Drainage salt-washing method for green belt of heavy saline-alkali land development region in coastal area
A technology for saline-alkali land and development zones, which is applied in the fields of soil preparation methods, climate change adaptation, agricultural machinery and tools, etc. It can solve the problems of high sand content in heavy saline-alkali land, high cost of washing salt with fresh water, and shortage of fresh water resources. Enhance soil infiltration capacity and avoid the effect of too slow infiltration speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] A method for draining and washing salt in green belts of heavily saline-alkali land development zones in coastal areas, comprising the following steps: (1) spreading 50g to 80g of loose soil concentrate on the soil surface of each mu of heavily saline-alkali land, and laying 200 kg to 300 Kg of rice stalks can also be replaced by corn stalks or wheat stalks. The soil in heavy saline-alkaline land is turned over to make the straw evenly mixed in the soil. The depth of 50cm, the root system of trees is mostly around 60cm, in order to ensure that the water can quickly reach the root system of the vegetation and facilitate the absorption of the root system, so the depth of the soil is set to 50cm ~ 80cm;
[0019] (2) Bury alkali discharge pipes on the inclined embankment at the bottom of the heavy saline-alkali land, and set up a drainage ditch and a reservoir on the side of the heavy saline-alkali land. The reservoir is equipped with a water pump and a water delivery pump, ...
Embodiment 2
[0023] This example is the verification of the infiltration rate of fresh water and brackish water in unimproved heavily saline-alkali soil.
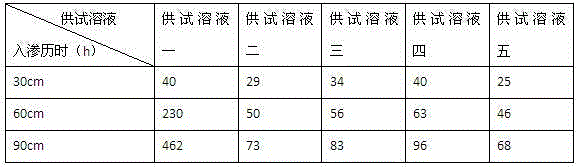
[0024] Preparation of the test soil column 1: The test soil was collected from the Xintan Salt Field Development Zone in Yancheng City. After air-drying, crushing and sieving, each layer is evenly mixed, it is layered into a PVC pipe with a height of 120cm and a diameter of 50cm. For the receiving device, there are salinity sensors buried at 30cm, 60cm, and 90cm in the PVC pipe. According to the data feedback of the salinity sensor, the time when the wetting peak reaches the corresponding embedding depth of the salinity sensor is determined.
[0025] Test solution one: fresh water with a salinity of 0.42g / L.
[0026] Test solution two: add sodium carbonate on the basis of test solution one, the degree of salinity is 2.92g / L, and the concentration of sodium carbonate is 2.5g / L.
[0027] Test solution three: add sodium carbonate on the ...
Embodiment 3
[0034] This example is the verification of the infiltration rate of fresh water and brackish water in heavy saline-alkali soil improved by straw.
[0035] The difference between this example and Example 2 lies in the preparation of the test soil column 2.
[0036] Preparation of the second soil column for the test: different from the first soil column for the test, 88.3g of 88.3g rice straw (equivalent to 300 kg of rice straw per mu, with a depth of 80 cm).
[0037] Table 2: Moisture migration characteristics of different test solutions in test soil column 2
[0038]
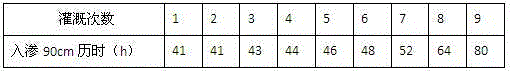
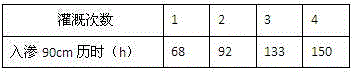
[0039] Experiments show that when the wetting peak reaches the 90cm place of the test soil column 2, use brackish water or brackish water made by adding sodium carbonate to fresh water, as shown in test solutions 2, 3, 4, and 5, the irrigation needs only 41 to 58 hours, while freshwater irrigation takes 277 hours. Compared with the related experiments in Example 2, the soil quality of the test soil column ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com