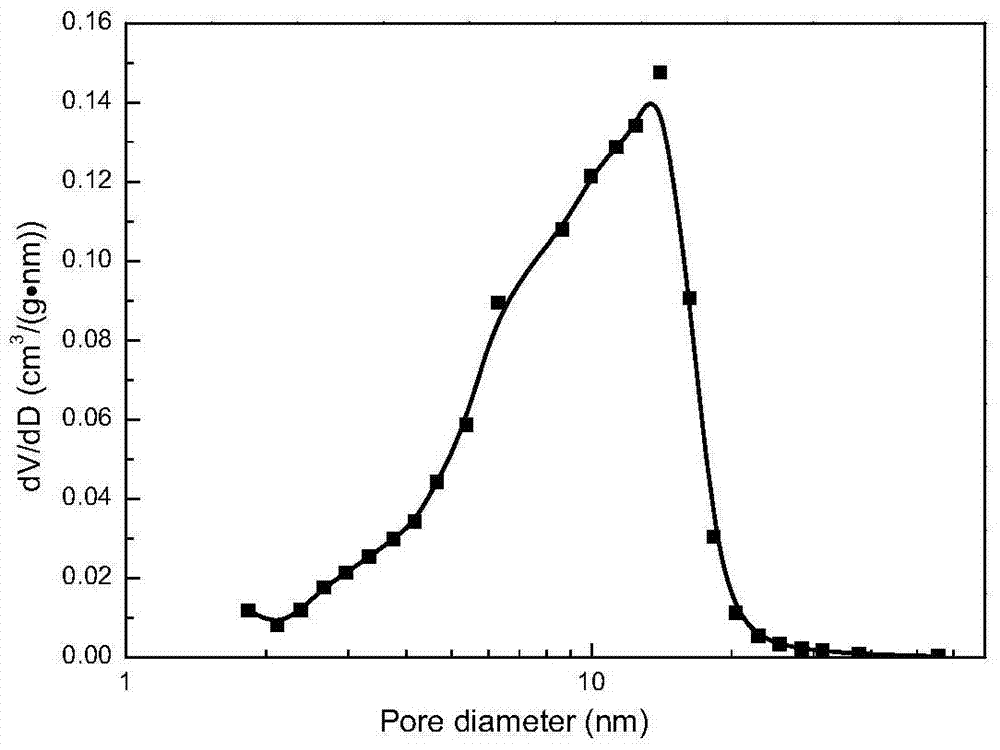
[0027] Product-related data is shown in Table 1, and the pore size distribution is as figure 2 Shown.
Embodiment 2
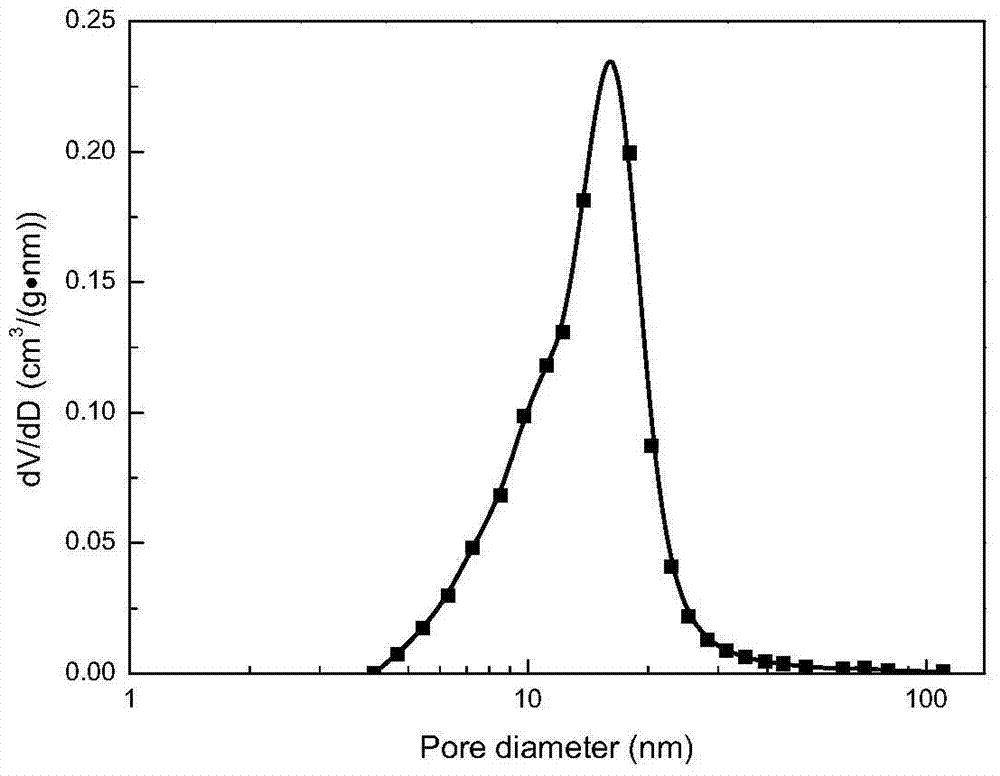
[0028] Embodiment 2: The operation steps are the same as in embodiment 1. The difference is that the solvent is added in a volume ratio of 5:0.3:1 (displacer: pore protectant: moisture content in the gel). Product-related data is shown in Table 1, and the pore size distribution is as image 3 Shown.
Embodiment 3
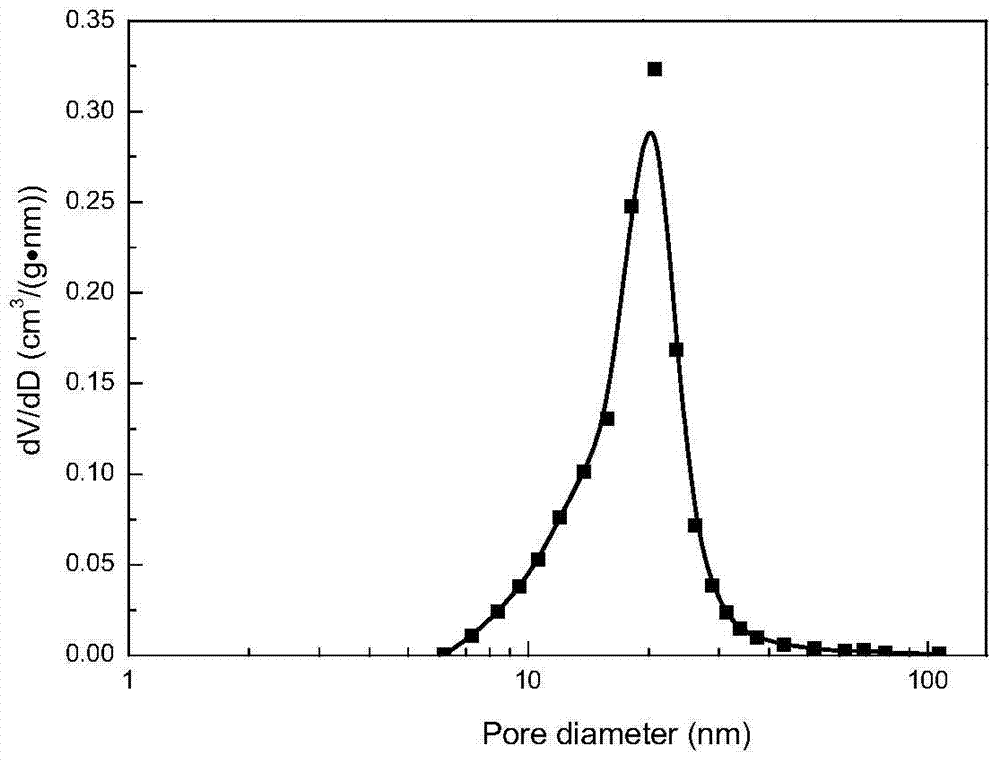
[0029] Embodiment 3: The operation steps are the same as in embodiment 1. The difference is that the solvent is added at a volume ratio of 5:1:1 (displacer: pore protectant: moisture content in the gel). Product-related data is shown in Table 1, and the pore size distribution is as Figure 4 Shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com