Method for detecting 20 mutation sites of deaf genes
A detection method and mutation site technology, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbe determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of low carrying rate of pathogenic mutation alleles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0136] Example 1: Use of the detection method in normal people
[0137] 1. Reagents used in this method: OMEGAE.Z.N.A. TM BloodDNAKit, AgenaComplete GoldGenotypingReagentSet10x384, PrimerP1P2Mix (500uMeach), PrimeP3Mix, absolute ethanol.
[0138] 2. Specimen collection, transportation and preservation:
[0139] (1) Specimen collection: The specimen is whole blood. The blood is routinely taken 5ml of venous blood, treated with EDTA for anticoagulation.
[0140] (2) Storage: It can be tested immediately and stored at 4°C for one week.
[0141] (3) Transportation: 0℃ curling should be used for specimen transportation.
[0142] 3. Detection steps and result analysis:
[0143] (1) Extract genomic DNA from whole blood:
[0144] 1) Transfer ≤250μL of blood to the EP tube. If the blood is less than 250μL, use ElutionBuffer to make up 250μL.
[0145] 2) Add 25μLOB protease and 250μL BufferBL, vortex at high speed for 25s to mix.
[0146] 3) Water bath at 65°C for 10 minutes. During the water bath...
Embodiment 2
[0176] Example 2: Application of this method to detect abnormal GJB2SNP locus
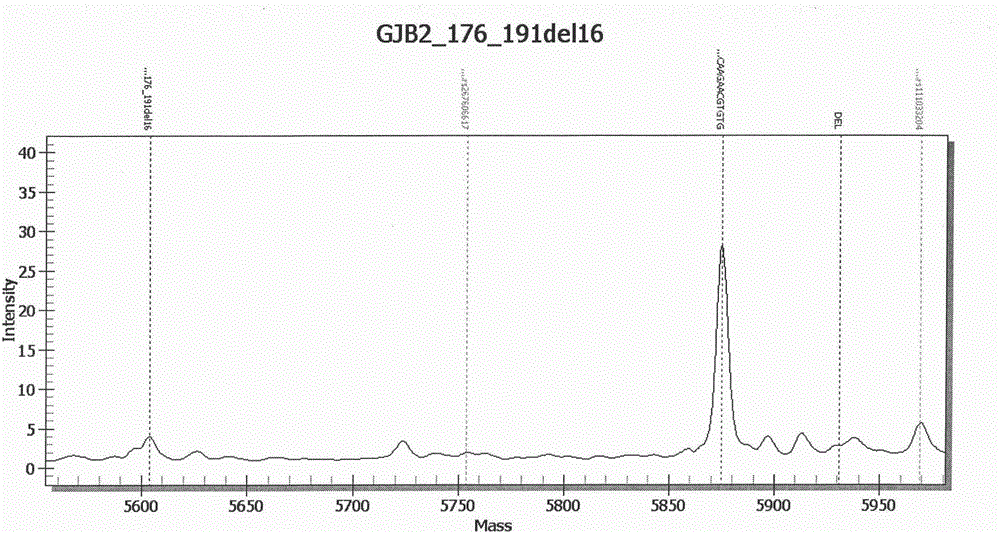
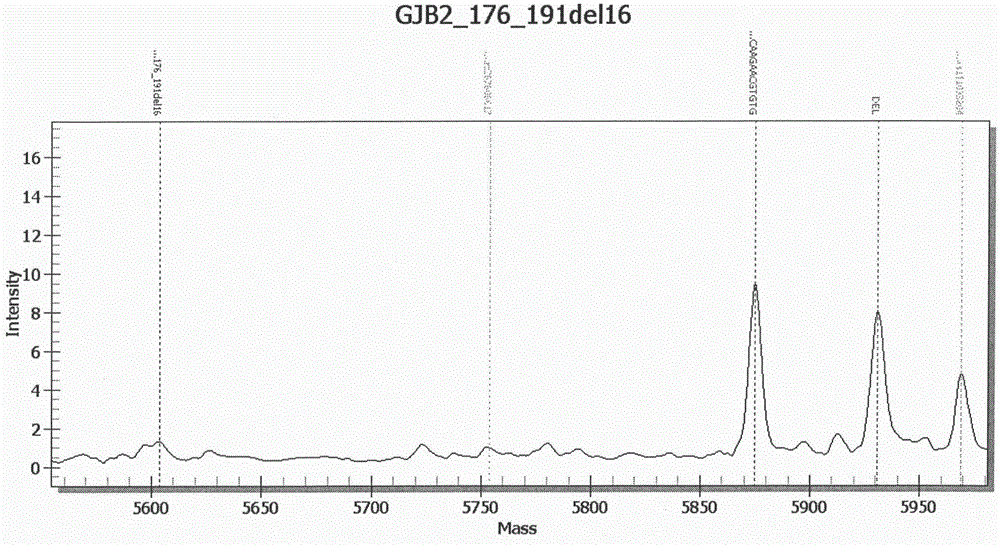
[0177] A blood sample was selected, and the patient was suspected of deafness. The kit of Example 1 was used to extract DNA according to the above-mentioned standard procedure, and then PCR was performed to amplify chromosome-specific SNP sites, and the SAP enzyme treatment was used to make the previous PCR step The dNTP in the dNTP loses its activity, and then undergoes a single-base extension reaction, which is finally detected and analyzed by a mass spectrometer. There is a loss of heterozygosity at this site of GJB2 (GJB2_176-191del16). This method can realize the rapid detection of GJB2SNP locus abnormalities. among them Figure 1B GJB2 (GJB2_176-191del16) abnormal mass spectrum analysis chart.
Embodiment 3
[0178] Example 3: Application of this method to detect abnormal GJB3SNP locus
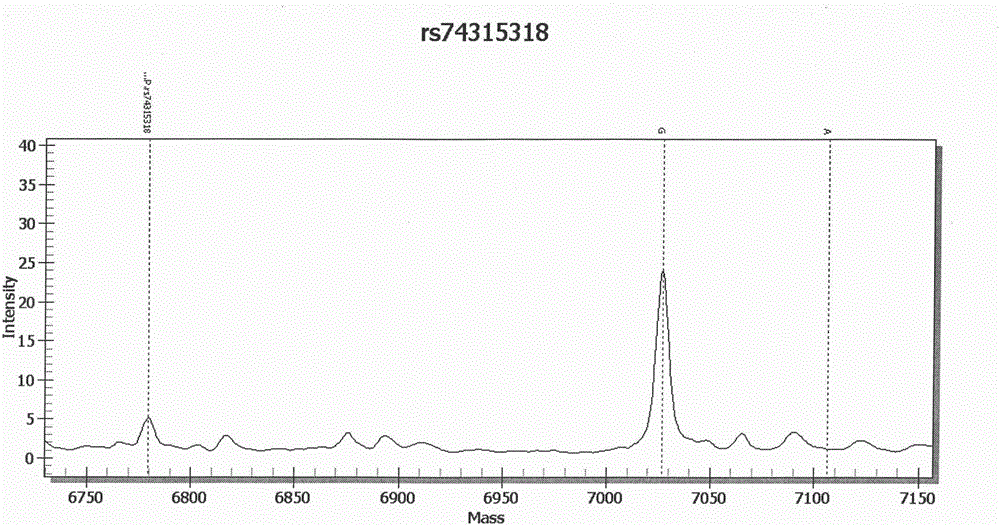
[0179] A blood sample was selected, and the patient was suspected of deafness. The kit of Example 1 was used to extract DNA according to the above-mentioned standard procedure, and then PCR was performed to amplify chromosome-specific SNP sites, and the SAP enzyme treatment was used to make the previous PCR step The dNTP in the dNTP loses its activity, and then undergoes a single-base extension reaction, which is finally detected and analyzed by a mass spectrometer. There is a heterozygous mutation in this position (rs74315318) of GJB3. This method can realize rapid detection of GJB3SNP site abnormalities. among them Figure 2A GJB3 (rs74315318) abnormal mass spectrometry analysis chart.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com