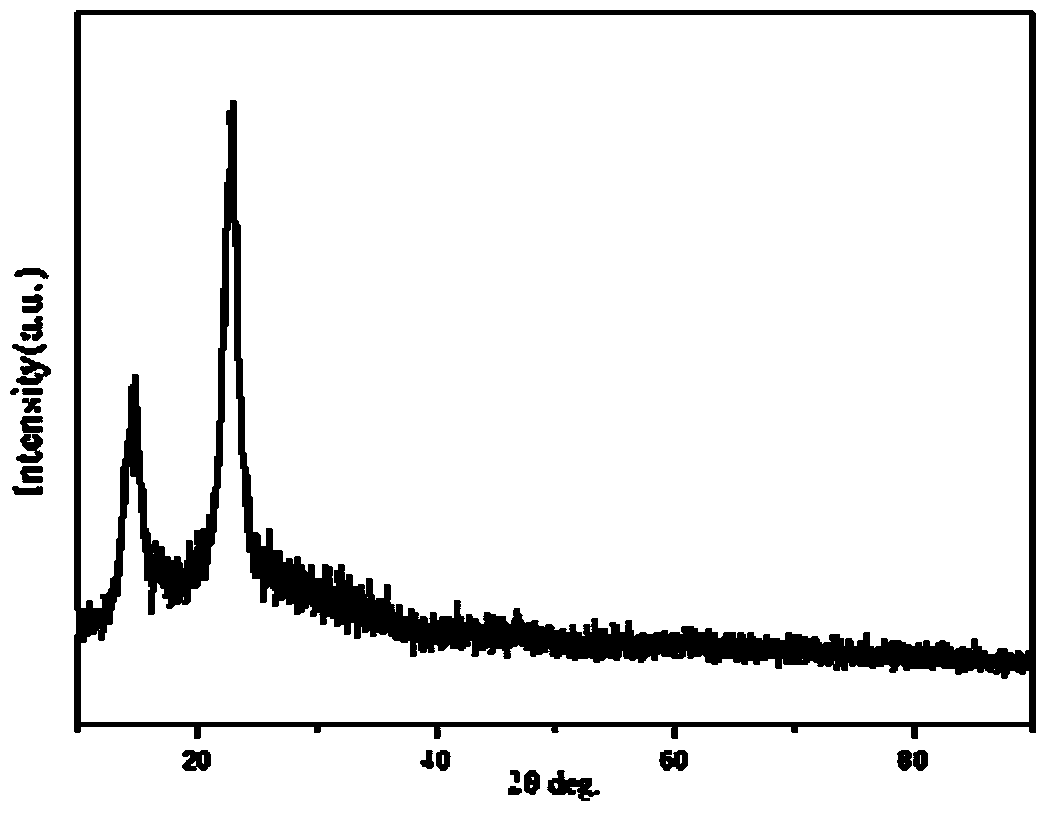
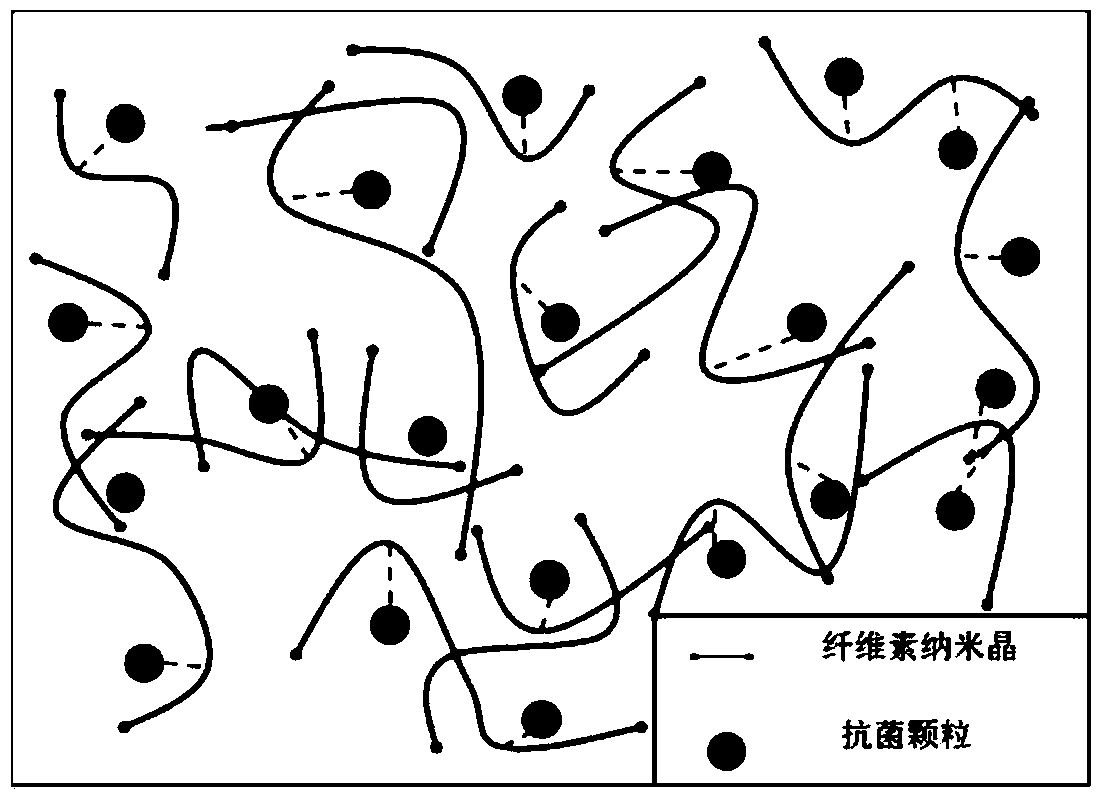
Preparation of functionalized bacterial cellulose compound sol and composite material modified by light conversion antibacterial particles
A technology of bacterial cellulose and photoconversion, which is used in the preparation of antibacterial compound sols and antibacterial composite materials, the field of dispersion activation and the preparation of bacterial cellulose, can solve the problems of uneven fiber size, consumption of large acid, disappearance of antibacterial properties, etc. , to achieve the effect of green and environmental protection in the preparation process, simple and easy process, and realization of process control.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0080] Step 1. Weigh 100 mg of titanium dioxide composite antibacterial agent, grind it into flour, put the ground composite powder in a small beaker with 10 mL of concentrated ammonia water, and shake it in the same direction; place the beaker in a powerful ultrasonic machine During the process, five intermittent ultrasounds were performed at room temperature, about 20 minutes each time, the temperature was controlled at room temperature, and the fully reacted particles were refrigerated and centrifuged, rinsed with deionized water and sealed for later use.
[0081] Step 2. Rinse the front and back surfaces of the bacterial cellulose membrane with clean water, and take it out after bathing in water at 80°C for 1 hour; then bathe in a NaOH solution with a concentration of 0.1mol / L above 80°C for 30 minutes, then filter out the lye, and use a large amount of Rinse the cellulose membrane with deionized water until neutral.
[0082] Step 3. Put the cellulose treated in step 2 int...
example 2
[0086] Step 1. Weigh 50 mg of titanium dioxide composite antibacterial agent, grind it into flour, put the ground composite powder in a small beaker with 10 mL of deionized water, and shake it in the same direction; place the small beaker at high temperature Under high-pressure water vapor atmosphere, after activation for 30 minutes, cool to room temperature, place the beaker in a powerful ultrasonic machine, and ultrasonicate intermittently at room temperature for 5 times, about 20 minutes each time, and store for use.
[0087] Step 2. Rinse the front and back surfaces of the bacterial cellulose membrane with clean water, and take it out after bathing in water at 80°C for 2 hours; then bathe in a NaOH solution with a concentration of 0.5 mol / L above 80°C for 30 minutes, then filter out the lye, and use a large amount of Rinse the cellulose membrane with deionized water until neutral.
[0088] Step 3. Put the cellulose treated in step 2 into a beaker after preliminary crushing...
example 3
[0092] Step 1. Weigh 100 mg of titanium dioxide composite antibacterial agent, grind it into flour, put the ground composite powder in a small beaker with 10 mL of deionized water, and shake it in the same direction; place the beaker in a strong ultrasonic In the machine, the room temperature is intermittently ultrasonicated 5 times, about 20 minutes each time, and stored for later use.
[0093] Step 2. Rinse the front and back surfaces of the bacterial cellulose membrane with clean water, take it out after bathing in water at 80°C for 1 hour; then bathe in water at a concentration of 1 mol / L above 80°C for 30 minutes in NaOH solution with a concentration of 1 mol / L, then filter out the lye, and use a large amount of Rinse the cellulose membrane with deionized water until neutral.
[0094] Step 3. Put the cellulose treated in step 2 into a beaker after preliminary crushing, add an appropriate amount of deionized water, break the bacterial cellulose into a paste on a shear crus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com