Power module and manufacturing method therefor
A technology of power module and manufacturing method, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical equipment structural parts, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to make a very large specific surface area, heavy weight, and reduced thermal conductivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
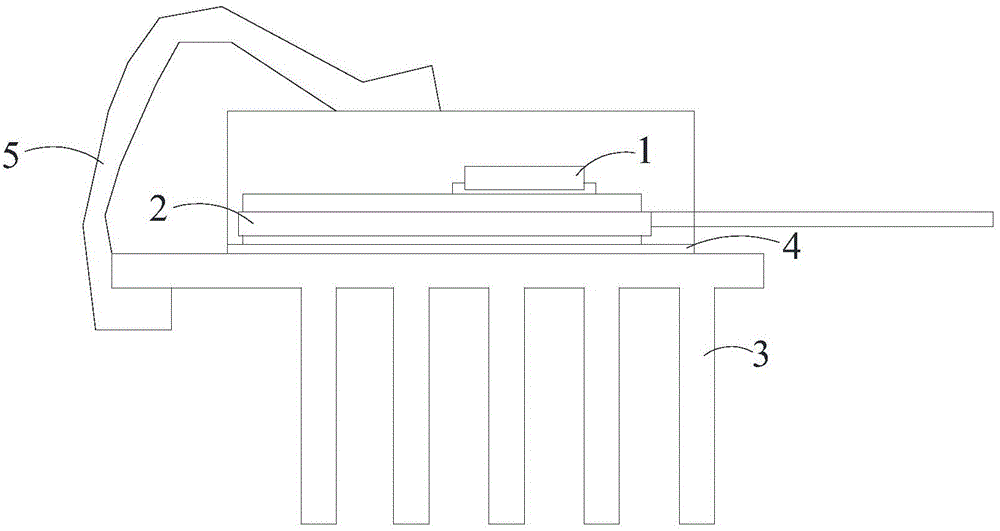
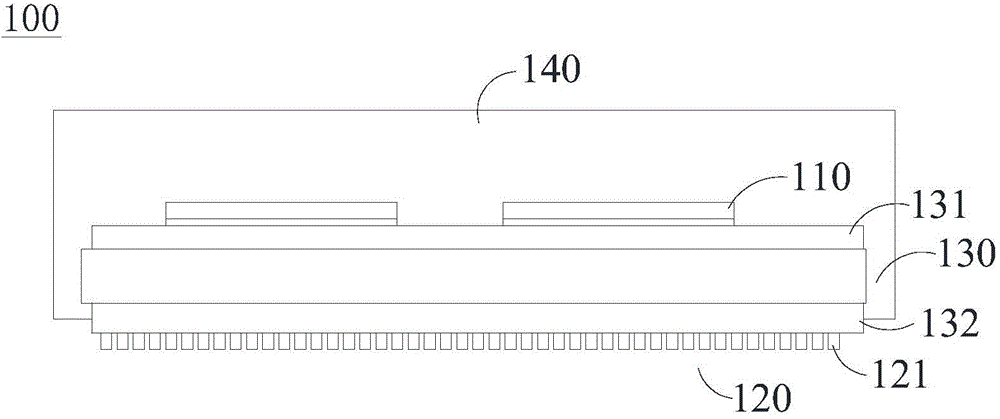
[0033] Please refer to image 3 As shown, a preferred embodiment of the present application provides a power module 100 , such as a power converter, which includes a substrate 130 , a power device 110 and an organic heat dissipation mechanism 120 . The substrate 130 has an opposite upper surface 131 and a lower surface 132. The power device 110 can be a MOSFET (such as a common SiMOSFET, GaN MOSFET, etc.), a diode, an IGBT, etc. In this embodiment, the power device 110 is a power chip. The power device 110 is bonded to the upper surface 131 of the substrate 130 . Wherein: the organic heat dissipation mechanism 120 includes a plurality of organic heat dissipation protrusions (fin) 121, and the organic heat dissipation mechanism 120 is located on the upper surface 131 side of the substrate 130 or the lower surface 132 side of the substrate 130 to dissipate the heat generated by the power device 110 Conducted to the outside through the substrate 130 and the organic heat dissipat...
no. 2 example
[0046] refer to Figure 6 The heat dissipation mechanism of the power module of this embodiment is different from that of the first embodiment in that: the lower surface 132 of the substrate 130 is pasted with a thermal adhesive 150 with a thermal spread 160, and the thermal spread 160 can usually be It is made of materials such as metal (copper / aluminum, etc.), graphite, and ceramics, and an organic heat dissipation mechanism 120 is provided on the windward side of the temperature uniform block 160 (the side away from the substrate 130 ). Other parts of the second embodiment are substantially the same as those of the first embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
no. 3 example
[0048] refer to Figure 7 The heat dissipation mechanism of the power module of this embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that: the organic heat dissipation mechanism 120 also includes a metal heat dissipation part 123, which is pasted on the lower surface 132 of the substrate through a thermally conductive adhesive 150, and the organic heat dissipation raised part 121 is formed on the lower surface of the metal heat dissipation part 123 . In this embodiment, the metal heat dissipation part 123 can be an existing heat sink (such as a heatsink), which includes a plurality of heat dissipation fins 124 . The organic heat dissipation protruding portion 121 is formed on the lower surface of the heat dissipation fins 124 by, for example, dispensing process. The metal heat dissipation part 123 can further expand the heat dissipation area. By partially disposing the organic heat dissipation protruding portion 121 under the existing common heat sink, the space can be ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com