A Noise Removal Method of Shock Noise Image
A technology that impacts noise and images, applied in image enhancement, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of reducing image signal-to-noise ratio, image blurring, etc., to improve the restoration of image signal-to-noise ratio, increase calculation speed, and improve denoising speed effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] This embodiment is used to compare and illustrate the effect of the image grid processing adopted in the present invention. To this end, two comparative experiments were set up: Experiment 1 without gridding processing, and Experiment 2 with gridding processing, and the image noise density in the experiment was set to 99%.
[0090] 1) In Experiment 1, set the grid size s=512, a=0, which is equivalent to not performing grid processing, and the experimental results are as follows image 3 shown. It can be seen from the experimental results that choosing the least squares filter SLSF effectively repairs the salt and pepper noise pollution pixels, but the processing time is 220 seconds.
[0091] 2) In Experiment 2, set grid size s=256, a=0, the experimental results are as follows Figure 4 As shown, the processing time was reduced to 40 seconds, from Figure 4 As a result, it can be seen that compared image 3 There is no obvious difference in the results of Experiment ...
Embodiment 2
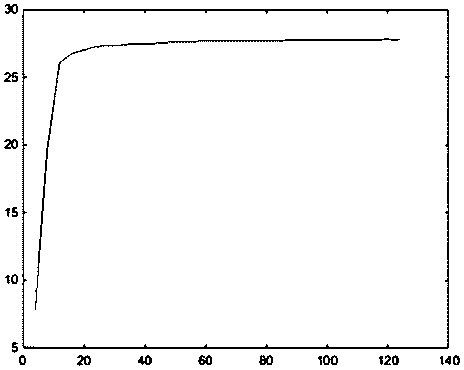
[0094] This embodiment is used to illustrate the effect of using different grid sizes s for different noise pollution densities in the present invention. Four experiments were carried out, namely experiments 3-6.
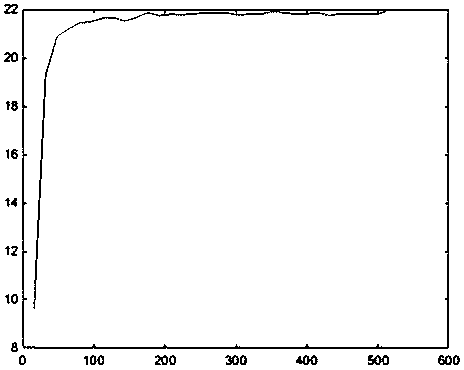
[0095] Experiment 3: The noise pollution density is 99%, the image block size is a multiple of 16*16, the smallest image block is 16*16, and the largest is 512*512. The relationship between image grid size s and denoising image quality PSNR is as follows: Figure 5 As shown, where the ordinate is PSNR, and the abscissa is the image grid size s. The experimental results show that when the noise density is 99%, when the image grid size is 32, the PSNR reaches a high value. Before the image block is 176, the PSNR of the image changes significantly, and after exceeding 176, the change is relatively slow .
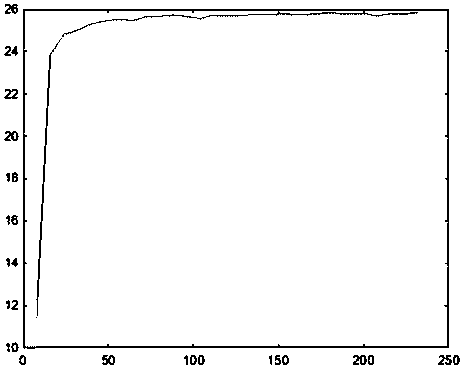
[0096] Experiment 4: The noise pollution density is 95%, the image block size is a multiple of 8*8, the smallest image block is 8*8, and the largest is 232*232. ...
Embodiment 3
[0101] This embodiment is used to illustrate the effect of using the extended image block to eliminate the block effect of the denoising image.
[0102] Experiment 7: The noise density is 90%, the image grid size s=40, a=0, the experimental results are as follows Figure 9 As shown, it can be seen that there are obvious block effects in the denoising results.
[0103] Experiment 8: The noise density is 90%, the image grid size s=40, a=2, the experimental results are as follows Figure 10 shown, it can be seen Figure 9 The blocking effect phenomenon in the system has been well suppressed.
[0104] Experiment 9:
[0105] Taking the Lena image as an example, the simulation test is carried out, and the comparison and analysis results with the existing salt and pepper noise denoising algorithm are as follows: figure 2 shown. exist figure 2 In , the existing algorithm and the effect diagram of noise reduction of the algorithm of the present invention under the condition of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com