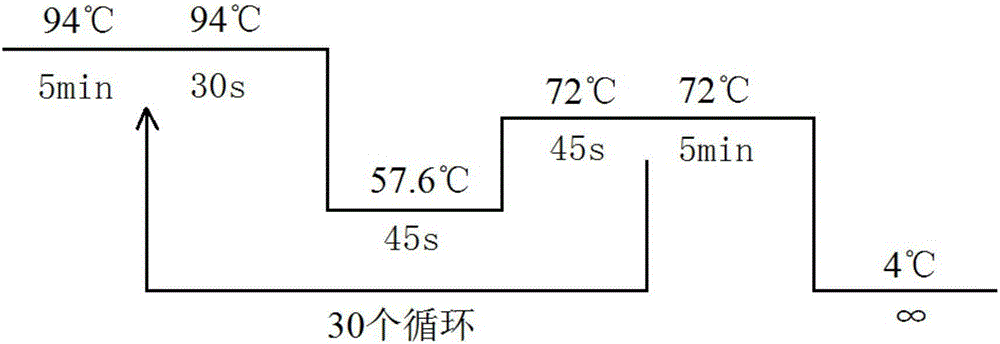
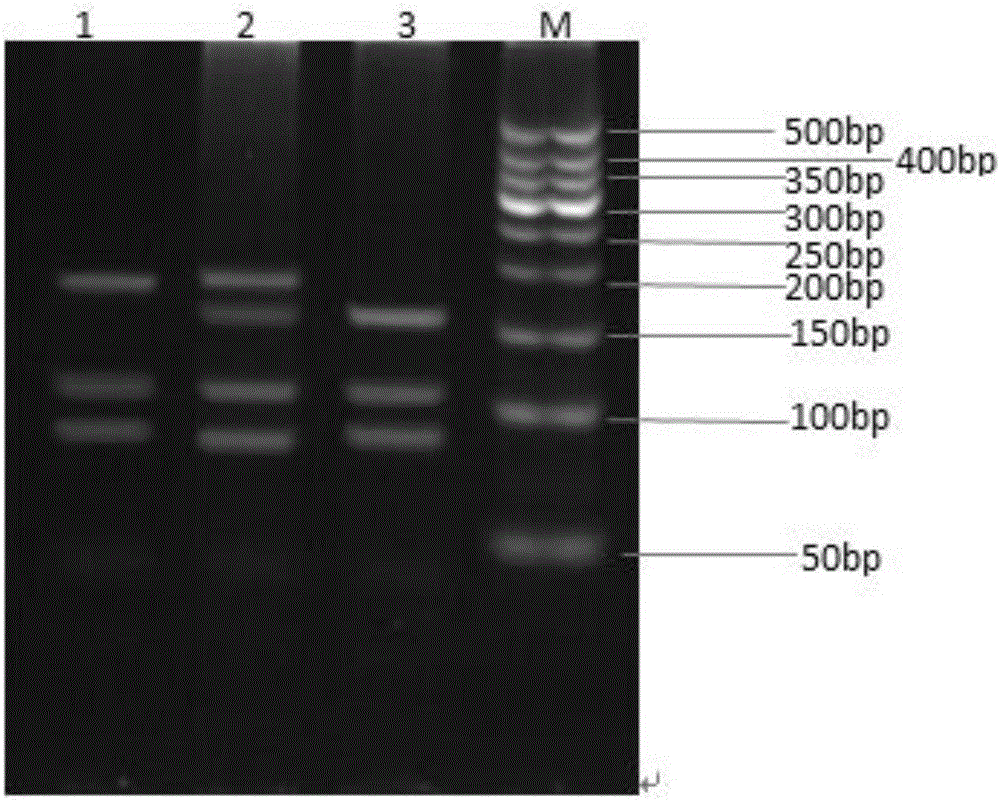
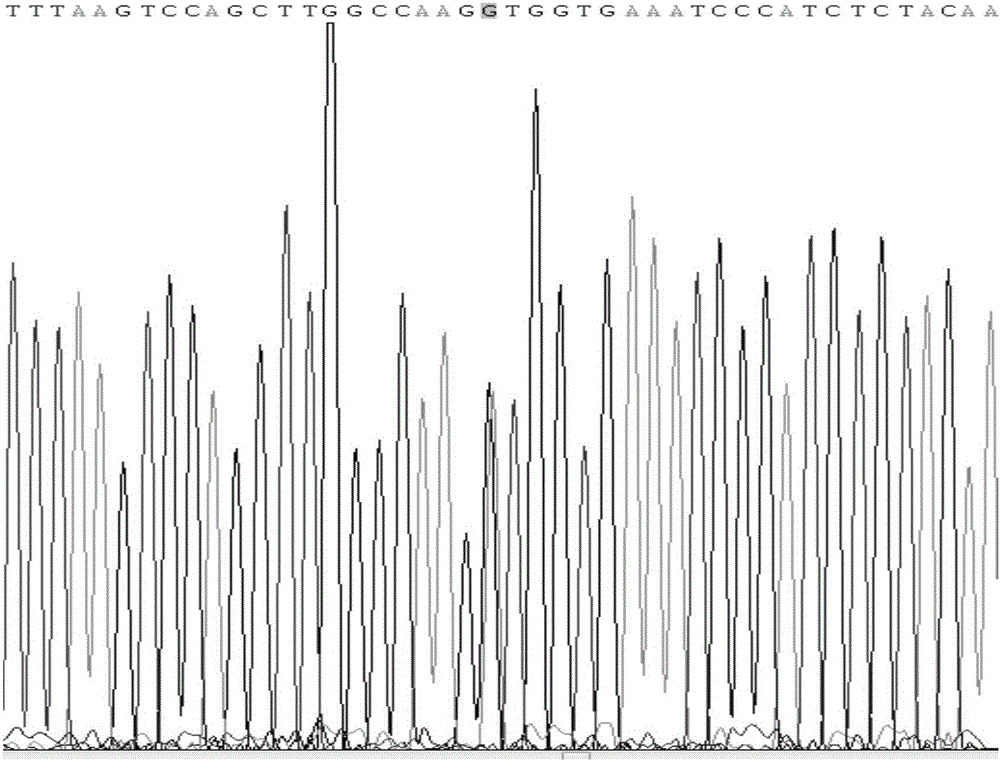
Method for identifying polymorphism of human breast cancer genes RAD51 rs7180135 by aid of BccI
A breast cancer, polymorphism technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of difficult universal use, expensive restriction endonucleases, and high experimental costs, and achieves simple operation, Low cost, predicts the effect of susceptibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Example 1. Determination of human RAD51rs7180135 polymorphism in human breast cancer tissue samples.
[0076] In a specific embodiment of the present invention, the specific steps for detecting the human RAD51 gene polymorphism rs7180135 are as follows:
[0077] (l) Obtain surgically removed gastric cancer tissue, and use the phenol-chloroform method to extract the genomic DNA of the gastric cancer tissue as the DNA to be tested. The extraction steps are as follows:
[0078] 1) Thaw the gastric cancer tissue block, wash away blood stains with normal saline, cut out 0.1g of tissue for grinding, add 1ml of sterilized water, mix upside down, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 10min, discard the supernatant, repeat the above steps twice
[0079] 2) Add 200 μl of DNA lysate and 5 μl of proteinase K, mix well, and digest overnight in a water bath at 55°C.
[0080] 3) After the digestion is completed, add an equal volume of phenol-chloroform mixture (1:1) and shake vigorously to make...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Example 2. Determination of Human RAD51rs7180135 Polymorphism in Whole Blood Specimen of Human Peripheral Blood
[0091] The steps are basically the same as in Example 1, except that the following method is used to extract genomic DNA from human peripheral blood as the DNA to be tested.
[0092] Follow the operation steps of NEP004-1 Whole Blood Genomic DNA Extraction Kit to extract the genomic DNA of the blood sample to be tested. The specific steps are as follows:
[0093] l) After adding 300 μl of blood cells into a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, add 900 μl of cell lysate and mix evenly. After placing it on ice for 10 minutes, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 minute in a centrifuge, discard the supernatant, add 900 μl of cell lysate again, and use a gun After blowing up the precipitate and mixing it, repeat the above steps;
[0094] 2) Add 600 μl solution B solution to the precipitate, gently blow up the precipitate with a pipette gun, add 10 μl proteinase K and mix well, pla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com