A kind of fermented milk with high viable bacteria count in shelf life and preparation method thereof
A high viable bacteria count, fermented milk technology, applied to dairy products, streptococcus/lactococcus, bacteria used in food preparation, etc., can solve problems such as difficult consumer acceptance, and achieve the effect of increasing the number of viable bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 A fermented milk with a high number of viable bacteria within the shelf life and its preparation method
[0033] A fermented milk with a high viable count during the shelf life, comprising the following ingredients:
[0034] 500g skimmed powder, 70g white sugar, 0.5×10 Lactobacillus bulgaricus 6 cfu / g, Streptococcus thermophilus 0.5×10 6 cfu / g, Lactobacillus plantarum N3117 10 6 cfu / g, distilled water 200g, starch 5g.
[0035] The above-mentioned method for fermented milk with a high number of viable bacteria within the shelf life is carried out in the following order:
[0036] (1) Preparation of reconstituted milk
[0037] a. Take raw milk and distilled water and stir evenly to prepare reconstituted milk a; wherein, the mass volume ratio of raw milk and distilled water is 1:9.
[0038] b. Stir the reconstituted milk a, white granulated sugar, sweetener (the weight of the sweetener in this example is 0) and stabilizer evenly and dissolve them fully to obt...
Embodiment 2-6
[0048] Example 2-6 Fermented milk with high viable bacteria count and preparation method thereof during shelf life
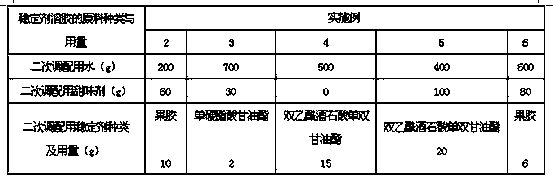
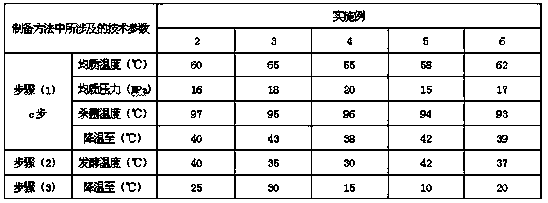
[0049] Examples 2-6 are a kind of fermented milk with a high number of viable bacteria within the shelf life and its preparation method, which are similar to Example 1, the difference is only in the types of raw materials, the amount used and the technology involved in the preparation method The parameters are different, as shown in the following table:
[0050]
[0051]
[0052] The raw material type and dosage of stabilizer sol are shown in the following table:
[0053]
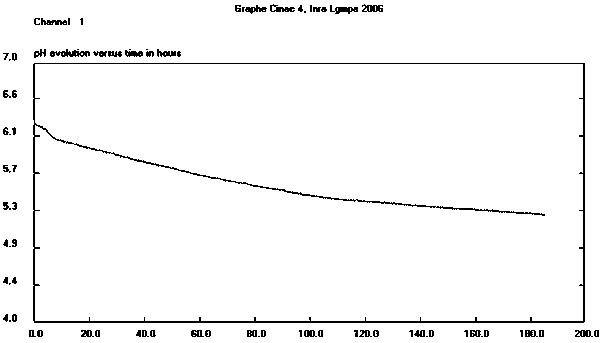
[0054] The fermented milk prepared in Examples 2-6 was placed at 30° C., and the shelf life was 21 days to measure the number of viable bacteria, acidity, and pH value. The experimental results are as follows:
[0055]
[0056]
[0057] It can be seen from the above table that the number of live bacteria in fermented milk added with Lactobacillus plantarum N3117 remained at 10 d...
Embodiment 7
[0058] Example 7 Autolysis of Lactobacillus plantarum N3117 strain
[0059] Bacterial autolysis refers to the process in which bacterial cells release autolytic enzymes that can hydrolyze the peptidoglycan grid structure of the cell wall to dissolve the bacterial cell murein under certain specific conditions, so that the intracellular substances are released to the surrounding environment. The autolysis characteristics of lactic acid bacteria have a great influence on the quality of fermented dairy products. For example, the autolysis of lactic acid bacteria in cheese can not only shorten the ripening cycle and reduce production costs, but also the various substances released after the bacteria autolysis can determine the flavor and quality of cheese. sensory properties.
[0060] After activating Lactobacillus plantarum N3117 for 2 generations, inoculate 1% of the inoculum into 200ml MRS liquid medium, culture at 37°C for 24h, centrifuge the above-mentioned cultivated strain a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com