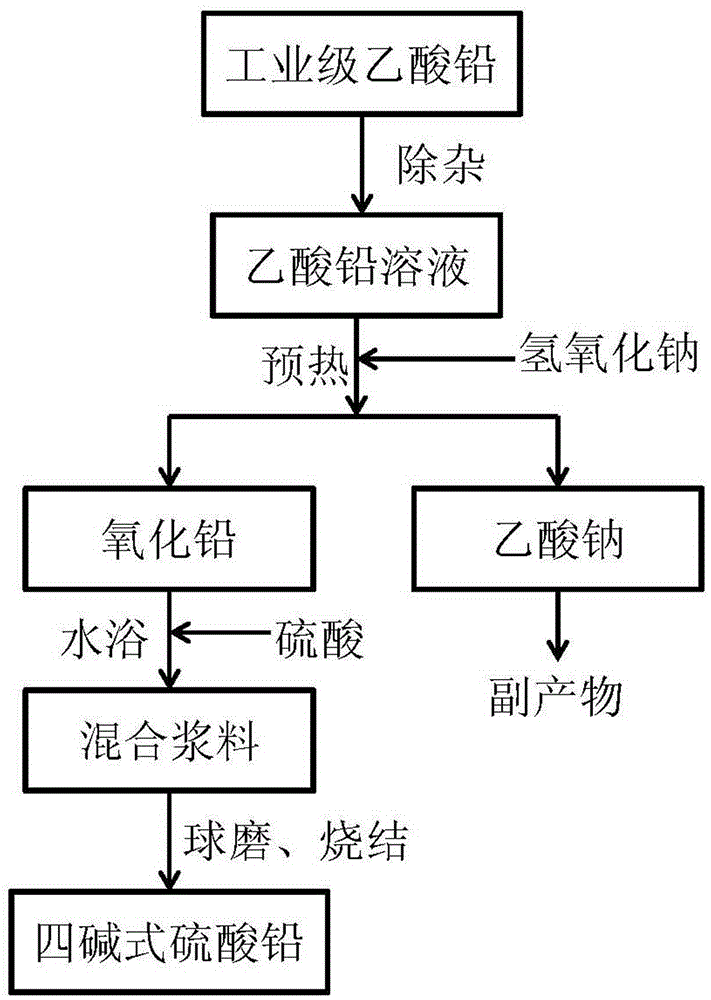
Method for preparing tetrabasic lead sulfate
A tetrabasic lead sulfate and sulfuric acid technology, applied in lead sulfate and other directions, can solve the problems of uneven particle size, low impurity content, and high equipment requirements, and achieve uniform and controllable particle size, high purity, and simple and controllable process. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
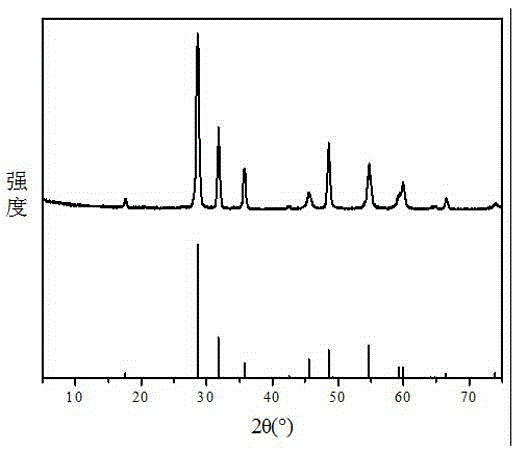
[0055] A lead acetate solution is obtained by leaching waste lead plaster with acetic acid, and the obtained lead acetate solution is adjusted to a pH of about 5 through ammonia water or sodium hydroxide, and filtered through a filter membrane to obtain a lead acetate solution from which impurities are removed. The concentration of the impurity-removing lead acetate solution was determined to be 0.7924mol / L, and the dosage of sodium hydroxide was determined according to the molar ratio of sodium hydroxide / lead acetate of 2.5:1. Heat 100 mL of impurity-removing lead acetate solution to 90° C., add 20.64 g of 40 wt % sodium hydroxide solution preheated to 90° C., stir and react for 30 minutes to obtain lead oxide, and its XRD pattern is as follows: image 3 shown. The obtained lead oxide and 20wt% sulfuric acid solution and deionized water are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:0.4484:4~10, stirred and reacted at 80°C for 1 hour, the obtained mixture is filtered, and the fil...
Embodiment 2
[0057] A lead acetate solution is obtained by leaching waste lead plaster with acetic acid, and the obtained lead acetate solution is adjusted to a pH of about 5 through ammonia water or sodium hydroxide, and filtered through a filter membrane to obtain a lead acetate solution from which impurities are removed. The concentration of the impurity-removing lead acetate solution was determined to be 0.8107mol / L, and the dosage of sodium hydroxide was determined according to the molar ratio of sodium hydroxide / lead acetate of 2.5:1. Heat 100 mL of impurity-removing lead acetate solution to 90° C., add 21.12 g of 40 wt % sodium hydroxide solution preheated to 90° C., and stir for 30 minutes to obtain lead oxide. The obtained lead oxide and 20wt% sulfuric acid solution and deionized water are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:0.4484:4~10, stirred and reacted at 80°C for 1 hour, the obtained mixture is filtered, and the filter residue is transferred to a tube furnace at 650°C. Si...
Embodiment 3
[0059] A lead acetate solution is obtained by leaching waste lead plaster with acetic acid, and the obtained lead acetate solution is adjusted to a pH of about 5 through ammonia water or sodium hydroxide, and filtered through a filter membrane to obtain a lead acetate solution from which impurities are removed. The concentration of the impurity-removing lead acetate solution was determined to be 0.8107mol / L, and the dosage of sodium hydroxide was determined according to the molar ratio of sodium hydroxide / lead acetate of 2.5:1. Heat 100 mL of impurity-removing lead acetate solution to 90° C., add 21.12 g of 40 wt % sodium hydroxide solution preheated to 90° C., and stir for 30 minutes to obtain lead oxide. The obtained lead oxide and 20wt% sulfuric acid solution and deionized water are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:0.4484:4~10, stirred and reacted at 80°C for 1 hour, the obtained mixture is filtered, and the filter residue is transferred to a tube furnace at 450 Sinte...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com