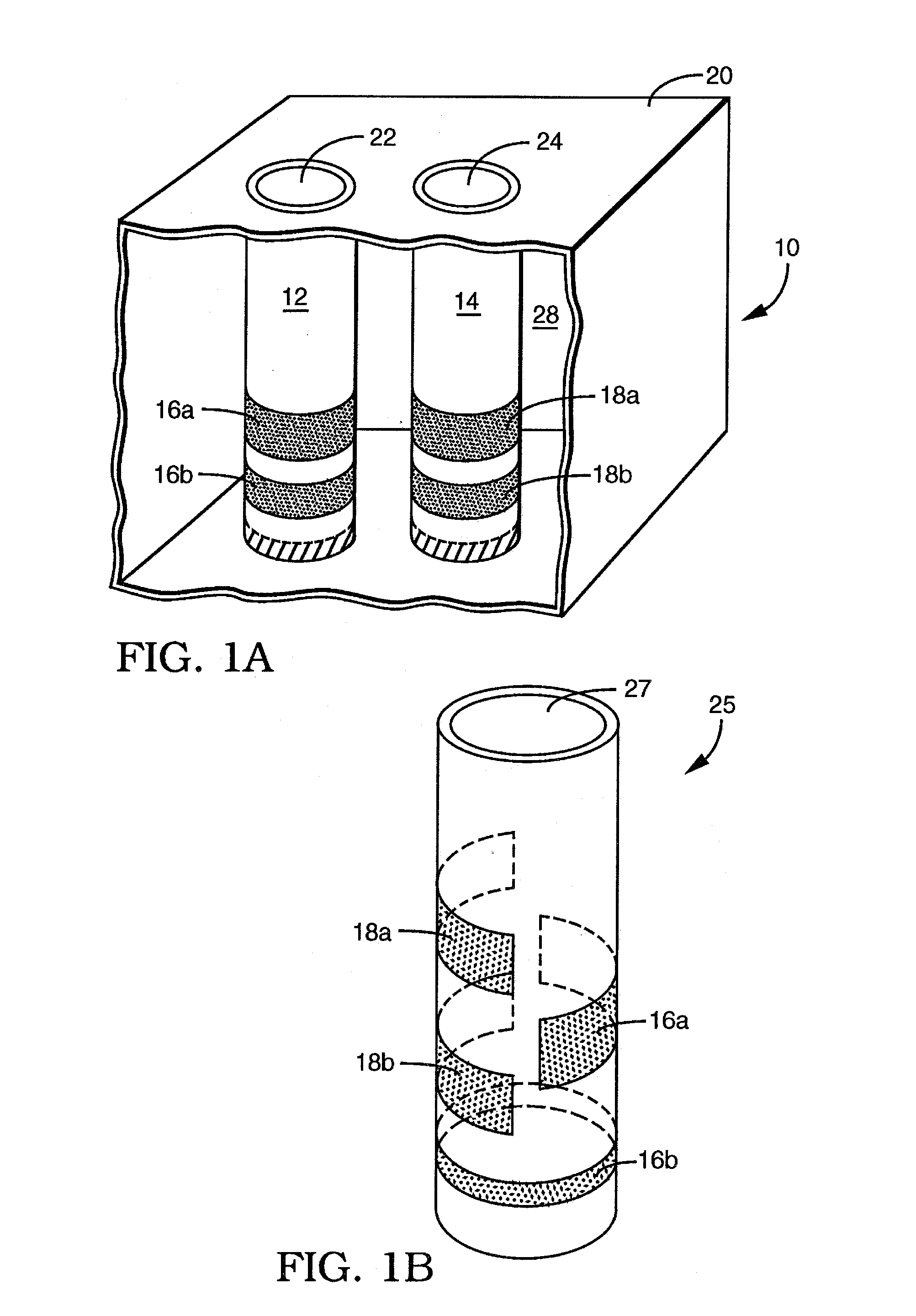
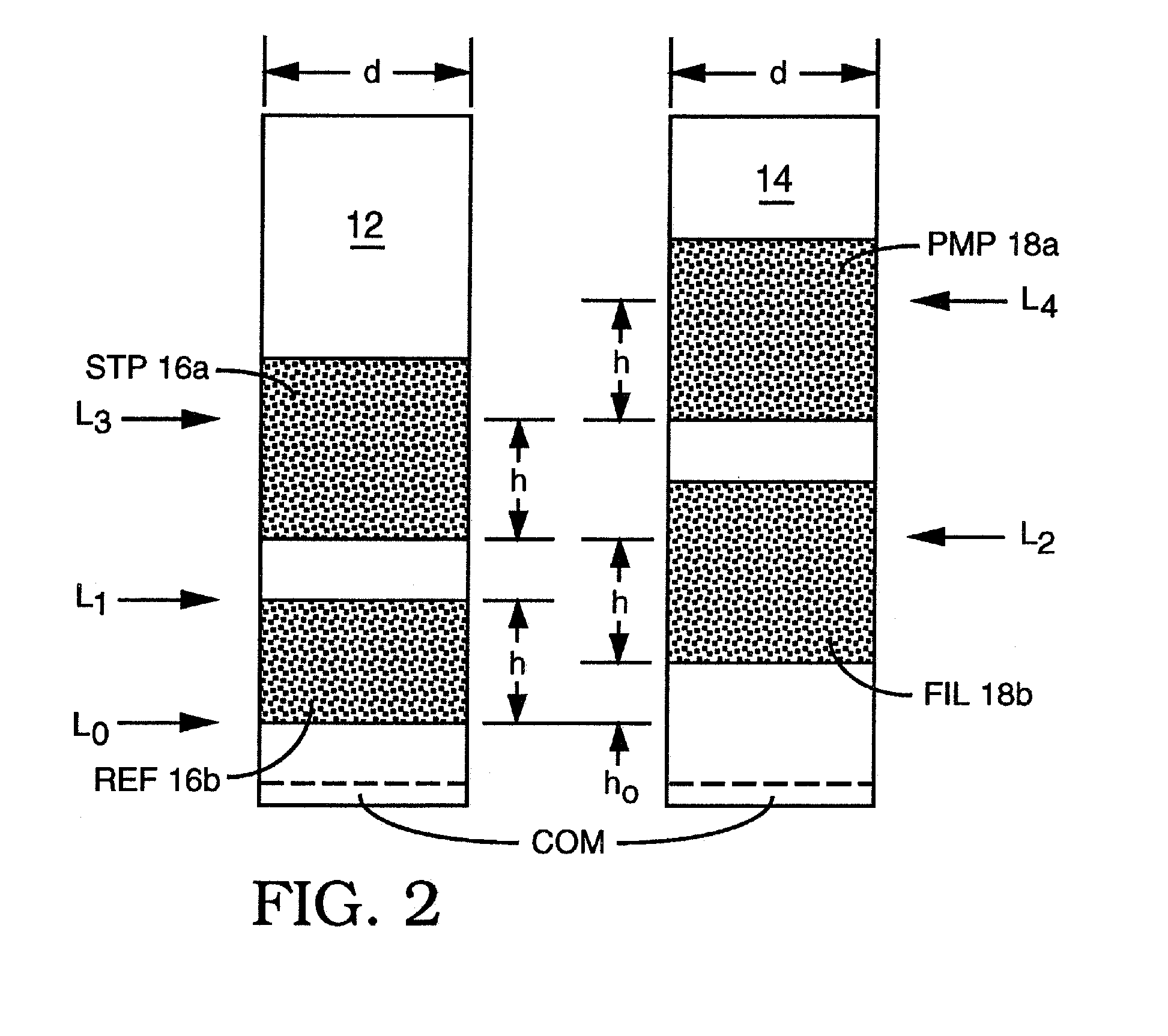
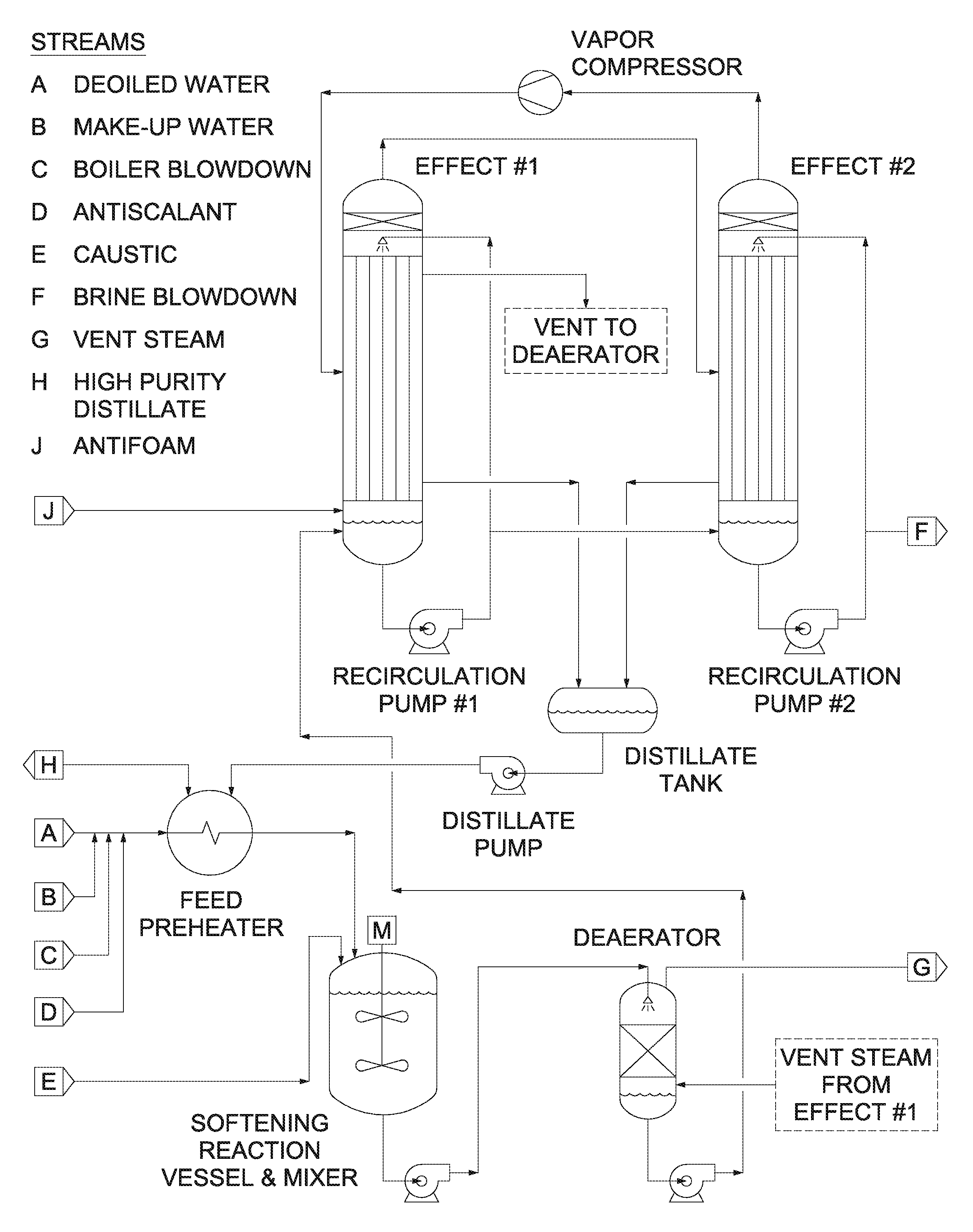
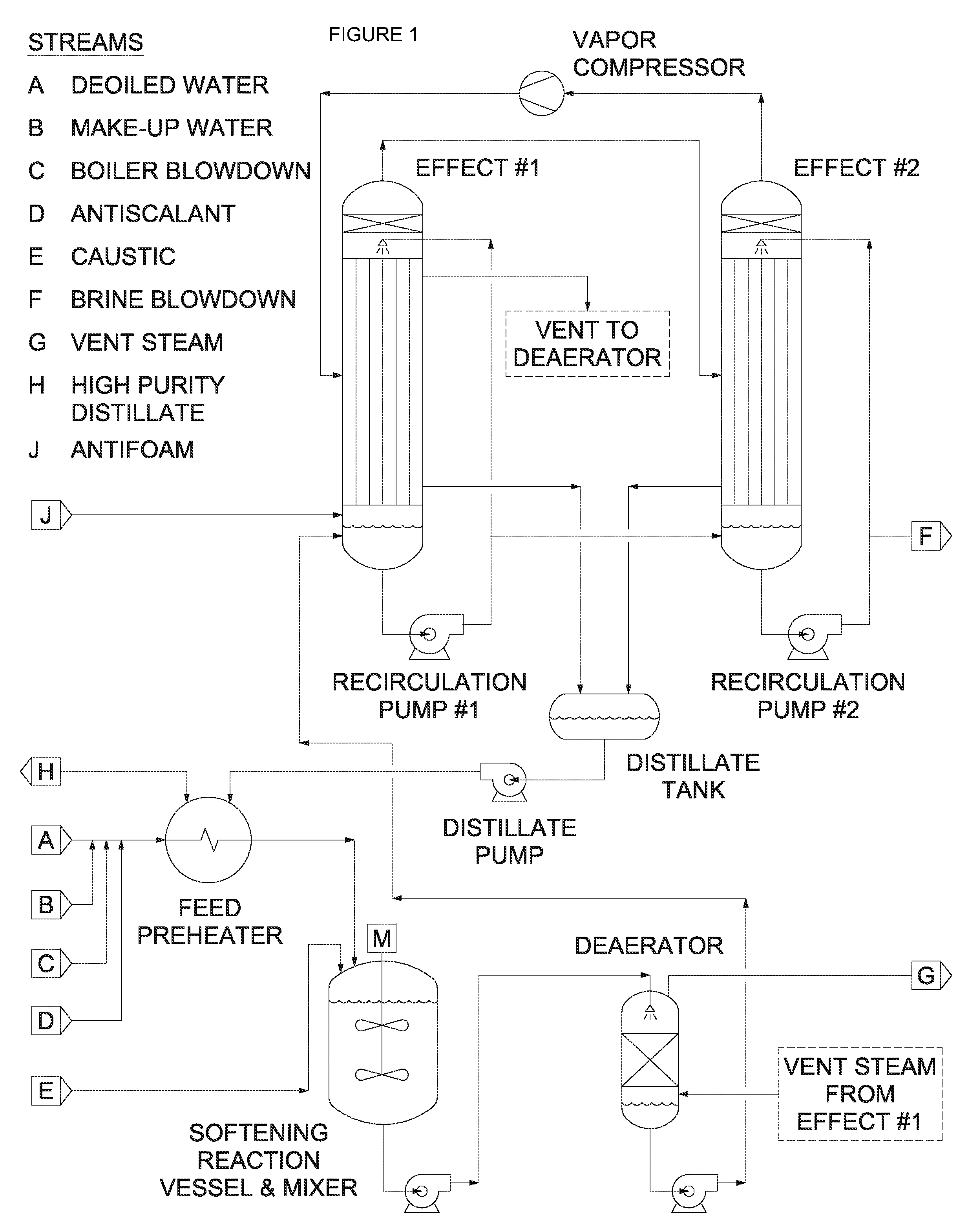
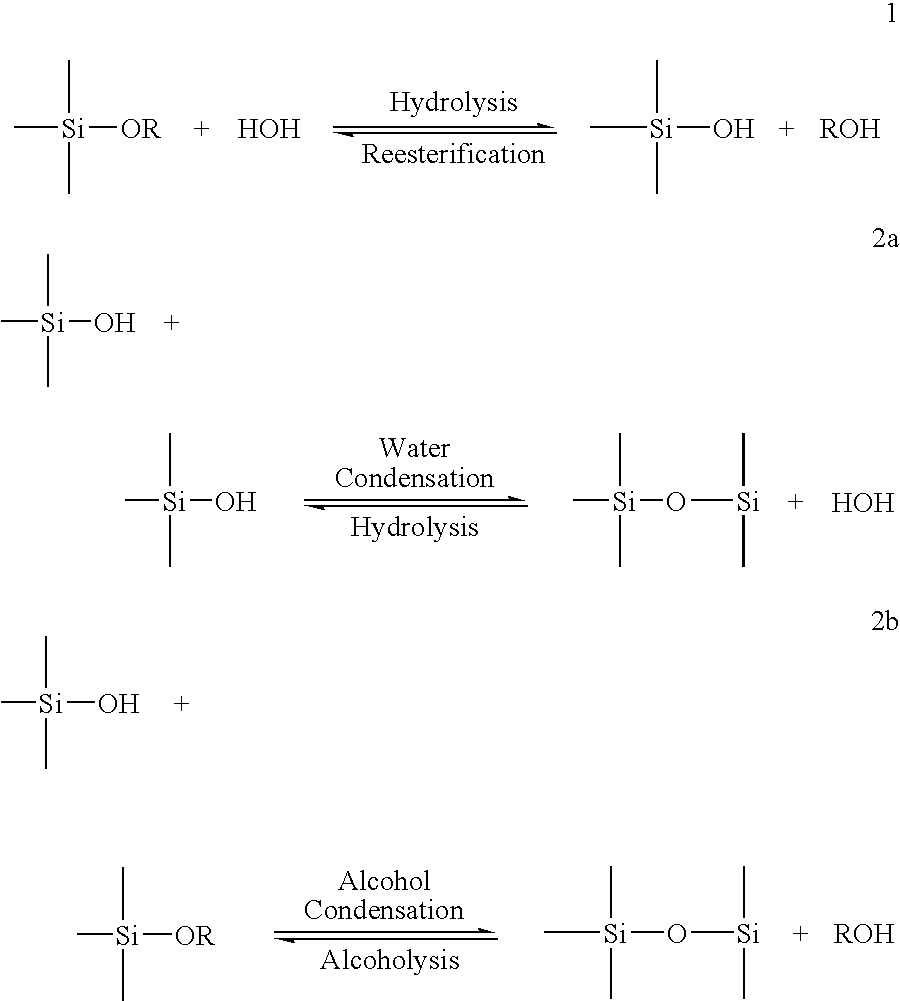
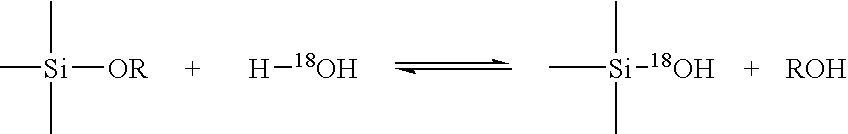Patents
Literature
139 results about "Water chemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
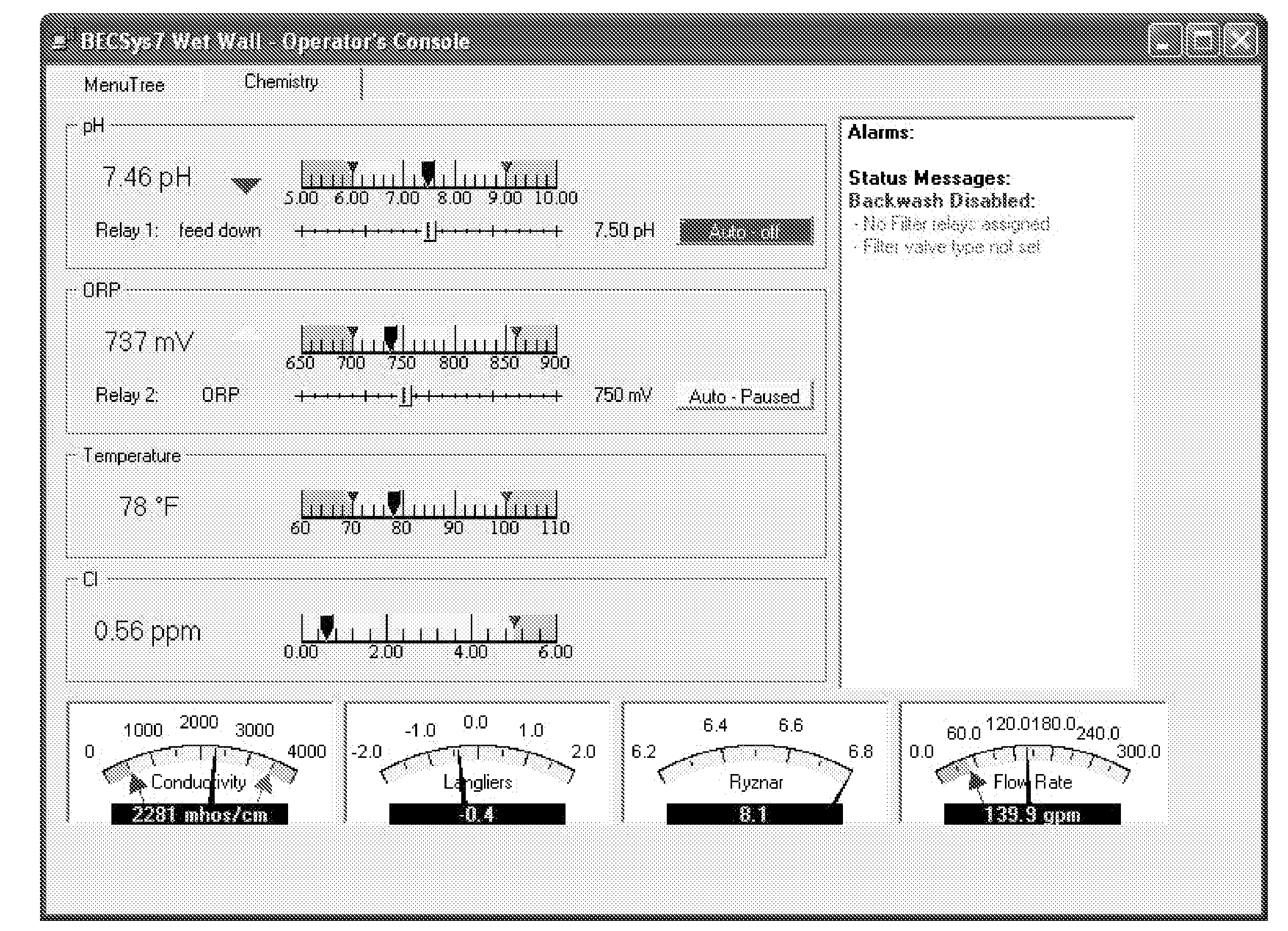
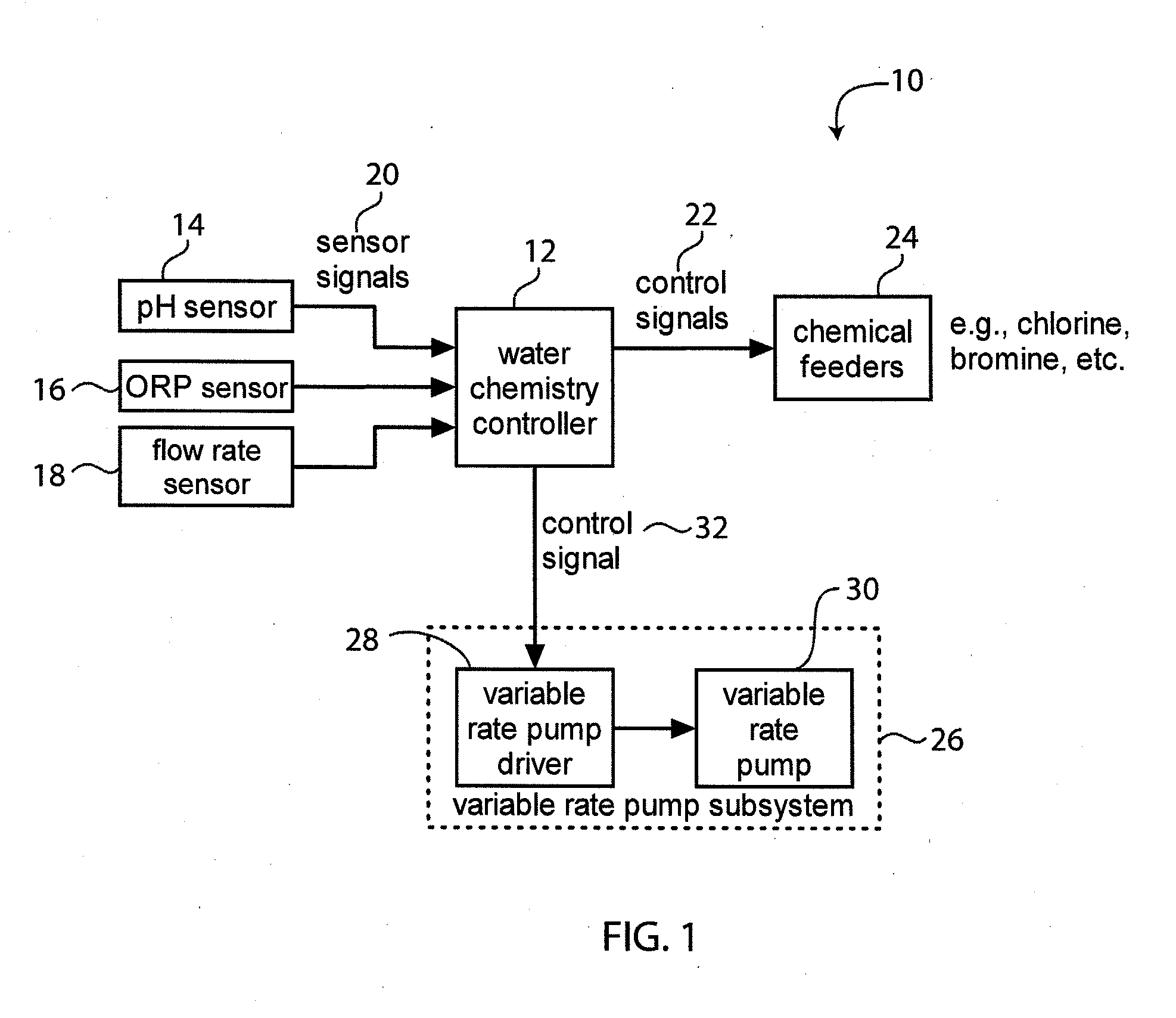
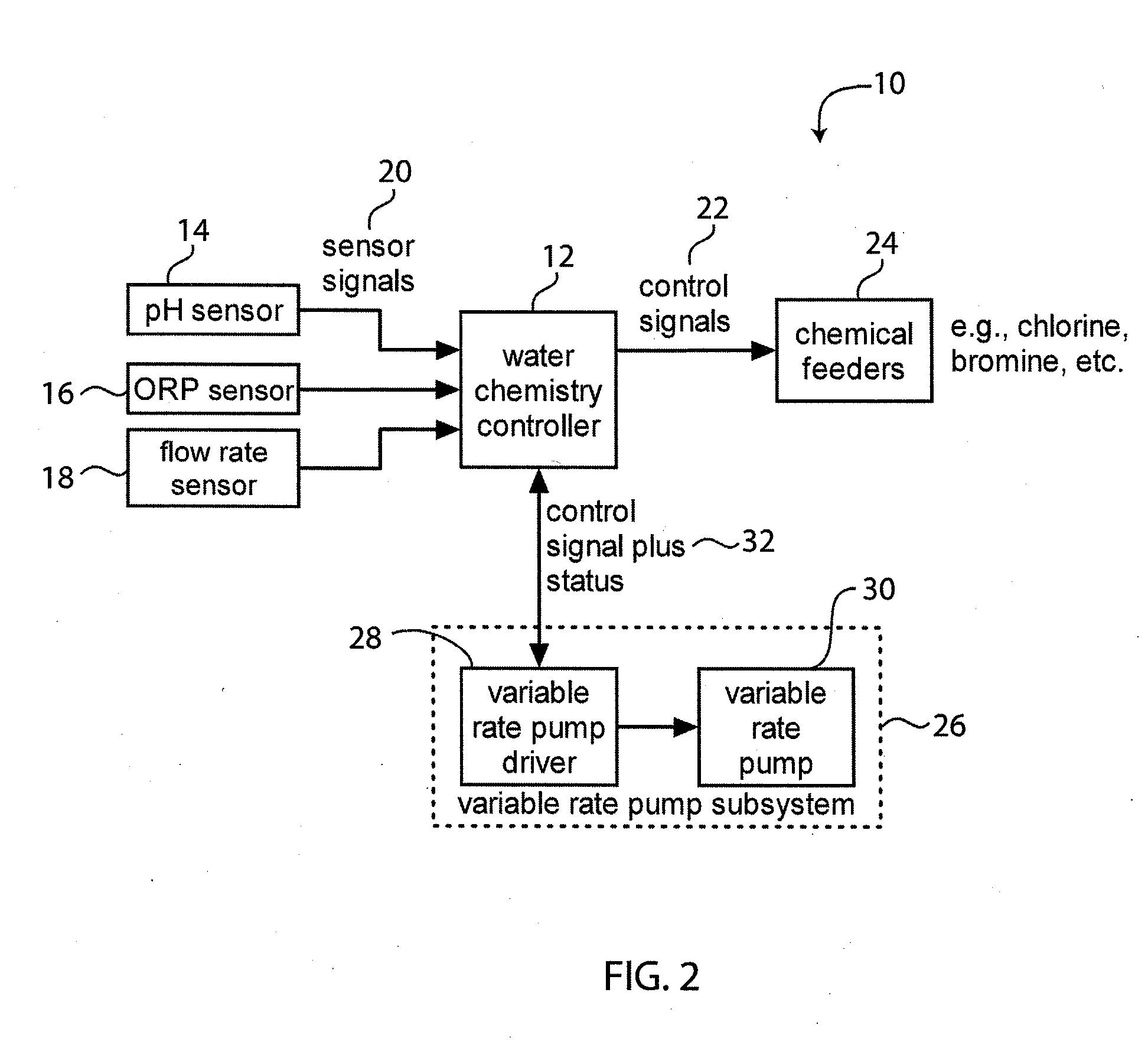
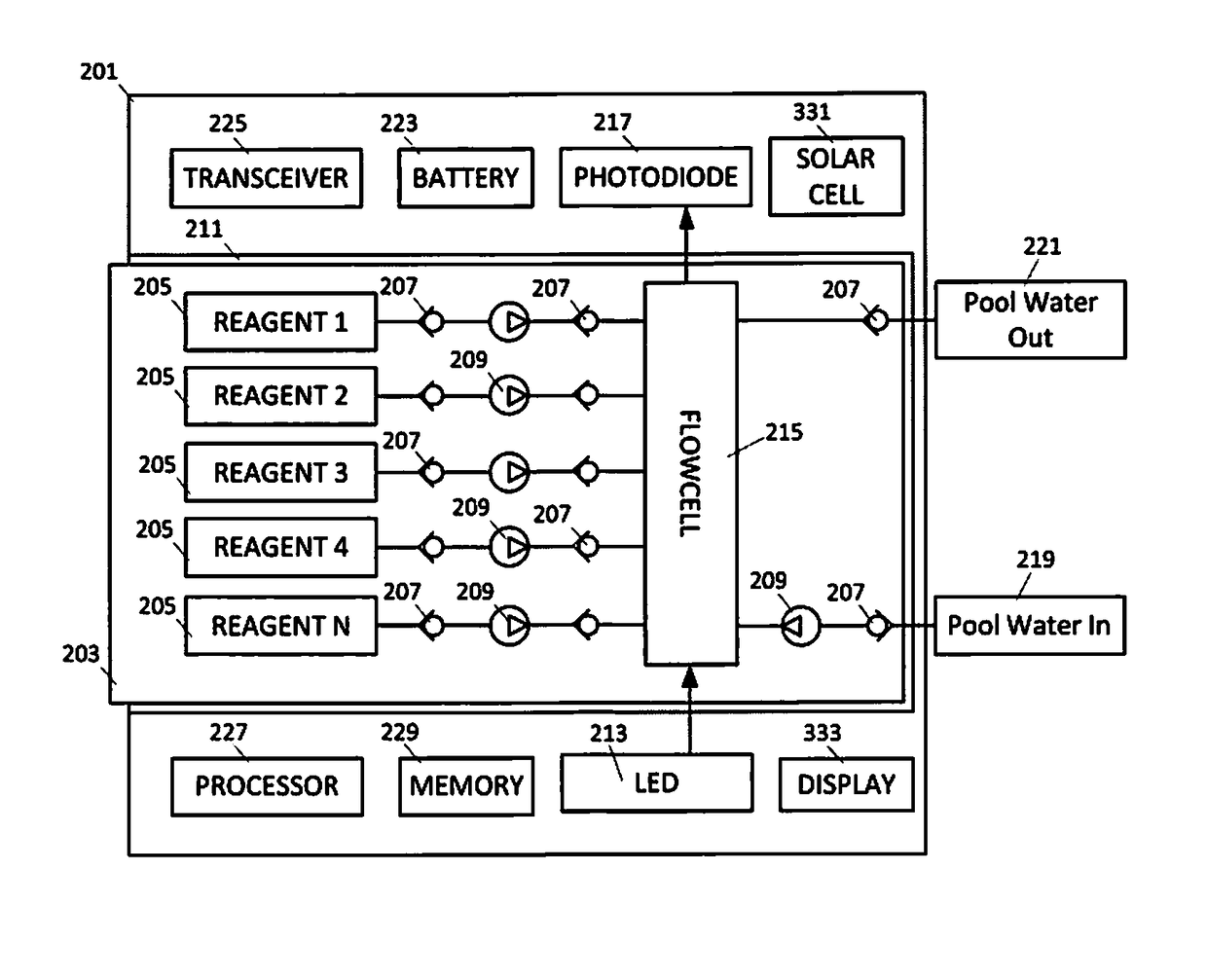
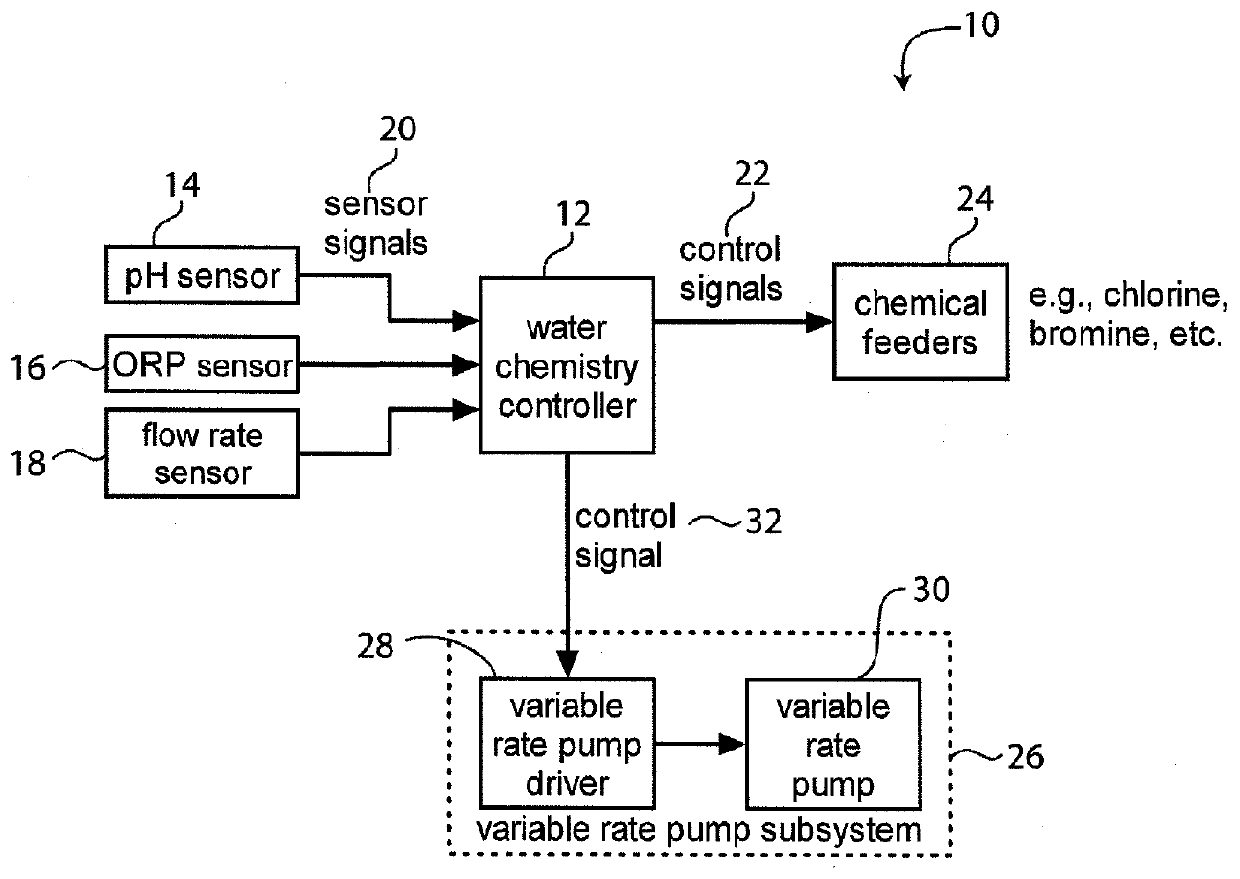
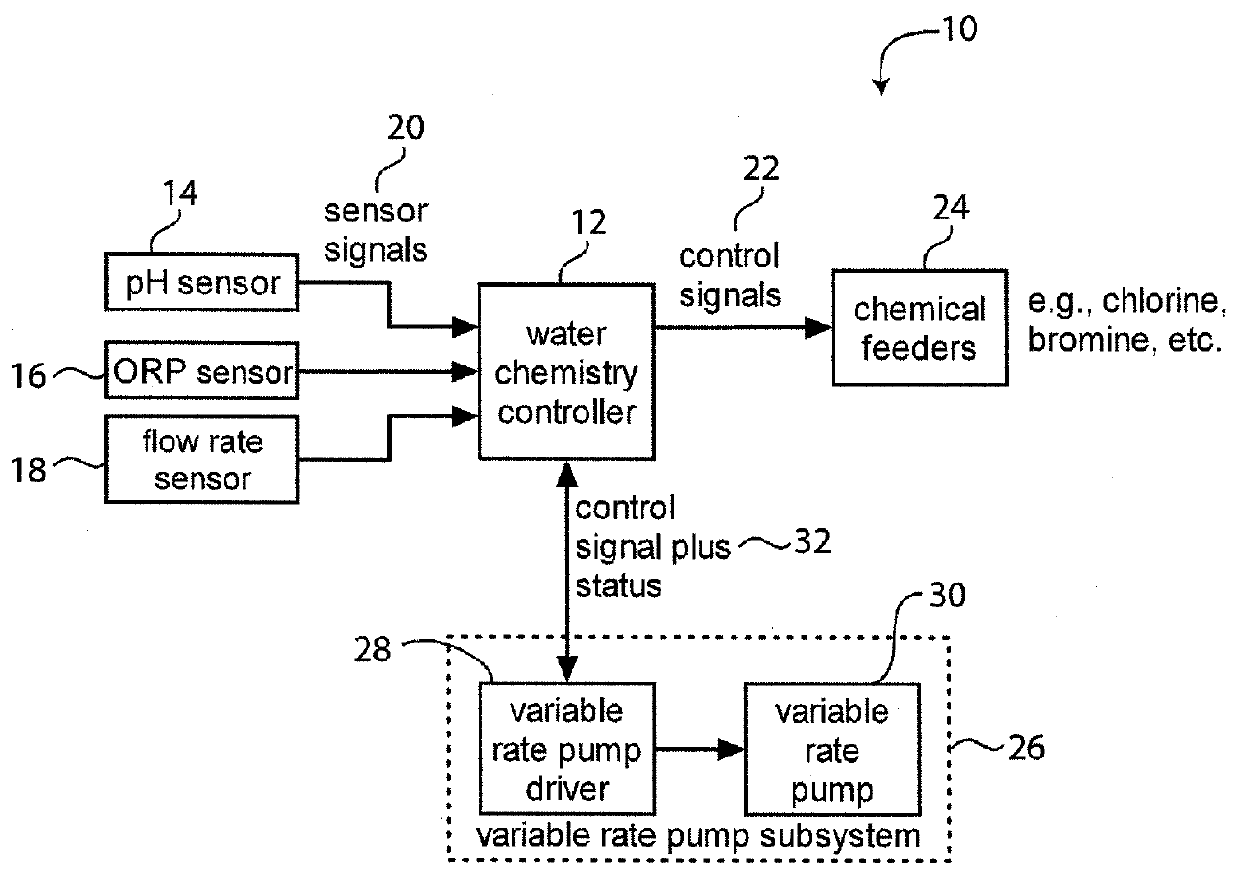
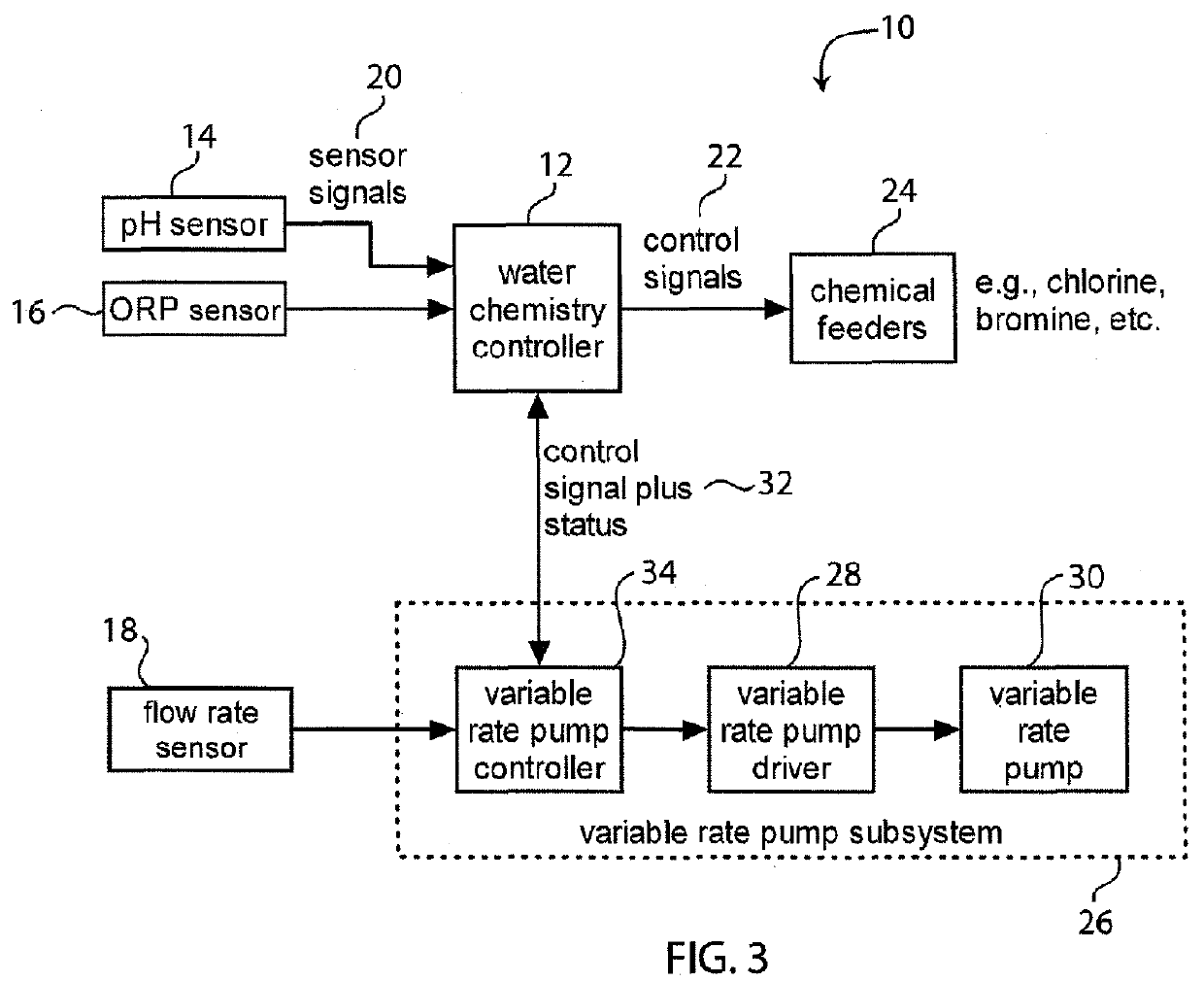
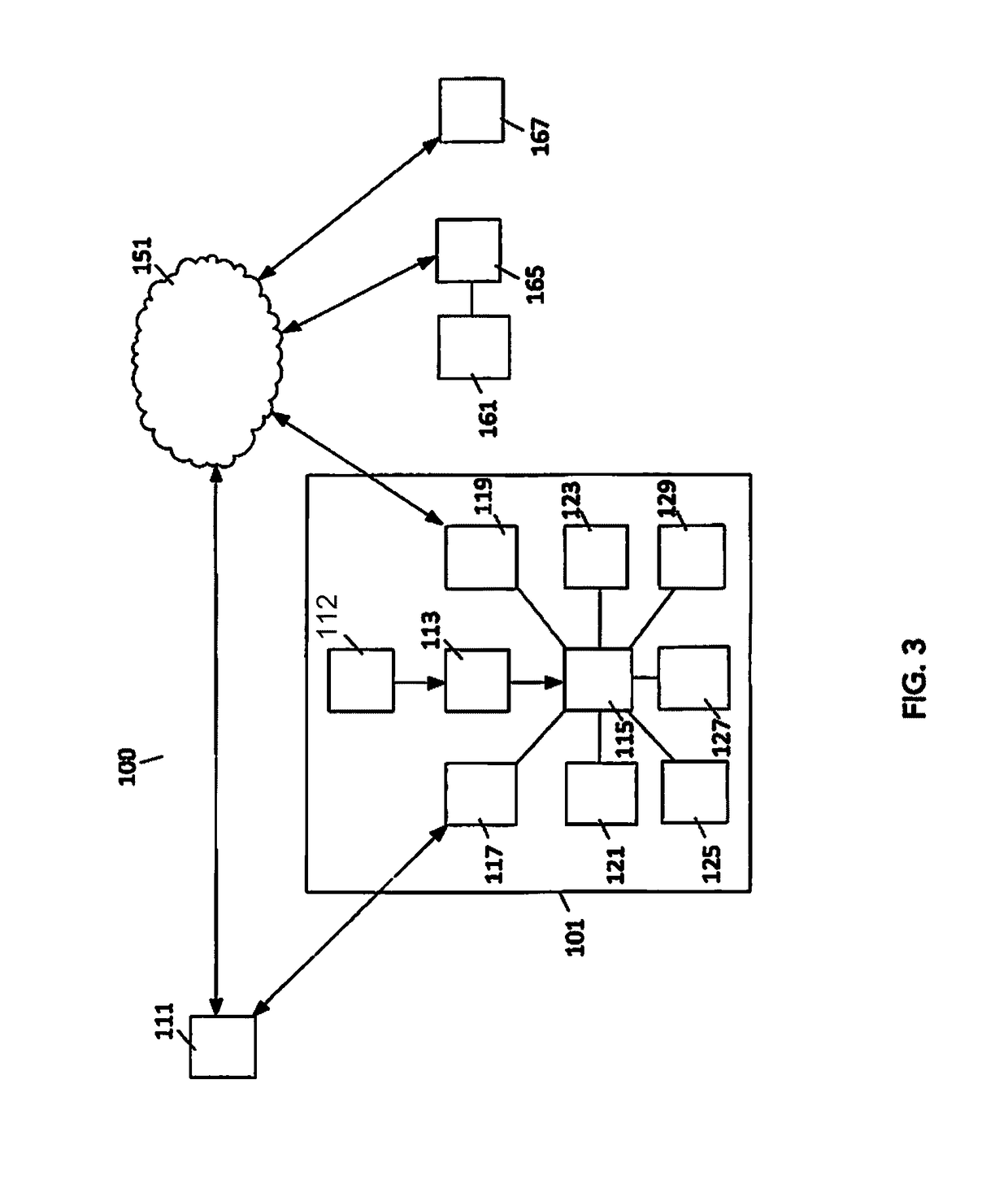
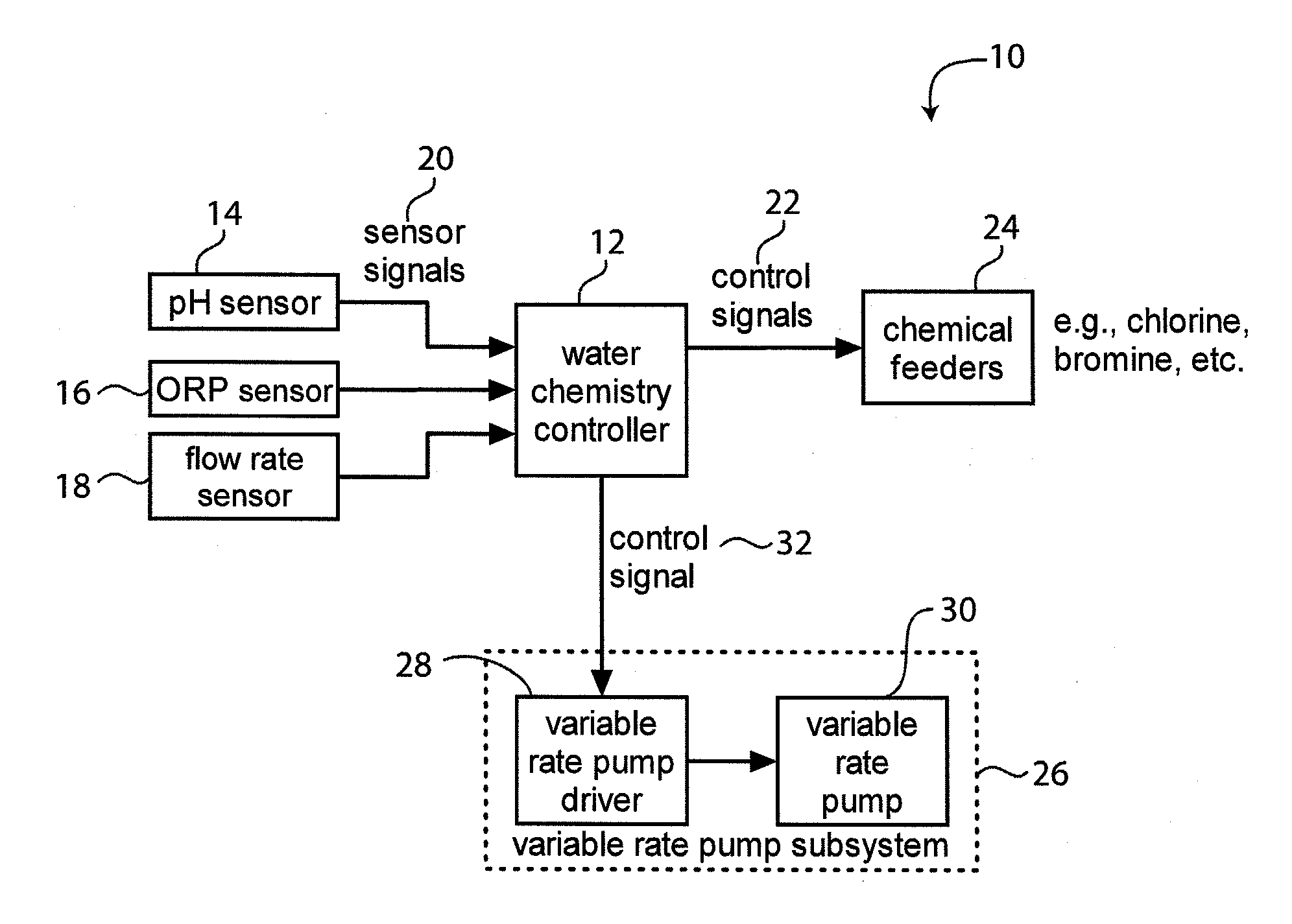
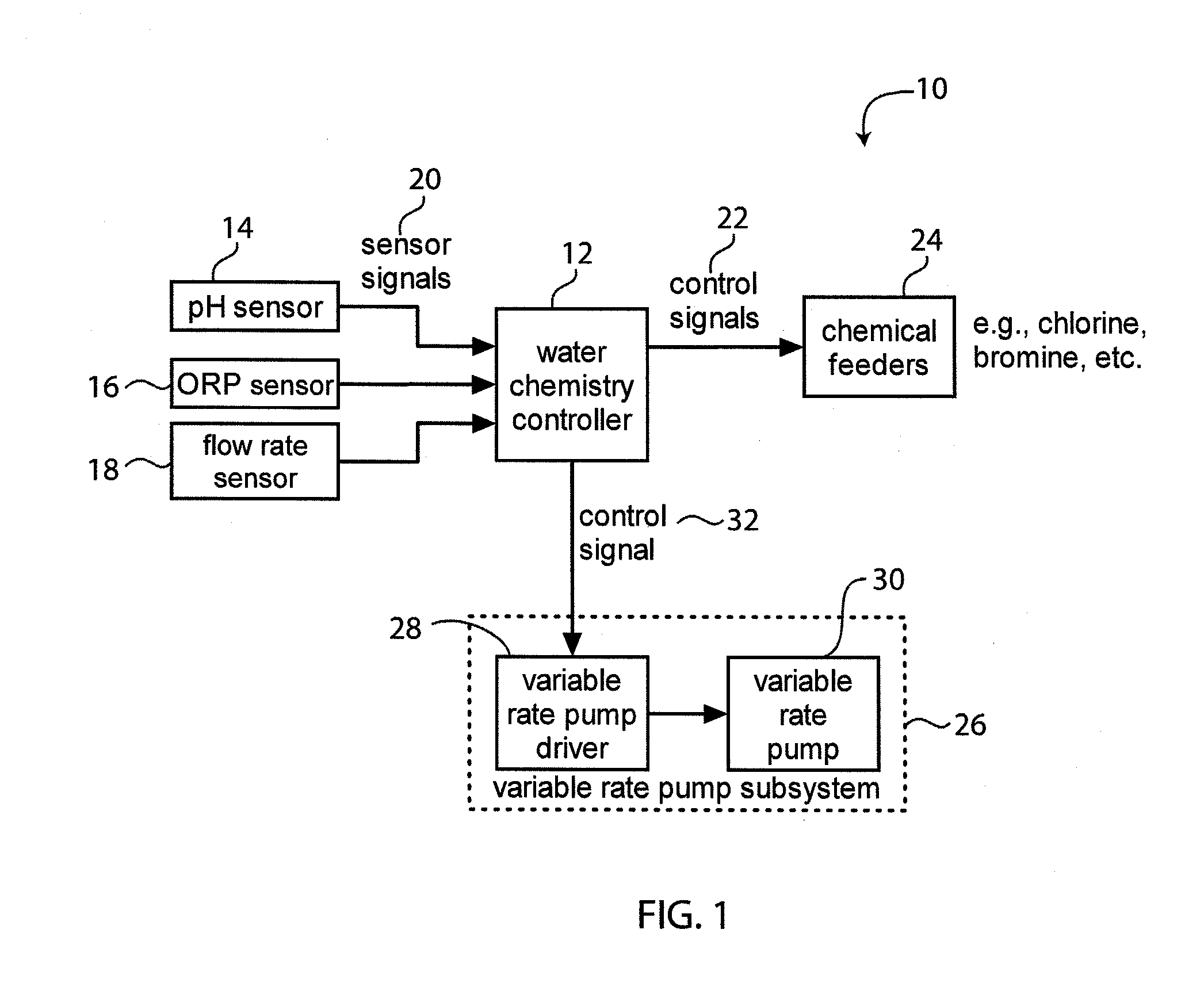
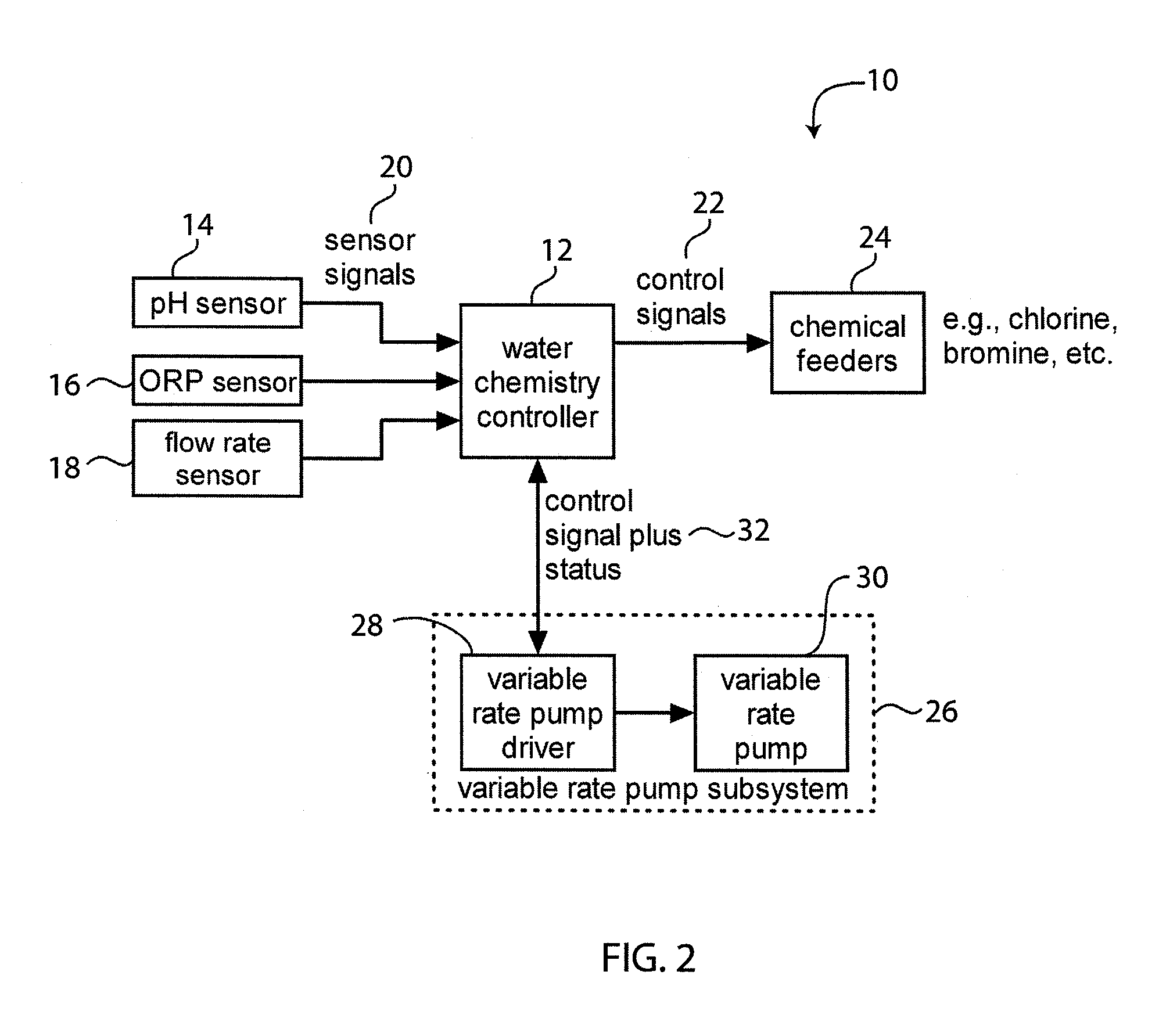
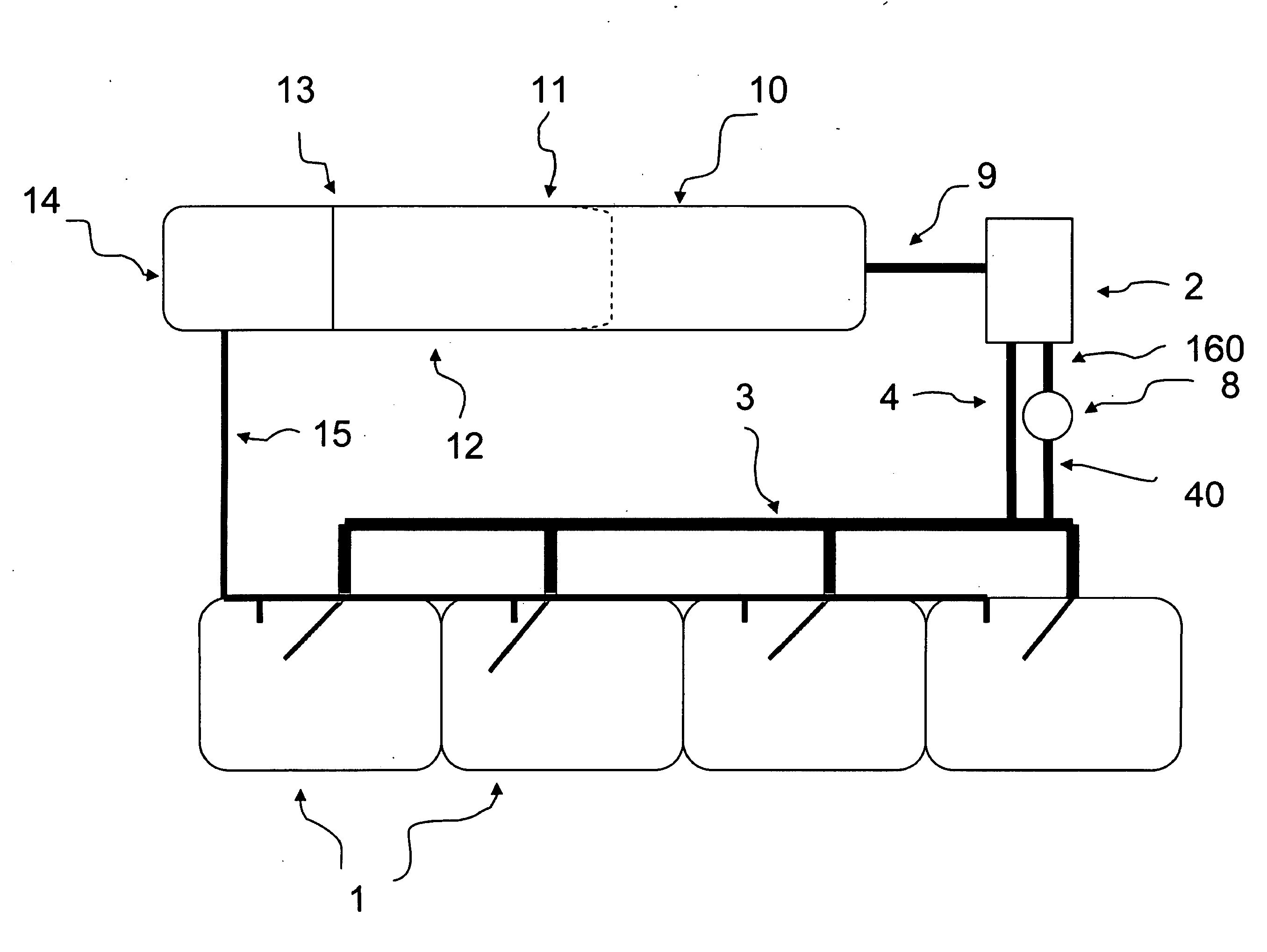
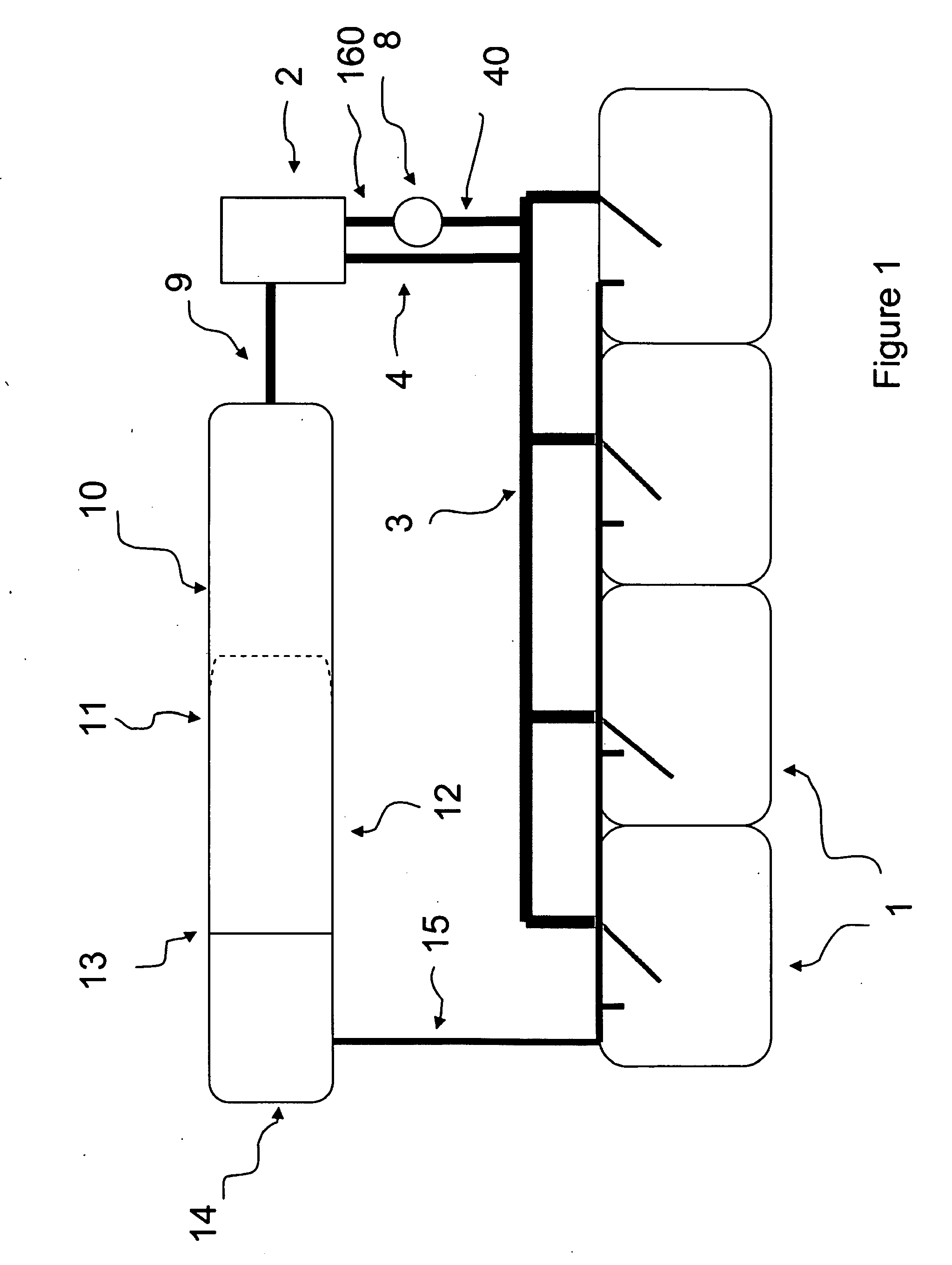
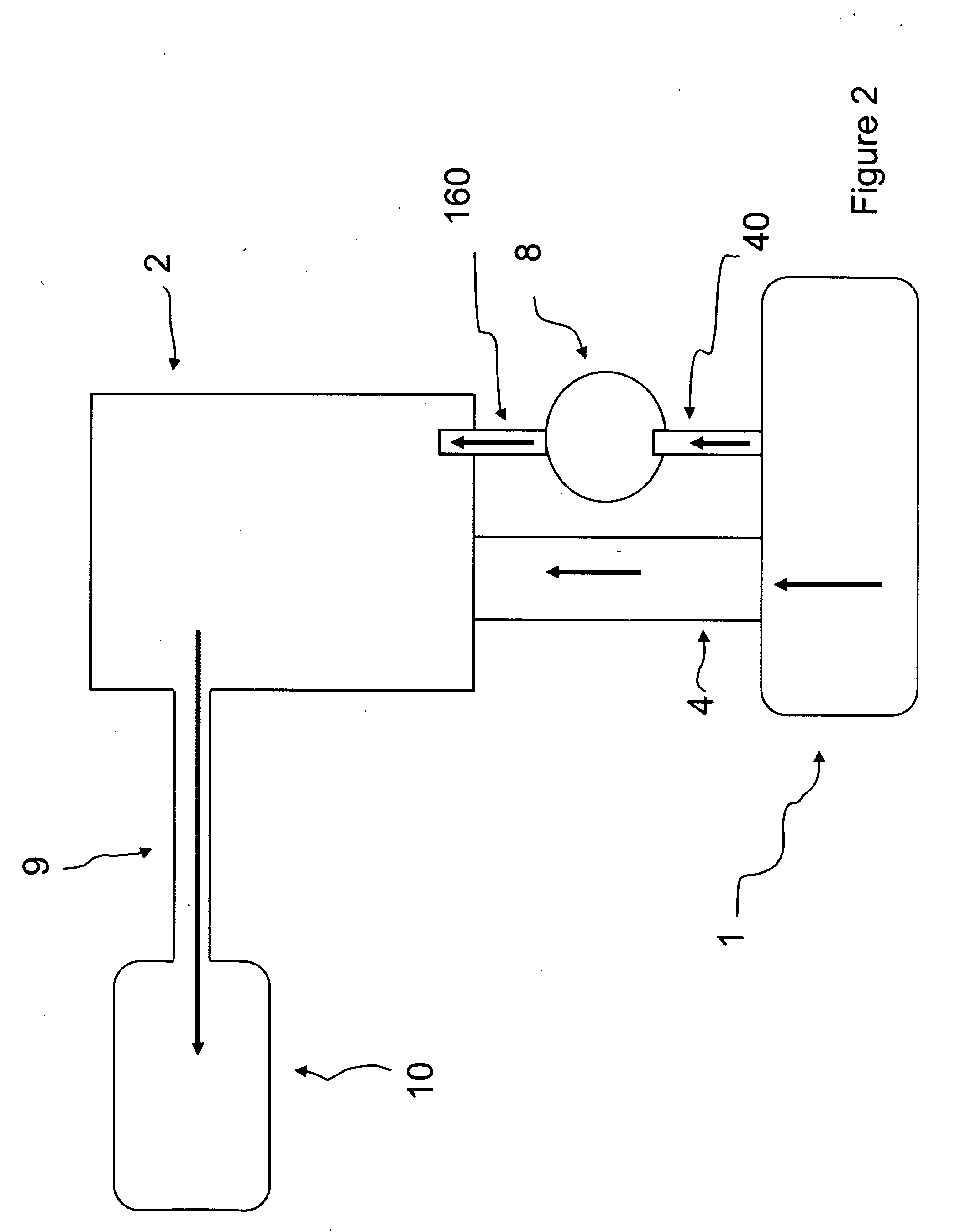
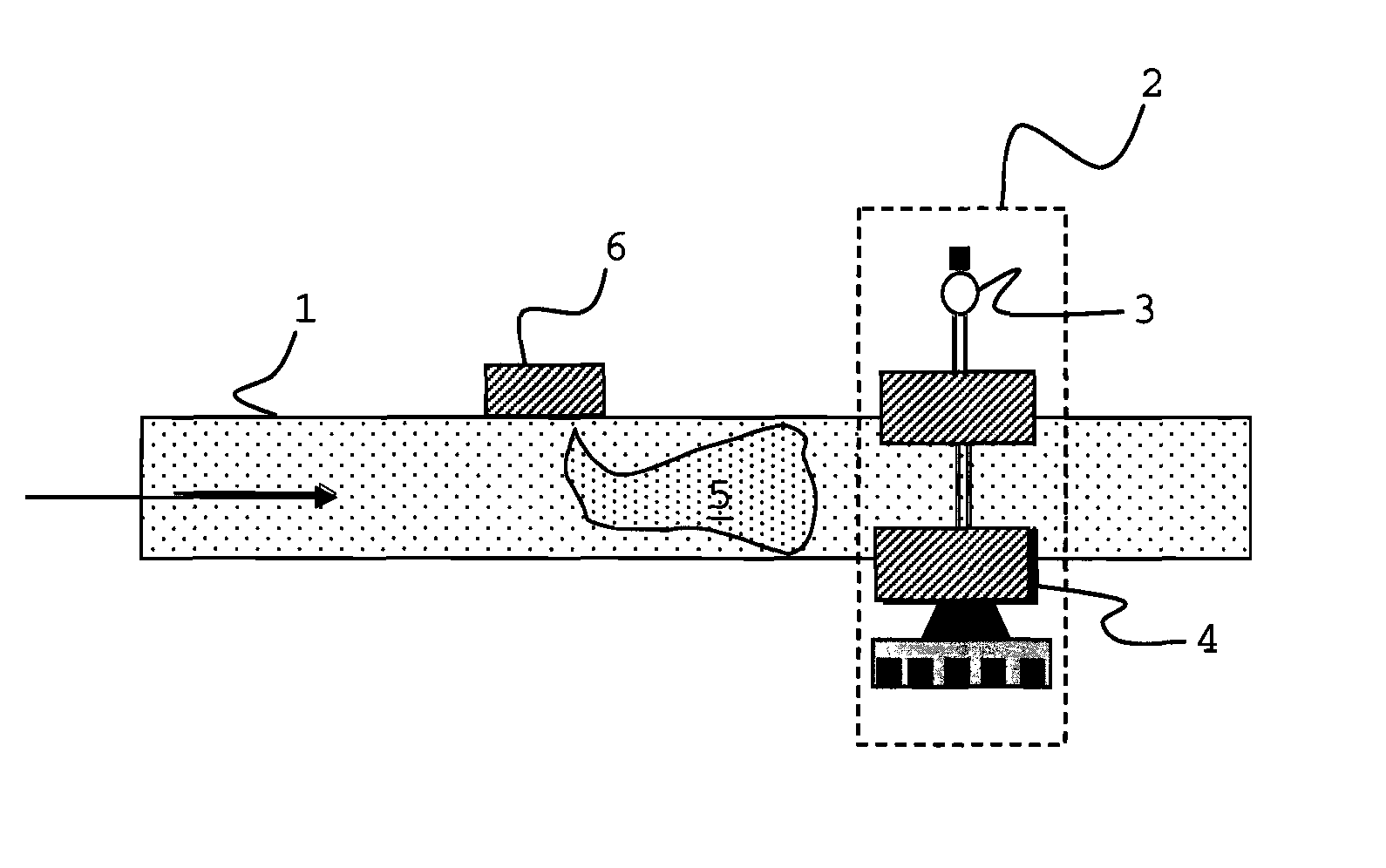
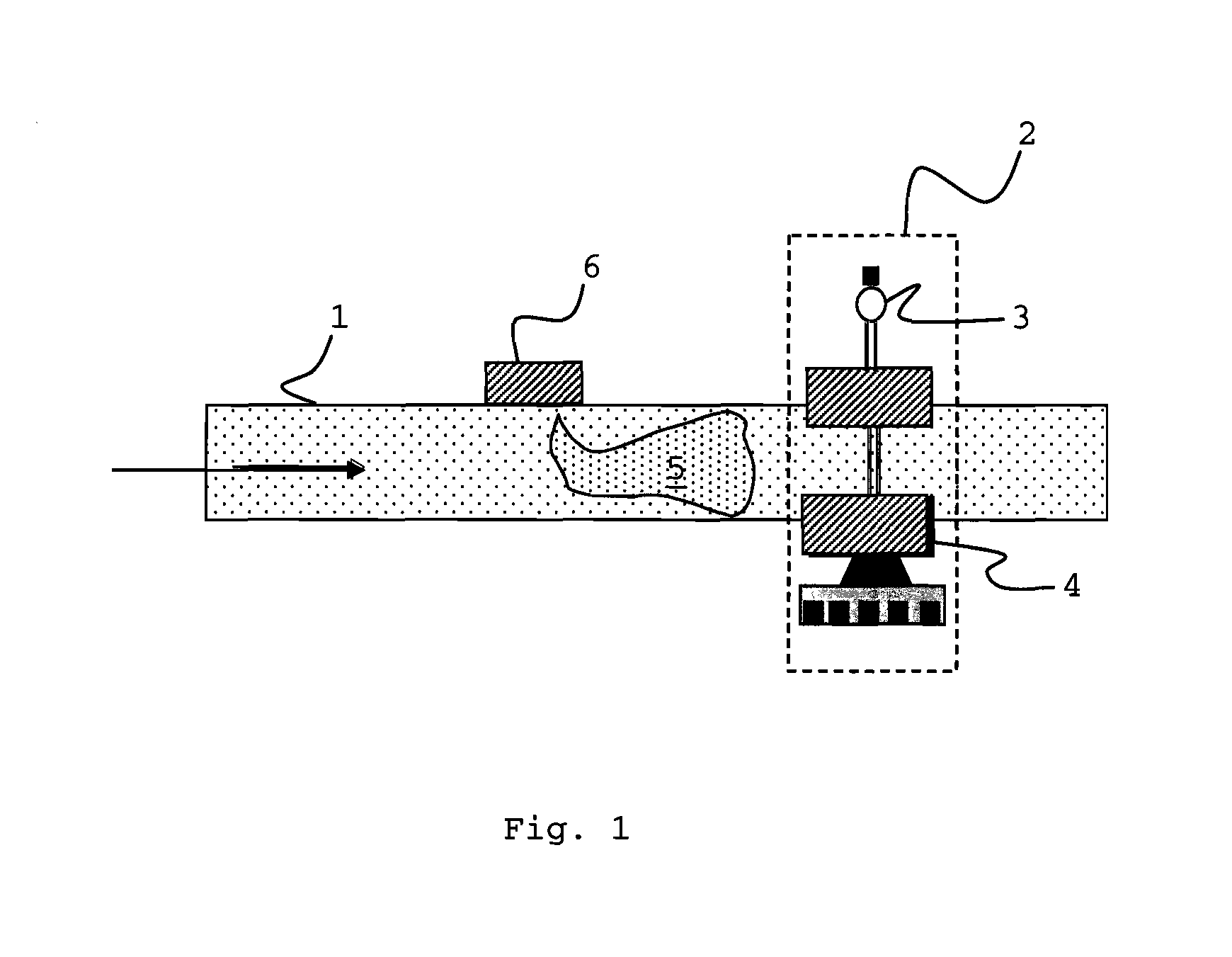
System for Controlling Water in an Aquatic Facility
InactiveUS20090200245A1GymnasiumWater/sewage treatment by oxidationMotor driveEnvironmental engineering
A system for controlling water within an aquatic facility includes a water chemistry controller, a variable rate water pump adapted to move water in the facility, and a variable rate motor driver operationally coupled to the water pump for variably energizing the water pump. The variable rate motor driver is coupled to the water chemistry controller to allow the water chemistry controller to manage the operation of the water pump.
Owner:BECS TECH
Wireless swimming pool water level system
InactiveUS7318344B2Increase surface areaPreserves watertight integrityLevel controlMachines/enginesTimerDevice failure
A wireless (e.g., radio) system and method for automatic water level maintenance of, e.g., a swimming pool utilizing capacitive liquid level sensing. A reference electrode allows water level sensing independent of the water chemistry or temperature. Capacitive electrodes having areas larger than the reference electrode sense various liquid levels when the liquid covers an area of any sensing electrode equal to the area of the reference electrode. Averaging is incorporated to filter out effects of wind or other disturbances. Upon sensing a given condition, the transmitter transmits a sensed condition to a remote receiver for control of valves and pumps for changing the water level in the pool. The receiver includes safety timers for filling and emptying to protect against equipment failure or communications faults. User selectable identification allows identical such radio systems to operate within proximity to each other. Power saving features are used to extend battery life.
Owner:HEGER RES
Process for culturing crabs in recirculating marine aquaculture systems
InactiveUS20030070624A1Climate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMarine aquacultureBroodstock
The present invention relates to a recirculating marine aquaculture process for production of a crab species, including (i) a broodstock conditioning, (ii) spawning, (iii) egg incubation, (iv) larval growth, (v) nursery post-larval growth, and (vi) grow-out of the crab to a final product weight, in which each stage (i)-(vi) of the process involves operation in an aqueous medium that is coupled in liquid recirculation relationship with means for removing waste components from the aqueous medium and returning purified aqueous medium to the external environment. The process involves operation in a closed, recirculating aquaculture system in which photoperiod, water temperature, water chemistry, and diet are optimized and then continuously monitored and controlled to obtain optimal production at each of the six phases (i)-(vi) of the life cycle.
Owner:MARYLAND BIOTECH INST UNIV OF +1
Process for culturing crabs in recirculating marine aquaculture systems
Owner:MARYLAND BIOTECH INST UNIV OF +1
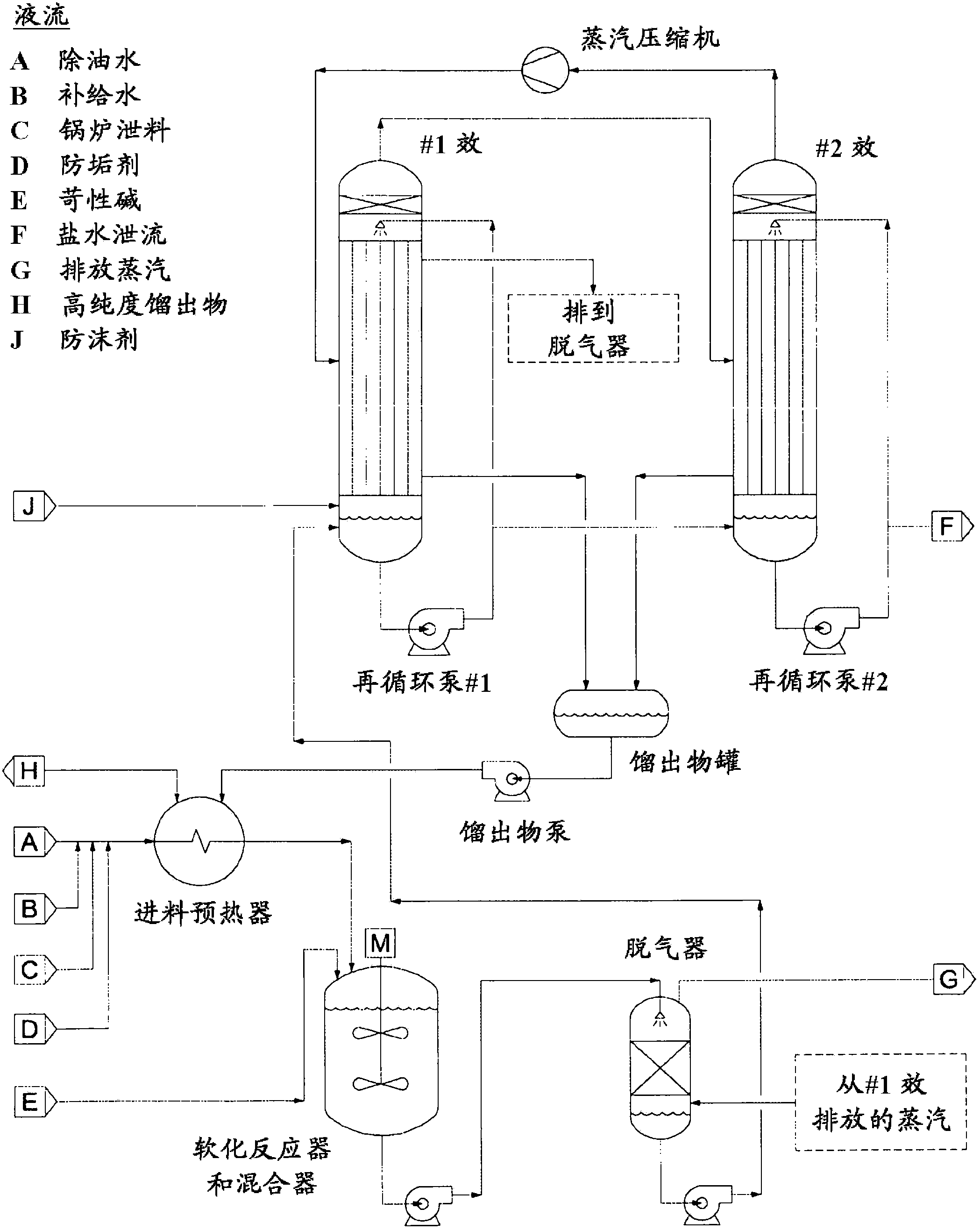
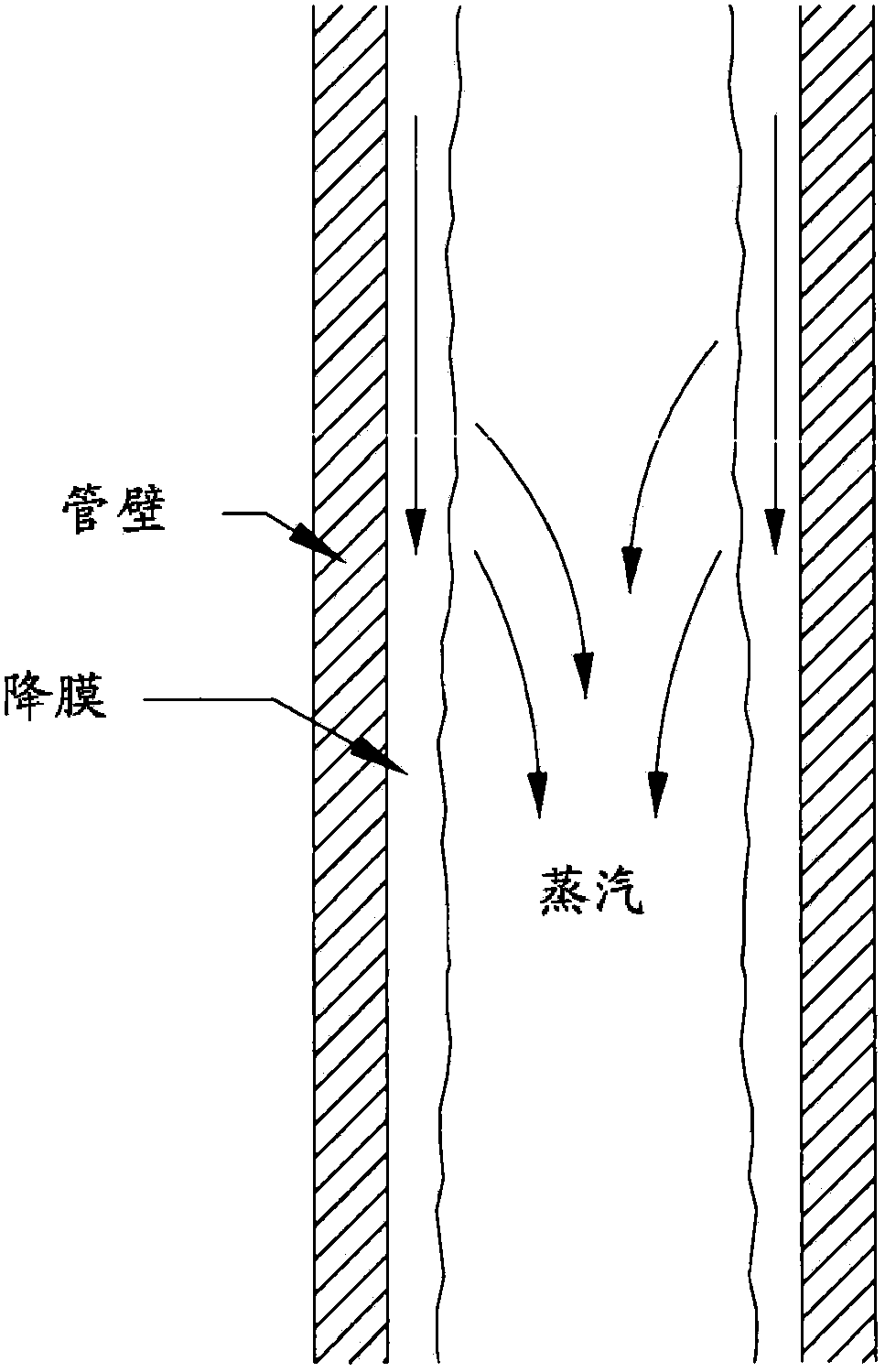
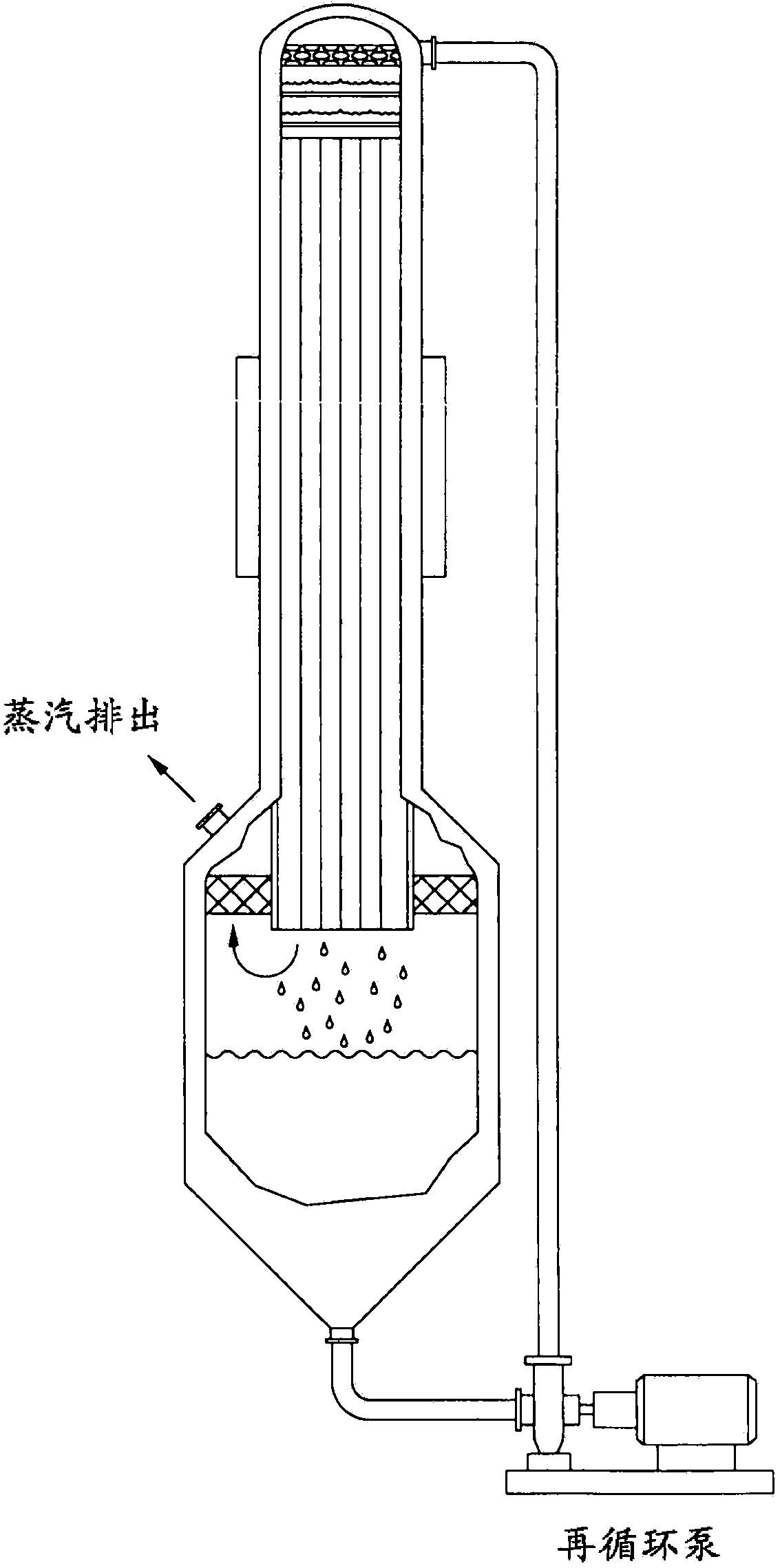
Method for recycling deoiled water using counterflow falling-film evaporators
ActiveUS20120145386A1High speedReduce chemical consumption requirementFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesEvaporation with vapour compressionWater useSaline water
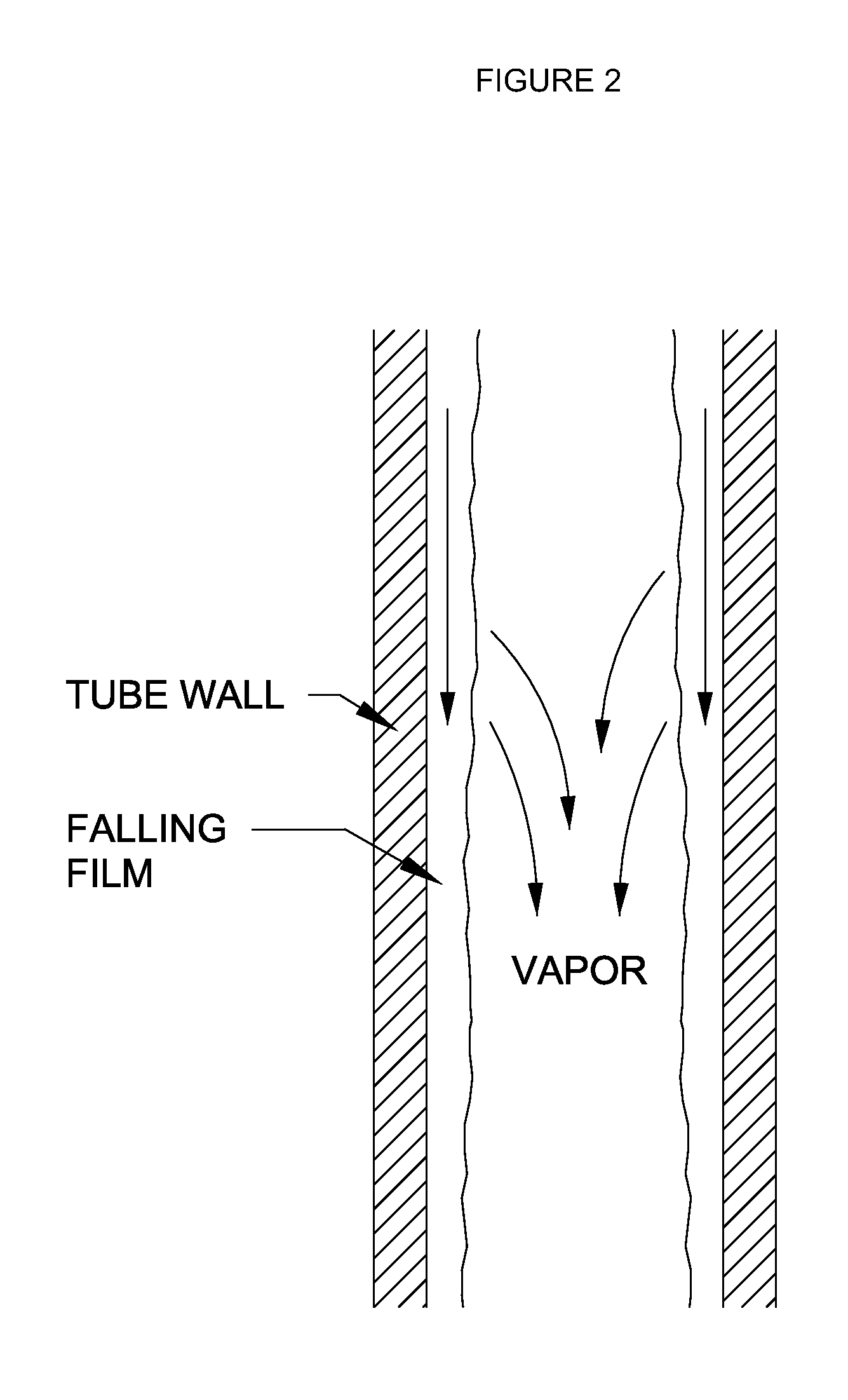
We provide an evaporator technology for treatment of produced water that may be deoiled water. Systems described herein utilize a vertical tube heat exchanger bundle where the brine is distributed in a falling film along the inside of the tube wall. Condensing steam causes a portion of the deoiled water to evaporate; this water vapor travels upward in a counterflow direction relative to the deoiled water. This evaporator technology provides several design advantages over the conventional vertical tube co-current flow evaporators (where the vapor flows downward with the falling film). These advantages include a minimal total installed cost (TIC) as well as offering optimal design features for water chemistry management.
Owner:AQUATECH INT LLC
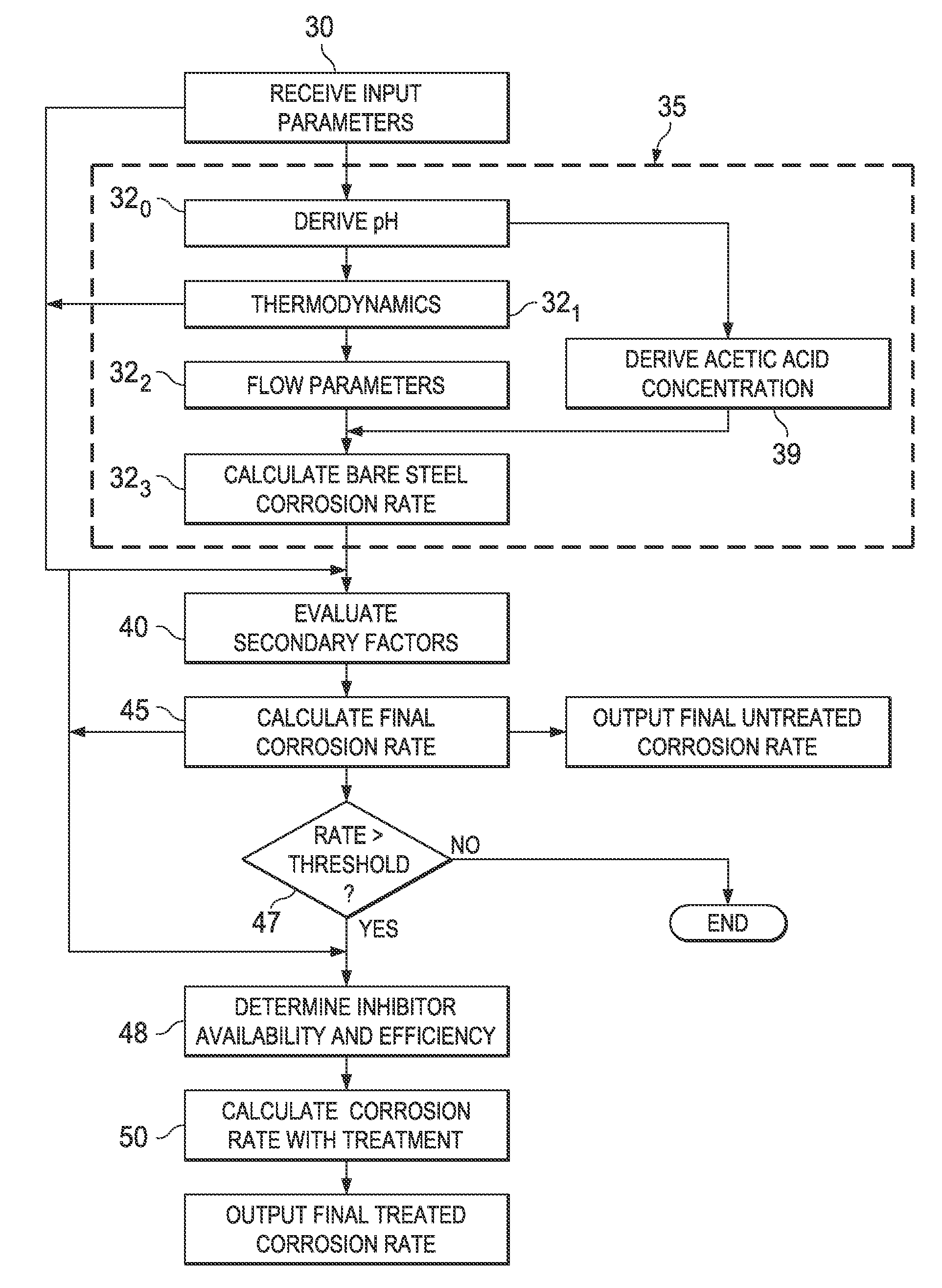
Method and system for predicting corrosion rates using mechanistic models
InactiveUS20100185401A1Efficient designPlug gaugesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCorrosion reactionMechanical models
A computer system and method for predicting the aqueous phase CO2 corrosion rate of a pipe useful in the production and transportation of oil and gas. Input parameter values corresponding to water chemistry and physical fluid and pipe properties are received. Based on these input parameter values, the system and method derive current-voltage relationships for multiple cathodic reduction reactions according to an electrochemical model of the corrosion reaction, and a current-voltage relationship for the anodic oxidation reaction of iron dissolution. A current density is obtained, at the intersection of an extrapolation of the anodic current-voltage relationship and an extrapolation of the summed cathodic current-voltage relationships. The predicted corrosion rate is then calculated from the obtained current density. The effects of secondary parameters such as scale and flow regime, and the efficacy of a corrosion inhibitor, can also be evaluated.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Water monitoring device and method
ActiveUS9776888B1Better chemical balanceMaintain chemical balanceWater treatment parameter controlGeneral water supply conservationAlkalinityWater Movements
A water monitoring device monitors and maintains swimming pool chemistry. The device includes sensors that detect water chemistry. The water monitoring device can communicate with computers and servers. This system can be used to determine if corrections to the water chemistry are required to maintain water sanitation. The device can monitor: pH, air temperature, water temperature, free chlorine levels, oxidation reduction potential, alkalinity, oxygen demand, water movement and velocity, and electrical conductivity.
Owner:SUTRO CONNECT INC +1
System for controlling water in an aquatic facility
ActiveUS8404117B1Ion-exchanger regenerationSedimentation separationMotor driveEnvironmental engineering
A system for controlling water within an aquatic facility includes a water chemistry controller, a variable rate water pump adapted to move water in the facility, and a variable rate motor driver operationally coupled to the water pump for variably energizing the water pump. The variable rate motor driver is coupled to the water chemistry controller to allow the water chemistry controller to manage the operation of the water pump.
Owner:BECS TECH
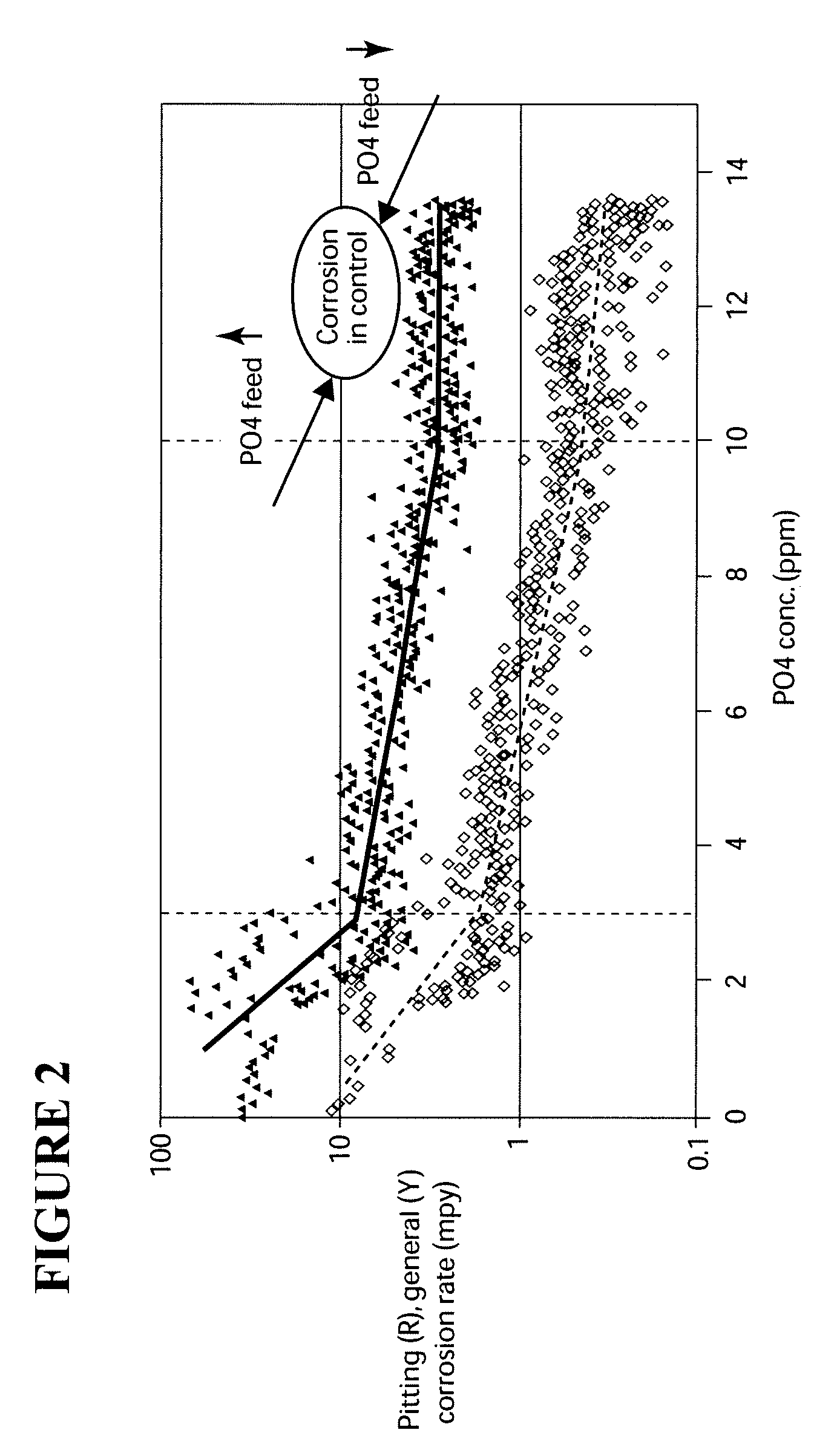
Cooling water scale and corrosion inhibition
A methods of the present invention for inhibiting silica scale formation and corrosion in aqueous systems where soluble silica residuals (SiO2) are maintained in excess of 200 mg / L, and source water silica deposition is inhibited with silica accumulations as high as 4000 mg / L (cycled accumulation) from evaporation and concentration of source water. The methods of the present invention also provides inhibition of corrosion for carbon steel at corrosion rates of less than 0.3 mpy (mils per year), and less than 0.1 mpy for copper, copper alloy, and stainless steel alloys in highly concentrated (high dissolved solids) waters. The methods of the present invention comprise pretreatment removal of hardness ions from the makeup source water, maintenance of electrical conductivity, and elevating the pH level of the aqueous environment. Thereafter, specified water chemistry residual ranges are maintained in the aqueous system to achieve inhibition of scale and corrosion.
Owner:WATER CONSERVATION TECH INT +1
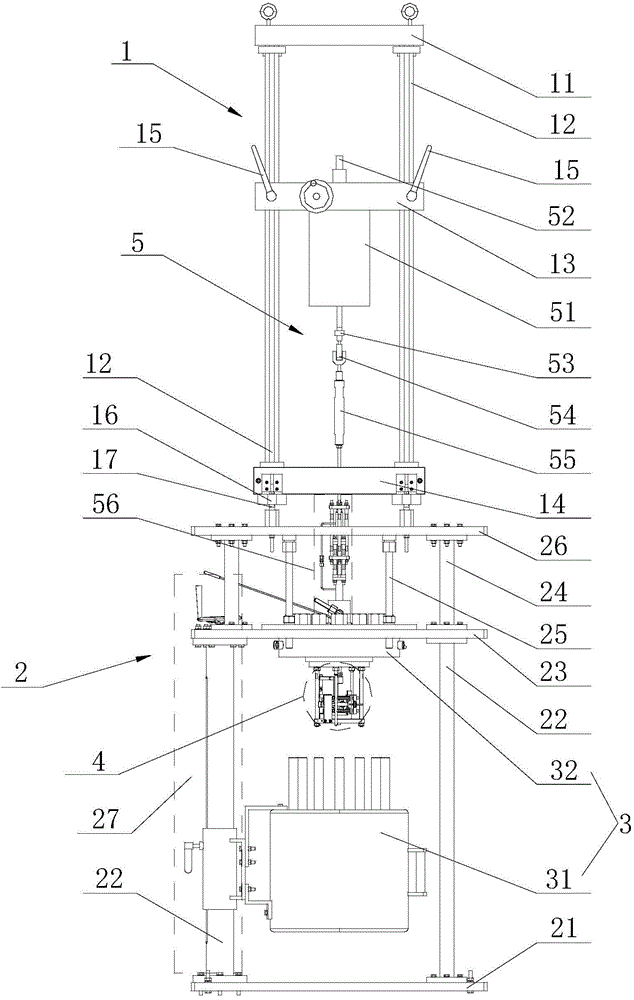
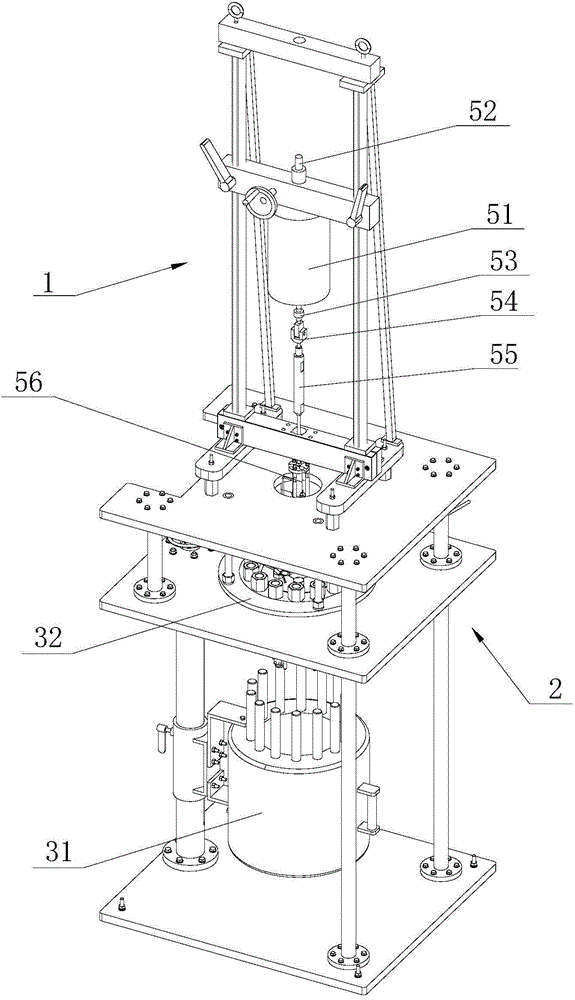
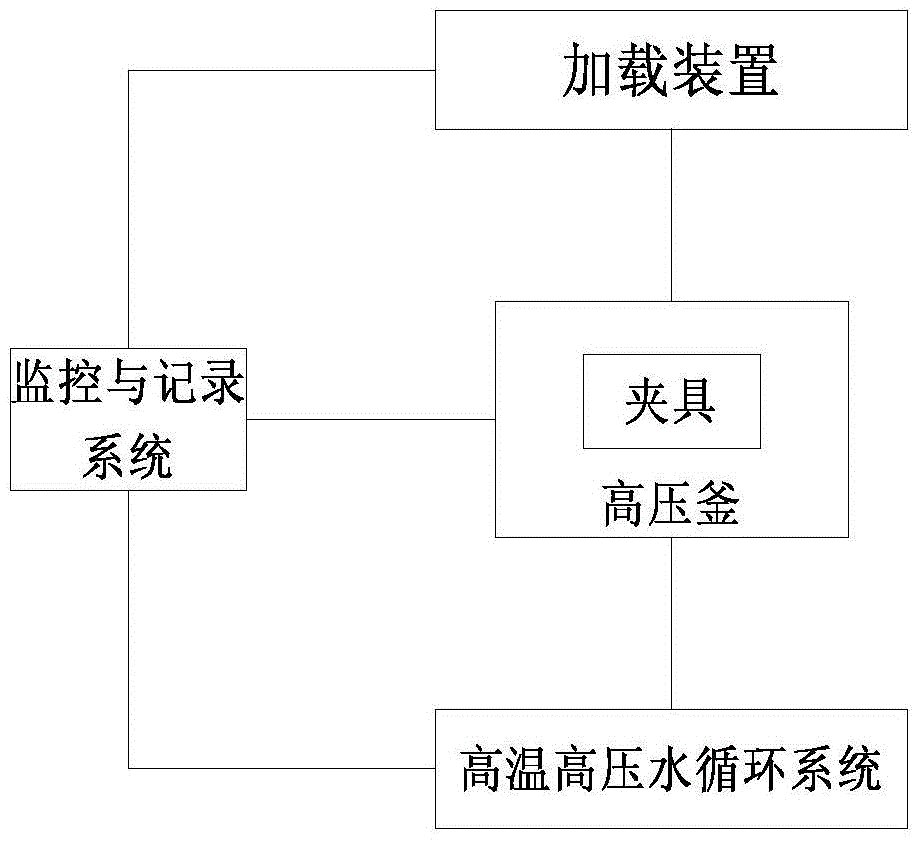
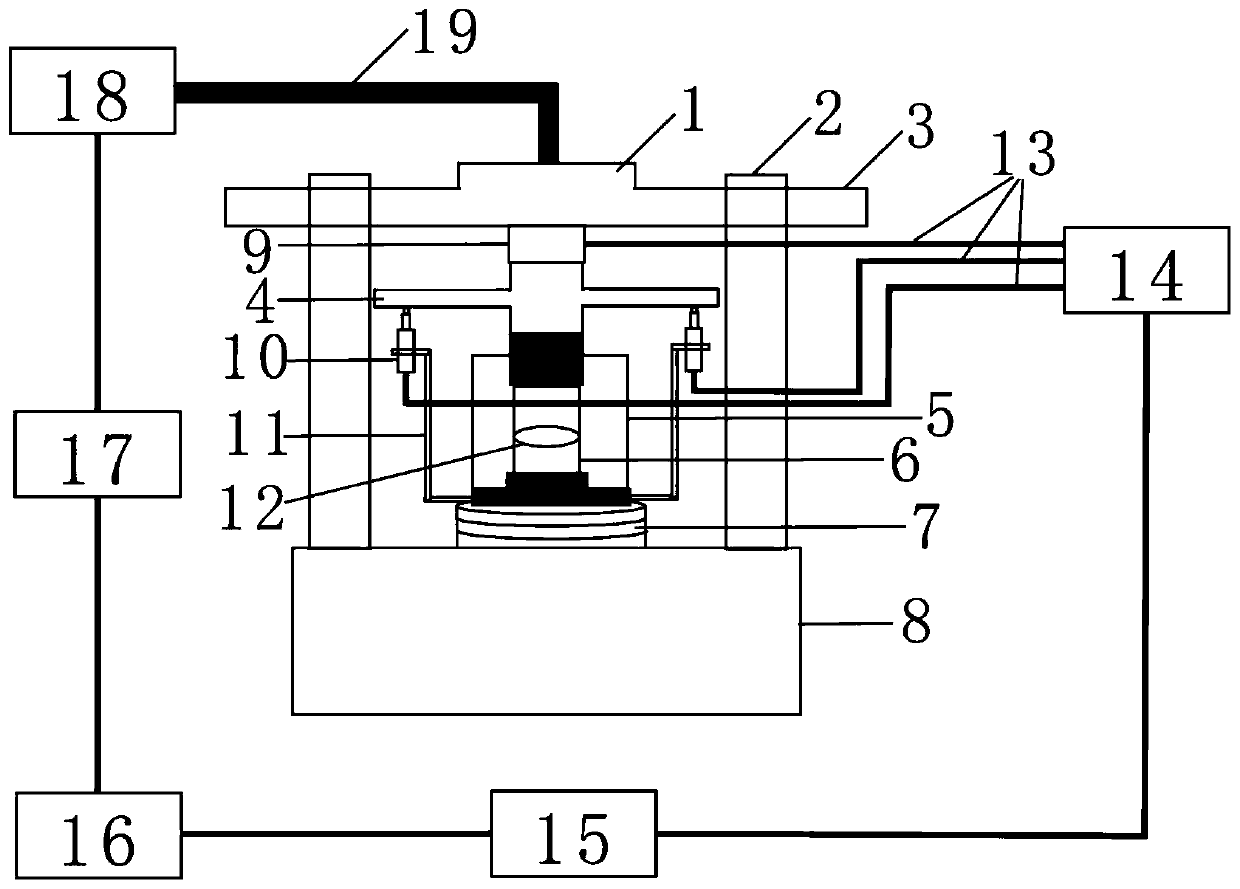
Fretting wear testing machine in high temperature and high pressure water or steam environment
ActiveCN104914042APayloadEffective displacement loadingUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisFrictional coefficientEngineering
The invention discloses a fretting wear testing machine in a high temperature and high pressure water or steam environment, wherein two workpieces for testing are clamped by arranging fixtures and placed in an autoclave which is positioned in the high temperature and high pressure water or steam environment by a high temperature and high pressure water circulating system, vibration excitation effect is applied to the testing workpieces in the autoclave by a loading device, and thereby the fretting wear test in high temperature and high pressure water or steam environment can be performed. The testing machine can simulate infinitesimal displacement amplitude and high vibration frequency fretting wear test under the primary and secondary loop temperature, pressure and hydrochemistry condition of nuclear power plant; the testing machine can perform slip wear test or impact wear test, and the friction coefficient and the wear coefficient between the friction pair can be obtained by measurement; the components of the testing machine are reasonably distributed, thus ensuring that the load and displacement loading of the testing machine is effective and reliable; the load control and measurement accuracy is high, and the friction force between the friction pair can be quantificationally obtained.
Owner:SUZHOU NUCLEAR POWER RES INST +2
Cooling water scale and corrosion inhibition
ActiveUS20050150834A1Avoid corrosionIncrease ionic strengthDrying using combination processesAuxillariesLimescaleEvaporation
A methods of the present invention for inhibiting silica scale formation and corrosion in aqueous systems where soluble silica residuals (SiO2) are maintained in excess of 200 mg / L, and source water silica deposition is inhibited with silica accumulations as high as 4000 mg / L (cycled accumulation) from evaporation and concentration of source water. The methods of the present invention also provides inhibition of corrosion for carbon steel at corrosion rates of less than 0.3 mpy (mils per year), and less than 0.1 mpy for copper, copper alloy, and stainless steel alloys in highly concentrated (high dissolved solids) waters. The methods of the present invention comprise pretreatment removal of hardness ions from the makeup source water, maintenance of electrical conductivity, and elevating the pH level of the aqueous environment. Thereafter, specified water chemistry residual ranges are maintained in the aqueous system to achieve inhibition of scale and corrosion.
Owner:WATER CONSERVATION TECH INT +1
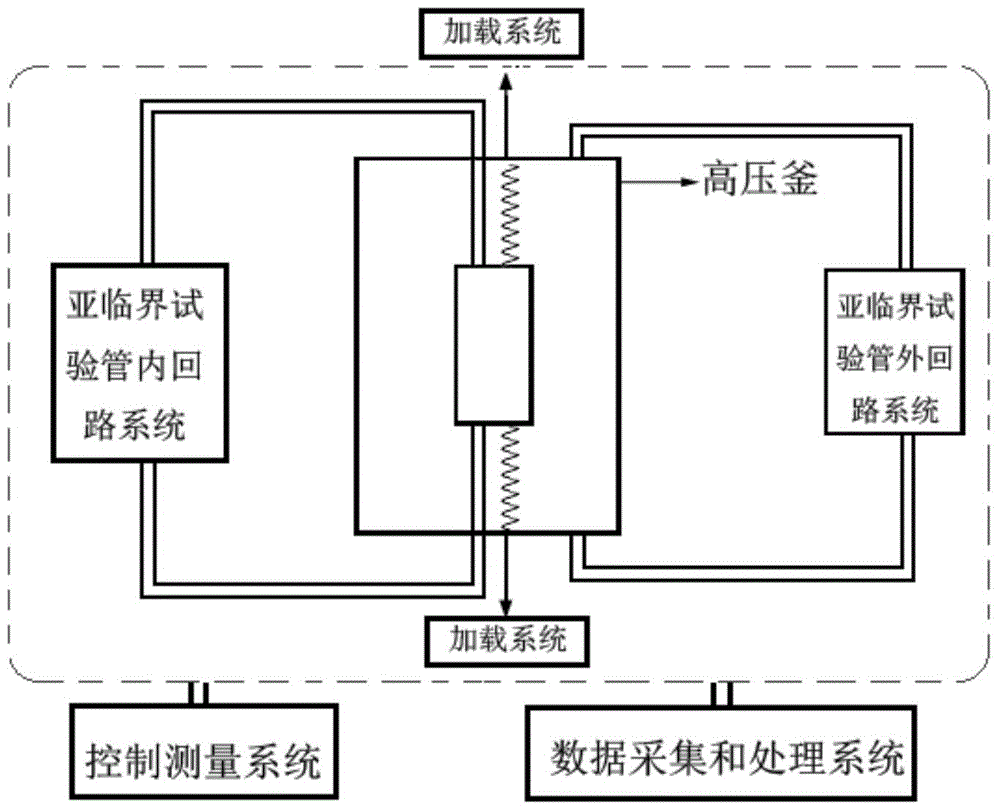
High-temperature and high-pressure water vapor environment structural material testing device
ActiveCN104458400AWeather/light/corrosion resistanceInvestigating abrasion/wear resistancePressurized water reactorData acquisition
The invention discloses a high-temperature and high-pressure water vapor environment structural material testing device. The testing device is provided with a pipe, wherein high-temperature water flows inside and outside the pipe. The testing device comprises an autoclave, a test tube loading system, a loop system inside a test tube, a loop system outside the test tube, a controlling and measuring system and a data acquisition and processing system. The testing device which can be used for simulating the temperature, pressure, flow velocity, water chemical conditions, load and the like of a high-temperature and high-pressure water vapor environment structural material is applicable to tests in the aspects of corrosion, stress corrosion, corrosion fatigue, flow accelerated corrosion and the like of tubular specimens through complex flow and complex load coupling effect. Especially, the working conditions of different flow, different inner-side and outer-side temperatures, different pressures and different water chemistry in a heat exchange tube of a steam generator in a nuclear reaction pressurized-water reactor can be simulated to carry out related testing and research on the heat exchange tube.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Water monitoring device and method
ActiveUS10150680B1Avoid spreadingLarger ppm increaseWater treatment parameter controlControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsAlkalinityWater Movements
A water monitoring device monitors and maintains swimming pool chemistry. The device includes sensors that detect water chemistry. The water monitoring device can communicate with computers and servers. This system can be used to determine if corrections to the water chemistry are required to maintain water sanitation. The device can monitor: pH, air temperature, water temperature, free chlorine levels, oxidation reduction potential, alkalinity, oxygen demand, water movement and velocity, and electrical conductivity.
Owner:DATA20 +1
System for controlling water in an aquatic facility
ActiveUS20130075311A1Ion-exchanger regenerationSedimentation separationMotor driveEnvironmental engineering
A system for controlling water within an aquatic facility includes a water chemistry controller, a variable rate water pump adapted to move water in the facility, and a variable rate motor driver operationally coupled to the water pump for variably energizing the water pump. The variable rate motor driver is coupled to the water chemistry controller to allow the water chemistry controller to manage the operation of the water pump.
Owner:BECS TECH
System and method for controlling water quality in a recreational water installation
A system for monitoring water chemistry of a recreational water installation includes a sensor configured to detect bather load in the recreational water installation and a controller configured to determine a required adjustment to the water chemistry of the recreational water installation based upon the detected bather load.
Owner:WATERGURU INC
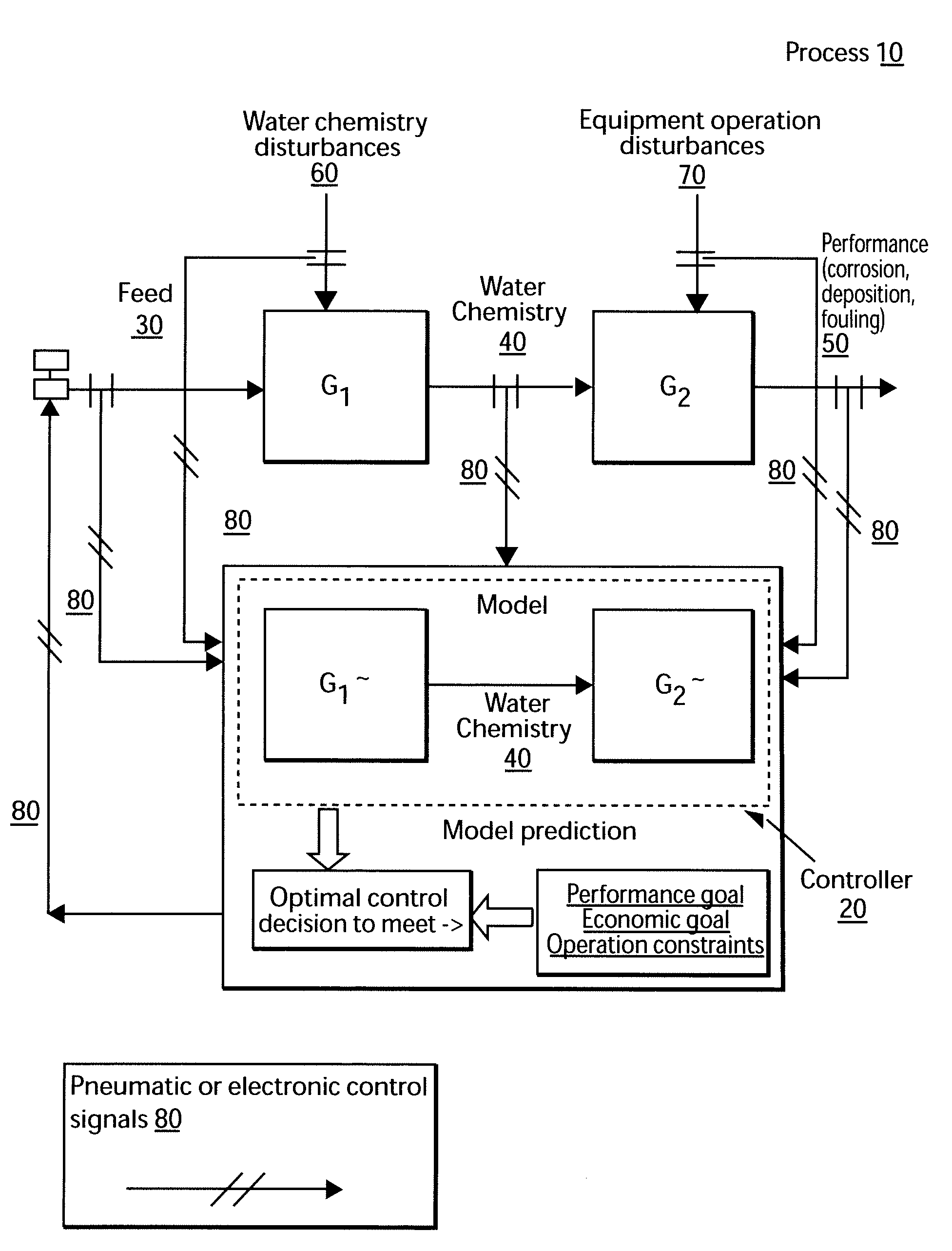
Control system for monitoring localized corrosion in an industrial water system
InactiveUS20100163469A1Low costMaximize inhibitionWater treatment parameter controlControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsChemical treatmentControl system
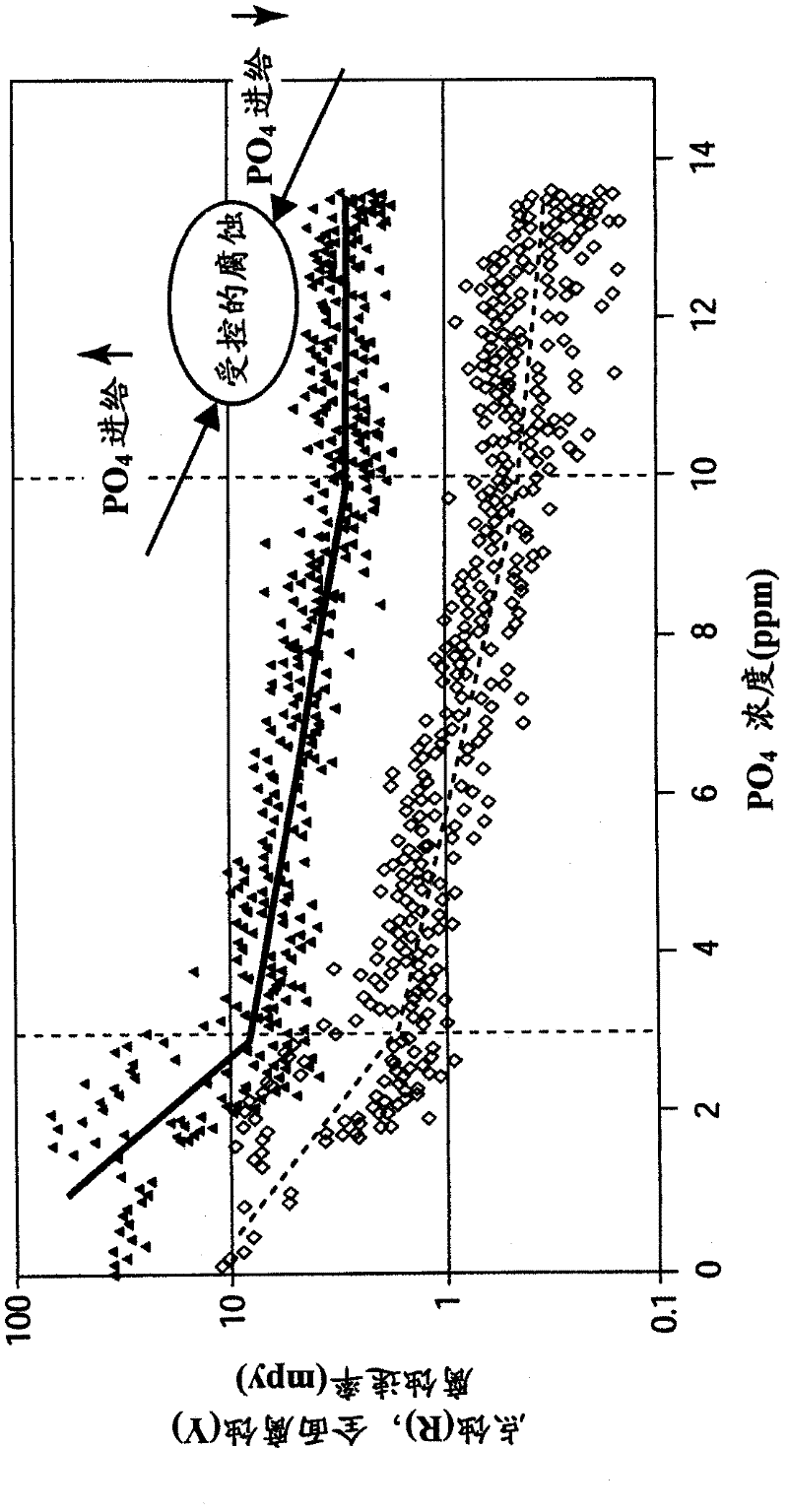
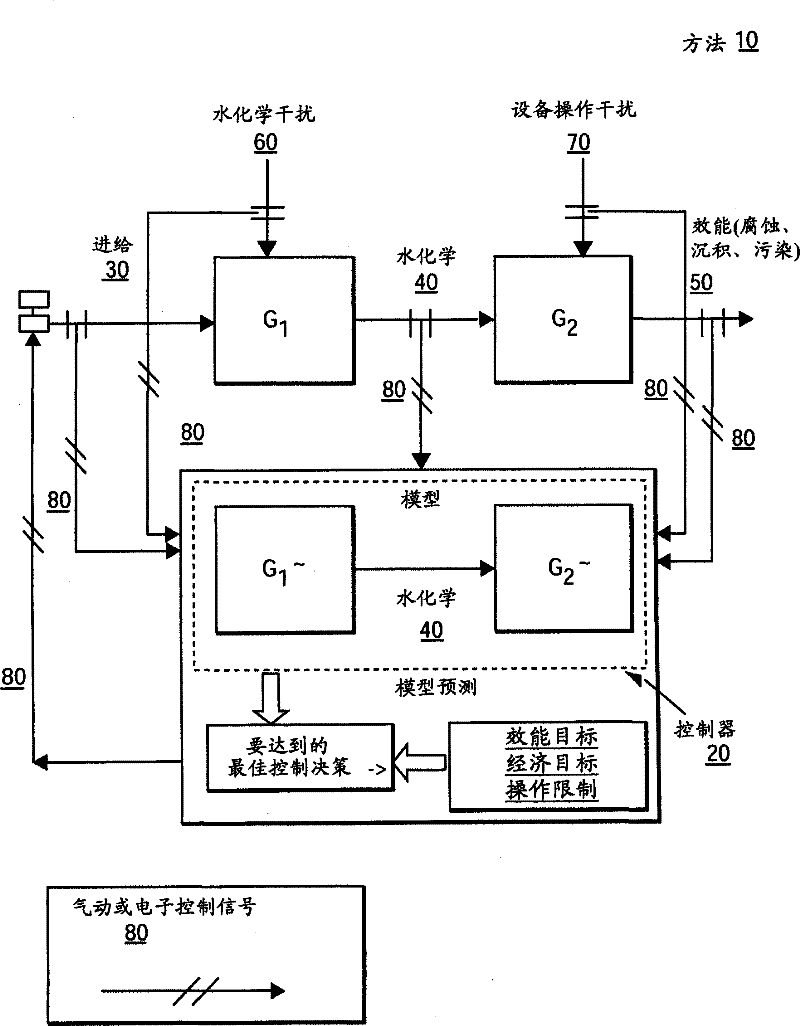
A control system is disclosed for monitoring and controlling localized corrosion in an industrial water system, comprising: measuring quantitative localized corrosion rate and at least one controllable water chemistry variable; identifying mathematical correlations between the quantitative localized corrosion rate and the at least one controllable water chemistry variable; establishing mathematical correlations between the controllable water chemistry variable and at least one chemical treatment feed; defining an index derived from current and future values of the localized corrosion rate and an index derived from current and future values of the at least one chemical treatment feed; utilizing a processor to minimize the index of the localized corrosion rate and the index of the at least one chemical treatment feed and determine current and future values of the at least one chemical treatment feed; and implementing only a current value of the at least one chemical treatment feed within the water system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Novel Arrangement of Denitrification Reactors in a Recirculating Aquaculture System
ActiveUS20090152192A1Maximize survivalSure easyWater treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesAquatic speciesFiltration
The present invention relates to a novel arrangement of denitrification reactors for removal of nitrate compounds in a recirculating aquaculture system. The novel arrangement of an aquaculture system of the present invention includes positioning one or more anaerobic denitrification reactors upstream of aerobic nitrification and degassing processes. One aspect of the present invention includes a flow of aqueous medium from aquatic species rearing tanks towards one or more denitrification reactors. Another aspect of the present invention includes flow of aqueous medium from aquatic species rearing tanks to a solids removing filter or mechanical filtration means for removal of solid waste matter or biomass prior to flow of aqueous medium towards one or more denitrification reactors. In a sequence of components comprising a system of the present invention, treated and denitrified aqueous medium exiting one or more denitrification reactors is directed towards a solids removing filter wherein treated and denitrified aqueous medium combines with untreated aqueous medium. Combined untreated aqueous medium and denitrified aqueous medium exits a solids removing filter and is directed towards an aerobic nitrification unit. Aqueous medium exiting the aerobic nitrification unit is degassed and oxygenated and returned to aquatic species rearing tanks. A system of the present invention which utilizes denitrification reactors positioned upstream of aerobic nitrification has advantages over existing aquaculture systems which use denitrification in reduction of nitrate concentrations. This results in greater mitigation of water chemistries and compounds which are harmful to aquatic species and more efficient use and conservation of water resources.
Owner:MOTE MARINE LAB
Cooling water corrosion inhibition method
ActiveUS20060151394A1Corrosion protection is enhancedPreventing PVM interferenceDrying using combination processesAuxillariesWater sourceEvaporation
Methods for inhibiting corrosion in aqueous evaporative systems where soluble silica (SiO2) is maintained at residuals between 10 Mg / L and saturation, but more preferably maintained at greater than 300 mg / L as SiO2, to provide corrosion inhibiting silica films that protect system metals. Silica is provided by evaporation of water and subsequent concentration and transformation of silica naturally contained in source water. The methods of the present invention provide highly effective inhibition of corrosion for mild steel, copper, stainless steel, aluminum, zinc, galvanized steel and various alloys of such metals. The methods of the present invention comprise pretreatment removal of polyvalent metal ions from the makeup source water, maintenance of concentration of monovalent metal ions, and controlling pH at a minimum of 7.0 in the presence of an elevated temperature aqueous environment. Thereafter, specified water chemistry residual ranges are maintained in the aqueous system to achieve inhibition of scale and corrosion.
Owner:WATER CONSERVATION TECH INT
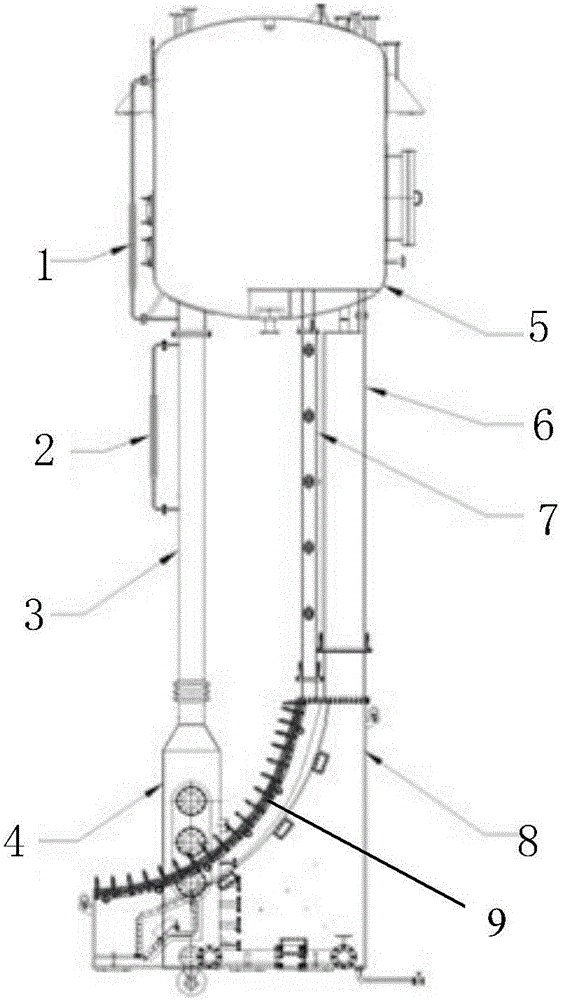
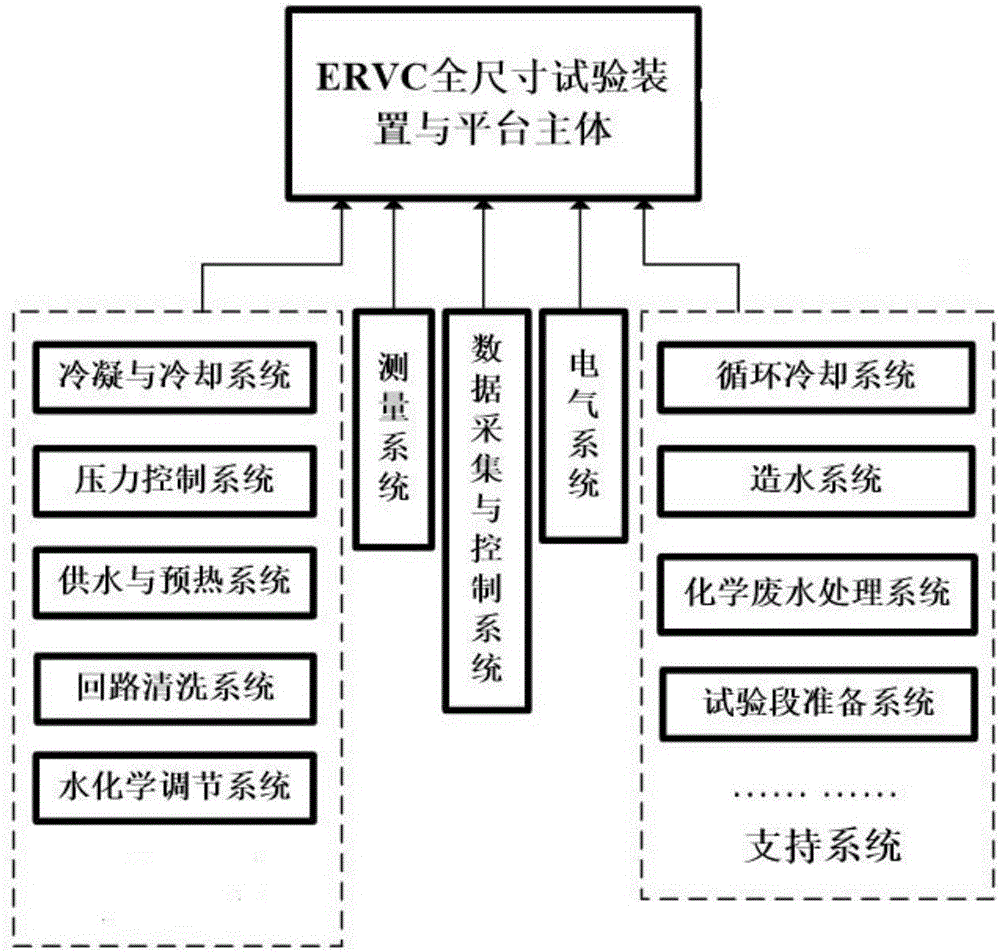
External-cooling full-height comprehensive test platform for large-scale advanced reactor pressure vessel
InactiveCN106653110AImprove flow characteristicsImprove heat transfer characteristicsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringTemperature controlReactor pressure vessel
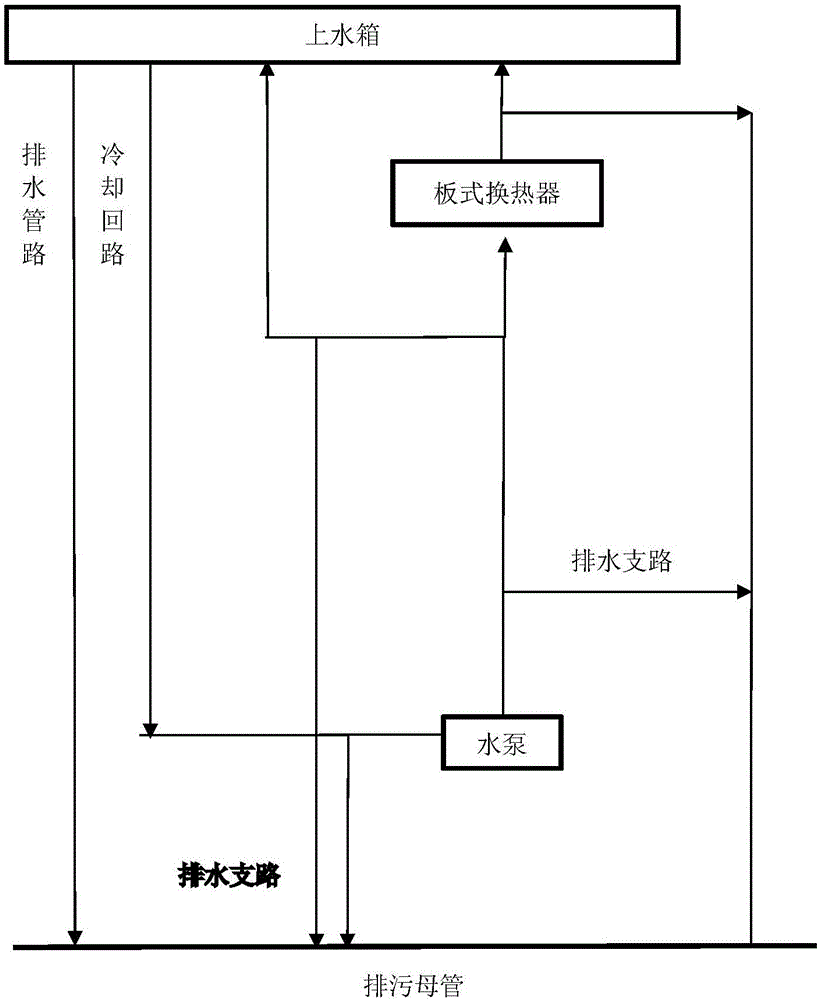
The invention provides an external-cooling full-height comprehensive test platform for a large-scale advanced reactor pressure vessel. The test platform comprises a main device loop system, a condensing and cooling system, a water supply and preheating system, a water chemistry adjusting system and a pressure control system, the condensing and cooling system is used for controlling and adjusting temperature of primary fluid in an upper water tank of the main device loop system and providing circularly cooling for test water in the upper water tank, the water supply and preheating system is used for providing the test water to the main device loop system, initially preheating the test water and keeping temperature, the water chemistry adjusting system is communicated with a lower water tank of the main device loop system and used for controlling solute and concentration of water chemistry solution in different tests, and the pressure control system is used for controlling pressure of the upper water tank. According to the test platform, engineering verification test of value and distribution of boiling heat transfer limit CHF (critical heat flux) of the outer wall of a lower sealing head of the pressure vessel can be determined when IVR-ERVC (in-vessel retention-external reactor vessel cooling) is implemented under severe accident conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
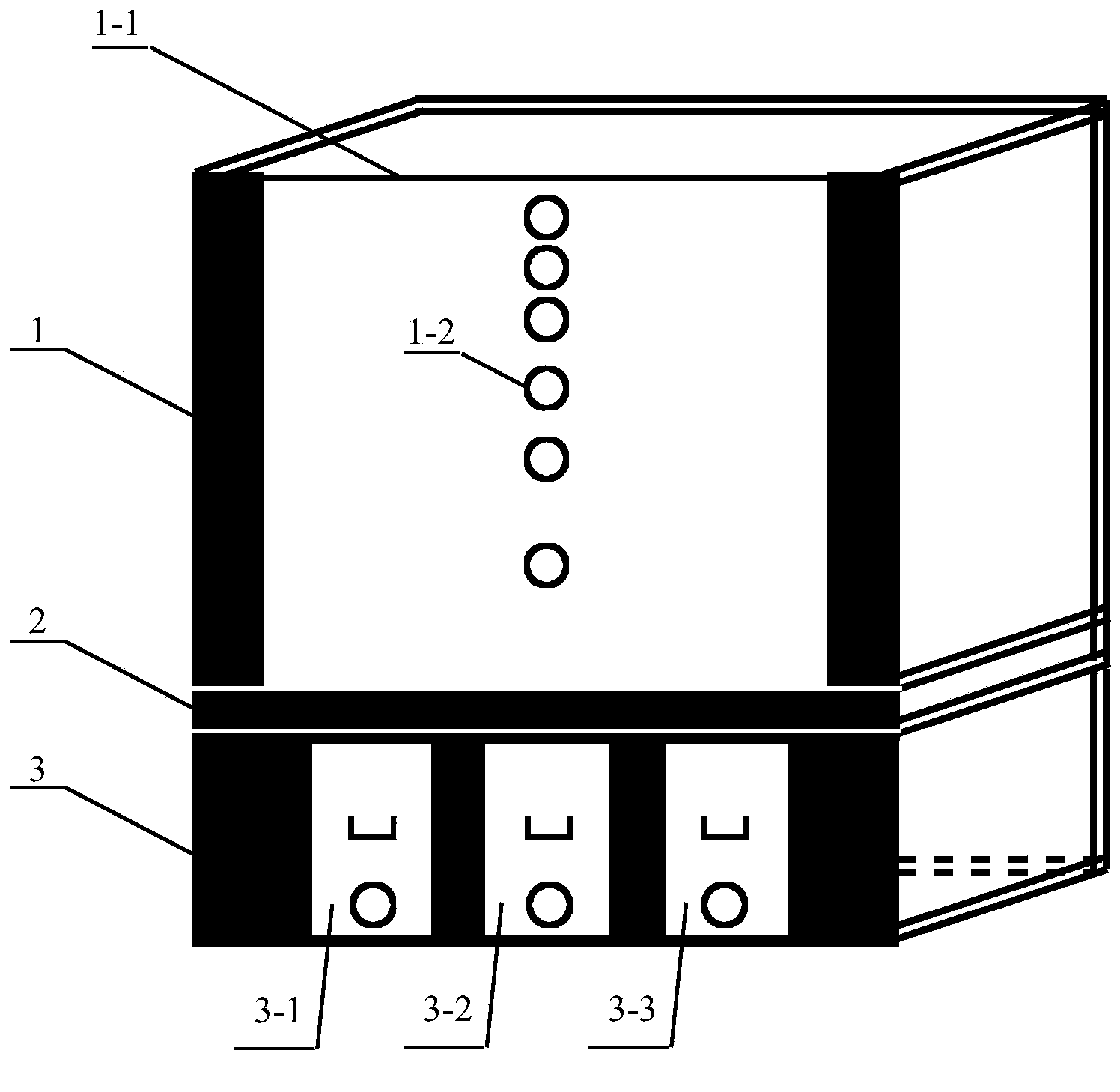
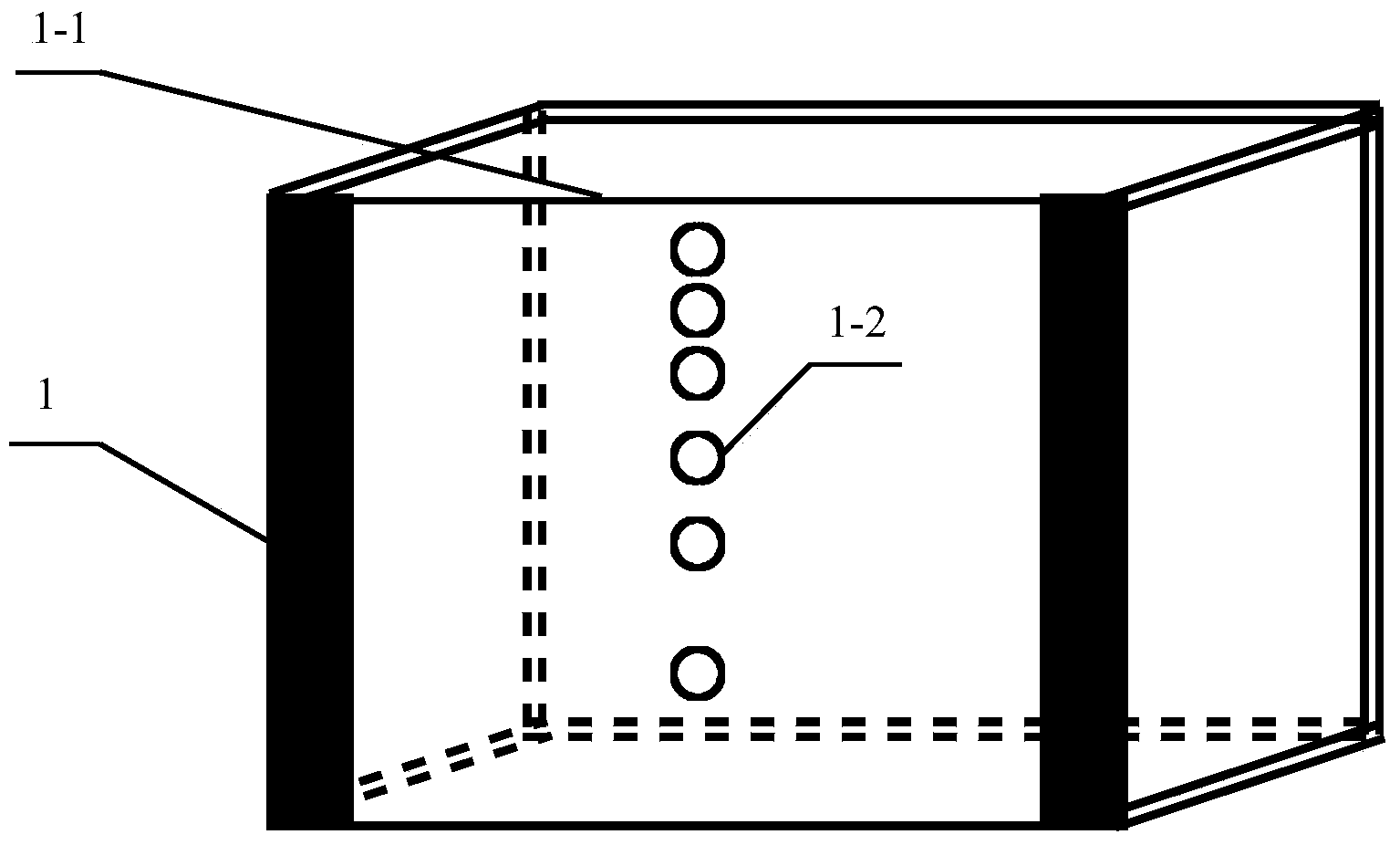
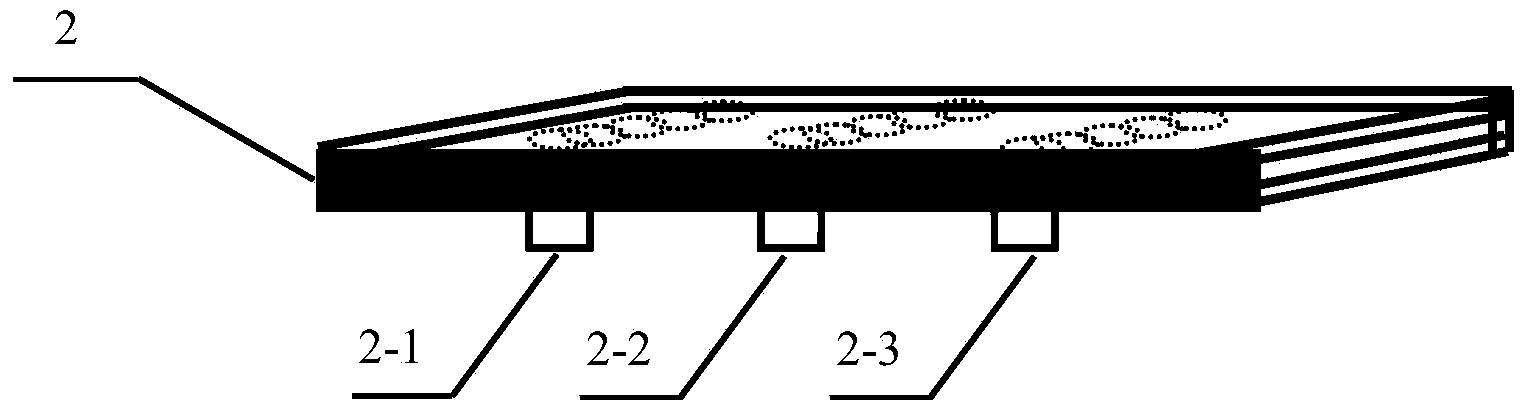
Soil erosion and nutrient migration simulating device applicable to Karst regions
The invention discloses a soil erosion and nutrient migration simulating device applicable to Karst regions, which consists of a receiving pool, a cement plate and a bearing foundation trench, wherein a prefabricated steel baffle is respectively connected with the receiving pool and the cement plate, the cement plate is connected with the bottom of the receiving pool, a first drain pipe is connected with a first stainless steel tank, a second drain pipe is connected with a second stainless steel tank, a third drain pipe is connected with a third stainless steel tank, the bearing foundation tank is connected with the lower end of the cement plate, and the three stainless steel tanks are located in holes of the bearing foundation tank. Stainless steel drain pipes and handles are respectively reserved at the bottom end and the middle part outside each of the first, second and third stainless steel tanks. The device is simple in structure and convenient to operate, and simulates migration conditions of soil solutes under different rock crack environments, so that the problems that simulation study in water and soil process and water chemistry of the Karst regions is complex and difficult, hard to regulate and the like are solved.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cooling water scale and corrosion inhibition
ActiveUS20050150838A1Avoid corrosionIncrease ionic strengthDrying using combination processesAuxillariesLimescaleEvaporation
A methods for inhibiting silica scale formation and corrosion in aqueous systems where soluble silica (SiO2) can be maintained at residuals below 200 mg / L, but more preferably maintained at greater than 200 mg / L as SiO2, without silica scale and with control of deposition of source water silica accumulations as high as 4000 mg / L (cycled accumulation) from evaporation and concentration of source water. The methods of the present invention also provide highly effective inhibition of corrosion for carbon steel, copper, copper alloy, and stainless steel alloys. The methods of the present invention comprise pretreatment removal of hardness ions from the makeup source water, maintenance of electrical conductivity, and elevating the pH level of the aqueous environment. Thereafter, specified water chemistry residual ranges are maintained in the aqueous system to achieve inhibition of scale and corrosion.
Owner:JOHN L KUBIS +1
Method and system for predicting corrosion rates using mechanistic models
InactiveUS8447529B2Efficient designPlug gaugesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCorrosion reactionMechanical models
A computer system and method for predicting the aqueous phase CO2 corrosion rate of a pipe useful in the production and transportation of oil and gas. Input parameter values corresponding to water chemistry and physical fluid and pipe properties are received. Based on these input parameter values, the system and method derive current-voltage relationships for multiple cathodic reduction reactions according to an electrochemical model of the corrosion reaction, and a current-voltage relationship for the anodic oxidation reaction of iron dissolution. A current density is obtained, at the intersection of an extrapolation of the anodic current-voltage relationship and an extrapolation of the summed cathodic current-voltage relationships. The predicted corrosion rate is then calculated from the obtained current density. The effects of secondary parameters such as scale and flow regime, and the efficacy of a corrosion inhibitor, can also be evaluated.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Rock creep triaxial test system and method capable of continuously acting in water environment
ActiveCN110749497ALow costGood expansion performanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesHydration reactionChemical solution
The invention discloses a rock creep triaxial test system and method capable of continuously acting in a water environment, and belongs to the technical field of rock mechanics tests. According to thetechnical scheme, a pressurizing cylinder is connected with a cross beam, the cross beam is supported on a testing machine base through a supporting column, a water environment confining pressure system is arranged between the base and the cross beam, a dynamic stress-strain collecting system is connected with the water environment confining pressure system, and the dynamic stress-strain collecting system is sequentially connected with a computer, a digital controller, a servo controller, a hydraulic source and an oil conveying pipe. The rock creep triaxial test system and method have the beneficial effects that the hydration reaction of an expanding agent is used for replacing a constant-flow pump to provide confining pressure for a triaxial test, the cost is reduced, and the rock creeptriaxial test system and method are continuous and stable; the long-term mechanical property of the rock can be tested under the continuous action of chemical solutions with different components; thelong-term mechanical properties of the rock in static and flowing water environments can be tested, the pH value change of the water environment caused by corrosion of water to the rock can be monitored in real time, and the hydrochemical reaction characteristics of the rock are obtained; and moreover, the mixed expanding agent is good in expanding effect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for controlling operation of water plant by stages according to water treatment capacity
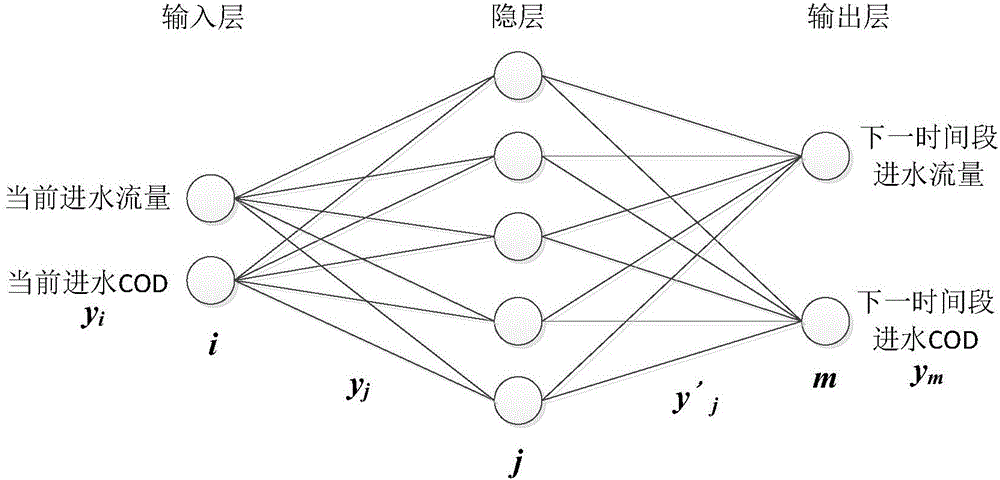
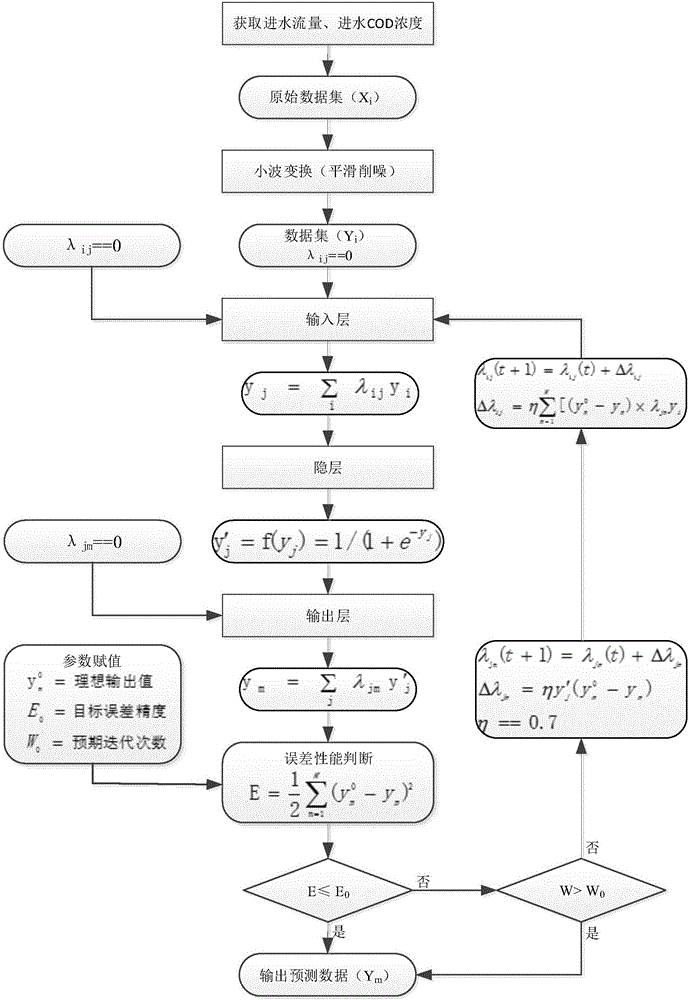
ActiveCN106200381AKeep abreast of the amount of water inflowKeep abreast of influent CODNeural learning methodsAdaptive controlChemical oxygen demandSewage treatment
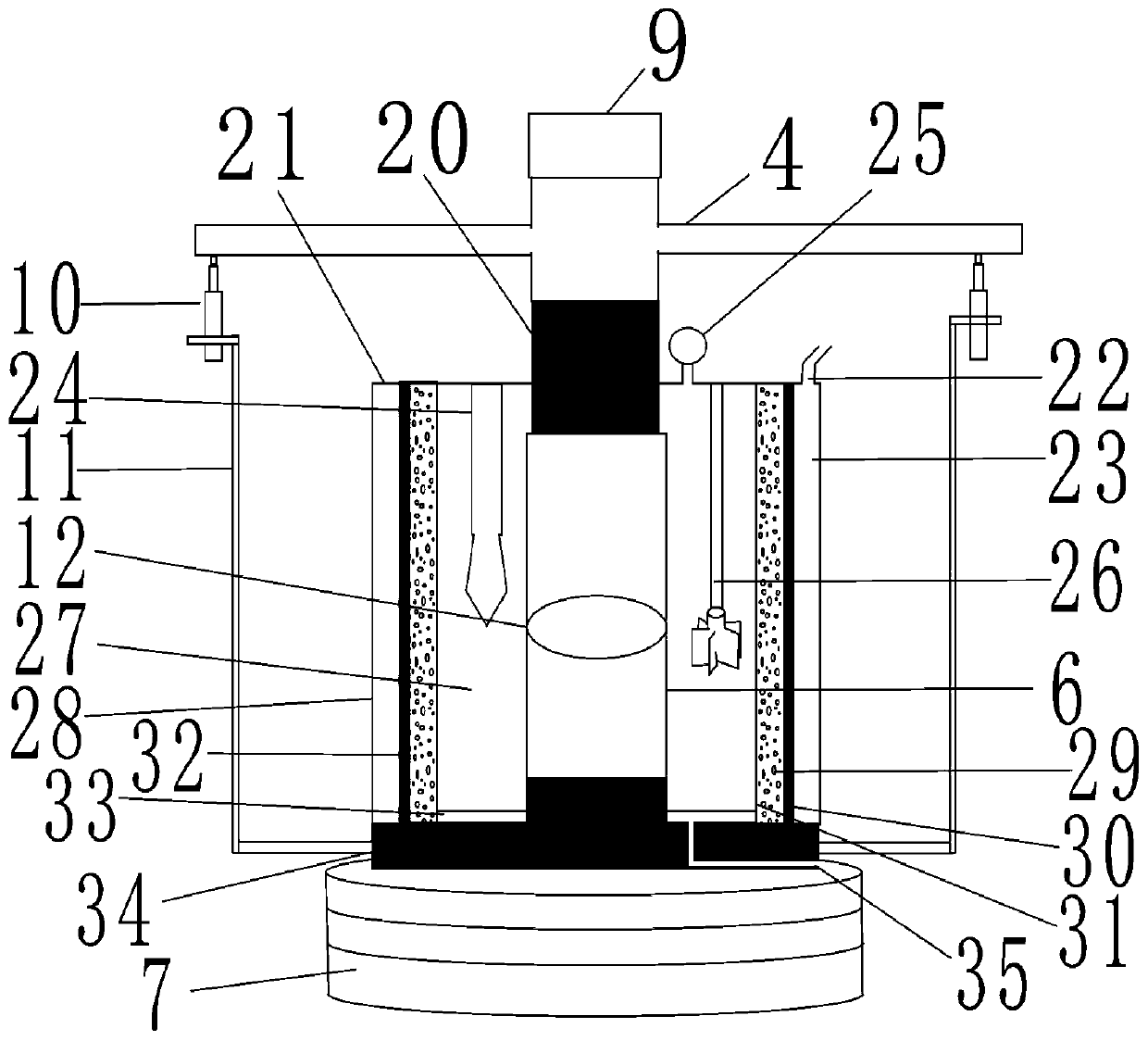
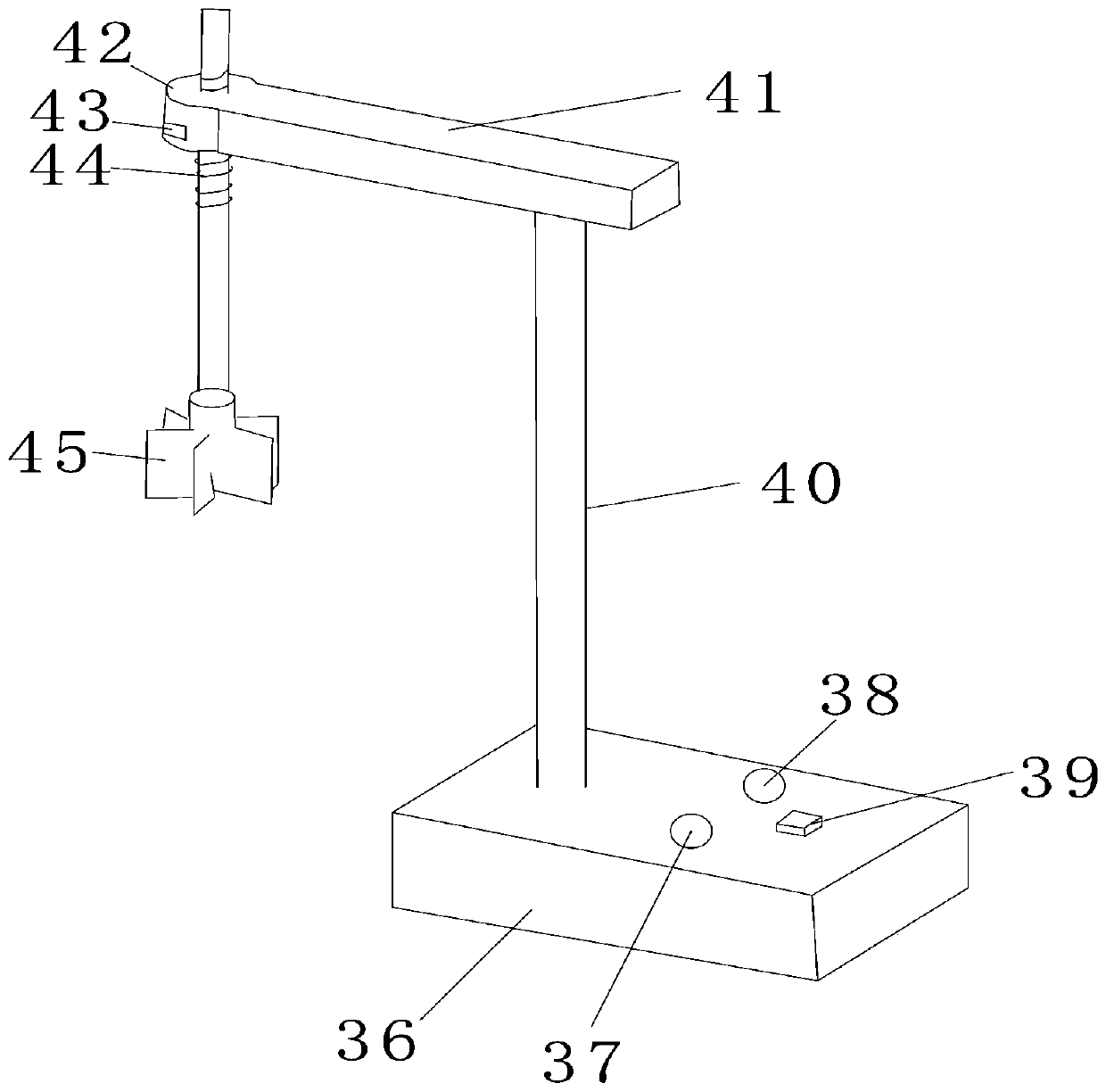
The invention discloses a method for controlling operation of a water plant by stages according to the water treatment capacity. The method comprises the following steps that S100, real-time inflow rate data of a sewage treatment plant is collected, the current inflow chemical oxygen demand is calculated, and the collected real-time inflow rate and inflow chemical oxygen demand data and corresponding time points are stored in a database; S200, a data curve of the collected data is established with the real-time inflow rate and inflow chemical oxygen demand data being vertical coordinates and the time point corresponding to the real-time inflow rate data being horizontal coordinates, and smooth denoising is conducted on the data curve; S300, a neural network technology is adopted for establishing a data prediction model of the data subjected to smooth denoising; S400, the data at a selected moment is predicted, and a predicted value is acquired; S500, operation of the sewage treatment plant is controlled according to the acquired predicted value. By the adoption of the method, it can be guaranteed that the process is adjusted in time, process operation is slightly adjusted according to change in inflow, and the purposes of stable outflow and up-to-standard emission are achieved.
Owner:HUADIAN WATER TECH CO LTD +1
Method for recycling deoiled water using counterflow falling-film evaporators
InactiveCN103391898ATotal installation costs minimizedIncrease the rate of foulingFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesEvaporation with vapour compressionVertical tubeWater use
We provide an evaporator technology for treatment of produced water that may be deoiled water. Systems described herein utilize a vertical tube heat exchanger bundle where the brine is distributed in a falling film along the inside of the tube wall. Condensing steam causes a portion of the deoiled water to evaporate; this water vapor travels upward in a counterflow direction relative to the deoiled water. This evaporator technology provides several design advantages over the conventional vertical tube co-current flow evaporators (where the vapor flows downward with the falling film). These advantages include a minimal total installed cost (TIC) as well as offering optimal design features for water chemistry management.
Owner:AQUATECH INT LLC
Apparatus and method for analysing downhole water chemistry
The invention concerns an apparatus for analysing water chemistry. According to the invention, the apparatus is adapted to operate downhole and comprises a colouring agent supply device for supplying a colouring agent to a water sample, the colour of the water sample thus supplied being indicative of the water sample chemistry, and a colorimetric analyser arranged to determine the colour of the water sample.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Control system for monitoring localized corrosion in an industrial water system
InactiveCN102334022ALow costEnsure performance goalsSampled-variable control systemsWater treatment parameter controlChemical treatmentControl system
A control system is disclosed for monitoring and controlling localized corrosion in an industrial water system, comprising: measuring quantitative localized corrosion rate and at least one controllable water chemistry variable; identifying mathematical correlations between the quantitative localized corrosion rate and the at least one controllable water chemistry variable; establishing mathematical correlations between the controllable water chemistry variable and at least one chemical treatment feed; defining an index derived from current and future values of the localized corrosion rate and an index derived from current and future values of the at least one chemical treatment feed; utilizing a processor to minimize the index of the localized corrosion rate and the index of the at least one chemical treatment feed and determine current and future values of the at least one chemical treatment feed; and implementing only a current value of the at least one chemical treatment feed within the water system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
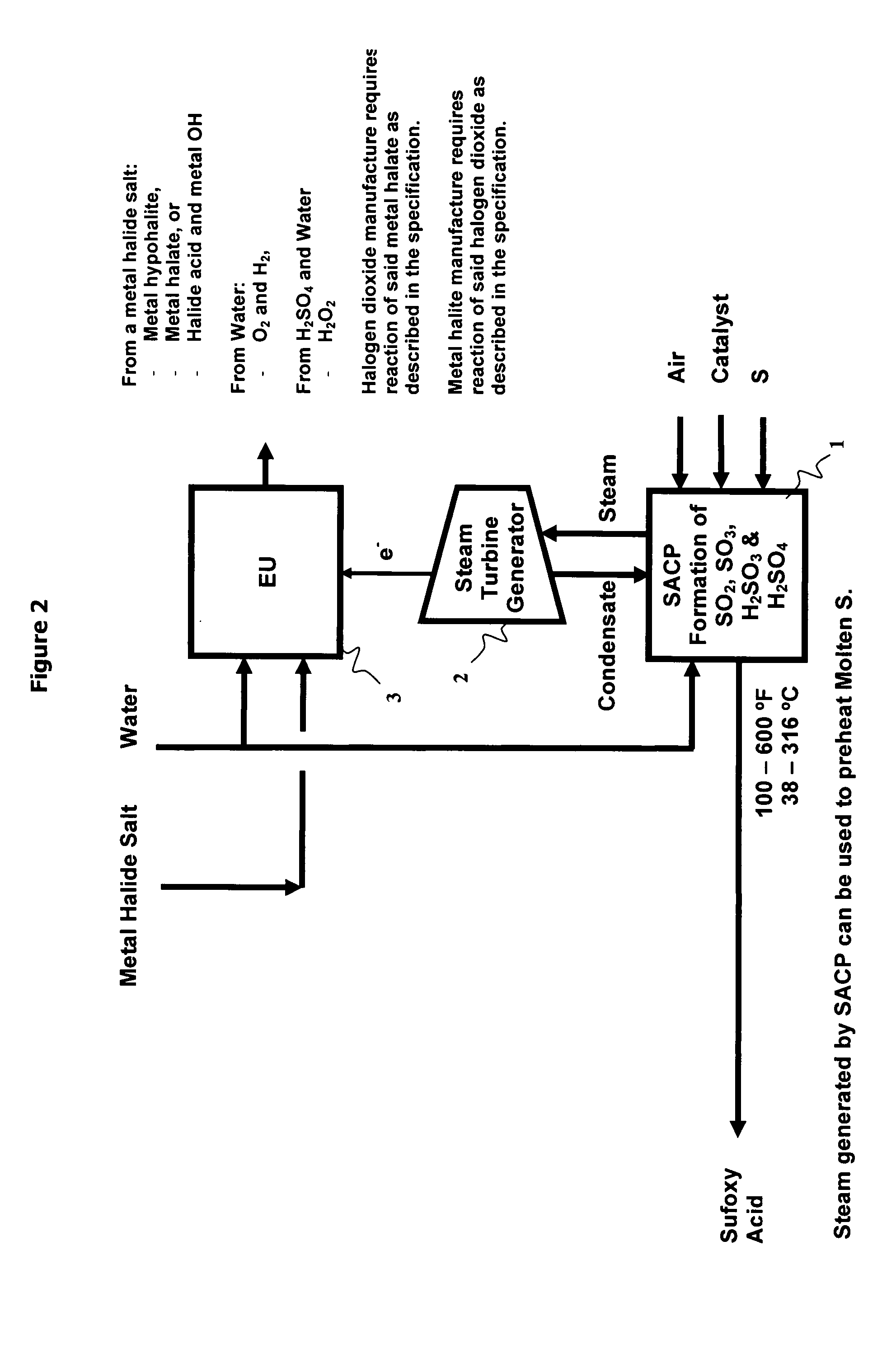
Manufacture of water chemistries
InactiveUS20080053104A1Effective and efficient and economically feasible processEfficient and effective processNitrogen compoundsElectrostatic separationPresent methodDisinfectant
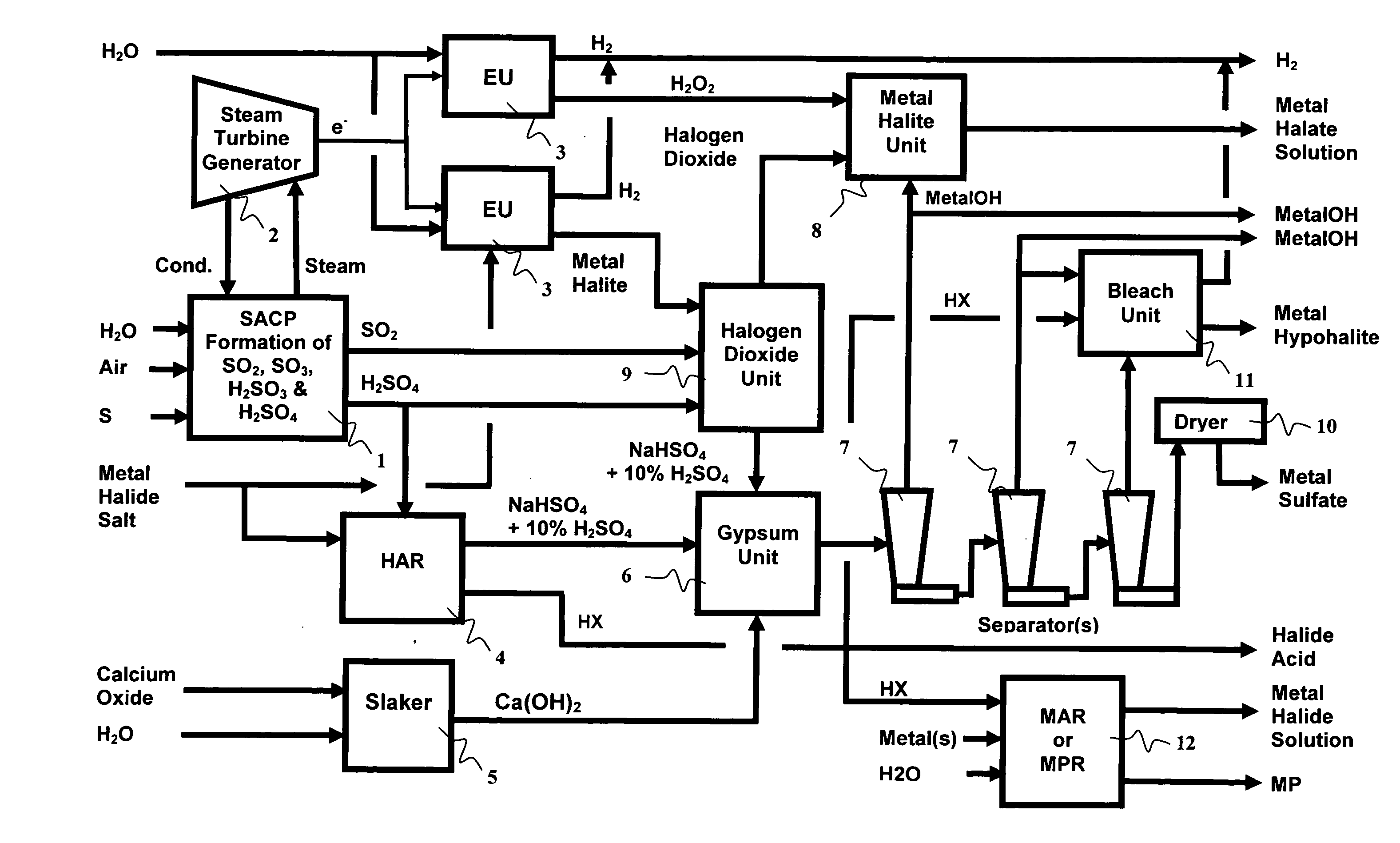
As population density increases, the transportation of hazardous chemicals, including acids and disinfectants, lead to an increased incidence of spills while the consequences of spills become more serious. While solutions of halide acids, hypohalites and halites are safer disinfectants for transportation, handling, storage and use than traditional gaseous chlorine, the manufacturing cost of these disinfectants has here-to-fore limited their use. Economical processes are presented for the manufacture of O2, halogen oxides, halide acids, hypohalites, and halates; as well as polynucleate metal compounds, metal hydroxides and calcium sulfate hydrate (gypsum). The instant invention presents methods and processes that incorporate the use of sulfur. This is while environmental regulators, such as the US EPA, require an increased removal of sulfur from hydrocarbon fuels, thereby creating an abundance of sulfur, such that the refining industry is in need of a way to dispose of said abundance of sulfur.
Owner:CLEARVALUE TECH
Sample preparation device for ring shearing experiment of soil body under water-chemistry condition
InactiveCN103411811AGuaranteed stiffness requirementsOvercome the defect that it is easy to squeeze out from the gapPreparing sample for investigationChemical conditionEngineering
The invention relates to a sample preparation device for a ring shearing experiment of a soil body under the water-chemistry condition. The sample preparation device mainly comprises an upper bearing plate, a lower bearing plate, an upper inner ring, a lower inner ring, an upper outer ring, a lower outer ring, an upper rigid bearing column, a lower rigid bearing column, a fastening sleeve, an upper water-permeable cover plate, a lower water-permeable cover plate and a ring sample containing groove. By design of the upper outer ring, the separable lower outer ring, the inner rings and the rigid bearing columns which are separable, the sample preparation device meets the accurate control for the sample specification in the ring shearing experiment, not only is used for preparing a ring shearing sample of the soil body, but also can be used for preparing a ring-shearing sample for contact between soil and concrete. According to the sample preparation device, the outer rings, the inner rings and the water-permeable cover plates are all made of toughened glass material. The device is applicable to consideration about the influence of the corrosion condition of the water-chemistry solution on sample preparation equipment, and the phenomenon that the soil body sample gets expanded and loose after being soaked for a long time is effectively overcome. The sample preparation device is reasonable in structure, convenient in disassembly and high in reliability and can be widely applied to the ring shearing experiment for mechanical parameter testing of the soil body and the contact surface between the soil and the concrete in the rock-soil slope engineering.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nuclear power plant steel detecting device
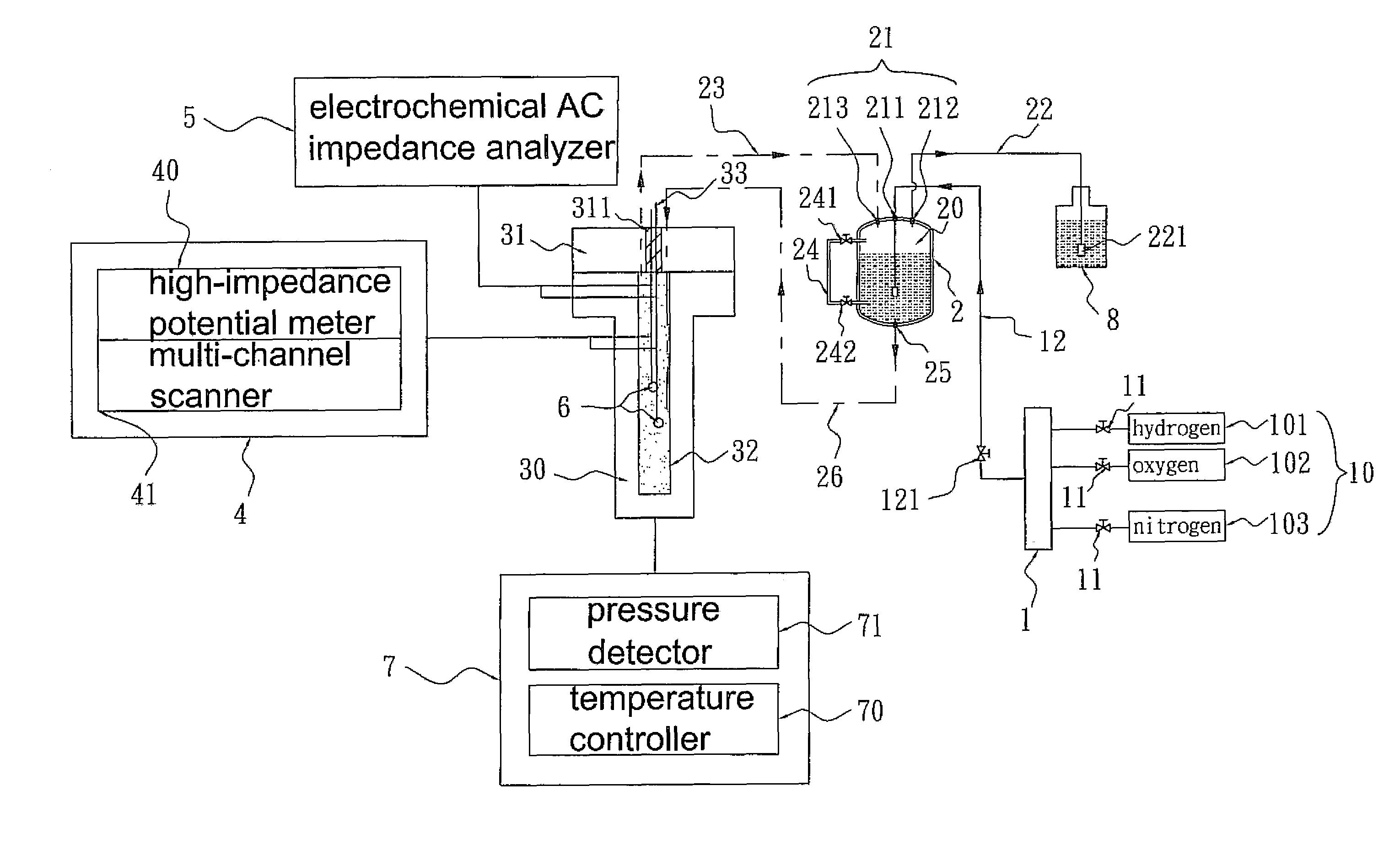
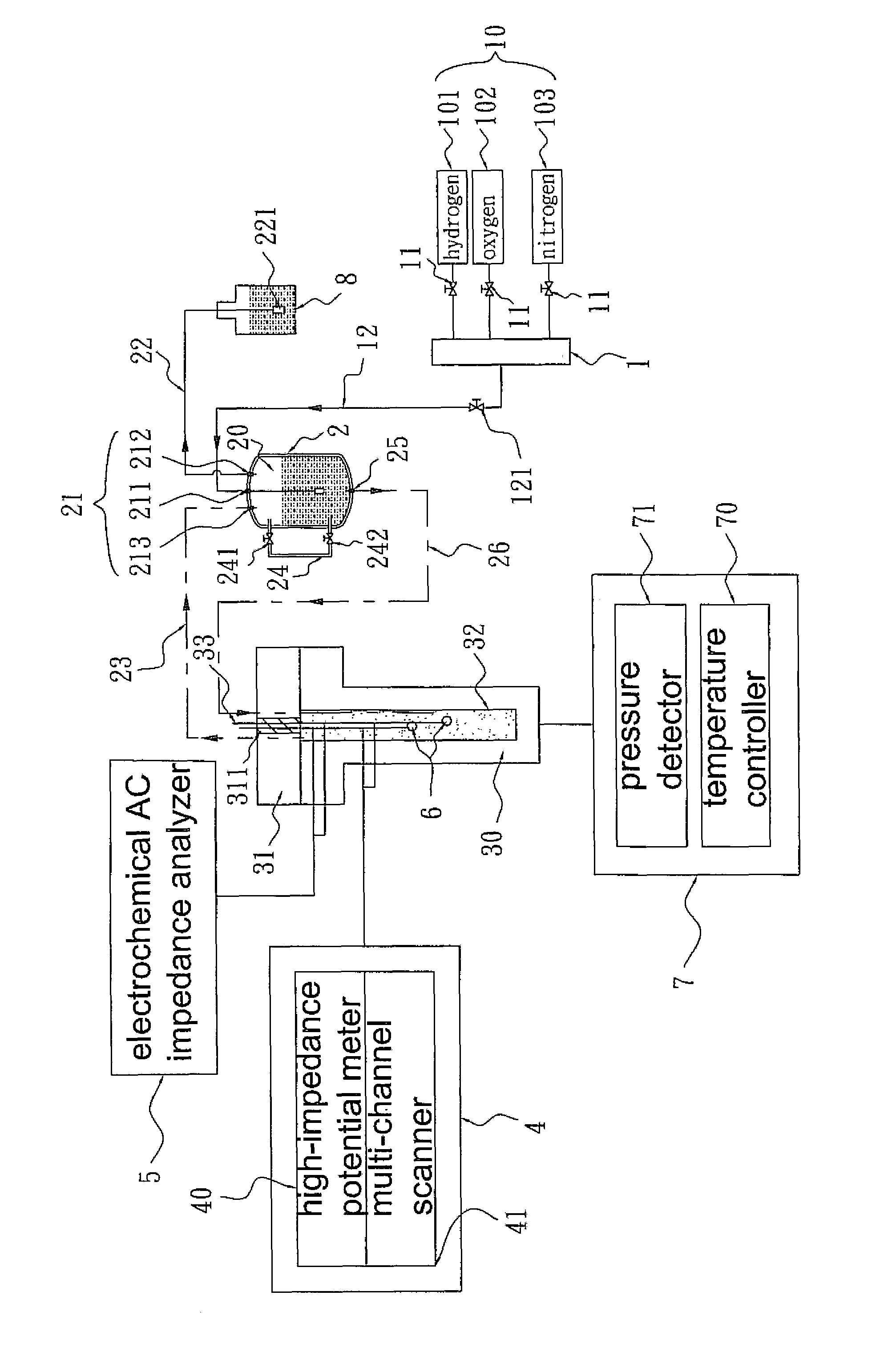
A device for detecting steel is provided. The steel is used in a nuclear plant. The device has a detecting circuit of electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) and alternative current (AC) impedance. An environment in a boiling water reactor (BWR) is simulated under hydrogen water chemistry (HWC). The environment is used for detecting intergranular stress corrosion cracking (IGSCC) of components coated with different precious metals. Thus, effect of coating different precious metals on steels can be evaluated for HWC.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com