Fabric flocking adhesive with low-temperature cured capacity
A technology of adhesives and fabrics, applied in the direction of adhesives, adhesive types, polyether adhesives, etc., can solve problems such as increased production costs, easy fires, pollution, etc., to improve heat resistance and heat resistance level, good Effects of chemical stability and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
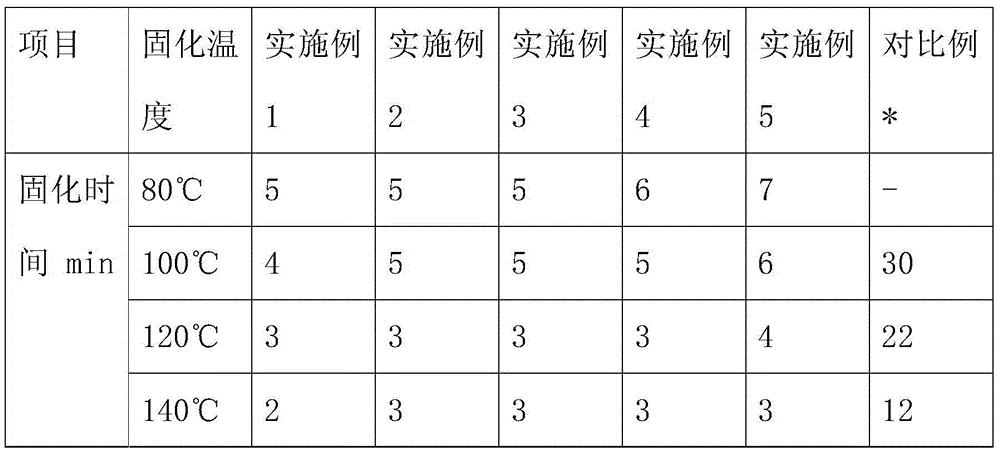
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: A low-temperature curing fabric flocking adhesive, including the following raw materials in parts by weight: 35 parts of acrylate emulsion, 4 parts of polyaryl ether, 6 parts of acryloyl-β-cyclodextrin ester, 1 part of composite crosslinking agent, 0.5 parts of crosslinking monomer initiator, 6 parts of composite emulsifier, 40 parts of deionized water;
[0021] The acrylic emulsion is a compound of methacrylic acid, methyl methacrylate, diethylene glycol dimethacrylate, and butyl acrylate, and its mass part ratio is: 10:1:2:3.
[0022] Further, the composite crosslinking agent includes 0.5 parts of N-methylolacrylamide and 0.5 parts of α-methacrylic acid, and the crosslinking monomer initiator includes 0.3 parts of ammonium nitrate and 0.2 parts of sodium persulfite, The compound emulsifier comprises 3 parts of sodium lauryl sulfate and 13 parts of emulsifier COPS-1.
[0023] The preparation method of described a kind of low-temperature curing fabric flocki...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2: A low-temperature curing fabric flocking adhesive, including the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30 parts of acrylate emulsion, 2 parts of polyaryl ether, 3 parts of acryloyl-β-cyclodextrin ester, 0.5 parts of composite crosslinking agent, 0.5 parts of crosslinking monomer initiator, 4 parts of composite emulsifier, 30 parts of deionized water;
[0030] The acrylic emulsion is a compound of methacrylic acid, methyl methacrylate, diethylene glycol dimethacrylate, and butyl acrylate, and its mass part ratio is: 10:1:1:2.
[0031] Further, the composite crosslinking agent includes 0.1 part of N-methylolacrylamide and 0.4 part of α-methacrylic acid, and the crosslinking monomer initiator includes 0.4 part of ammonium nitrate and 0.1 part of sodium persulfite, The compound emulsifier includes 1 part of sodium lauryl sulfate and 13 parts of emulsifier COPS-1.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3: A low-temperature curing fabric flocking adhesive, including the following raw materials in parts by weight: 45 parts of acrylate emulsion, 5 parts of polyaryl ether, 8 parts of acryloyl-β-cyclodextrin ester, 2 parts of composite crosslinking agent, 1 part of crosslinking monomer initiator, 8 parts of composite emulsifier, 50 parts of deionized water;
[0033] The acrylic emulsion is a compound of methacrylic acid, methyl methacrylate, diethylene glycol dimethacrylate, and butyl acrylate, and its mass part ratio is: 10:2:4:4.
[0034] Further, the composite crosslinking agent includes 1.4 parts of N-methylolacrylamide and 0.6 parts of α-methacrylic acid, and the crosslinking monomer initiator includes 0.8 parts of ammonium nitrate and 0.2 parts of sodium persulfite, The compound emulsifier comprises 5 parts of sodium lauryl sulfate and 13 parts of emulsifier COPS-1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com