Riparian zone sewage reduction method
A riparian belt and river bank technology, applied in the field of non-point source pollution control, to achieve the effect of improving sewage interception capacity and water and soil retention capacity, wide sources, and good nitrogen and phosphorus pollution interception effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
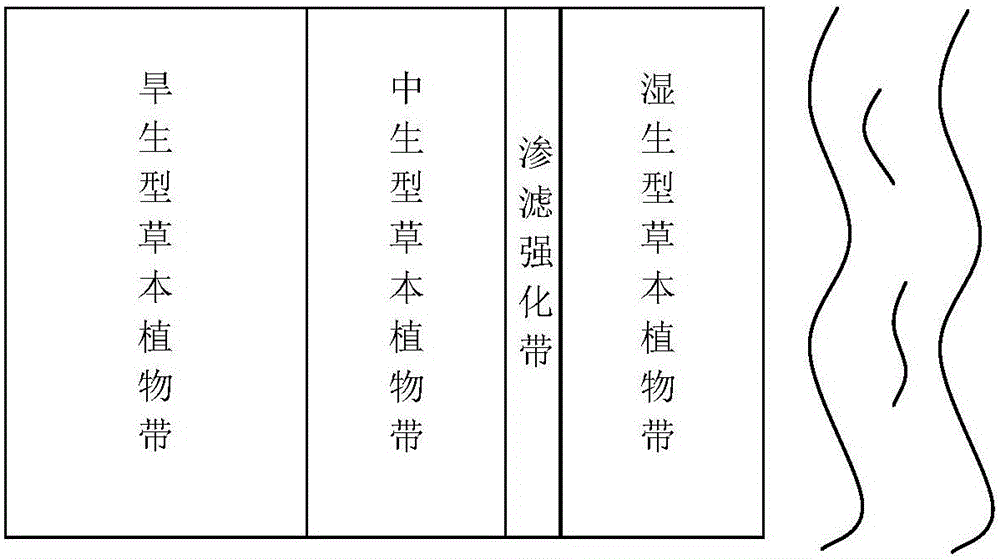
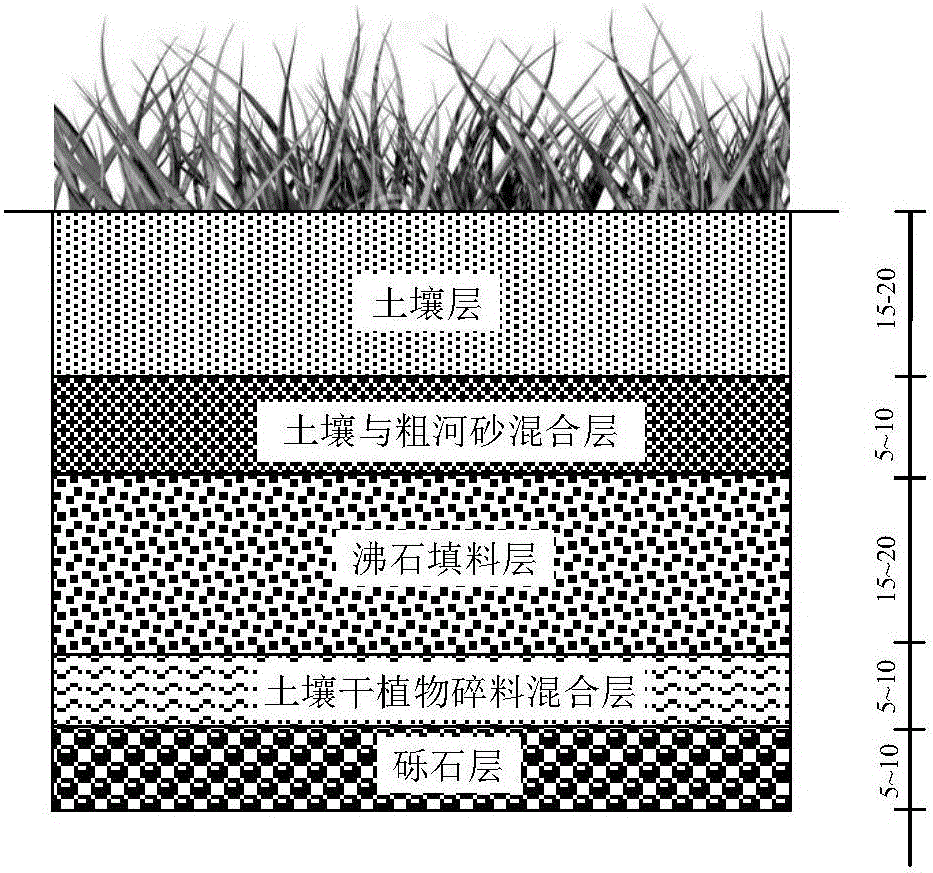
[0029] Using the riparian soil of the Chaobai River in Beijing, a small test was conducted to simulate the treatment of runoff pollution in the enhanced infiltration zone, and at the same time compare the differences in the removal of pollutants by surface seepage. The simulation experiment device of percolation strengthening zone is made of plexiglass. Its main part is 310mm high, 1500mm long, and 150mm wide. A thick sawdust-soil mixture layer with a dry weight ratio of 1:7, and a layer of geotextile is laid between the gravel layer and the sawdust-soil mixture layer to prevent the particulate matter in the seepage flow from entering the bottom outlet; in the sawdust-soil mixture layer The upper part is the percolation layer, which is composed of 7cm thick coarse river sand with a dry weight ratio of 1:1 mixed with filler, and the filler is zeolite. At the same time, considering the growth of herbaceous plants, a 15cm thick soil layer is set on the upper part of the mixture l...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Using the simulated small test device in Example 1, all of them were filled with riparian zone soil, and ryegrass, annual sansevieria, and paradise grass were planted respectively, and the simulated riparian zone pollution interception experiment was carried out. Four small test devices are connected in series to simulate a riparian zone with a width of 6 meters. The initial pollutant concentration in simulated runoff is: total nitrogen 7mg / L, ammonia nitrogen 3mg / L, nitrate nitrogen 4mg / L, and total phosphorus 0.8mg / L. The results showed that ryegrass had a better removal effect on total nitrogen, ammonia nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and total phosphorus. The removal rates of ryegrass to the four pollutants were 30.1%, 21.9%, 33.6% and 40.5%, respectively, and the treatment effect was higher than that of Sansevieria (26.7%, 18.0%, 23.5% and 31.2%) and Paradise grass (24.6%, 19.2%, 22.1% and 29.4%). This shows that perennial herbaceous plants planted in the riparian zon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com