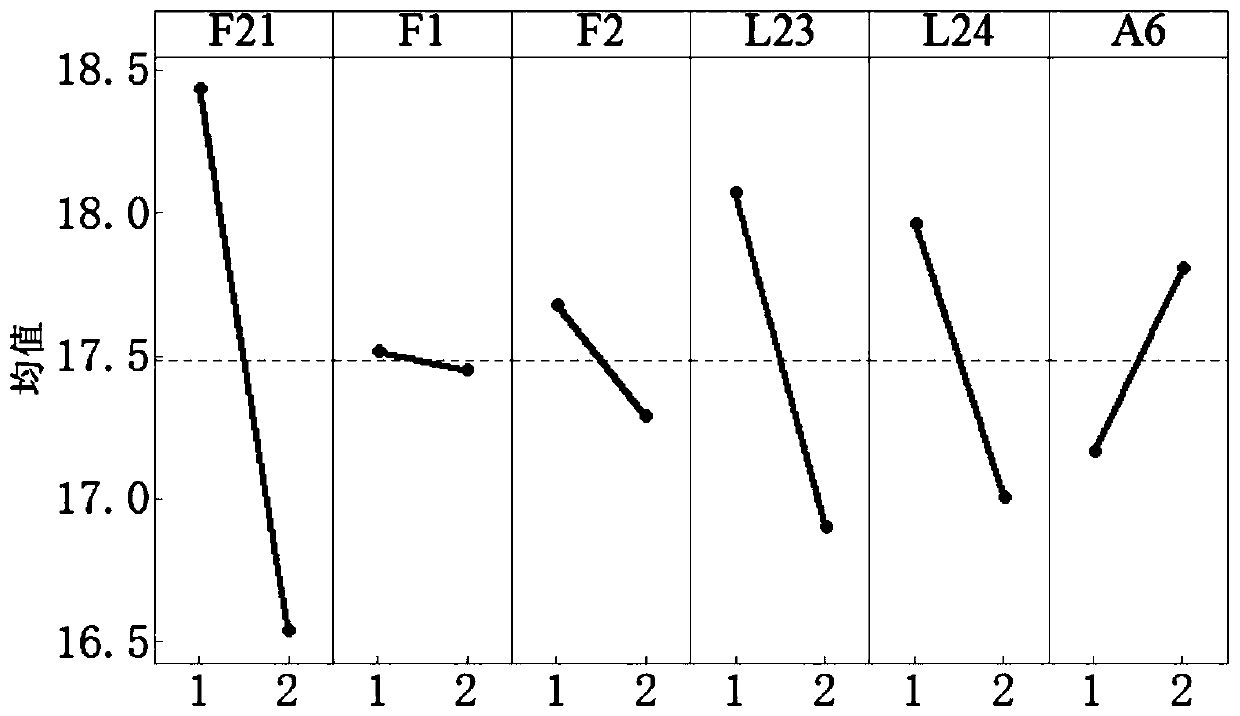
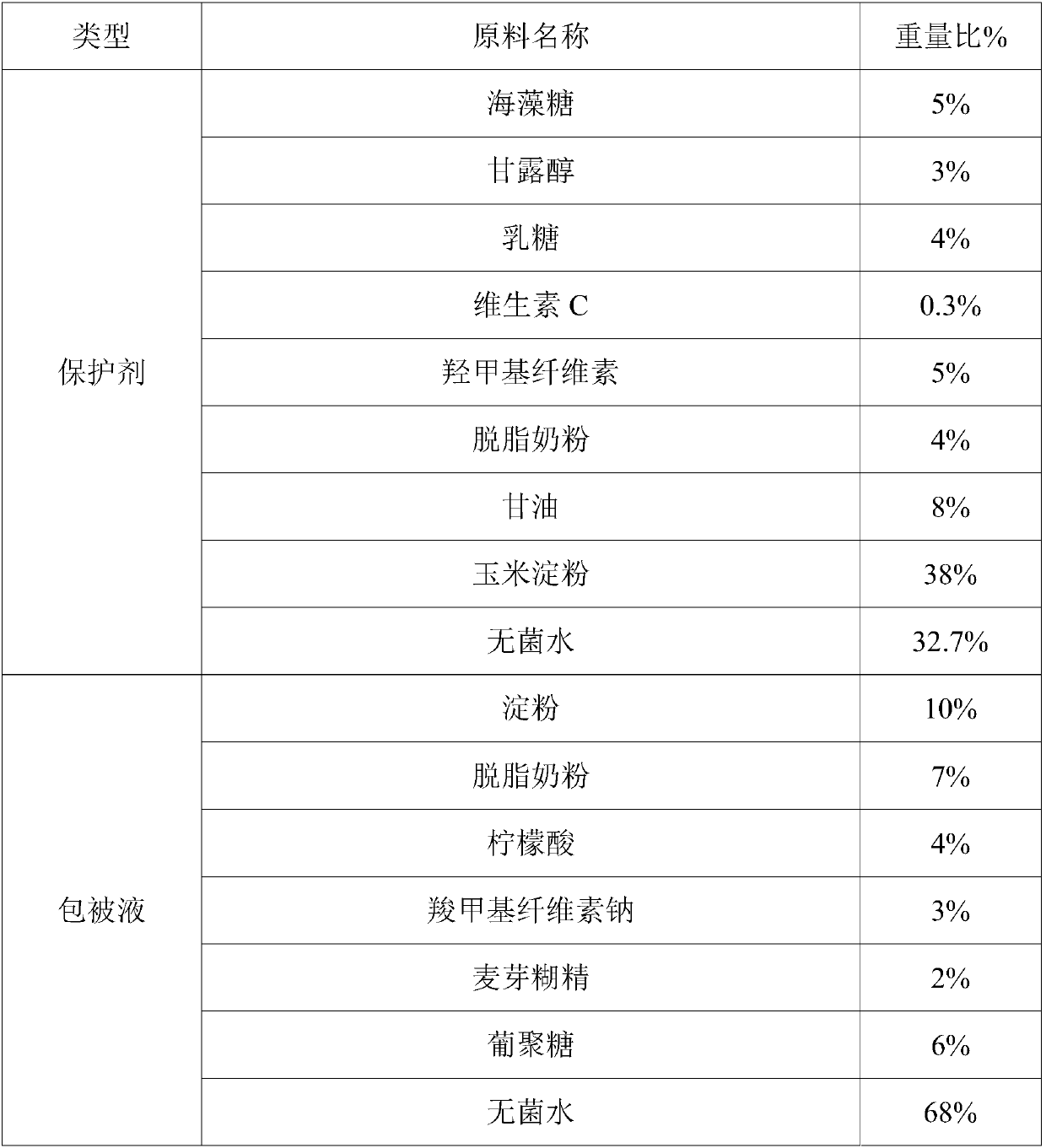
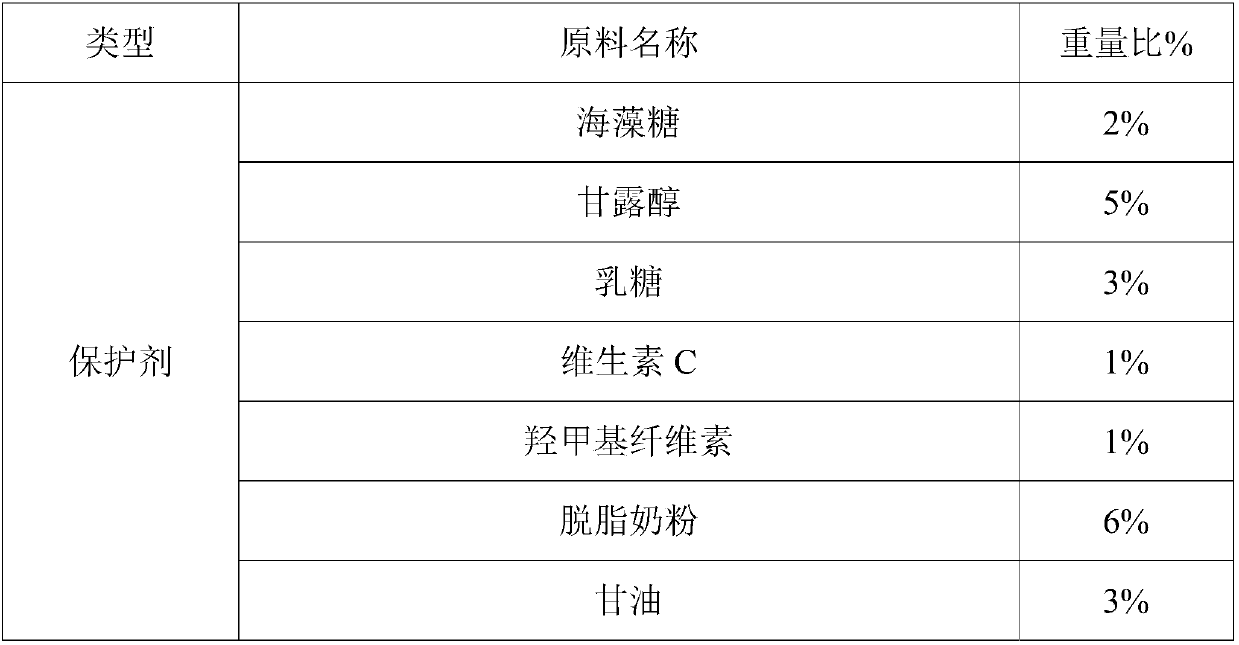
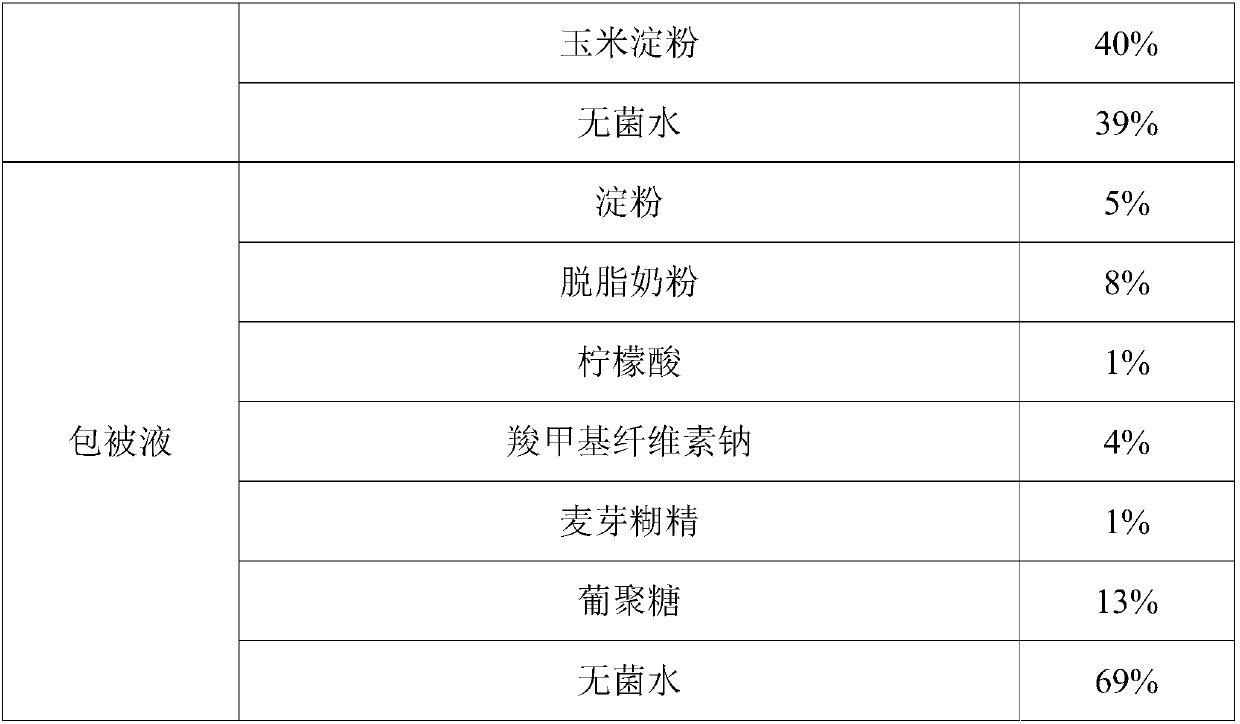
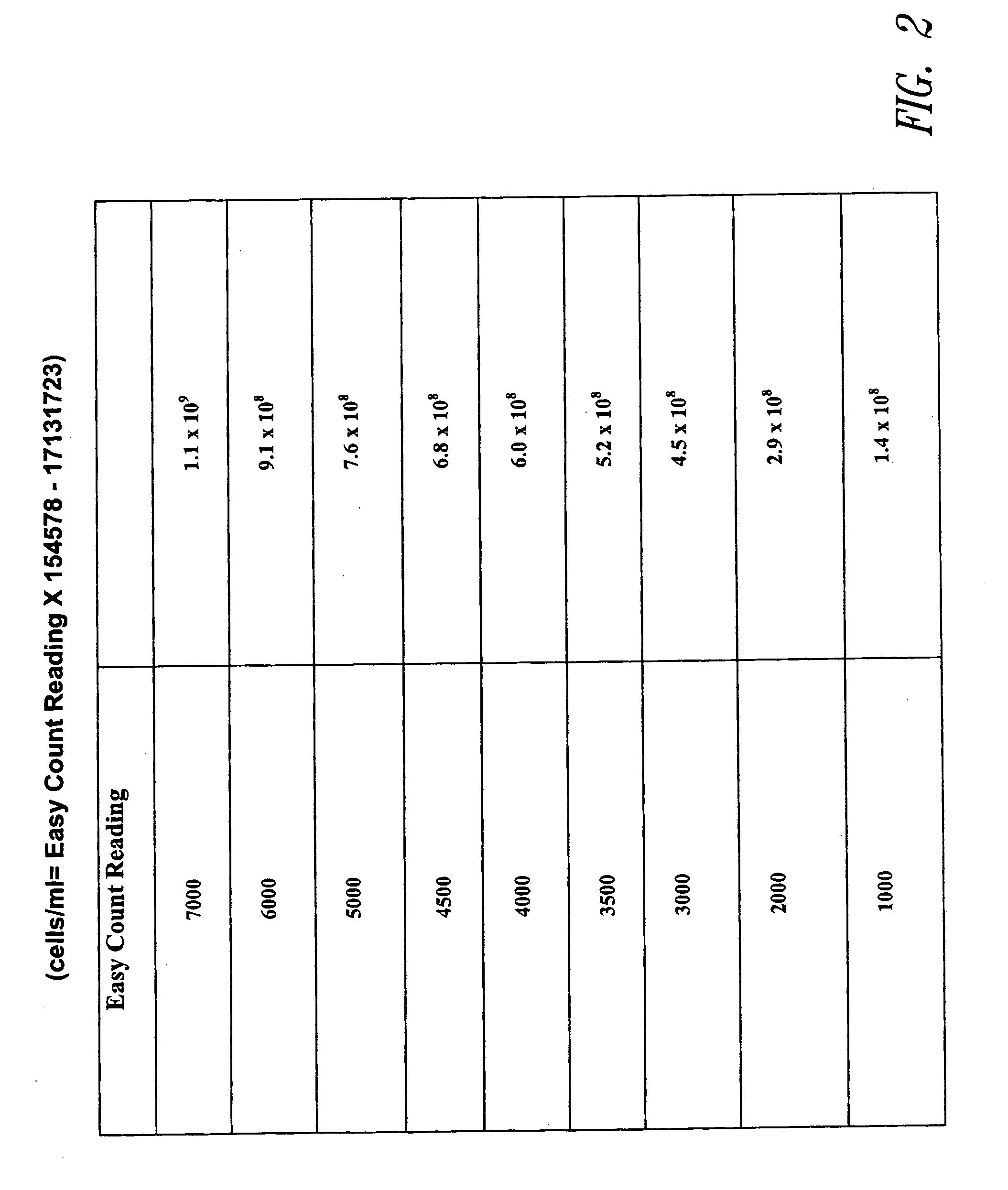
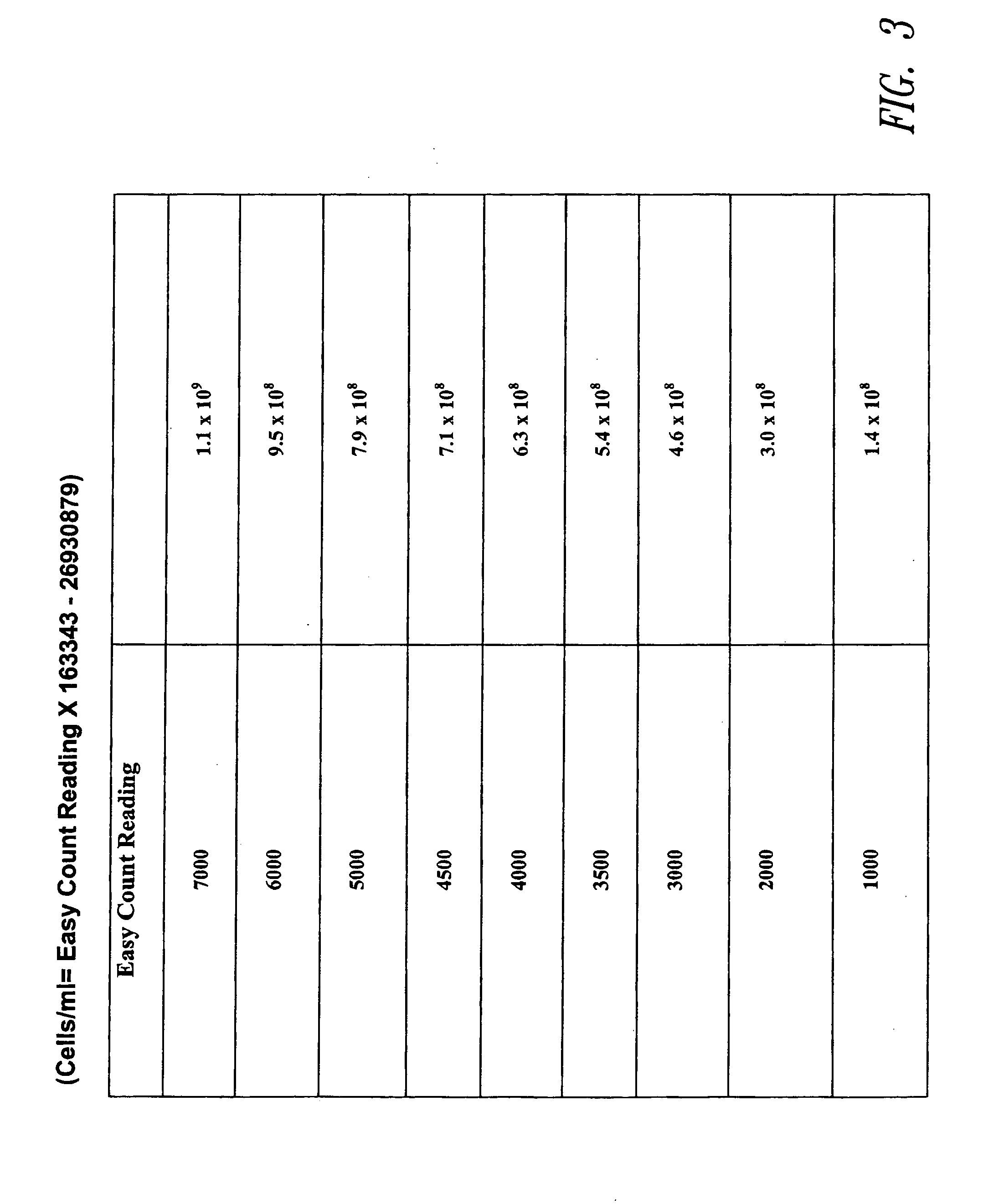
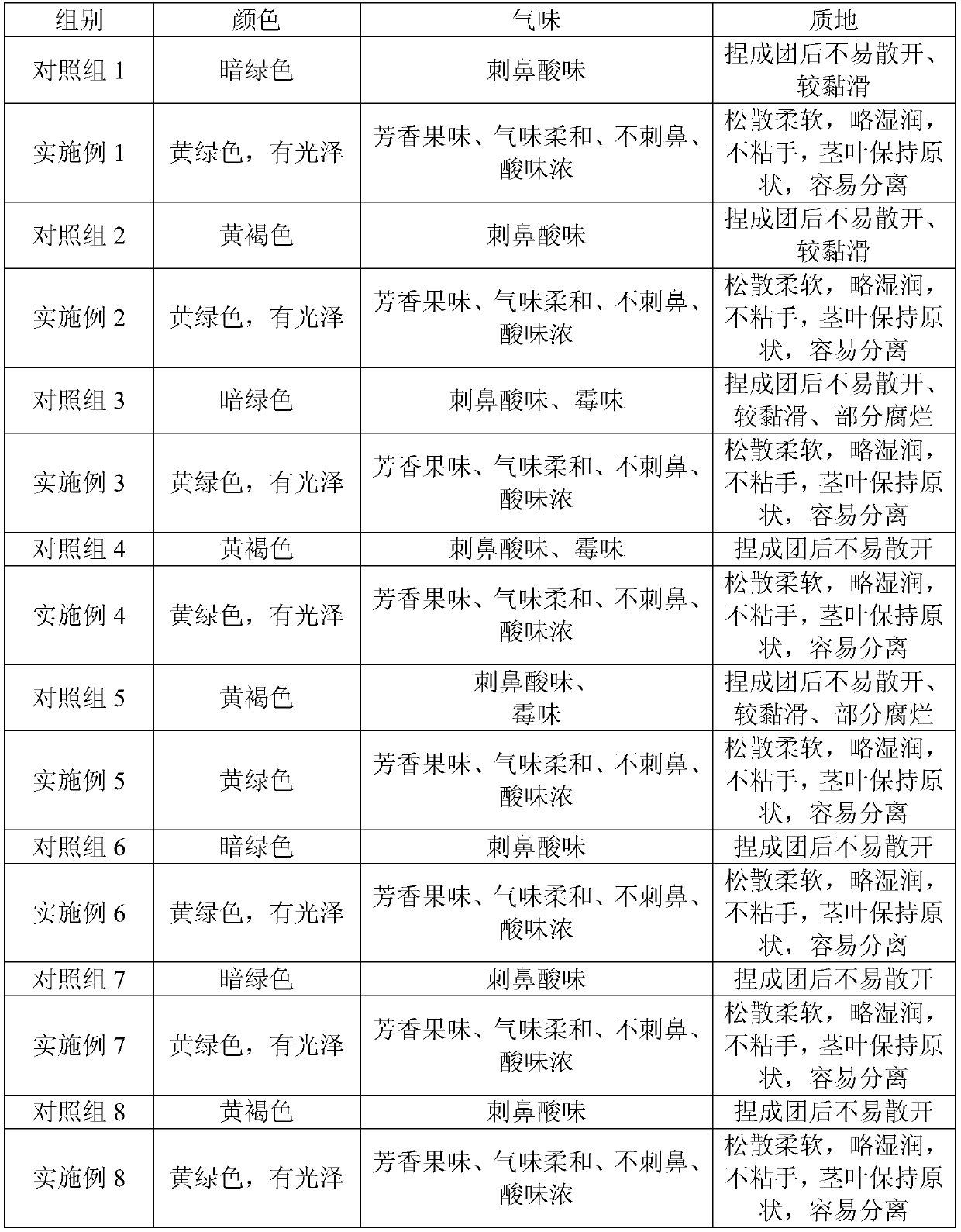
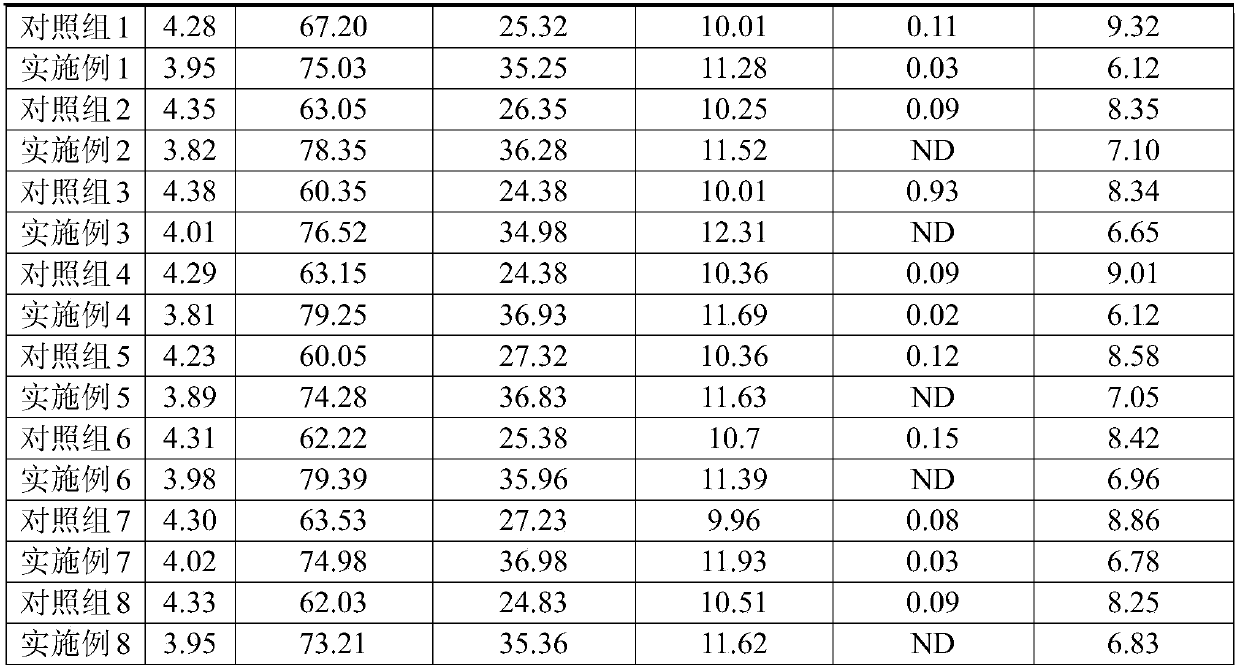
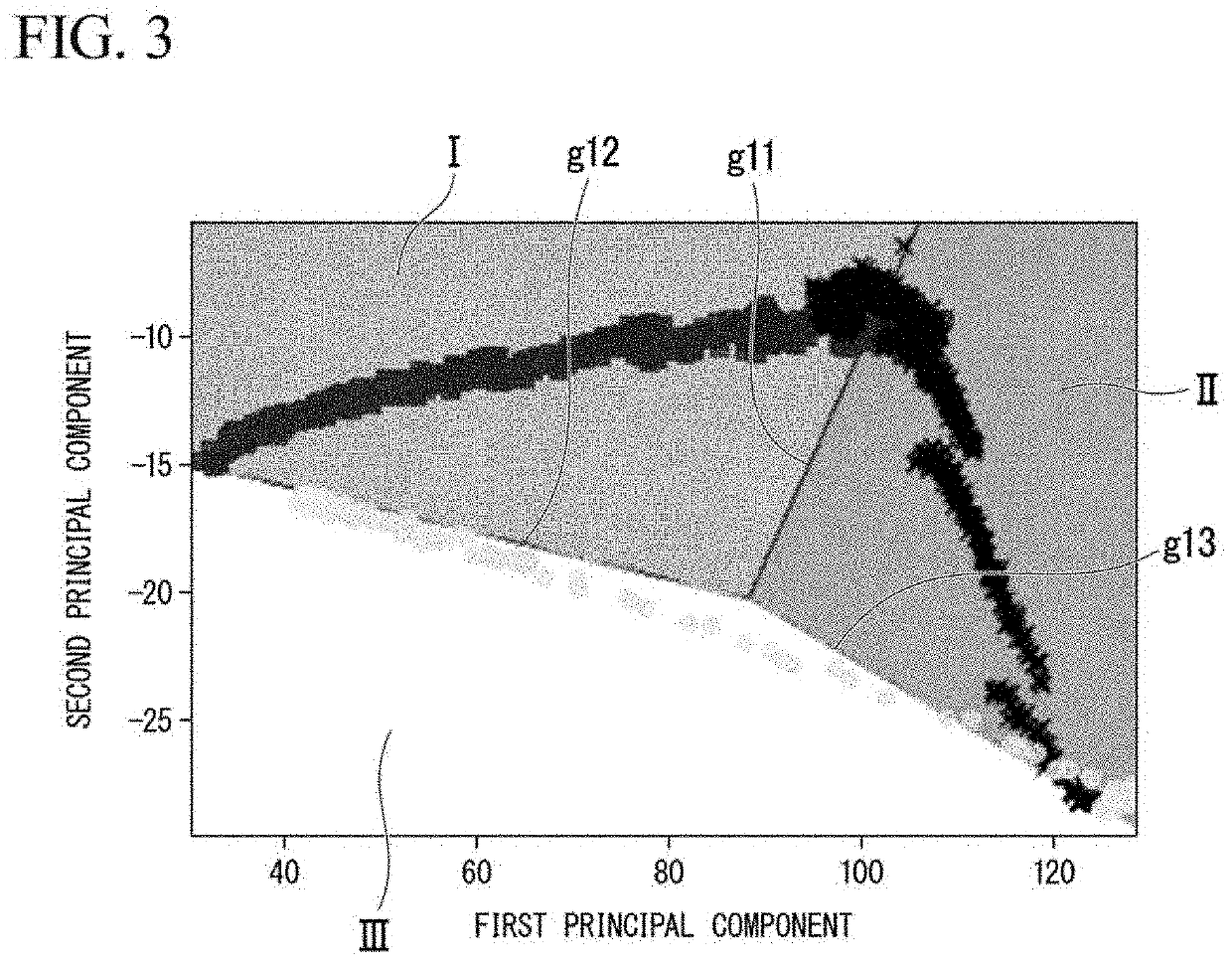
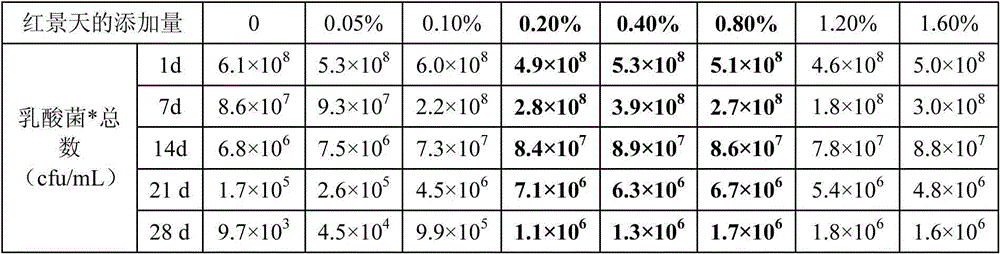
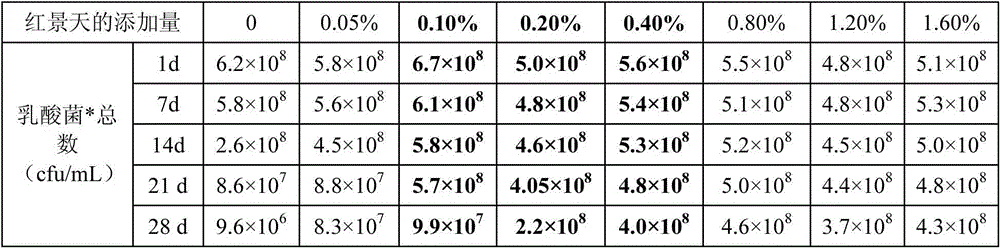
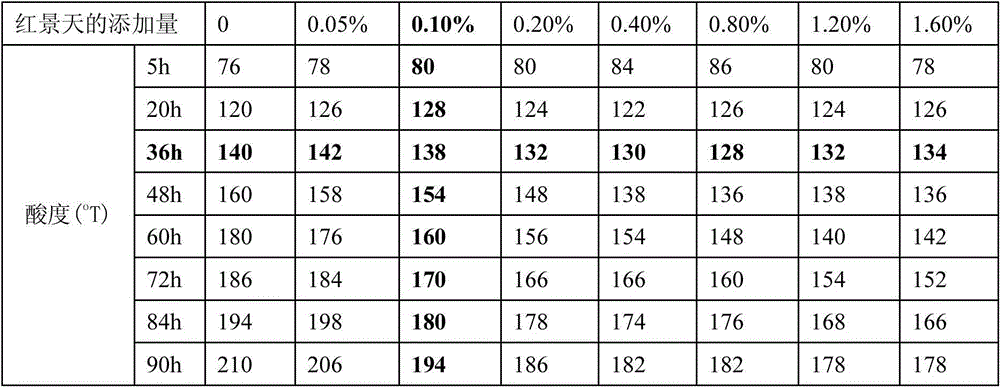
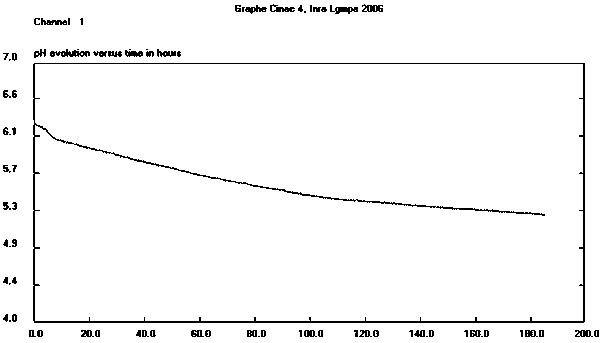
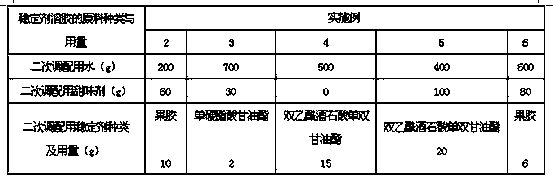
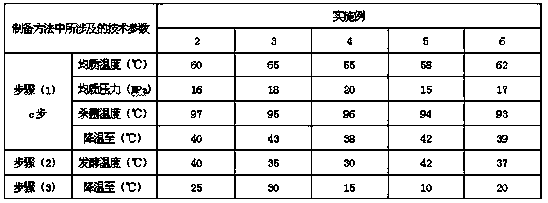
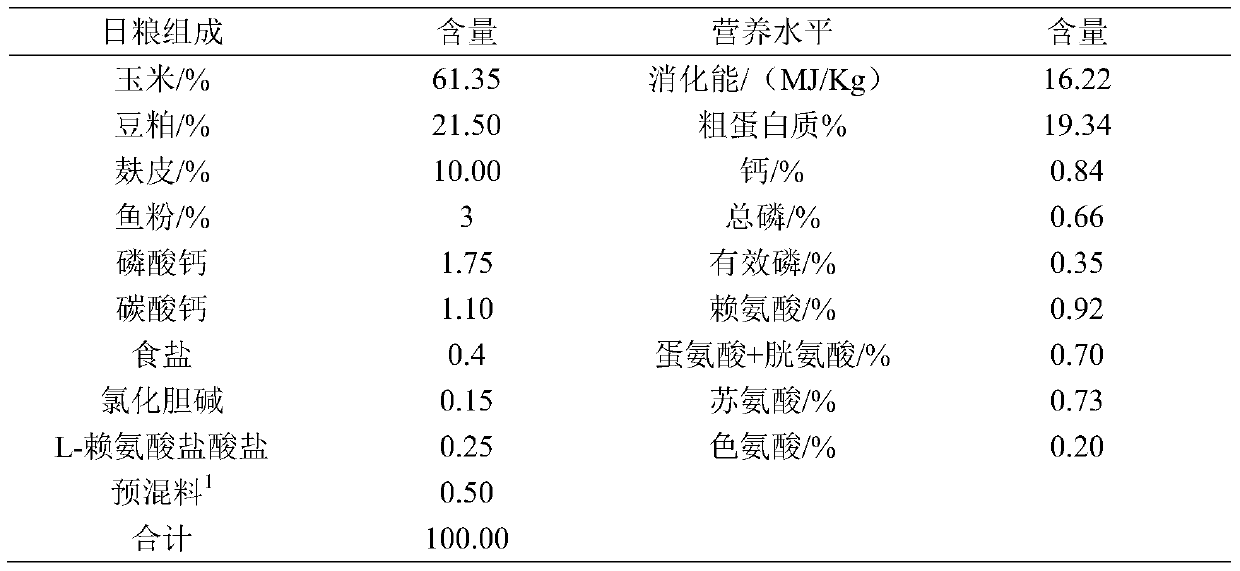
Patents
Literature
49 results about "Viable Cell Count" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
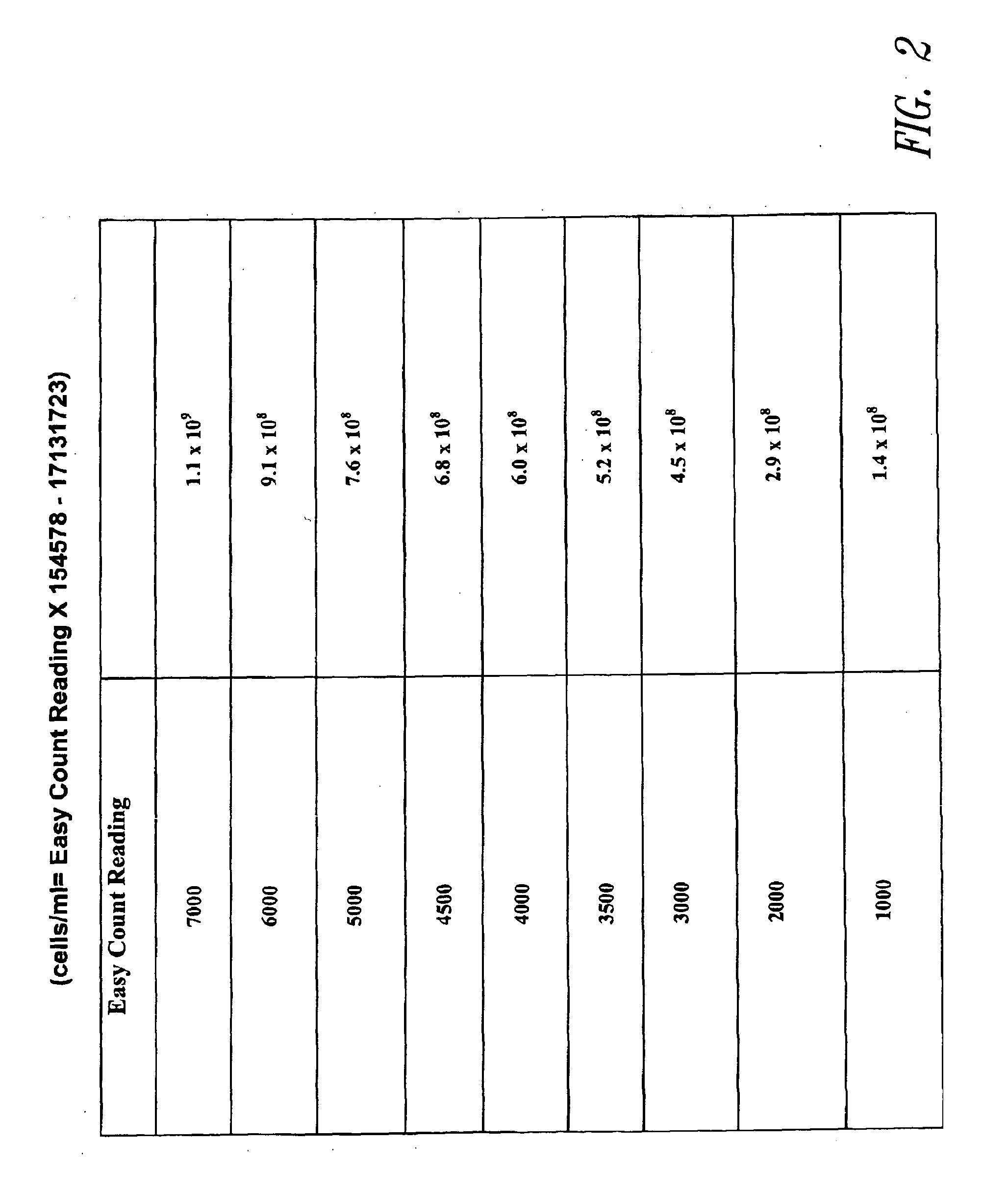
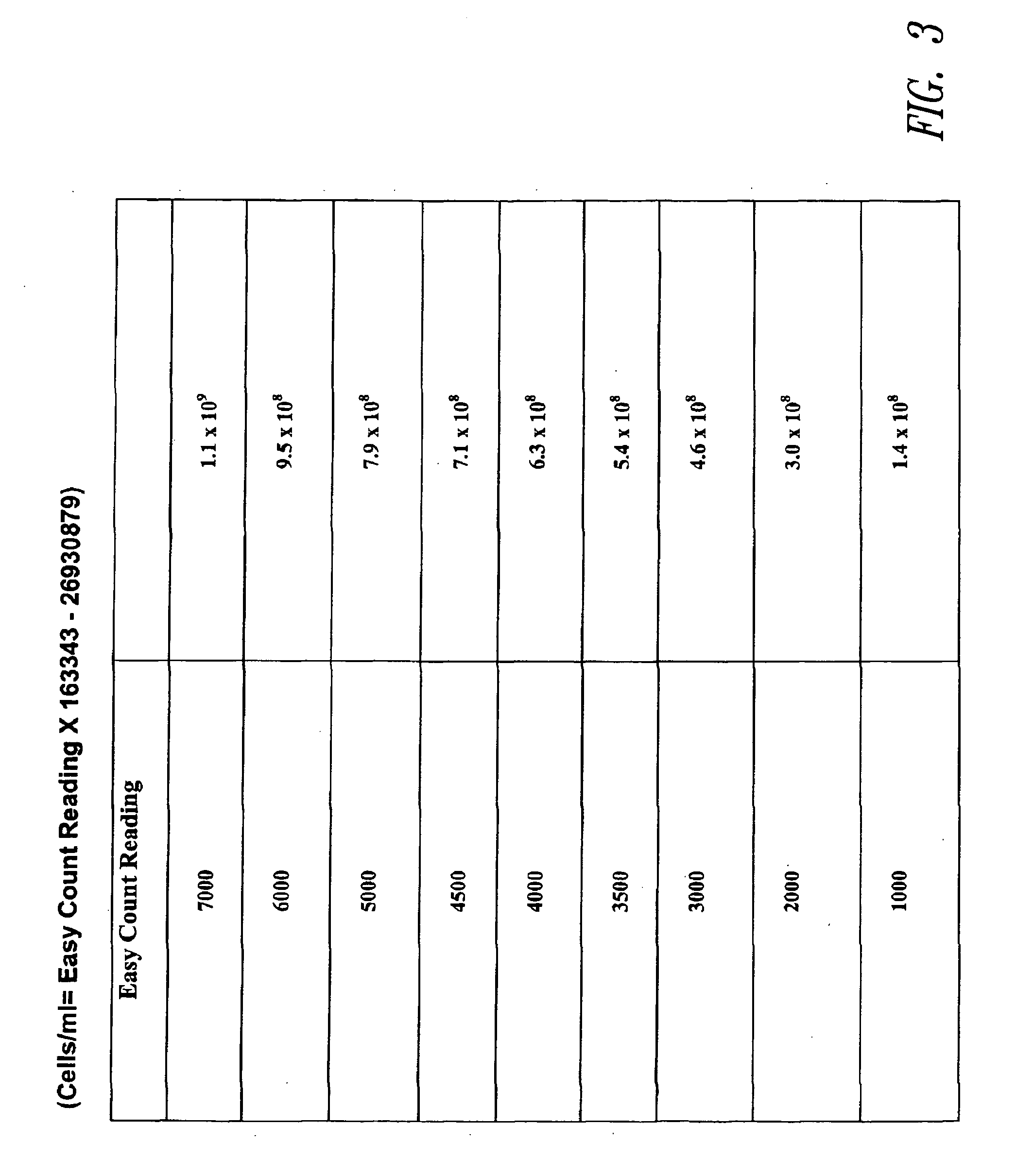
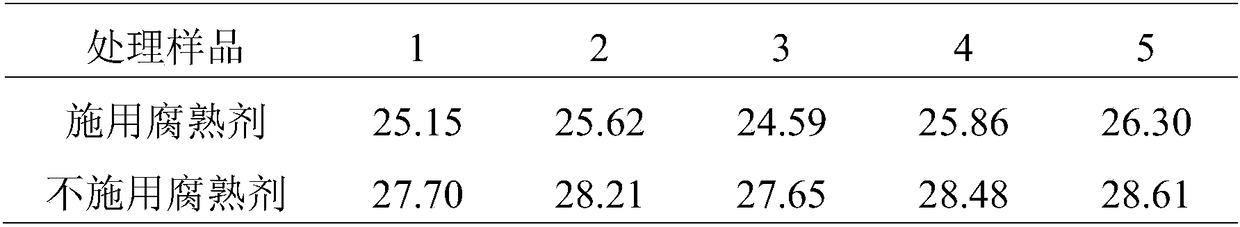
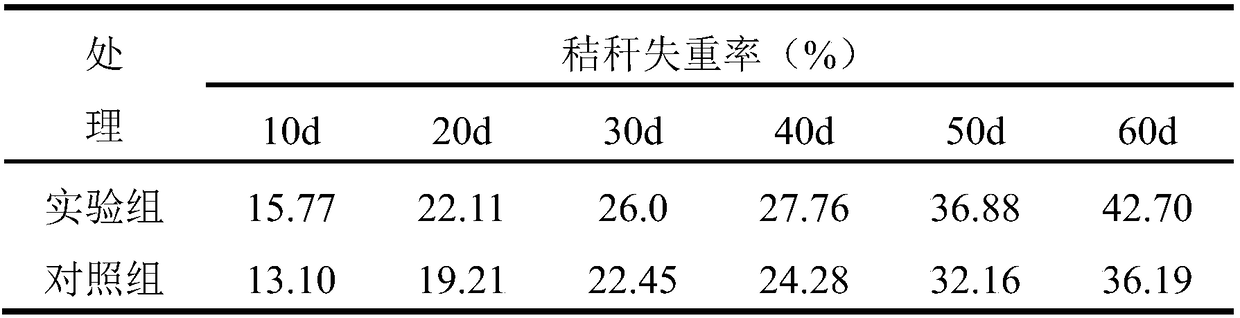
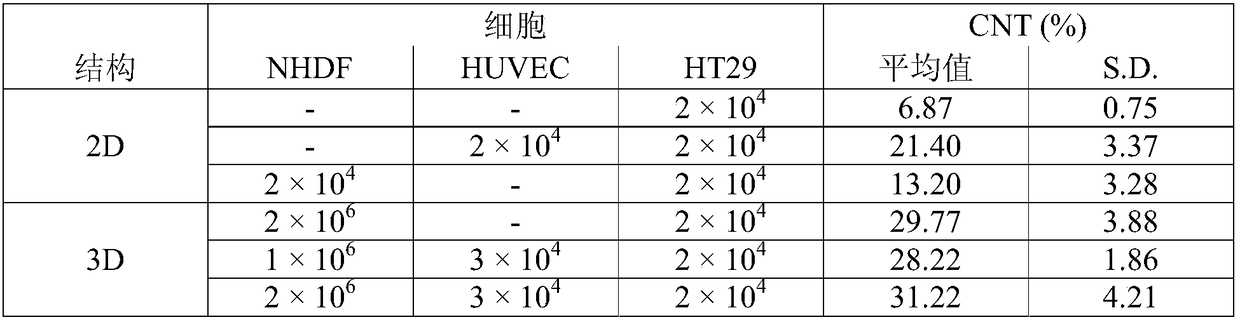
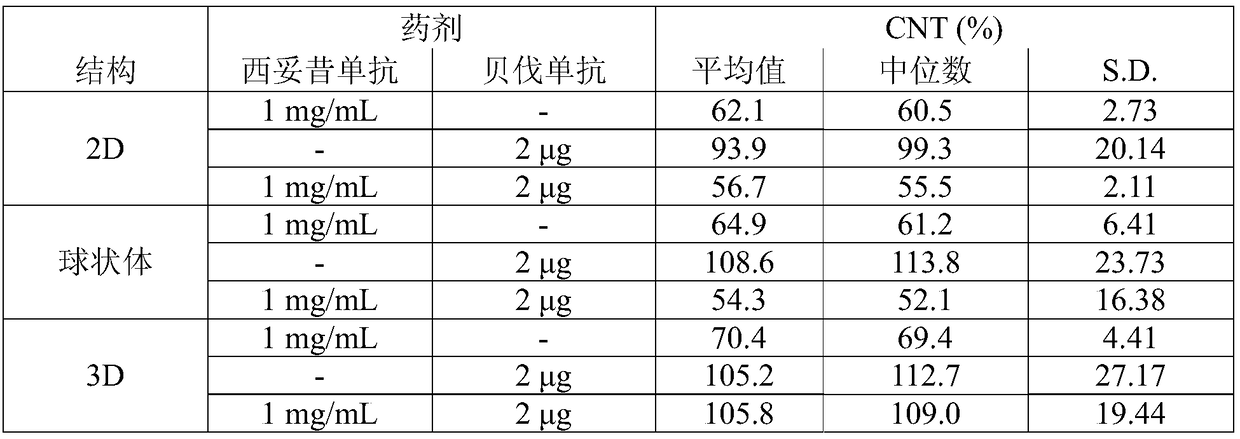
The determination of the number of viable cells in a sample.
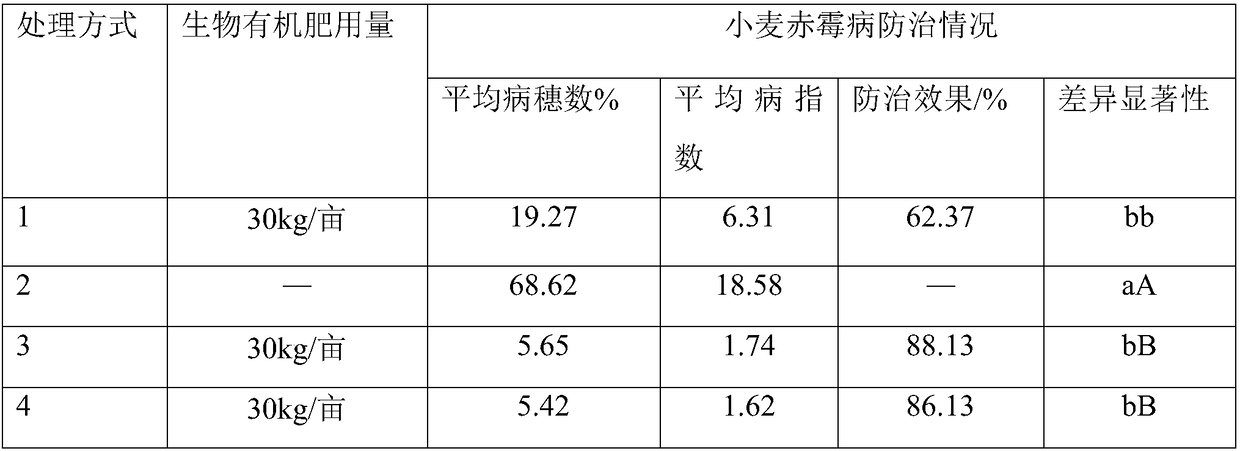
Microorganism-containing compound fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108341712AIncrease productionPlant weightAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersPhosphateMicrobial agent
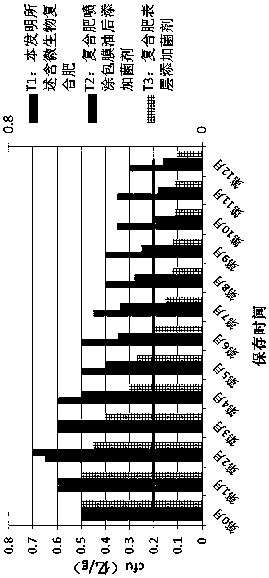
The invention discloses microorganism-containing compound fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The microorganism-containing compound fertilizer has a water content of less than or equal to 5.0%; based on a mass fraction, the total nutrient of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium is more than or equal to 35%, and the effective viable cell count is not less than 2.0*10<7> CFU / g; the compound fertilizer is mainly prepared from 10-40% of urea, 10-35% of monoammonium phosphate, 10-40% of ammonium sulfate, 10-40% of potassium sulfate, 10-35% of potassium chloride, 2-15% of calcium-magnesium-phosphate fertilizer, 2-15% of clay, 0.3-0.5% of coating material and 0.01-1% of microbial powder. The preparation method provided by the invention effectively avoids the influence of high temperature on effective viable counts of microorganisms in a fertilizer production process; the yield, single plant weight and Vc content of lettuce treated by using the compound fertilizer provided by the invention are generally higher than those of lettuce treated by using the common compound fertilizer; the effect of the compound fertilizer is significantly higher than that of the similar products in the market; the compound fertilizer can increase the yield and improve the quality, maintains the survival rate of the microbial agent, and has certain stability.
Owner:中化化肥有限公司临沂农业研发中心
Process of preparing fermented milk beverage keeping high viable cell count at ambient temperature
ActiveUS20100009034A1Extended shelf lifeLow viable cell countMilk preparationMicroorganismsLactobacillus rhamnosusFreeze-drying
The invention provides a process of preparing fermented milk beverage keeping high viable cell count at ambient temperature. The process includes the steps of adding regular yoghurt lactobacillus into milk for fermentation, fermenting until pH value to 3.8-4.8, diluting, mixing and sterilizing with conventional method, adding concentrated culture, concentrated frozen culture or freeze dried culture containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC 53103 into mixed milk beverage at aseptic condition. According to various pH value of finished product, it can be stored at ambient temperature for 1-6 months, and the viable cell count will not be less than 105 cfu / ml milk beverage. The indexes of storage period and viable cell count are much higher than fermented milk beverage produced by conventional process. Thereby the defect that fermented milk beverage has short shelf life and low viable cell count at ambient temperature is overcome efficiently.
Owner:BEIJING YIHECUN TECH CO LTD
Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermented Substance and Fermented Milk Food Product Containing the Same
ActiveUS20080292751A1Enhance growth-promoting effectImprove overall utilizationMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologyFood material
An object of the invention is to provide a lactic acid bacteria fermentation product, which has been obtained by culturing lactic acid bacteria on a medium containing an extract of at least one food material selected from the group consisting of rice bran, persimmon leaves, perilla, Houttuynia cordata Thunb, Eucommia ulmoides Oliv., turmeric, clove, cinnamon and Rubus suavissimus S. Lee (Rosaceae). By adding and mixing the extract used for the preparation of the fermentation product to a medium, it is possible to increase simply the viable cell count of lactic acid bacteria, without affecting the flavor of the product. It is possible, by using the extract, to obtain a lactic acid bacteria fermentation product which contains many viable lactic acid bacteria with their activities highly maintained, and further to provide beverages or foods using the product.
Owner:YAKULT HONSHA KK
Novel lactobacillus classified as lactobacillus plantarum, and use thereof
Disclosed is a novel lactic acid bacterium belonging to Lactobacillus plantarum, which has an excellent fermentative ability affording high achievable cell counts even if various vegetable or fruit juices are used as fermentative substrates. The lactic acid bacterium belonging to Lactobacillus plantarum is characterized by the achievable viable cell counts being 108 CFU / ml or more in both cases when 100% juice of grape or of orange is used as fermentative substrate.
Owner:YAKULT HONSHA KK
Cell viability detection kit and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101551382AExtended storage timeControl reaction timeColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingDiluentViable Cell Count
The invention relates to a cell viability detection kit and a preparation method and an application thereof. The invention is applicable to live cell counting, and is a determining method for directly detecting the cell proliferation, and is also a detection method for estimating the cell totoxicity of the drugs, peptide growth factors and other substances, and is applicable to detect the suspended cell and the anchorage-dependent cell cultured in the cell culture plates. The invention consists of a WST-8 mixed solution storage solution, a reaction stop solution and a buffer diluent solution, wherein the WST-8 mixed solution storage solution contains 50mmol / L WST-8 solution, 2mmol / L PMS and 1mmol / L PIPES buffer solution; the reaction stop solution is 10%(W / V) sodium dodecyl sulfate; and the buffer diluent solution is 1mmol / L PIPES solution.
Owner:ZHENJIANG XUANGUANG BIOCHEM
Method of membrane separation
ActiveUS20140124442A1Avoid cloggingLow adhesivenessWater treatment parameter controlMembranesWater qualityBiological membrane
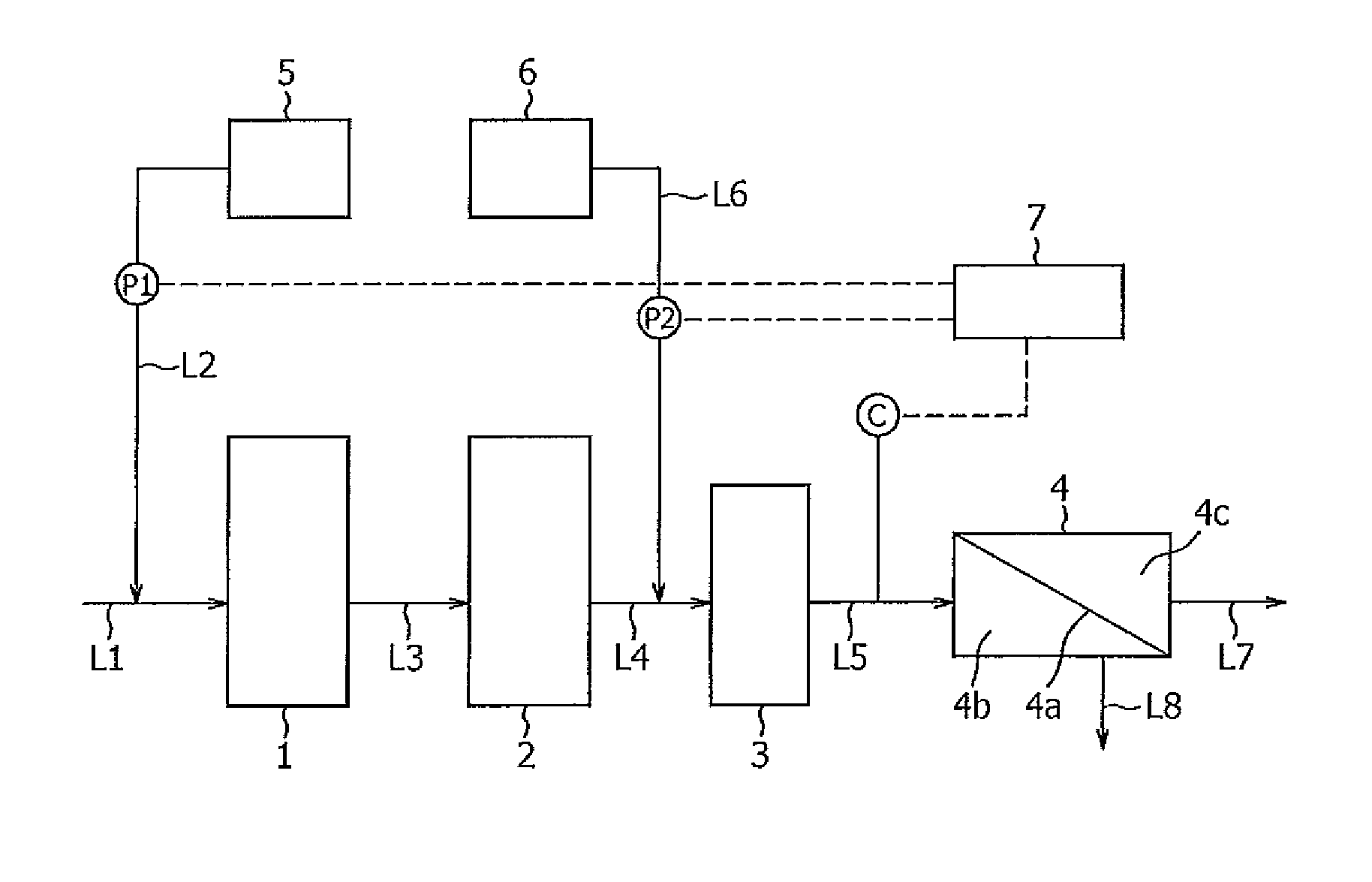
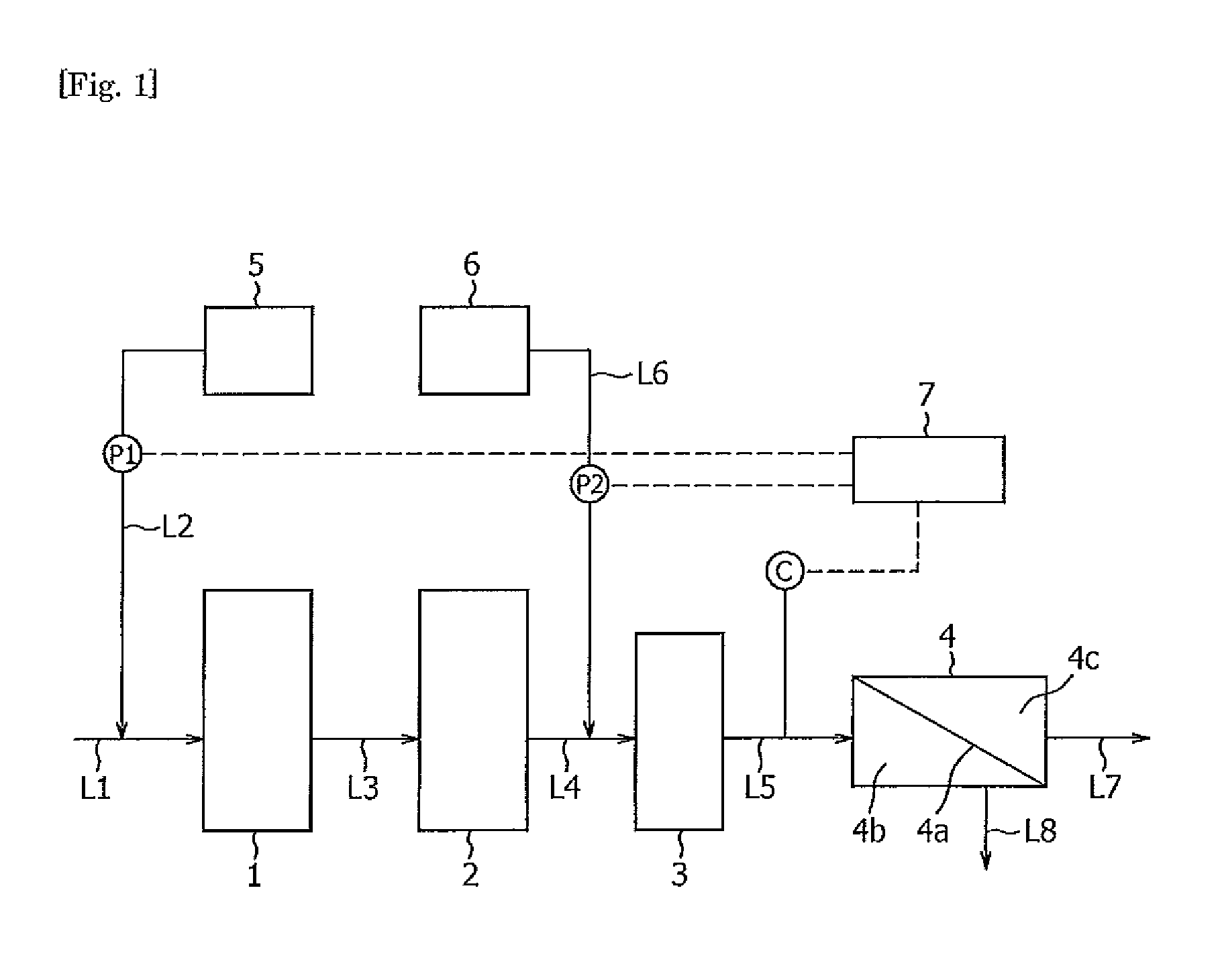
Clogging of membrane by slime adhesion is efficiently prevented and stable treatment can be carried out for a long period of time at a low cost by a small amount of chemicals without the membrane deterioration and trihalomethane formation even if applied to the water having a large number of viable cell counts and having water quality of harsh. The method comprises supplying water to be treated to a membrane separation apparatus 4, adding intermittently to the water to be treated a combined chlorine agent comprising sulfamic compound, and repeating a non-addition feeding period in which water to be treated is supplied for 6-120 hours without addition of combined chlorine agent, and an intermittent addition feeding period in which water to be treated is supplied for 0.5-40 hours under addition of a combined chlorine agent at biofilm exfoliating concentration in an early stage of biofilm formation during the non-addition feeding period, wherein viable cell count (log CFU / mL) of water to be treated is 3 or more, and the concentration of the combined chlorine agent in the water in the intermittent addition feeding period is 0.5-20 mg / L as total chlorine, and additive amount of the combined chlorine agent added in the intermittent addition feeding period is the amount in which R represented by the following Formula [4] is 3 or more.R=(Intermittent addition feeding period (h)×[1000×Intermittent addition concentration (mg-Cl / L)]2.5 / (Non-addition feeding period (h)3.0×10log CFU / mL) [4]
Owner:KURITA WATER INDUSTRIES LTD
Process of preparing direct-acidified milk beverage keeping high viable cell count at ambient temperature
InactiveUS20100015285A1Solution value is not highHigh indexMilk preparationMicroorganismsNutritive valuesLactobacillus rhamnosus
Owner:BEIJING YIHECUN TECH CO LTD
Composite microbial agent for water environment treatment and application thereof
ActiveCN110217895AStable denitrification effectAvoid Compatibility ProblemsWater treatment parameter controlBacteriaMicroorganismPseudomonas otitidis
The invention relates to composite microbial agents, in particular to a composite microbial agent for water environment treatment and an application thereof. The composite microbial agent comprises: Pseudomonas otitidis, Pseudomonas kunmingensis, Pseudomonas asiatica, and Alcaligenes sp., and the total viable cell count of the microbial agent is not less than 1 x 10<9> cfu / mL. The composite microbial agent has low cost and no pollution to environment, a polluted water body is treated at an adding ratio of 0.01%-0.1%, after 1-2 weeks, removal efficiency of ammonia nitrogen is close to 100%, andtotal nitrogen elimination is up to 60% or more. At the same time, no accumulation of nitrites and nitrates is caused, the functional strain is traced in situ after repairing is completed, and thus relatively strong adaptability of the microbial agent in an actual water environment is verified. The composite microbial agent can be used for water environment treatment, and a feasible method for elimination of black odorous water body in China is provided.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compound microecological preparation and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107828680AImprove qualityIncrease production capacityFungiBacteriaProduction rateViable Cell Count
The invention provides a composite microecological preparation and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite microecological preparation is prepared from lactobacillus plantarum, bacillus subtilis and saccharomyces cerevisiae. The composite microecological preparation as a feed additive for laying hens has a higher viable cell count, has the advantages of improving the productionperformance of the laying hens, delaying the decline of an egg production rate, and improving the quality of eggs, and has broad application prospects and great market value.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOFEED TECH CO LTD
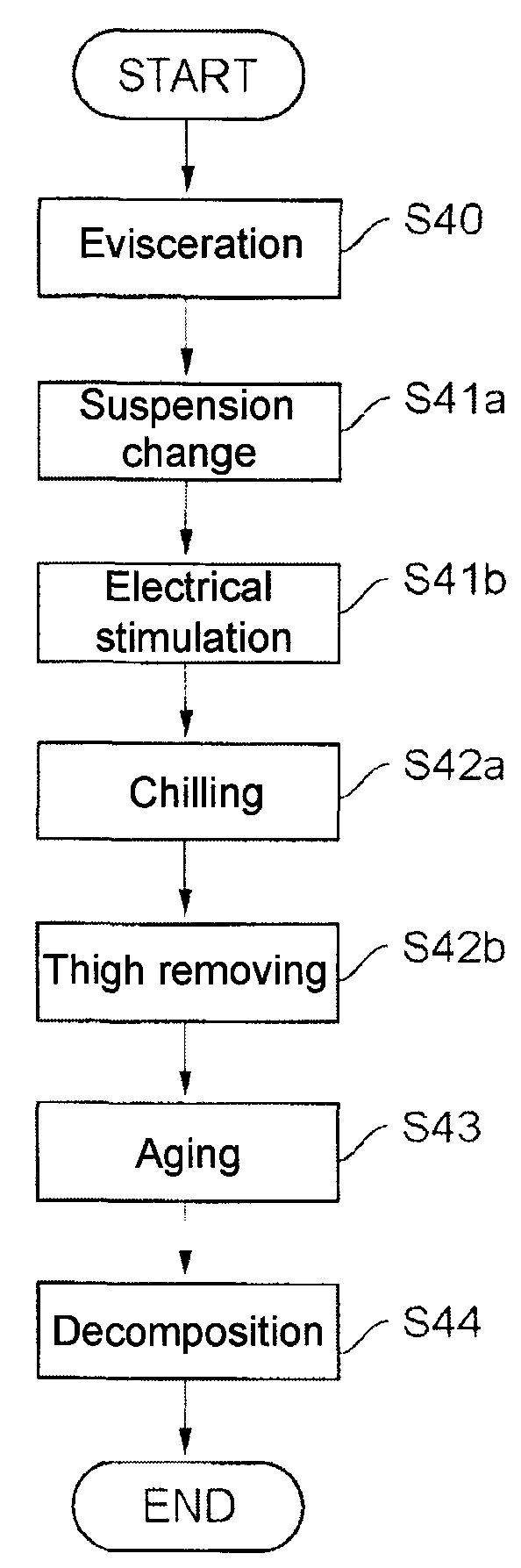
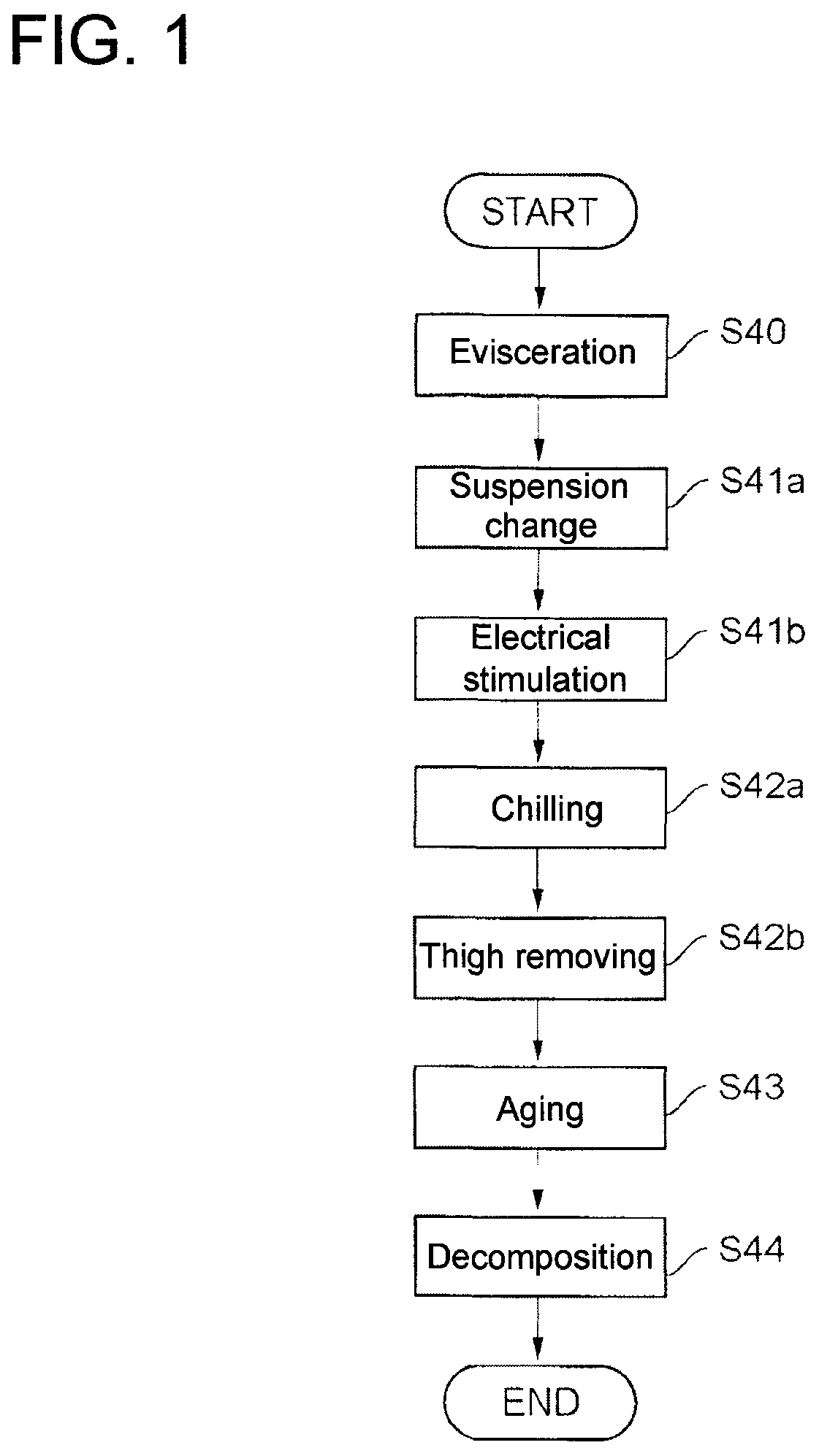
Carcass processing apparatus and method
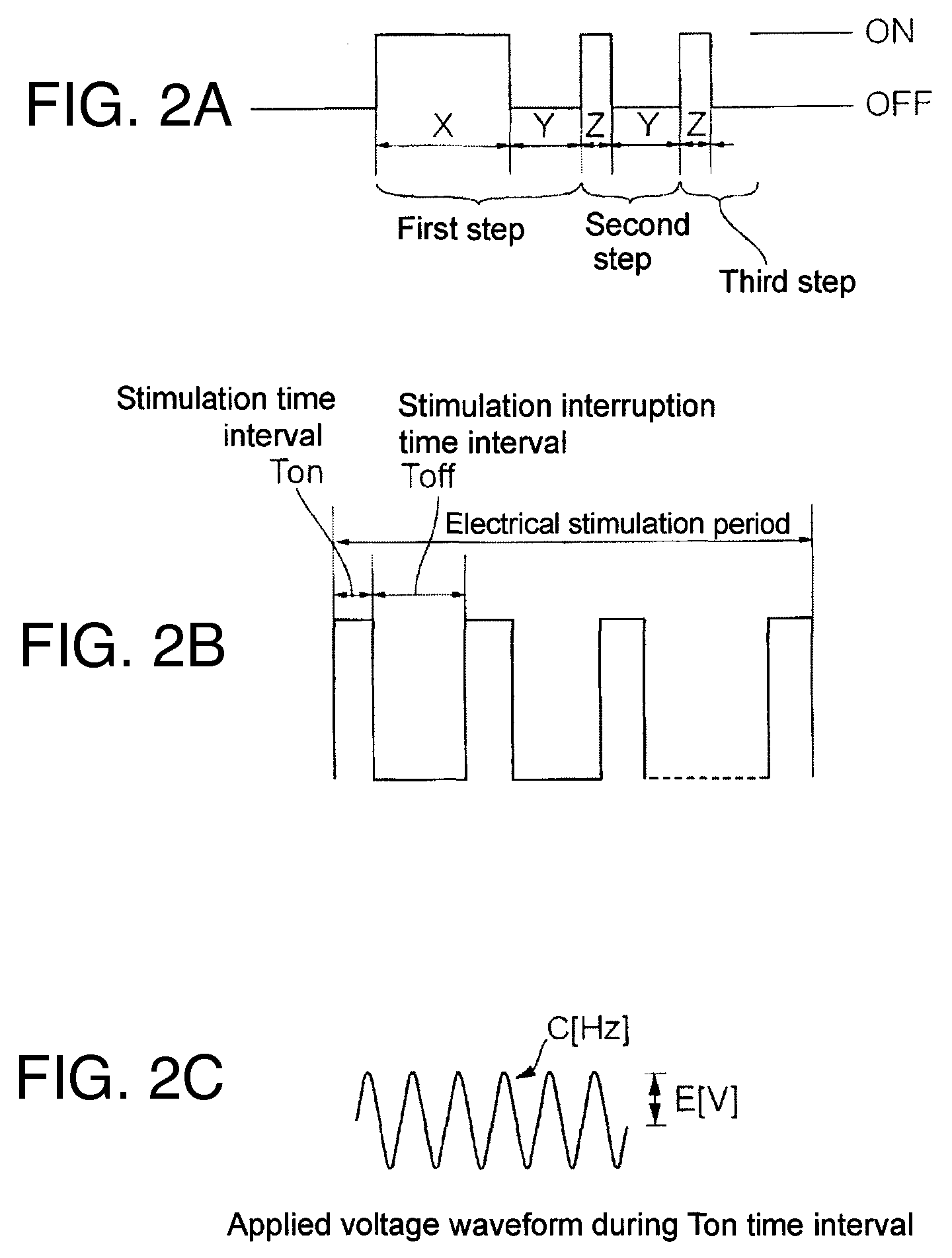
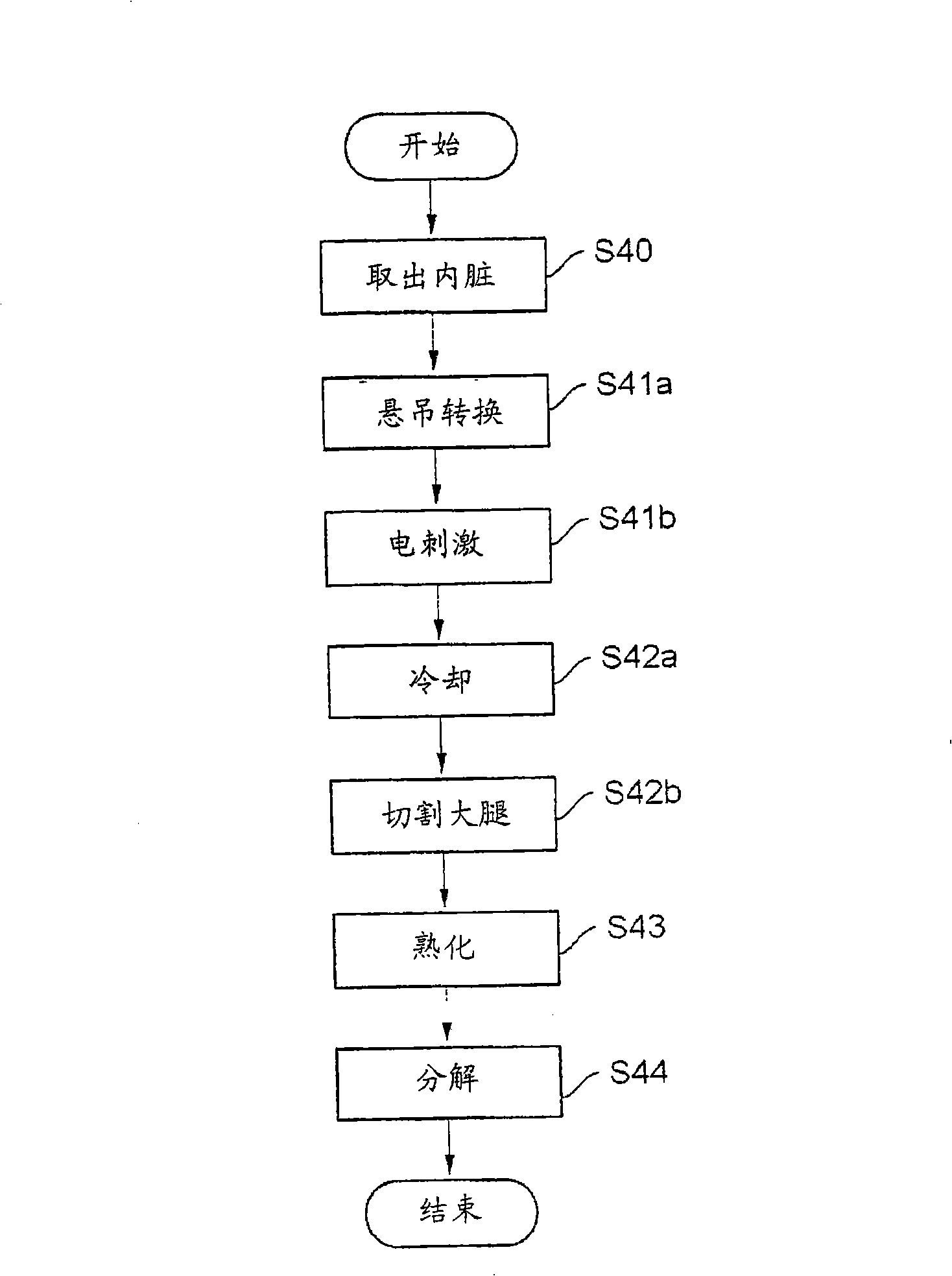
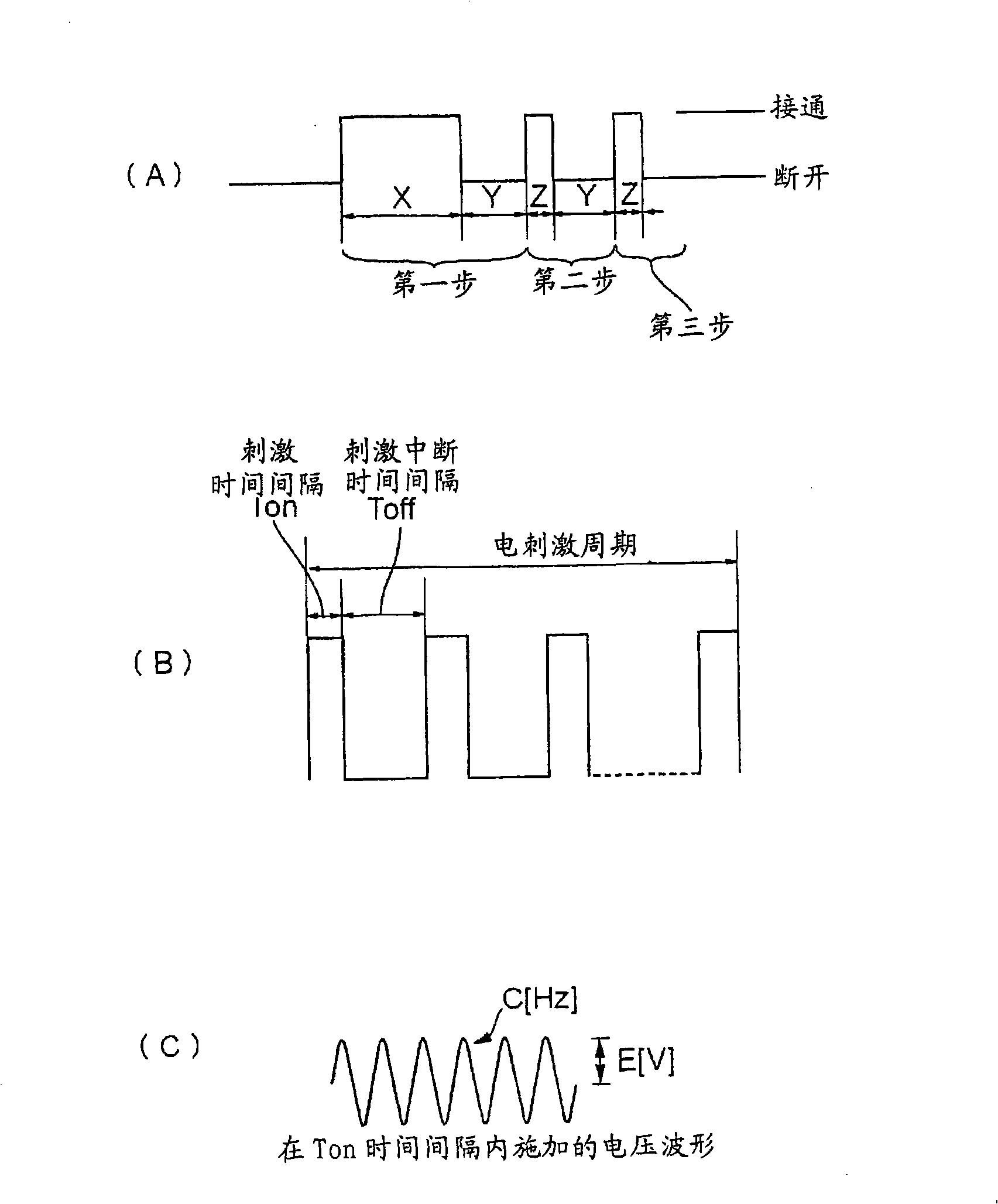
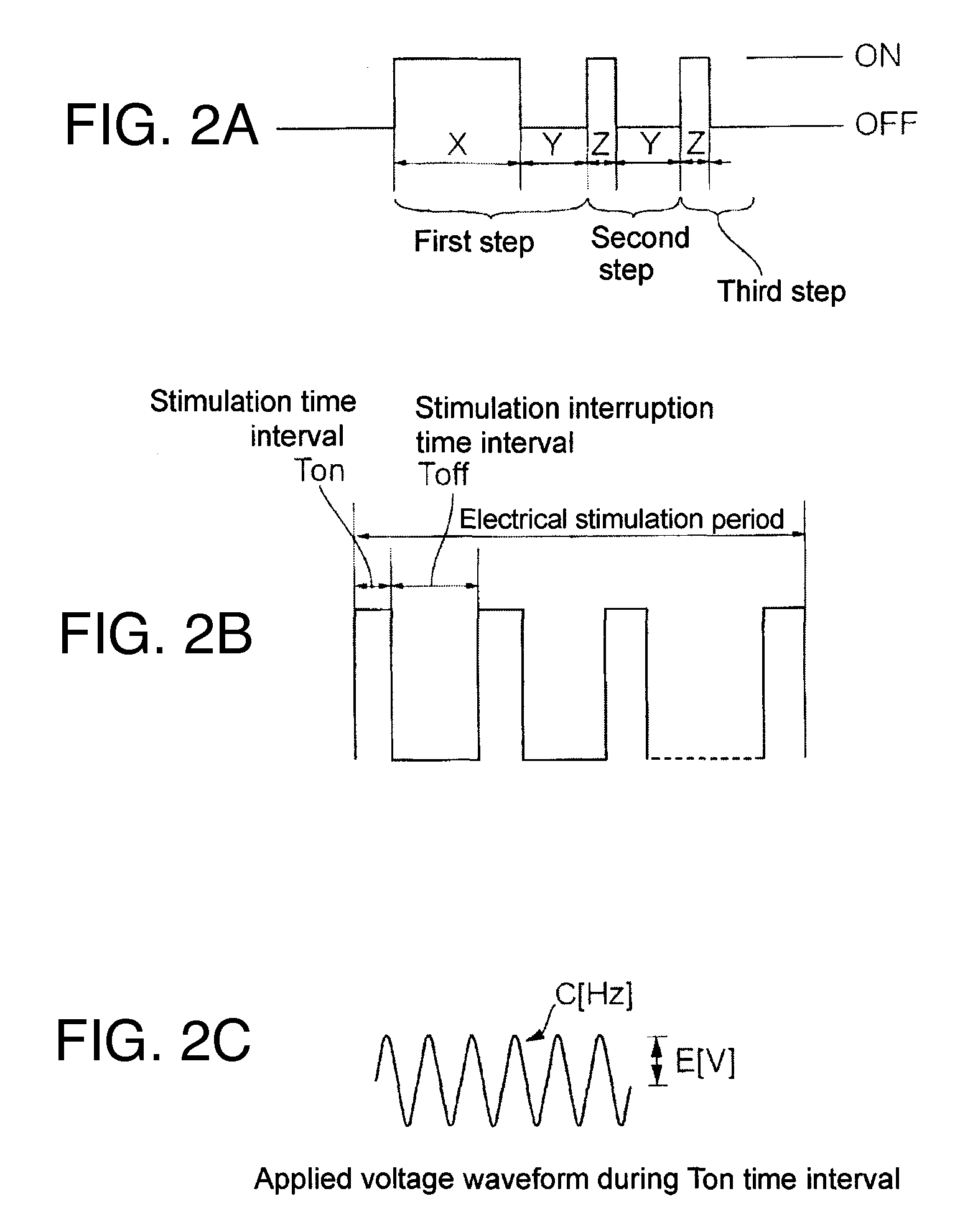
ActiveUS7686679B2Shorten the timeShorten aging timeElectric-based meat tenderisingPoultry processingElectricityViable Cell Count
To shorten a long aging time required for meat processing and reducing the viable cell count of a carcass before being cooked, an electric stimulus is imparted by applying an AC voltage via from electrode needles to at least the neck and legs of the meat carcass. The AC voltage is turned on for a time Ton and then turned off for a time Toff, and the application of the voltage is repeated a predetermined number of cycles. The Ton period is not longer than the Toff period, although the first Ton period can be longer than the Toff period. The voltage is not higher than 100V, and the frequency is not higher than the commercial frequency (maximum, 60 Hz). The aging effect is improved by stimulating the entire meat carcass electrically from at most three points.
Owner:MAYEKAWA MFG CO LTD
Mixed inoculant agent for effective degradation of mushroom bran, and preparation method and application thereof
The present invention relates to a mixed inoculant agent for effective degradation of mushroom bran. The mixed inoculant agent is prepared by mixing a straw fermentation broth with a crude fiber degrading broth by 1:5-5:1 to prepare a mixed inoculant stock solution, then inoculating 0.25%-1.0% of the mixed stock solution into sterile distilled water, adding a mixed broth containing Aspergillus niger and Penicillium and accounting for 1.0-5.0 wt.% of the sterile distilled water, and stably culturing for 2-3 d. The preparation method of the mixed broth is as follows: inoculating Aspergillus niger and Penicillium to a PDA slant medium for 3-4 d respectively, washing the spores on the slant with sterile water to prepare a spore suspension with viable cell count of 106 CFU / mL; and conducting liquid fermentation culture on the Aspergillus niger and Penicillium according to the proportion of 15%-25% for 7-8 d to obtain a mixed fermentation broth. The mixed inoculant agent of the present invention to is convenient for the mushroom bran degradation, and has obvious degradation effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for viable and nonviable prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell quantitation
InactiveUS20050282244A1Increase uptakeImprove conversion rateMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceClinical settingsMammal
A rapid method for the quantitation of various live cell types is described. The method may include a variety of steps including: 1) suspending the cells in a detergent-like compound, 2) isolating the washed cells by centrifugation or filtration, 3) resuspending the cells in a solution that contains a preservative, a fluorescent dye and a compound such as dequalinium which can be taken up by the cells, 4) measuring the fluorescence increase over time of the cell-dye mixture with a simple fluorometer, and 5) measuring the native fluorescence of the cells. This new cell fluorescence method correlates with other methods of enumerating cells such as the standard plate count, the methylene blue method and the slide viability technique. The method is particularly useful in several applications such as: a) quantitating bacteria in milk, yogurt, cheese, meat and other foods, b) quantitating yeast cells in brewing, fermentation and bread making, c) quantitating mammalian cells in research, food and clinical settings. The method is especially useful when both total and viable cell counts are required such as in the brewing industry. The method can also be employed to determine the metabolic activity of cells in a sample. The apparatus, device, and / or system used for cell quantitation is also disclosed.
Owner:GENPRIME
Composite microbial treatment agent for fermenting silage and hay silages and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109666597AInhibition of growth and reproductionHigh nutritional valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPropanoic acidMicrobial agent
The invention relates to the field of biology, in particular to a composite microbial treatment agent for fermenting silage and hay silages and a preparation method thereof. The composite microbial treatment agent is characterized by being prepared from, by weight, 10-30 parts of lactobacillus plantarum, 15-30 parts of bacillus coagulans, 15-30 of lactobacillus rhamnosus and 10-30 parts of lactobacillus buchneri, and the effective viable cell count of the microbial treatment agent is 1.0 to 9.9*109 CFU / mL. Compared with the prior art, the method uses the bacillus coagulans, the lactobacillus plantarum, the lactobacillus rhamnosus and the lactobacillus buchneri composite microbial agent for silage / hay silage fermentation, and can effectively inhibit the growth of hybrid bacteria, after fermentation, the pH can be increased to 3.7-4.1, the total organic acid content such as acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid is increased, the ammonia nitrogen content is reduced, a finished product has an aromatic fruit flavor, thereby reducing a taste beneficial to improving the feeds, and the nutritional value of the feeds is improved.
Owner:BIOGROWING CO LTD
Method and apparatus for viable and nonviable prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell quantitation
InactiveUS20090104652A1Increase uptakeSpeed up rate conversionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClinical settingsMammal
A rapid method for the quantitation of various live cell types is described. This new cell fluorescence method correlates with other methods of enumerating cells such as the standard plate count, the methylene blue method and the slide viability technique. The method is particularly useful in several applications such as: a) quantitating bacteria in milk, yogurt, cheese, meat and other foods, b) quantitating yeast cells in brewing, fermentation and bread making, c) quantitating mammalian cells in research, food and clinical settings. The method is especially useful when both total and viable cell counts are required such as in the brewing industry. The method can also be employed to determine the metabolic activity of cells in a sample. The apparatus, device, and / or system used for cell quantitation is also disclosed.
Owner:GENPRIME
Paenibacillus macerans and straw decomposing agent
ActiveCN108504586AShort degradation timeDecomposition is stableBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaMicrobiologyViable Cell Count
The invention discloses a straw decomposing agent which comprises components of Paenibacillus macerans CGMCC No. 14564 and Bacillus subtilis CICC No. 10089; the total effective viable cell count in the decomposing agent is 0.5*10<8>-2*10<8> / g, and the effective viable cell count of the Paenibacillus macerans is 65%-70% of the total effective viable cell count; the invention also discloses a preparation method of the straw decomposing agent, compared with use of various strains to prepare the decomposing agent in the prior art, the preparation method has a small variety of raw materials, and has a simple preparation process, the Bacillus subtilis whoch is not used in the prior art is used in the preparation method as one of the raw materials to interact with the Paenibacillus macerans, andthe use effect is remarkable, so that the preparation method can be promoted in related enterprises.
Owner:四川明湖环保科技有限公司
Anti-cancer drug assessment method
ActiveCN109072276AImprove reliabilityEasy to implementCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAnticarcinogenCancer cell
This anti-cancer drug assessment method involves: a culturing step for culturing a cell structure containing cells which constitute cancer cells and stromal tissue while in the presence of one or moretypes of anti-cancer drug; and an assessment step for assessing the anti-cancer effect of the anti-cancer drug, with the indicator thereof being the viable cell count of the cancer cells in the cellstructure following the culturing step.
Owner:TOPPAN INC
Device and method for processing meat carcass
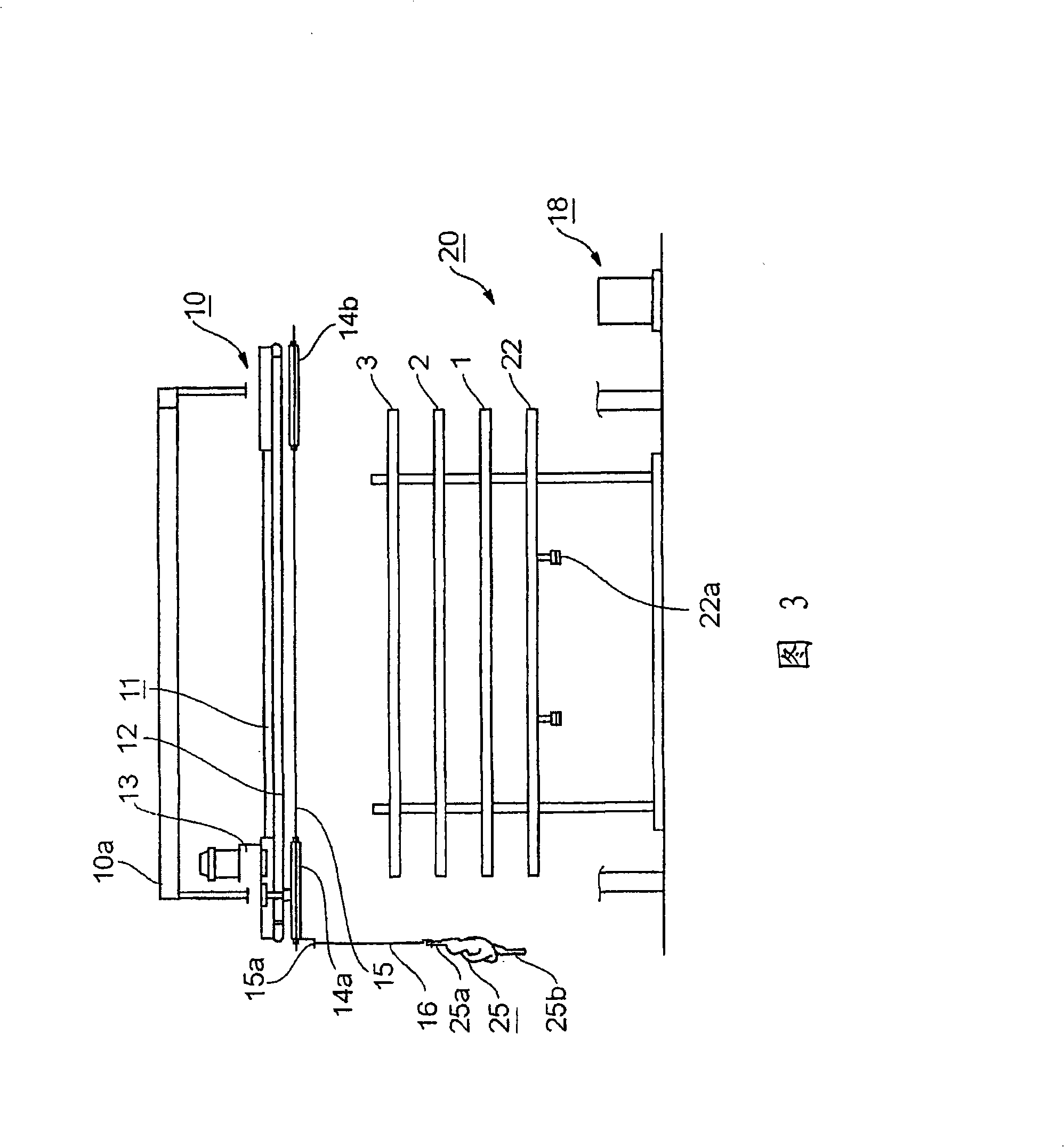
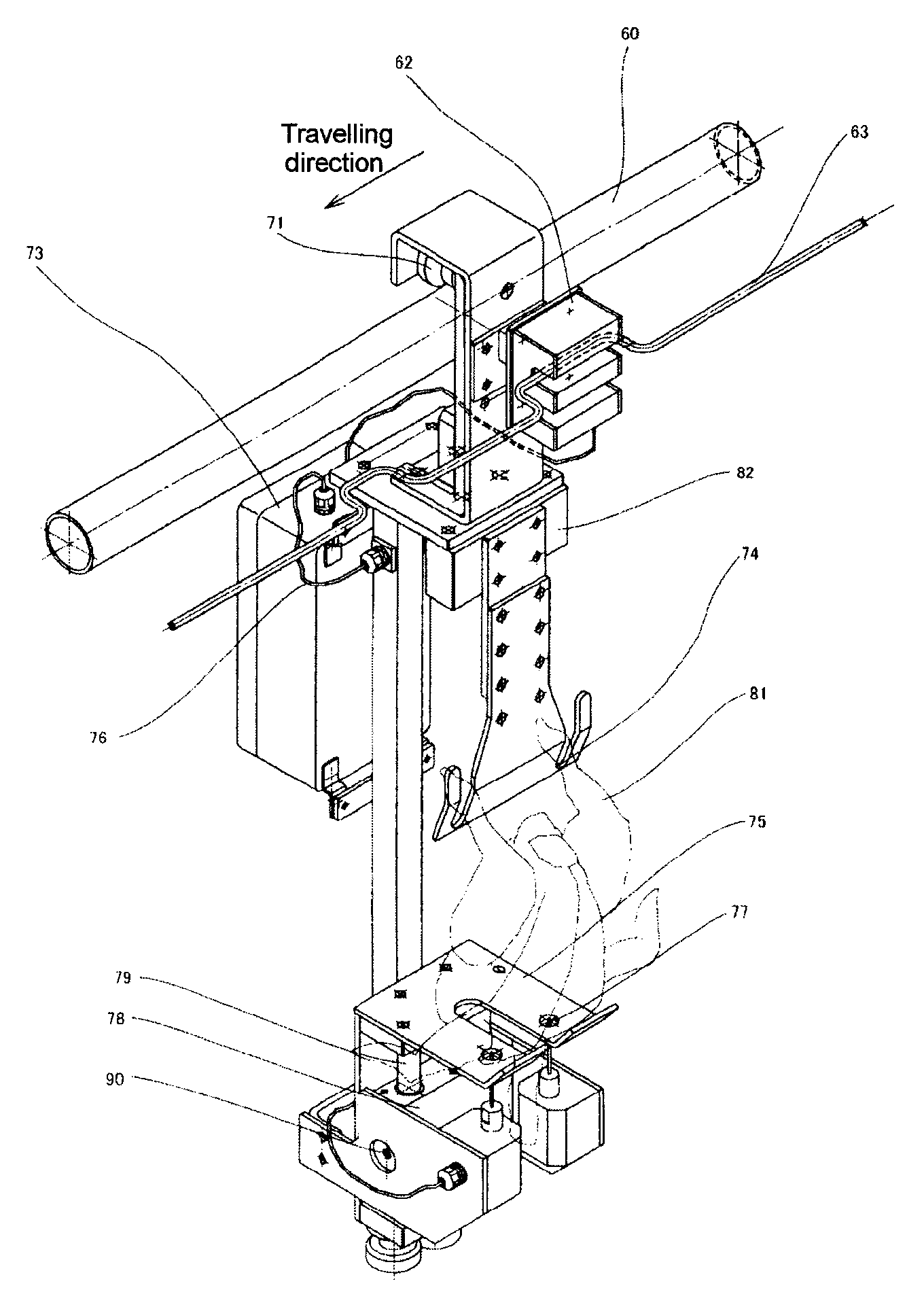
InactiveCN101316515AGood for growth controlShorten the ripening timeElectric-based meat tenderisingPoultry processingElectricityViable Cell Count
The present invention discloses a device and method for processing meat carcass. In order to shorten a long aging time required for meat processing and reducing the viable cell count of a carcass before cooked, an electric stimulus is imparted by applying an ac voltage from electrode rails (1, 2, 3) to the neck, chest and legs of the meat carcass respectively. The ac voltage is turned on for a time Ton and then turned off for a time Toff and the application of the voltage is repeated a predetermined number of cycles. Ton is not longer than Toff, the voltage is not higher than 100V and the frequency is not higher than the commercial frequency (maximum, 60 Hz). A needle (51) for chest is supported by a metal support (52) and brought into pressure contact with the electrode rail (2), and a needle (53) for neck is supported by a metal support (54) and brought into pressure contact with the electrode rail (1) through a meal support (57). Legs of the meat carcass are energized by the electrode rail (3). Aging effect is improved by stimulating the entire meat carcass electrically from at most three points.
Owner:MAYEKAWA MFG CO LTD
Granular bacillus compound microbial fertilizer as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN109456119AEasy to upgradeEasy to prepareOrganic fertilisersFertilizer mixturesGrowth promotingViable Cell Count
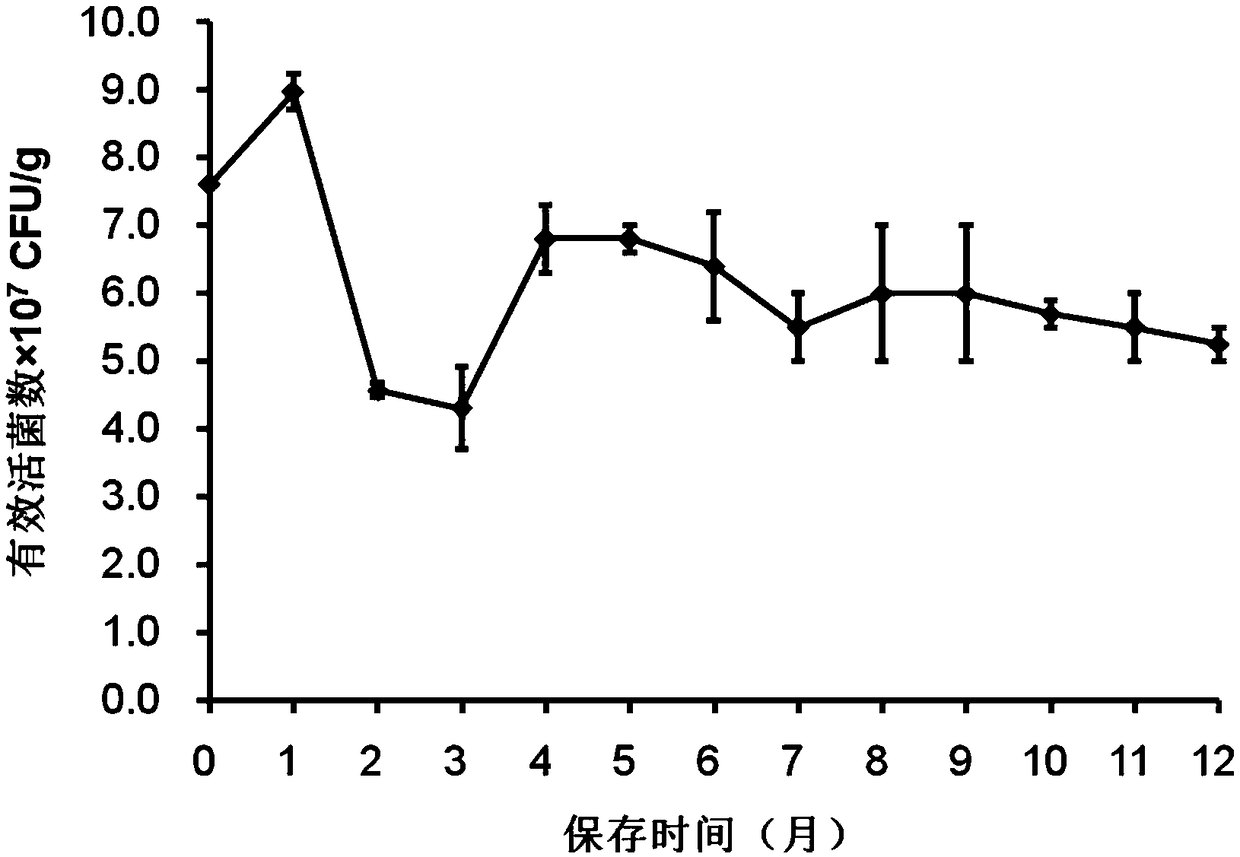
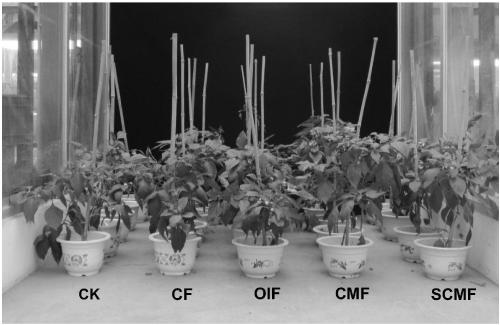
The invention provides granular bacillus compound microbial fertilizer as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the process, bacillus fermentation broth (with abacteria density of more than or equal to 7*108 CFU / g) is fully and evenly mixed with granular organic-inorganic compound fertilizer (with total nutrient content (N-P2O5-K2O) of more than or equal to 15%, organic matter content of more than or equal to 20% and water content of less than or equal to 5%) in a proportion of 3-10% (v / w), and the obtained mixture is air-dried, so that the granular compound microbial fertilizer is prepared. The product has a viable cell count of more than 5*107 CFU / g after being stored for 1 year under normal temperature conditions, and is in line with national standards; theproduct shows a significant growth-promoting effect compared with fertilizer containing the same nutrients in pot experiments of chilies and tomatoes. The novel fertilizer combines the quick-acting effect of chemical fertilizer, the long-acting effect of organic fertilizer and the synergistic function of biological fertilizer, is good in growth-promoting effect, low in production cost and convenient to apply, and can be applied to food crops, vegetable crops and the like.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Lactobacillus classified as Lactobacillus plantarum, and use thereof
Disclosed is a novel lactic acid bacterium belonging to Lactobacillus plantarum, which has an excellent fermentative ability affording high achievable cell counts even if various vegetable or fruit juices are used as fermentative substrates. The lactic acid bacterium belonging to Lactobacillus plantarum is characterized by the achievable viable cell counts being 108 CFU / ml or more in both cases when 100% juice of grape or of orange is used as fermentative substrate.
Owner:YAKULT HONSHA KK
Carcass processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20080233853A1Shorten aging timeReduce viable cell countElectric-based meat tenderisingPoultry processingElectricityEngineering
To shorten a long aging time required for meat processing and reducing the viable cell count of a carcass before being cooked, an electric stimulus is imparted by applying an AC voltage via from electrode needles to at least the neck and legs of the meat carcass. The AC voltage is turned on for a time Ton and then turned off for a time Toff, and the application of the voltage is repeated a predetermined number of cycles. The Ton period is not longer than the Toff period, although the first Ton period can be longer than the Toff period. The voltage is not higher than 100V, and the frequency is not higher than the commercial frequency (maximum, 60 Hz). The aging effect is improved by stimulating the entire meat carcass electrically from at most three points.
Owner:MAYEKAWA MFG CO LTD
Preparation method of multifunctional ready-to-eat fermented yoghurt powder
The invention discloses a preparation method of multifunctional ready-to-eat fermented yoghurt powder. Raw material milk is prepared according to a specific ratio; introduction of a preferred freeze-drying carrier effectively ensures the efficient effects of the yoghurt powder in a viable cell count, brewing reconstitution properties and a preservation period, and ensures that the yoghurt powder has high nutritional value, good solubility, high stability, and delicate taste after brewing; and in addition, flavor functional powder is prepared independently, so that flavor and nutritional functions can be changed according to consumer preferences and desired functions, and therefore, the multifunctional ready-to-eat fermented yoghurt powder has good market prospects. The multifunctional ready-to-eat yogurt powder disclosed by the invention has a protein content of 30.38-48.25% and a fat content of 5.6-11.3%.
Owner:HUAIBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
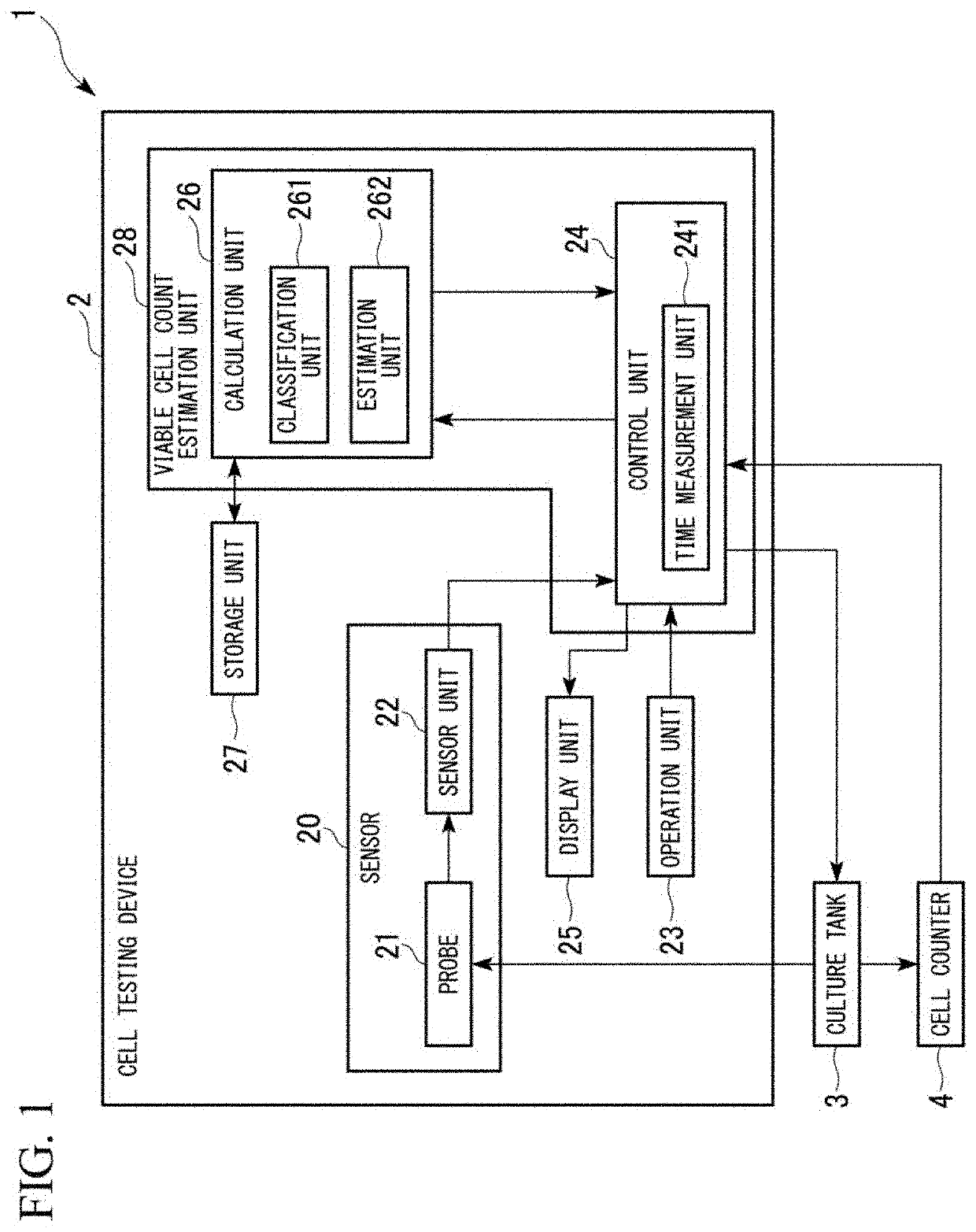
Cell testing device, cell testing method, program, and recording medium
PendingUS20200400603A1Improve accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrobiologyViable Cell Count
A cell testing device according to one aspect of the present invention includes: an impedance sensor configured to measure impedance of a culture solution; a storage unit configured to store a coefficient for estimating the number of viable cells present in the culture solution during a prescribed period using the impedance for each of a plurality of periods into which the prescribed period within a culture period from the start of cell culture to death is divided; and a viable cell count estimation unit configured to acquire the impedance and estimate the number of viable cells using at least one of the acquired impedance and a coefficient for each period stored in the storage unit.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Method for producing fermented milk food
ActiveUS20180042252A1Increase acidityGreat tasteMilk preparationBacteriaLactobacillusAdditive ingredient
An object of the present invention is to provide a fermented milk food, in which the viability of lactic acid bacteria during storage is high, the increase in acidity is suppressed, the viable cell count is less reduced, and the flavor is less deteriorated. A method for producing a fermented milk food by which the object was achieved is characterized by inoculating and culturing lactic acid bacteria in a culture medium containing a milk as a main component and supplemented with glucose in such an amount that glucose is substantially entirely assimilated at the time of completion of culturing and fructose in an amount twice or more the amount of glucose in a mass ratio.
Owner:YAKULT HONSHA KK
Method for maintaining the number of viable bacteria in yogurt or active lactic acid bacteria beverage
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Microbial composite organic fertilizer for preventing and controlling wheat scab, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108690815AEasy to trainImprove disease resistanceFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyViable Cell Count
The invention provides a microbial composite organic fertilizer for preventing and controlling wheat scab, and a preparation method thereof. The microbial composite organic fertilizer comprises a microbial composite bacterial agent and an organic waste according to a weight ratio of (4-8):(2-6), wherein the microbial composite bacterial agent comprises Trichoderma harzianum, Bacillus subtilis, Lactobacillus and yeast, and based on the weight of the microbial composite organic fertilizer, the effective viable count of Trichoderma harzianum is not less than 300 million cfu / g, the effective viable cell count of Bacillus subtilis is not less than 500 million cfu / g, the effective viable cell count of Lactobacillus is not less than 300 million cfu / g, and the effective viable cell count of yeastis not less than 300 million cfu / g. According to the present invention, with the microbial composite organic fertilizer, the disease resistance of wheat is significantly improved; and the production process is simple, the strain is easy to culture, the method is suitable for large-scale production, and a certain social and economic benefit can be achieved.
Owner:安徽莱姆佳生物科技股份有限公司
A kind of Lactobacillus plantarum preservative for low-salt meat products
The invention relates to a plant lactobacillus preservative for low-salt meat products. The strain used in the Lactobacillus plantarum preservative is Lactobacillus plantarum Lactobacillus plantarum , preserved in China General Microorganism Culture Collection Center (CGMCC). The Lactobacillus plantarum antistaling agent is a light white translucent suspended bacterial liquid, and the number of viable cells of the antistaling agent is 10 9 CFU / mL; Use the spray method to evenly inoculate the above-mentioned preservatives on the surface of low-salt meat products; quickly vacuum-pack the inoculated low-salt meat products, and store them at 4±2°C. The plant lactobacillus fresh-keeping agent of the present invention significantly inhibits the growth of spoilage bacteria, delays the fat oxidation of products, and prolongs the shelf life of low-salt meat products.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
A kind of fermented milk with high viable bacteria count in shelf life and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses fermented milk with a high number of viable bacteria within the shelf life, which increases the number of viable bacteria in the fermented milk without changing the flavor of the fermented milk during the shelf life. The preparation method of fermented milk can ensure that there will be no after-acid problem, so the bacteria can be used for the preparation of yogurt or beverage with high viable count. Taking advantage of the low autolysis of Lactobacillus plantarum N3117, in the case of imperfect cold chain, the number of viable bacteria will not change significantly, and there will be no after-acid problem, so this bacteria can be used in yogurt with high viable count or Preparation of drinks. In the preparation process, the addition amount of Lactobacillus plantarum N3117 ranged from 10 5 -10 8 Cfu / g, can increase the number of viable bacteria in the final fermented milk, and the number of viable bacteria does not change significantly during the 21-day shelf life at 37°C, and the number of viable bacteria remains at more than 10 7 cfu / g. The present invention is suitable for fermented milk that can have a high number of viable bacteria within the shelf life.
Owner:JUNLEBAO DAIRY GRP CO LTD
A probiotic traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation for promoting sow lactation and improving milk quality
ActiveCN104920787BRegulate or maintain microecological balanceIncrease daily weight gainAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsFeed conversion ratioViable Cell Count
The invention discloses a probiotic traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation for promoting lactation of sows and improving milk quality, which is compounded from a traditional Chinese medicine compound and probiotics; the traditional Chinese medicine compound is made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: angel yeast 0.5 1.5 parts, 5‑15 parts of fructooligosaccharides, 1‑4 parts of vitamin E, 5‑15 parts of Wang BuliuXing, 1‑3 parts of Tongcao, 4‑6 parts of compound enzyme preparation, 1‑3 parts of soybean isoflavones, wheat 45-50 parts of rice stone powder, 17-25 parts of cornstarch; the probiotics are mixed bacteria powder of Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus plantarum. In the probiotic traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation, the number of live bacteria of Bacillus subtilis is greater than or equal to 2×108cfu / g, and the number of viable bacteria of Lactobacillus plantarum is greater than or equal to 3×108cfu / g. The probiotic traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation of the present invention can increase the expression level of prolactin, promote the lactation of sows, reduce the ratio of feed to weight and improve the utilization rate of feed through the compounding of probiotics and traditional Chinese medicine.
Owner:山东宝来利来生物工程股份有限公司 +1
A kind of composite microbial agent for water environment treatment and its application
ActiveCN110217895BImprove denitrification effectAvoid Compatibility ProblemsWater treatment parameter controlBacteriaAmmoniacal nitrogenMicroorganism
The invention relates to composite microbial agents, in particular to a composite microbial agent for water environment treatment and an application thereof. The composite microbial agent comprises: Pseudomonas otitidis, Pseudomonas kunmingensis, Pseudomonas asiatica, and Alcaligenes sp., and the total viable cell count of the microbial agent is not less than 1 x 10<9> cfu / mL. The composite microbial agent has low cost and no pollution to environment, a polluted water body is treated at an adding ratio of 0.01%-0.1%, after 1-2 weeks, removal efficiency of ammonia nitrogen is close to 100%, andtotal nitrogen elimination is up to 60% or more. At the same time, no accumulation of nitrites and nitrates is caused, the functional strain is traced in situ after repairing is completed, and thus relatively strong adaptability of the microbial agent in an actual water environment is verified. The composite microbial agent can be used for water environment treatment, and a feasible method for elimination of black odorous water body in China is provided.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
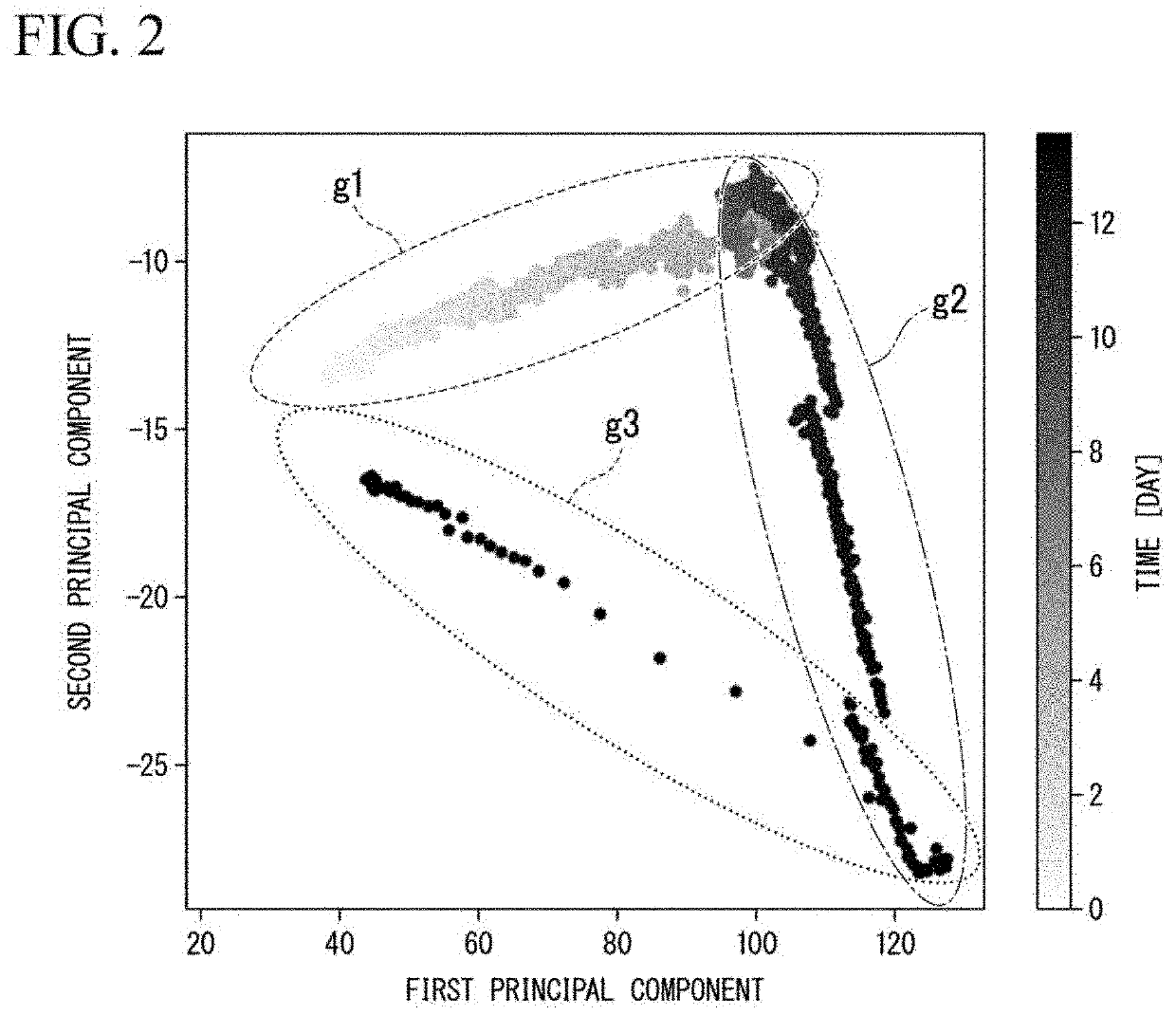
Device for estimating survival cell count, computer program, and recording medium
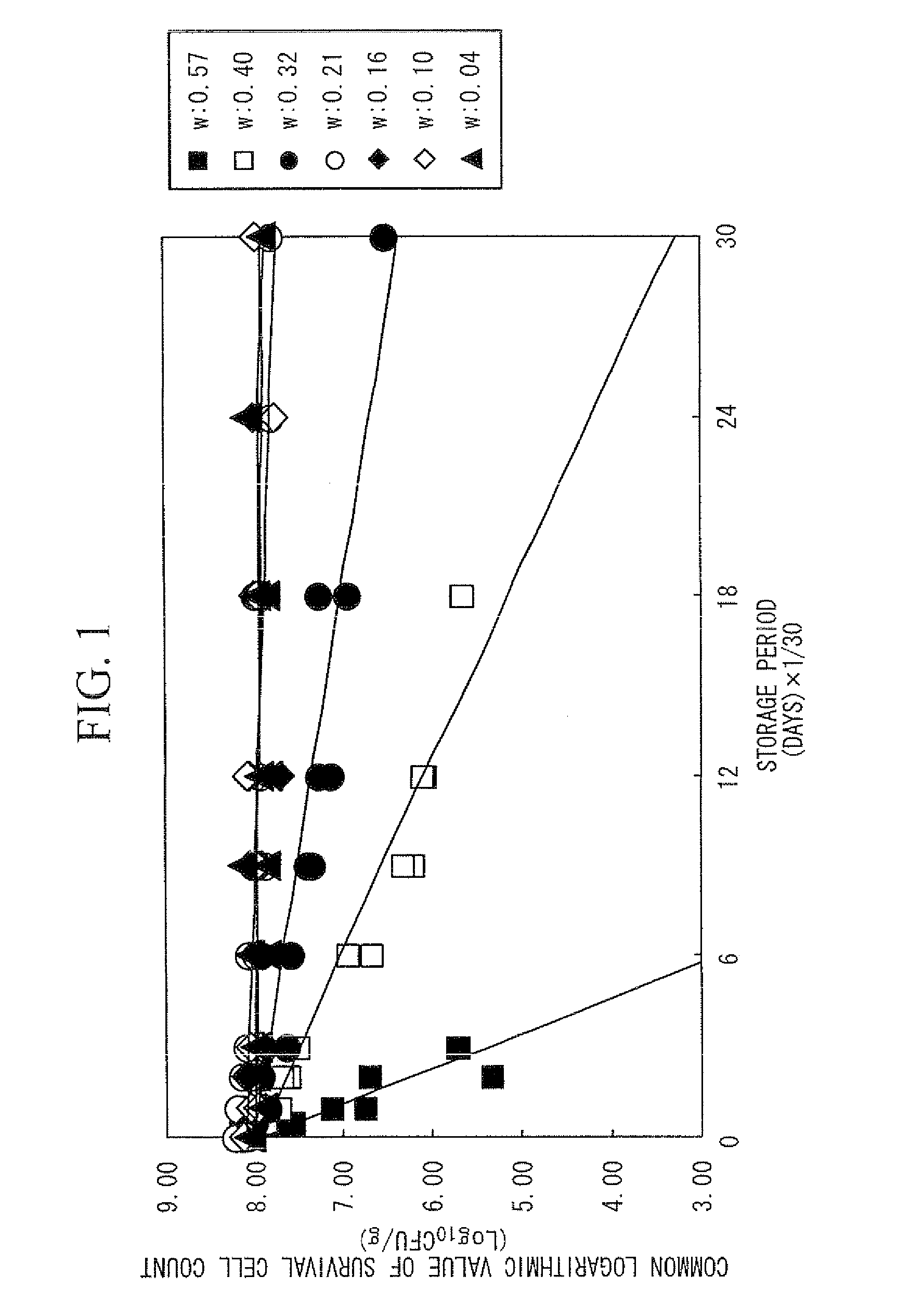
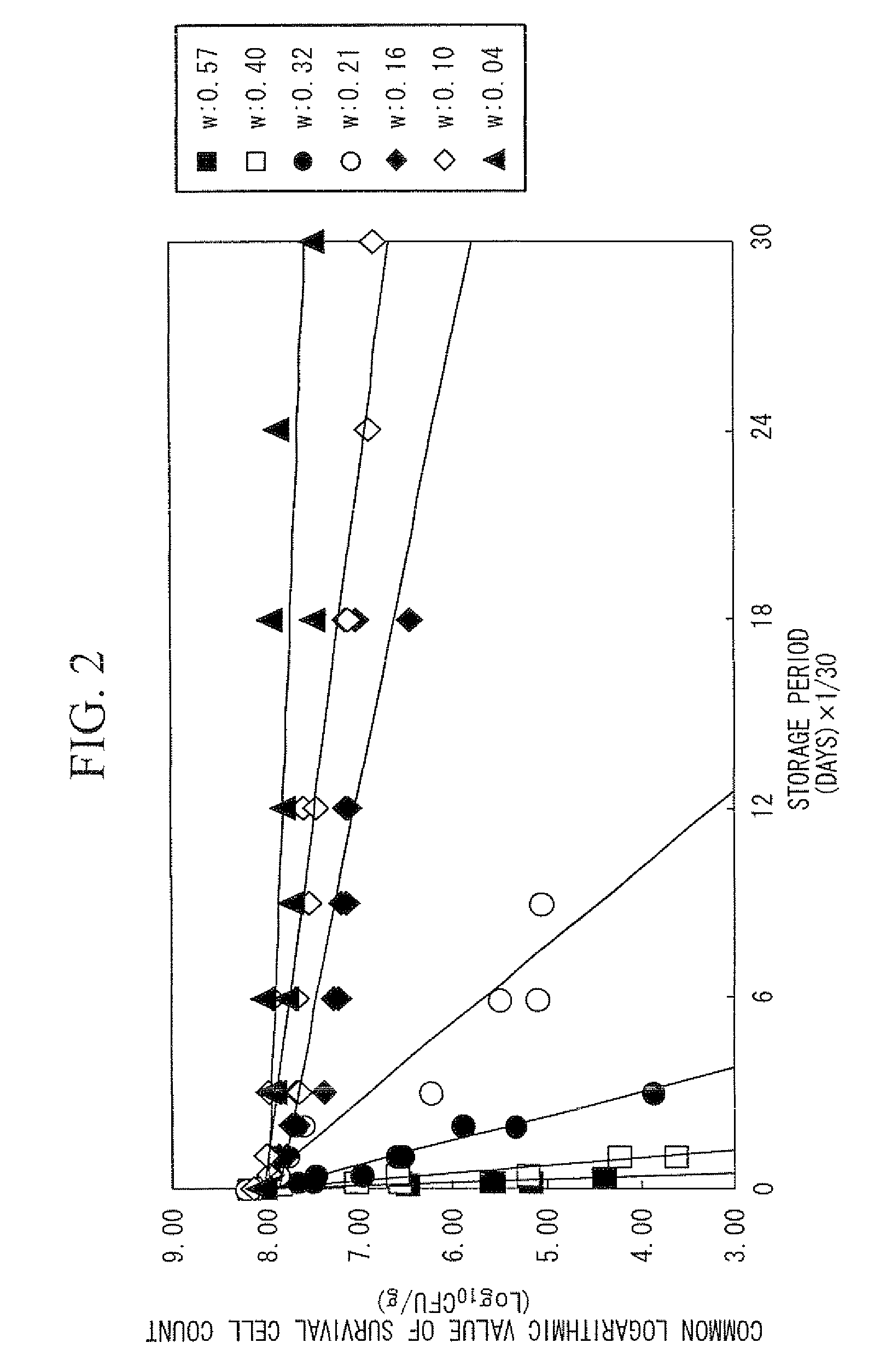
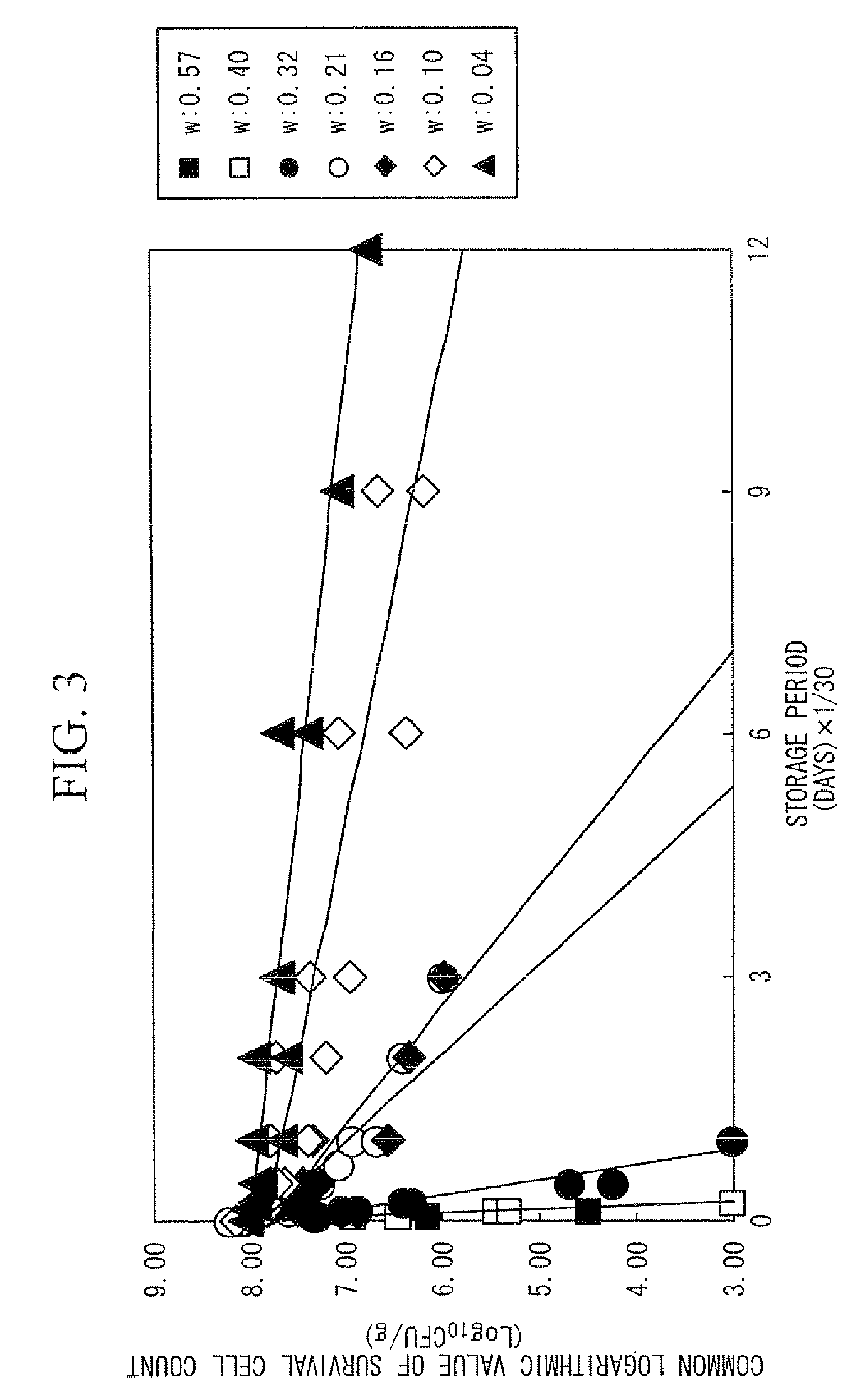
InactiveUS9014990B2Shorten the timeThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingStrain specificityWater activity
By accurately estimating the survival cell count in a probiotic product, the time for developing the product can be shortened. In a device (1) for estimating survival cell count, a calculation unit (14) calculates an estimated result of the survival cell count nt (CFU / g) of a specific strain contained in a composition after storage, in accordance with the following equation (I). (I) Log10nt=Log10n0−t×EXP{(AT×T+BT)w+(CT×T+DT)}, provided that t stands for the storage period (days)× 1 / 30, nt stands for the survival cell count (CFU / g) of the strain contained in the composition after the storage period t (days), n0 stands for the viable cell count (CFU / g) of the strain contained in the composition at the initiation of storage, T stands for the storage temperature (° C.), w stands for the water activity value of the composition, AT and CT stand for experimentally determined coefficients specific to the strain, and BT and DT stand for experimentally determined constants specific to the strain.
Owner:MORINAGA MILK IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com