Method of adopting simultaneous distillation and extraction technology to extract volatile oil in agilawood leaf
An extraction technology and agarwood leaf technology are applied in the field of extracting volatile oil from agarwood leaves, and can solve problems such as unsuitability for industrialization, volatilization, and environmental pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example 1
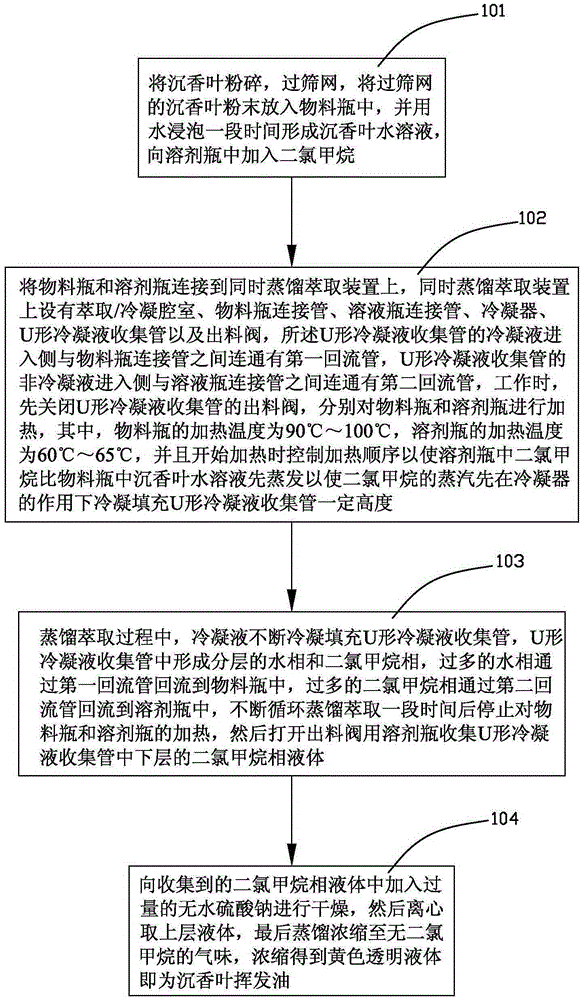
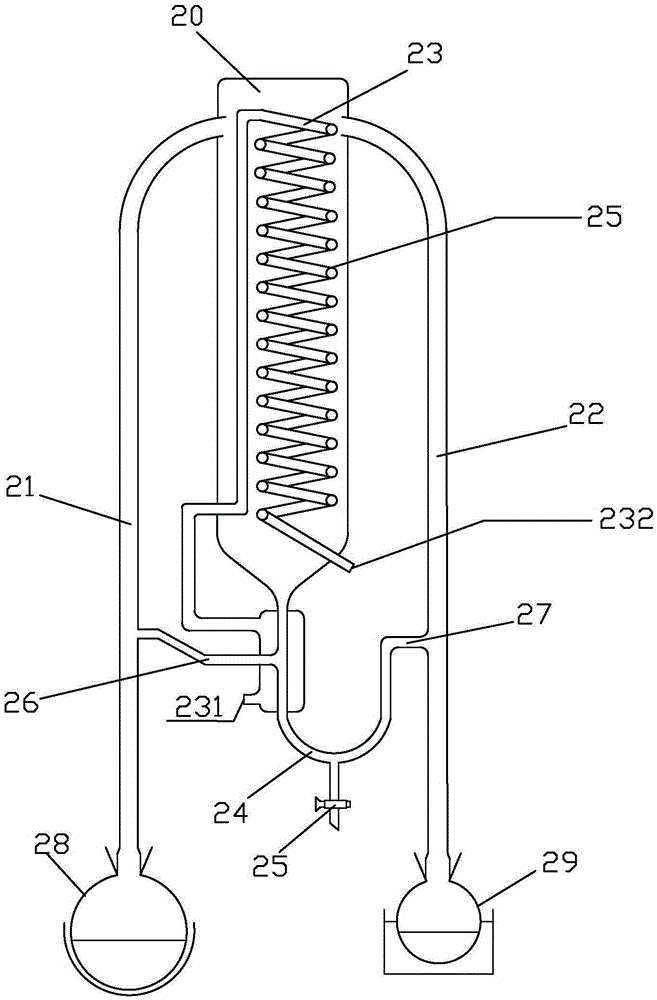
[0038] The agarwood leaves are crushed and passed through a 20-mesh sieve, sealed for later use. Accurately weigh 50.00 g of Agarwood leaf powder after sieving, place in 3L material bottle 28, add water 400mL, soak for 8 hours, add a little zeolite, as figure 2 As shown, it is connected to the left side of the simultaneous distillation and extraction device, another 25mL of dichloromethane is placed in a 100mL solvent bottle 29, connected to the right side of the simultaneous distillation and extraction device, the condenser 23 is opened, the discharge valve 25 is closed, and then heated The solvent bottle 29 makes the condensed dichloromethane liquid fill the U-shaped condensate collecting pipe 24 to a certain height, and then heats the material bottle 28. The material bottle 28 is heated with an electric heating mantle, the temperature is controlled between 90-100°C, and the water is kept boiling to generate steam. The solvent bottle 29 is heated with a constant temperature...
specific example 2
[0040] The agarwood leaves are crushed and passed through a 20-mesh sieve, sealed for later use. Accurately weigh 75.00g of Agarwood leaf powder after sieving, place in 3L material bottle 28, add water 550mL, soak for 10 hours, add a little zeolite, such as figure 2 As shown, connect to the left side of the simultaneous distillation extraction device, take another 25mL dichloromethane and place it in a 100mL solvent bottle 29, connect it to the right side of the simultaneous distillation extraction device, open the condenser 23, close the discharge valve 25, and start heating The solvent bottle 29 makes the condensed dichloromethane liquid fill the U-shaped condensate collecting pipe 24 to a certain height, and then heats the material bottle 28. The material bottle 28 is heated with an electric heating mantle, the temperature is controlled between 90-100°C, and the water is kept boiling to generate steam. The solvent bottle 29 is heated with a constant temperature water bath,...
example 3
[0042] The agarwood leaves are crushed and passed through a 20-mesh sieve, sealed for later use. Accurately weigh 100.00 g of Agarwood leaf powder after sieving, place in 3L material bottle 28, add water 700mL, soak for 9 hours, add a little zeolite, as figure 2 As shown, connect to the left side of the simultaneous distillation extraction device, take another 25mL dichloromethane and place it in a 100mL solvent bottle 29, connect it to the right side of the simultaneous distillation extraction device, open the condenser 23, close the discharge valve 25, and start heating The solvent bottle 29 makes the condensed methylene chloride liquid fill the discharge pipe, and then heats the material bottle 28. The material bottle 28 is heated with an electric heating mantle, the temperature is controlled between 90-100°C, and the water is kept boiling to generate steam. The solvent bottle 29 is heated with a constant temperature water bath, and the temperature is controlled between 60...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com