Induced differentiation method for human adipose-derived stem cells
An adipose stem cell and induced differentiation technology, applied in the field of human adipose stem cell induction and differentiation, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory motor neuron function and specificity, low directional transdifferentiation efficiency, etc., to improve the transdifferentiation efficiency and specificity. , good curative effect, high differentiation yield effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The human-derived adipose-derived stem cells in this example are isolated from adipose tissue obtained by human surgery or plastic liposuction, and the isolation, culture, and identification methods are as follows:
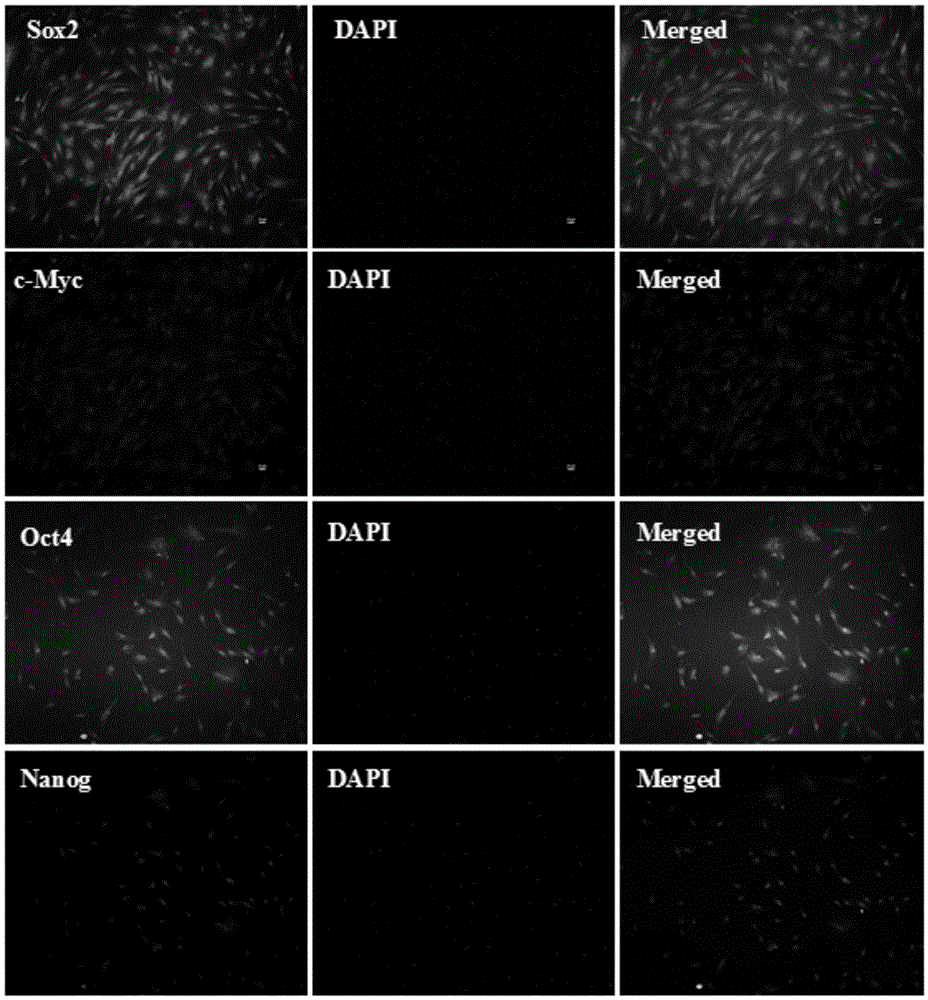
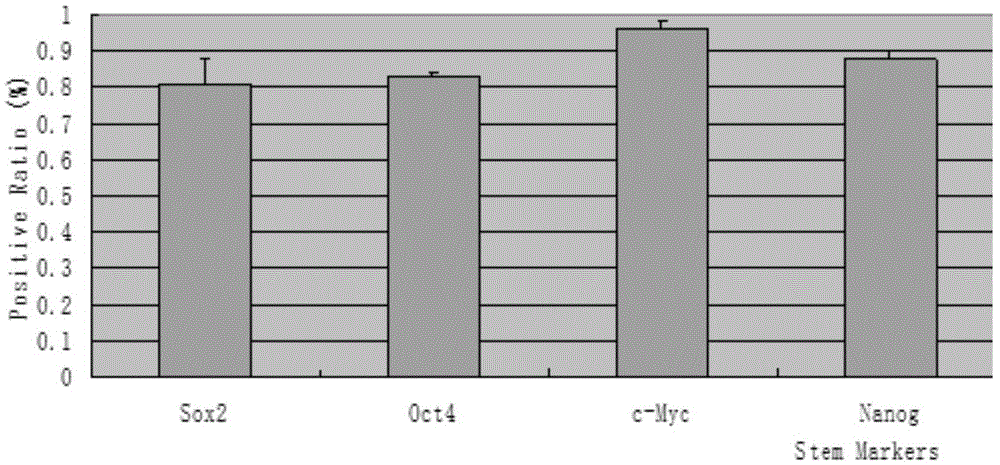
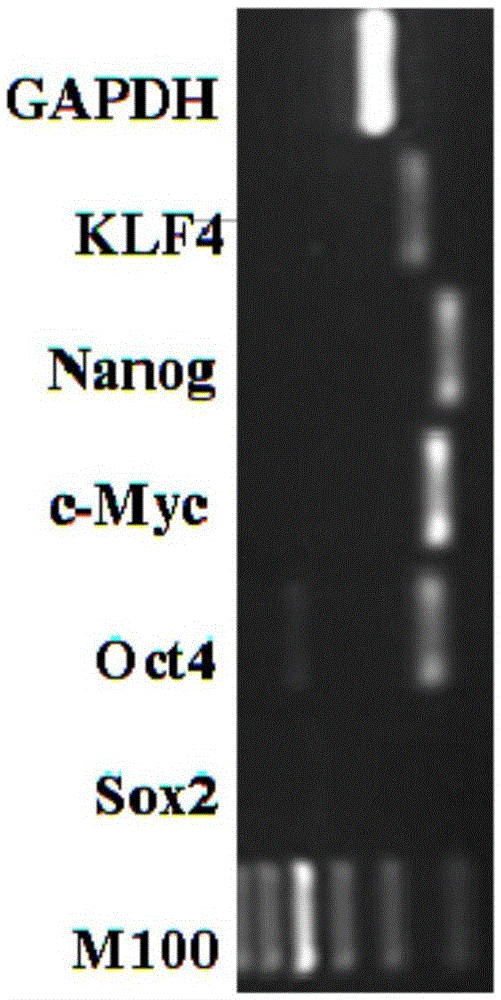
[0031] The human-derived adipose-derived stem cells were isolated and screened from adipose tissue by means of adherent culture, and the isolated human-derived adipose-derived stem cells were characterized from the spindle morphology and cell surface markers, and the isolated and obtained adipose-derived stem cells were analyzed by RT-PCR. Human-derived adipose-derived stem cells were identified, wherein the cell surface markers were CD immune surface markers; the universal markers for identifying the human-derived adipose-derived stem cells by RT-PCR were Sox2, Oct4, c-Myc, Nanog, and KLF4. The obtained human adipose stem cells are used for future use.
[0032] The method for inducing differentiation derived from human adipose stem cells in this embodiment...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The human-derived adipose-derived stem cells in this example are isolated from adipose tissue obtained by human surgery or plastic liposuction, and the isolation, culture, and identification methods are as follows:
[0037] Digest the adipose tissue in 0.075% type Ⅰ collagenase at a temperature of 37°C, and shake it every 5 minutes during the digestion process. After 40 minutes, use DMEM containing 10% serum and 1% P / S / F12 medium to neutralize collagenase, then centrifuge at 1500rpm / min for 10 minutes, discard the upper layer of fat and supernatant, suspend the cell mass at the bottom of the centrifuge tube with serum-containing medium, and let it pass through the 70um cells filter to remove tissue debris;
[0038] Spread the above-mentioned harvested cell filtrate into a 10 cm petri dish, and place it at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO 2 After culturing in a humidified incubator for 24 hours, change the medium and rinse with PBS, then add fresh medium to conti...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The human-derived adipose-derived stem cells in this example are isolated from adipose tissue obtained by human surgery or plastic liposuction, and the isolation, culture, and identification methods are as follows:
[0047] Digest the adipose tissue in 0.075% type Ⅰ collagenase at a temperature of 37°C, and shake it every 5 minutes during the digestion process. After 40 minutes, use DMEM containing 10% serum and 1% P / S / F12 medium to neutralize collagenase, then centrifuge at 1500rpm / min for 10 minutes, discard the upper layer of fat and supernatant, suspend the cell mass at the bottom of the centrifuge tube with serum-containing medium, and let it pass through the 70um cells filter to remove tissue debris;
[0048] Spread the above-mentioned harvested cell filtrate into a 10 cm petri dish, and place it at 37°C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO 2 After culturing in a humidified incubator for 24 hours, change the medium and rinse with PBS, then add fresh medium to conti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com