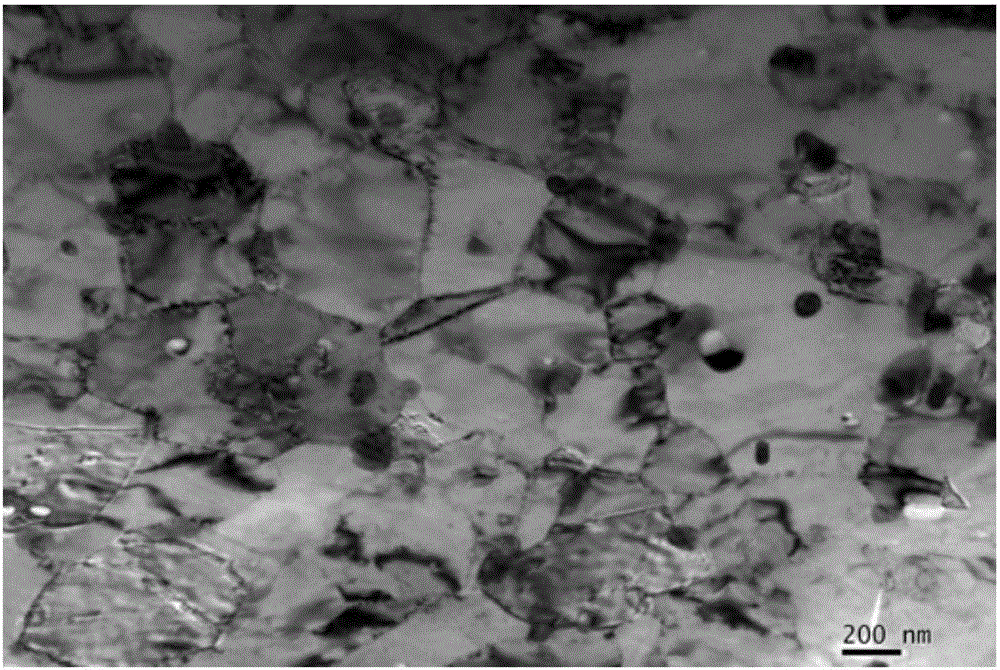
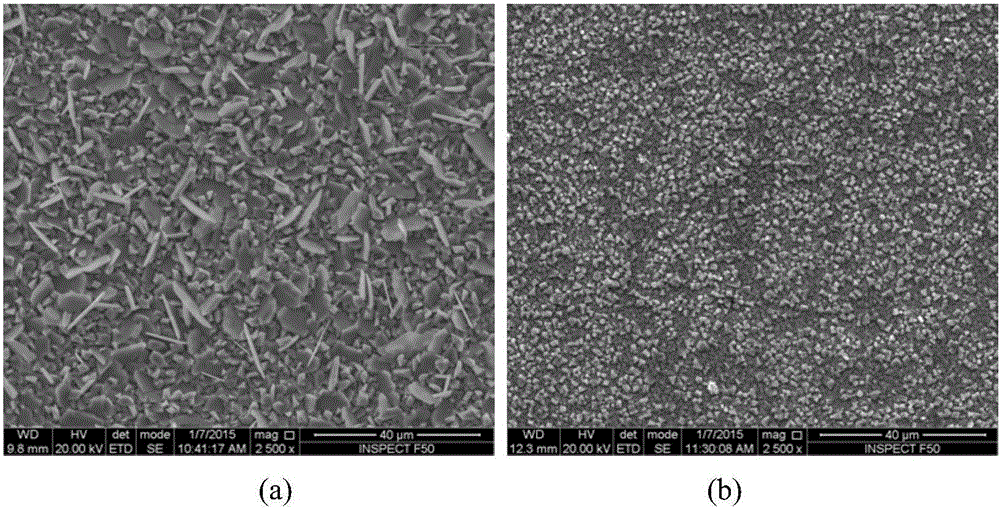
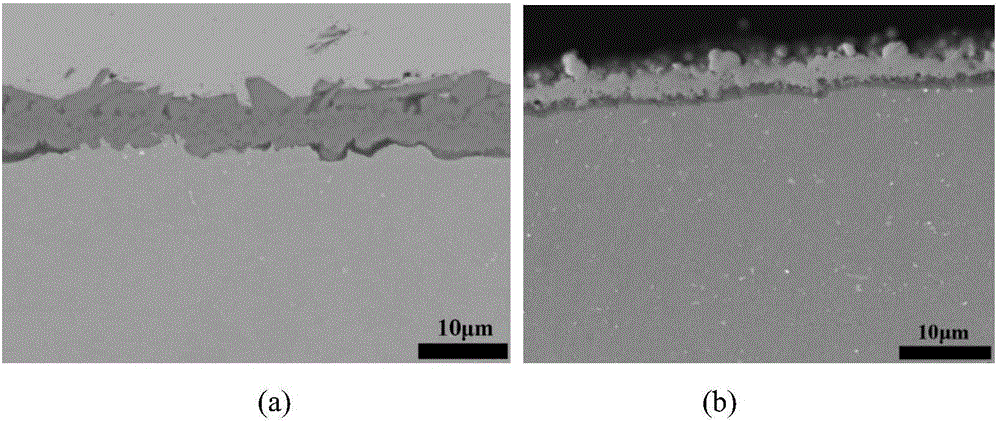
Method for increasing high-temperature strength and antioxidant property of reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steel
A low-activation ferrite, oxidation resistance technology, applied in the field of improving high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance of low-activation ferrite/martensitic steel, can solve the problem of high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance of low-activation ferrite/martensitic steel Oxidation resistance can not be taken into account and other issues, to achieve the effect of rapid formation, high temperature strength and plasticity, good oxidation resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] 1) Melting and thermal processing: 9Cr2WVTa low-activation ferrite / martensitic steel is smelted in a vacuum induction furnace, and the content of impurity elements is strictly controlled. The specific chemical composition (wt.%): C: 0.11%, Cr: 8.86%, W : 1.62%, V: 0.24%, Ta: 0.11%, Mn: 0.45%, Si: 0.05%, S: 0.005%, P: 0.005%, and the balance is Fe. Forging the ingot at 1100°C for 2 hours, the blank forging temperature is 1100°C, and the final forging temperature is above 900°C to obtain a forged plate with a thickness of 30mm;
[0030] 2) Heat treatment: heat the forged alloy in step 1) at 1050°C for 60 minutes, then water-cool; then hold at 750°C for 2 hours, then air-cool;
[0031] 3) Rotary forging deformation: the heat-treated alloy in step 2) is subjected to controllable deformation treatment in separate passes on a precision rotary forging machine. %, cumulative deformation 94%;
[0032] 4) Annealing treatment: heat the deformed alloy in step 3) at 700° C. for 20...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A method for improving high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance of low-activation ferrite / martensitic steel. The main difference from Example 1 is that alloys with different components and process parameters for rotary forging deformation are selected. The specific process steps are as follows:
[0040] 1) Melting and thermal processing: Vacuum induction furnace is used to melt 9Cr2WVTa low-activation ferrite / martensitic steel, and the content of impurity elements is strictly controlled. The specific chemical composition (wt.%): C: 0.13%, Cr: 8.70%, W : 1.74%, V: 0.25%, Ta: 0.10%, Mn: 0.47%, Si: 0.04%, S: 0.006%, P: 0.006%, and the balance is Fe. Forging the ingot at 1100°C for 2 hours, the blank forging temperature is 1100°C, and the final forging temperature is above 900°C to obtain a forged plate with a thickness of 30mm;
[0041] 2) Heat treatment: heat the forged alloy in step 1) at 1050°C for 60 minutes, then water-cool; then hold at 750°C for 2 hours, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com