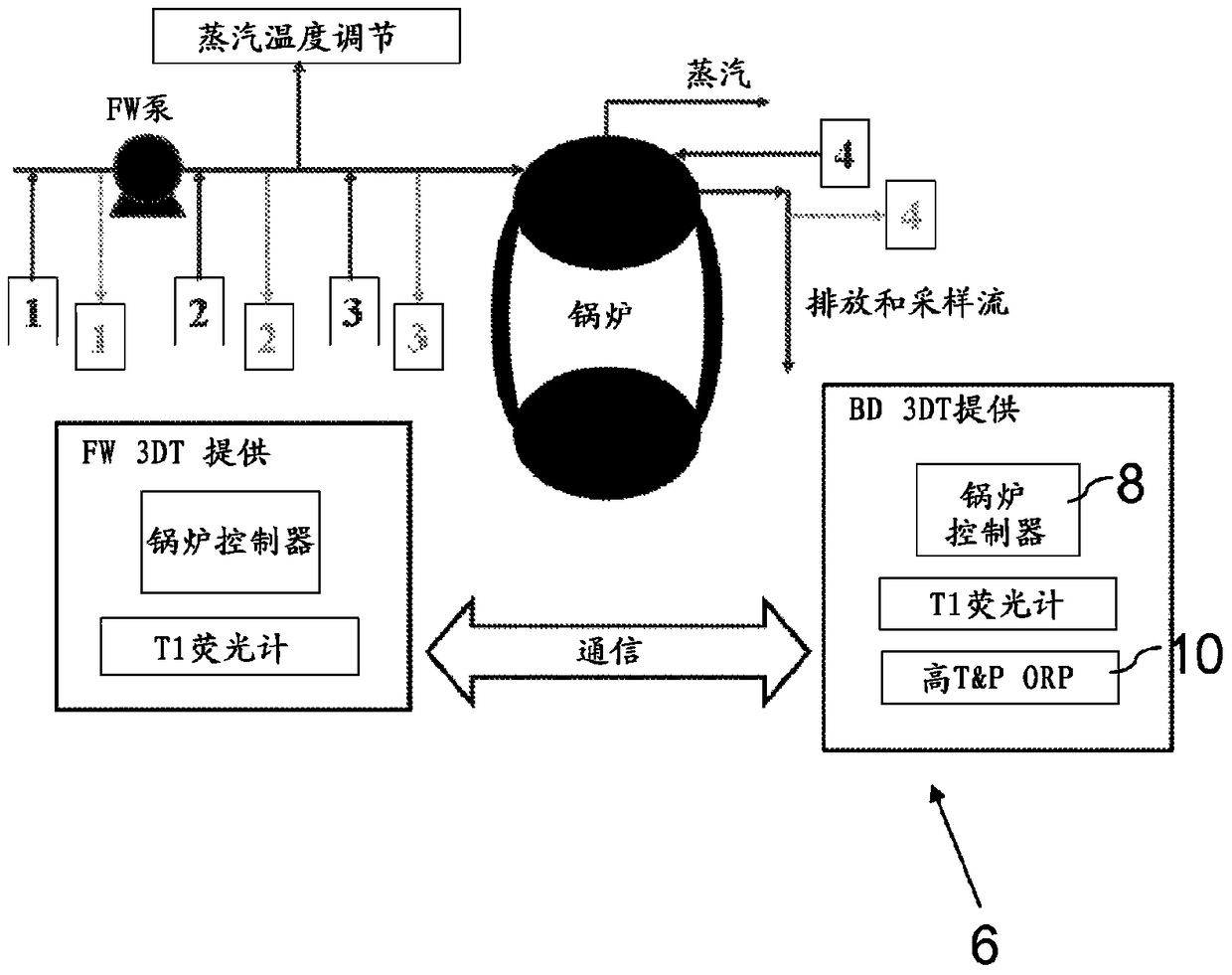
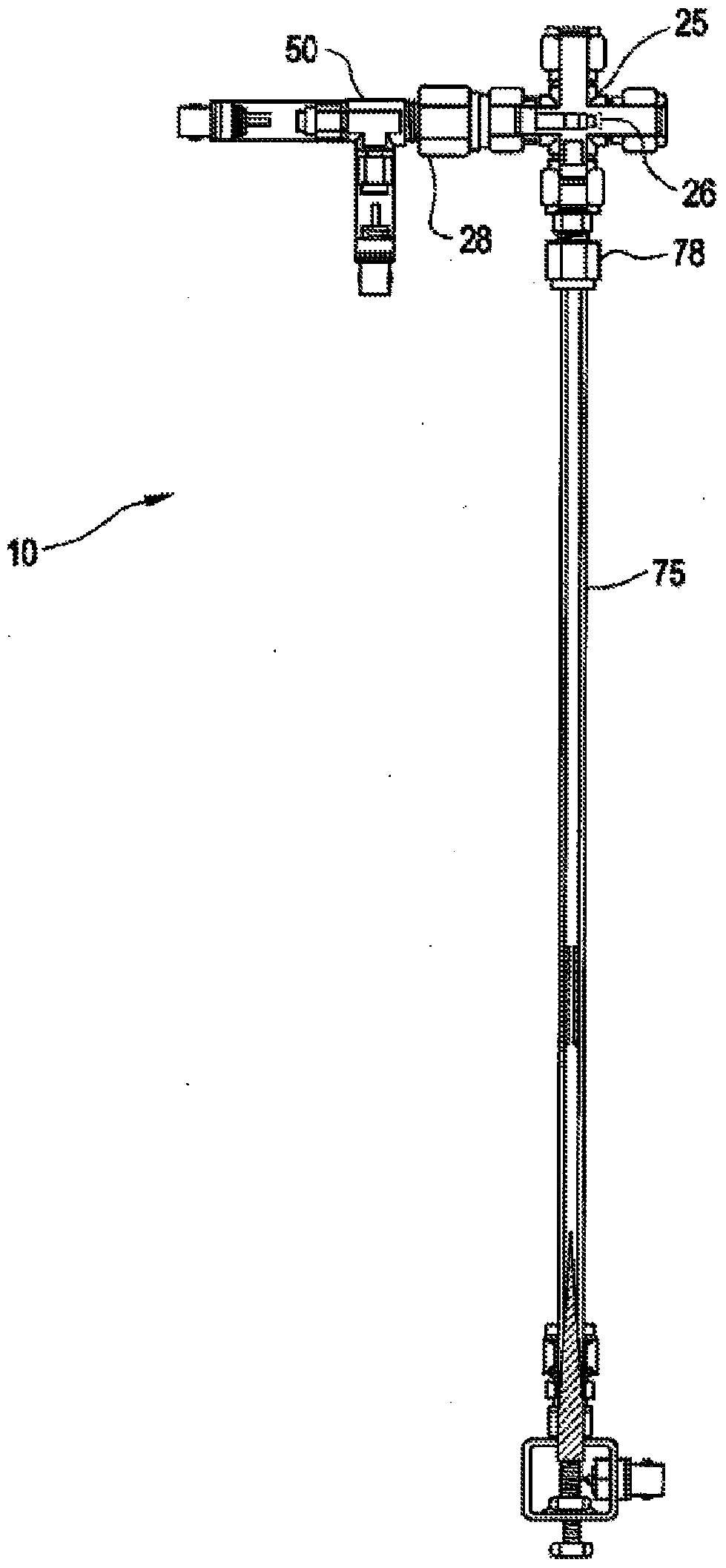
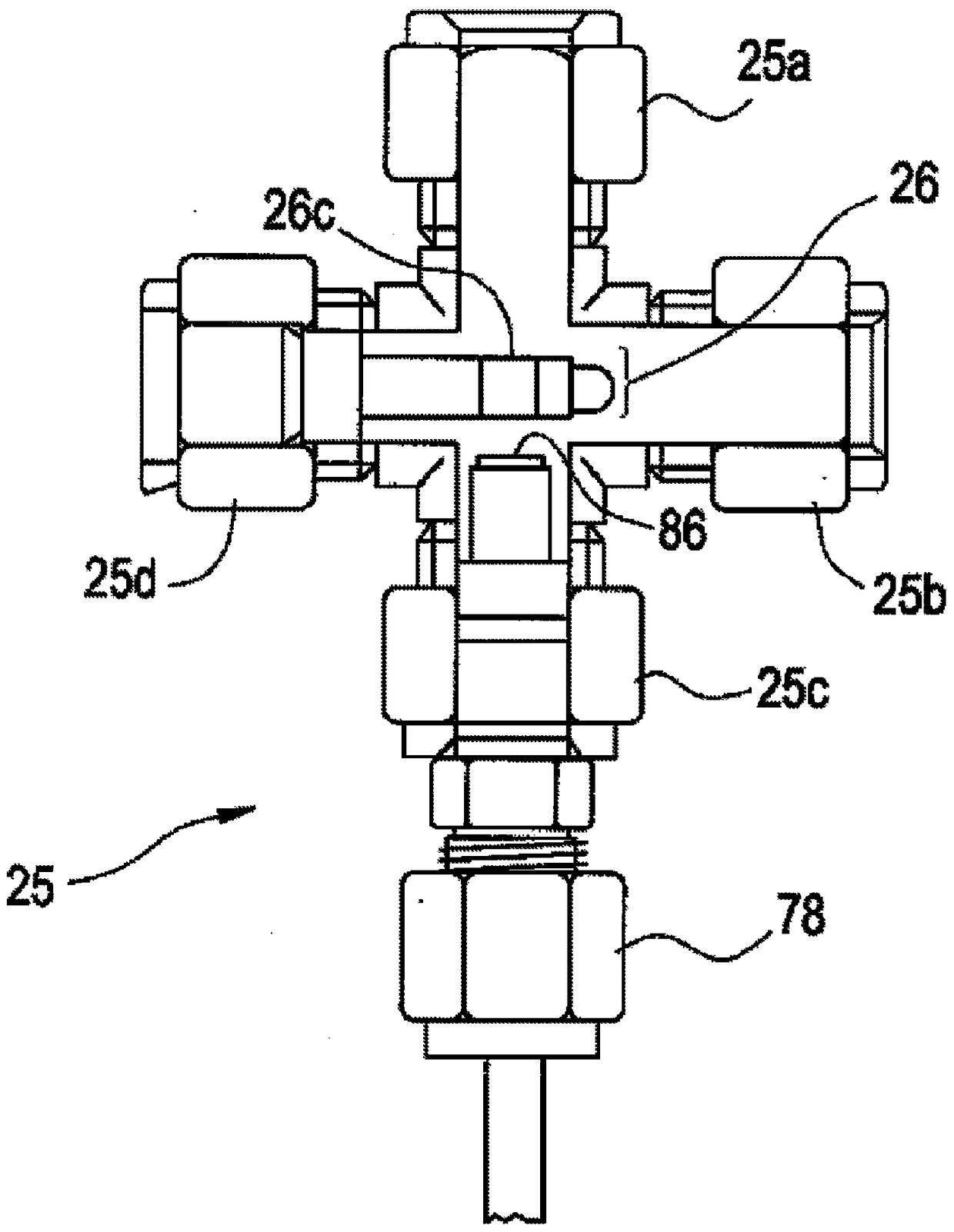
Systems and methods for monitoring and controlling corrosion in hot water systems
A hot water system and hot water technology, applied in the field of corrosion systems, can solve problems such as poor reliability, frequent calibration and maintenance, and easy polarization, and achieve the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0115] Figure 12 Depicts how the ORP settings for the system can be different at different temperatures. Figure 12 The temperatures shown may represent, for example, different equipment or different operational protection / control zones within the same equipment. In this embodiment, the ORP setting is an ORP setting range selected from a series of ranges represented as vertical lines marked with "preferred", "wider" and "widest". Depending on the sophistication (ie, operational constraints) of the devices in the apparatus, the available ORP setting ranges or points may vary. That is, some devices can handle a narrow or preferred range of ORP settings, while other devices can only handle a wider range of ORP settings. Typically a reference electrode is balanced against an external pressure with a 0.1 normal KCl fill solution ( Figure 12 specified as "EPBRE") to record the number of @T ORPs.
Embodiment 2
[0117] like Figure 13 As shown, this example shows the delivery of multiple REDOX actives at various locations to control the @T ORP at a single location. The control @T ORP detector was placed directly upstream of the feed location for REDOX active species #2. The @T ORP detector was used to measure @T ORP prior to feeding REDOX active #2. The @T ORP detector is then switched to control the supply of another REDOX active species (#1), which is supplied upstream of the single @T ORP detector. It should be noted that when REDOX active #2 (which was being manually controlled) was switched off, the effect of the absence of REDOX active #2 quickly permeated the device water chemistry and was sensed by the @T ORP detector. The controller (in this example, the controller is automated for REDOX active #1) immediately starts an additional supply of REDOX active #1 to replenish the shortage of REDOX active #2.
[0118] The controlled supply of REDOX active #1 was able to achieve an...
Embodiment 3
[0120] This example shows the unpredictable response of the @T ORP detector for direct measurement of corrosion events and how real-time ORP measurements can be used as a direct indicator of corrosion due to REDOX stress events in hot water systems.
[0121] The @T ORP detector responds to the formation of corrosion products in the FW. REDOX stress in FW involves complex-conjugated ion corrosion pairs such as Fe 2+ / Fe 3+ or Cu + / Cu 2+ . In an all-iron based FW heater, high DO (ie, greater than 500 ppb) water begins to enter the FW heater. Room temperature ORP and real-time ORP at the heater inlet were initially -125 mV and -280 mV, respectively. The room temperature ORP and real-time ORP at the heater inlet rose to -70 mV and -30 mV, respectively, upon experiencing an increased REDOX stress event. The sensitivity of the @T ORP detector (250 mV increase in real-time ORP) can be clearly seen when compared to the room temperature ORP detector (increase of only 55 mV). Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com