Equivalent method for cross-scale thermal analysis of fiber toughening composite material based on multiple criteria such as cross entropy and the like
A composite material and fiber toughening technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of lack of scholars, the difficulty of obtaining a single type of RVE, and the inability to fully reflect the physical properties and dispersion of CMC materials. To achieve the effect of precise correspondence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The cross-scale thermal analysis equivalent method of fiber toughened composite materials based on multiple criteria such as cross entropy in the present invention comprises the following steps:
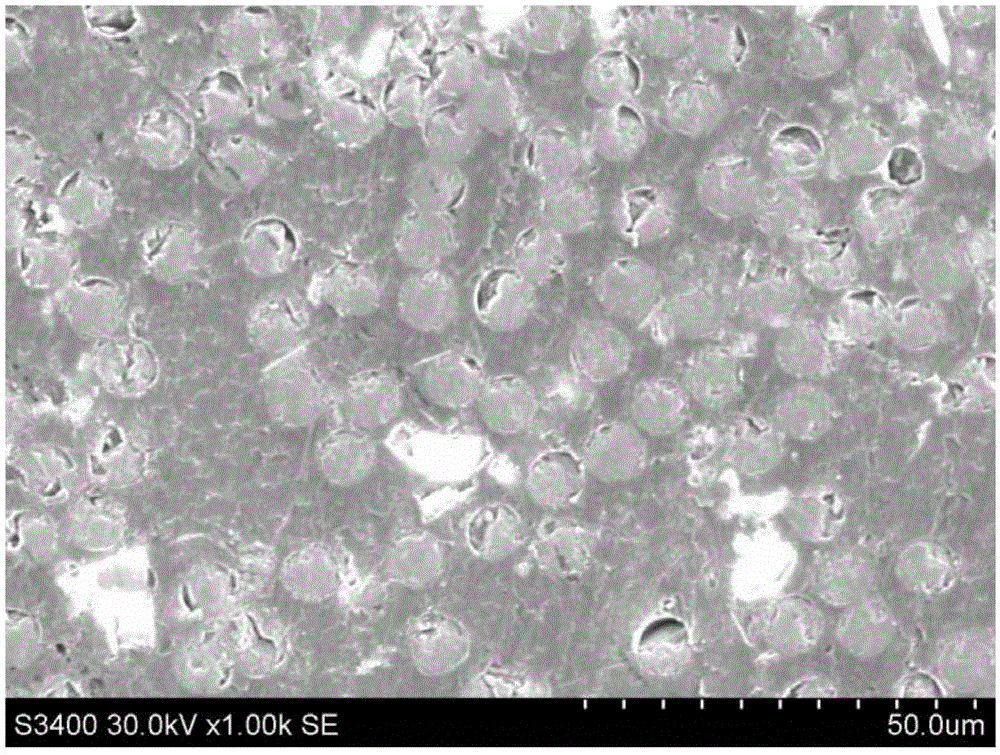
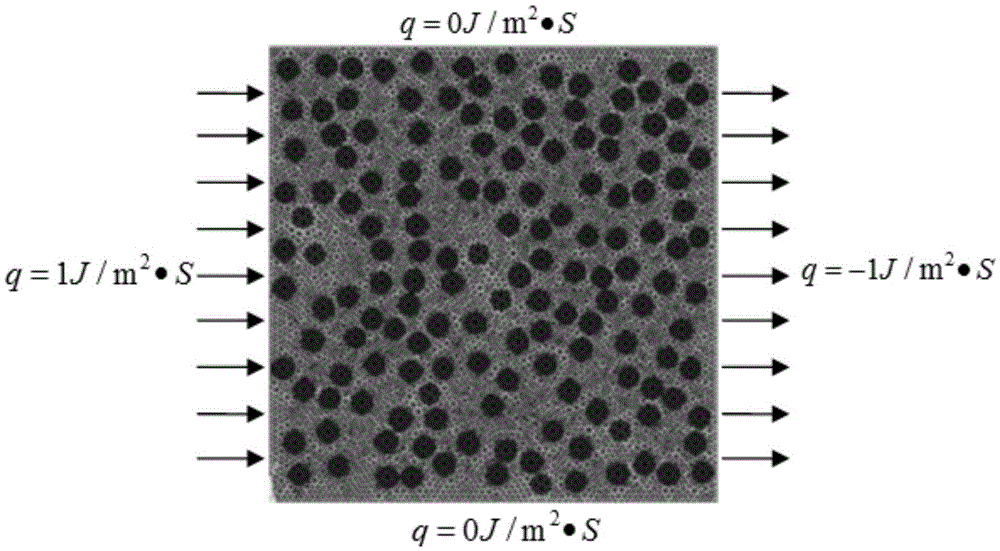
[0041] Step 1: Establish a representative unit (SRVE) with randomly distributed reinforcement phases for the internal structure of the composite material, and the side length of the unit is 20 times the diameter of the fiber reinforcement phase;
[0042] Step 2: Apply constant heat flow boundary conditions on the left and right sides of the SRVE, and apply adiabatic boundaries on the upper and lower sides;
[0043] Step 3: Use the finite element method to calculate the temperature field distribution of the unit, and obtain the corresponding material temperature gradient field, heat flux density field, and equivalent thermal conductivity through post-processing calculations;
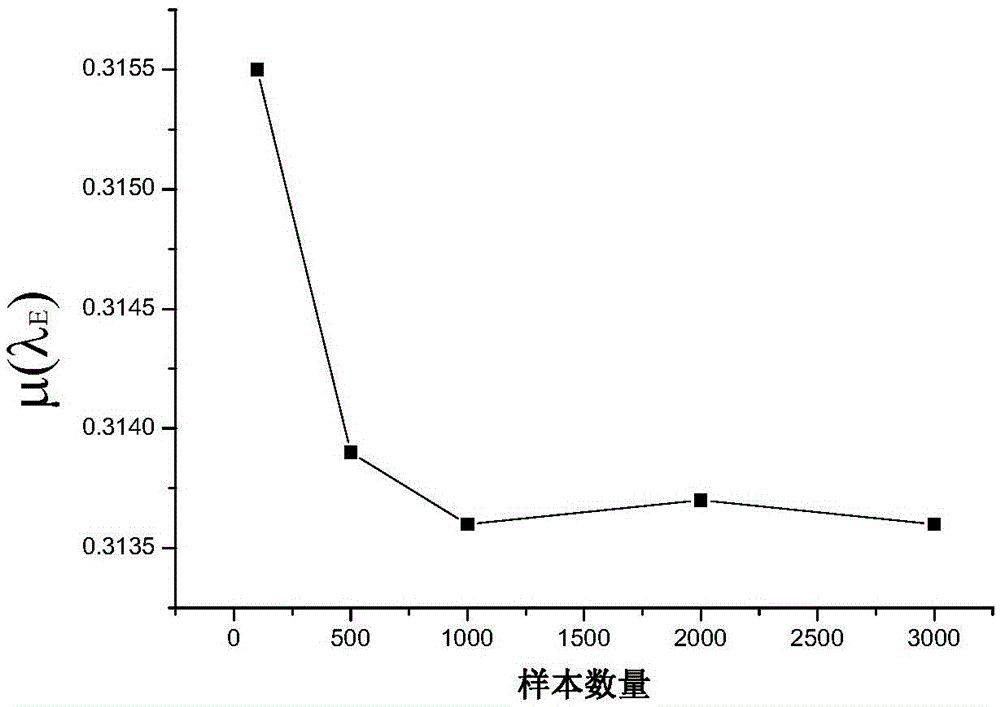
[0044] Step 4: Randomly generate representative units multiple times and use the finite element method...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com