Method for separating and recovering rare and precious metals in chlorination leaching liquid
A technology for chlorination leaching and rare and precious metals, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of high cost, low recovery rate, poor separation effect, etc., and achieve the effects of good adaptability, short process and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
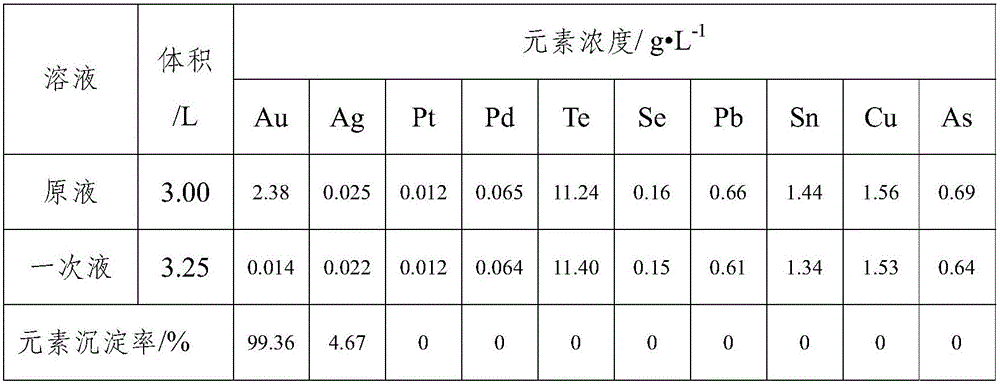
[0016] Accurately measure 3.00L of chlorinated leaching solution and pour it into an acid-resistant reactor, stir and adjust the solution to acidity, add a sodium sulfite solution with a concentration of 100g / L to the reaction solution at a rate of 50mL / min at room temperature, and monitor with a potentiometer The potential of the reaction solution, when the solution potential reaches
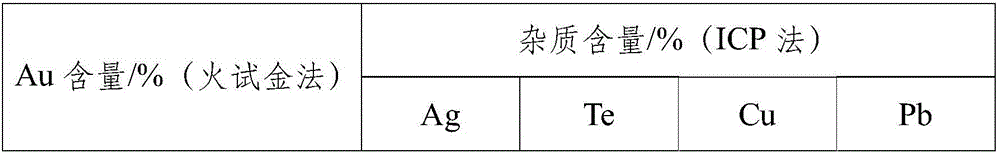
[0017] Stop at 750mV. Solid-liquid separation to obtain gold concentrate and liquid after primary reduction. The volume, composition and precipitation rate of each element of the solution before and after the reaction are shown in Table 1. The gold concentrate was washed with water and hydrochloric acid, dried, and sent to the main metal grade analysis and impurity content analysis. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0018] Table 1 Elemental analysis results before and after primary reduction of chlorinated leachate
[0019]
[0020] Table 2 Analysis results of main metal and impurity con...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Accurately measure 3.00L of chlorinated leaching solution and pour it into an acid-resistant reactor, stir and adjust the solution to acidity, heat to 40°C and feed SO at a flow rate of 40mL / min 2 Gas, and monitor the potential of the reaction solution with a potentiometer, stop when the potential of the solution reaches 690mV, and then separate the solid and liquid to obtain the gold concentrate and the liquid after primary reduction. The volume, composition and element precipitation rate of the solution before and after the reaction are shown in Table 7. The gold concentrate was washed with water and hydrochloric acid, dried, and sent to the main metal grade analysis and impurity content analysis. The results are shown in Table 8.
[0035] Table 7 Elemental analysis results before and after primary reduction of chlorinated leachate
[0036]
[0037]
[0038] Table 8 Analysis results of main metal and impurity content of fine gold ore
[0039]
[0040] Pour t...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Accurately measure 3.00L of chlorinated leaching solution and pour it into an acid-resistant reactor, stir and adjust the solution to acidity, add oxalic acid solid to the reaction solution at a rate of 5g / min at room temperature, and monitor the potential of the reaction solution with a potentiometer. Stop when the solution potential reaches 720mV. Solid-liquid separation to obtain gold concentrate and liquid after primary reduction. The volume, composition and precipitation rate of each element of the solution before and after the reaction are shown in Table 13. The gold concentrate was washed with water and hydrochloric acid, dried, and sent to the main metal grade analysis and impurity content analysis. The results are shown in Table 14.
[0052] Table 13 Elemental analysis results before and after primary reduction of chlorinated leachate
[0053]
[0054] Table 14 Analysis results of main metal and impurity content of fine gold ore
[0055]
[0056] Pour t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com