Method for recovering cobalt and lithium from waste lithium ion batteries
A technology of lithium-ion batteries and positive plates, which is applied in the field of waste metal recycling technology, can solve the problems of environmental secondary pollution, etc., and achieve the effect of low equipment requirements, short process flow, and no secondary pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
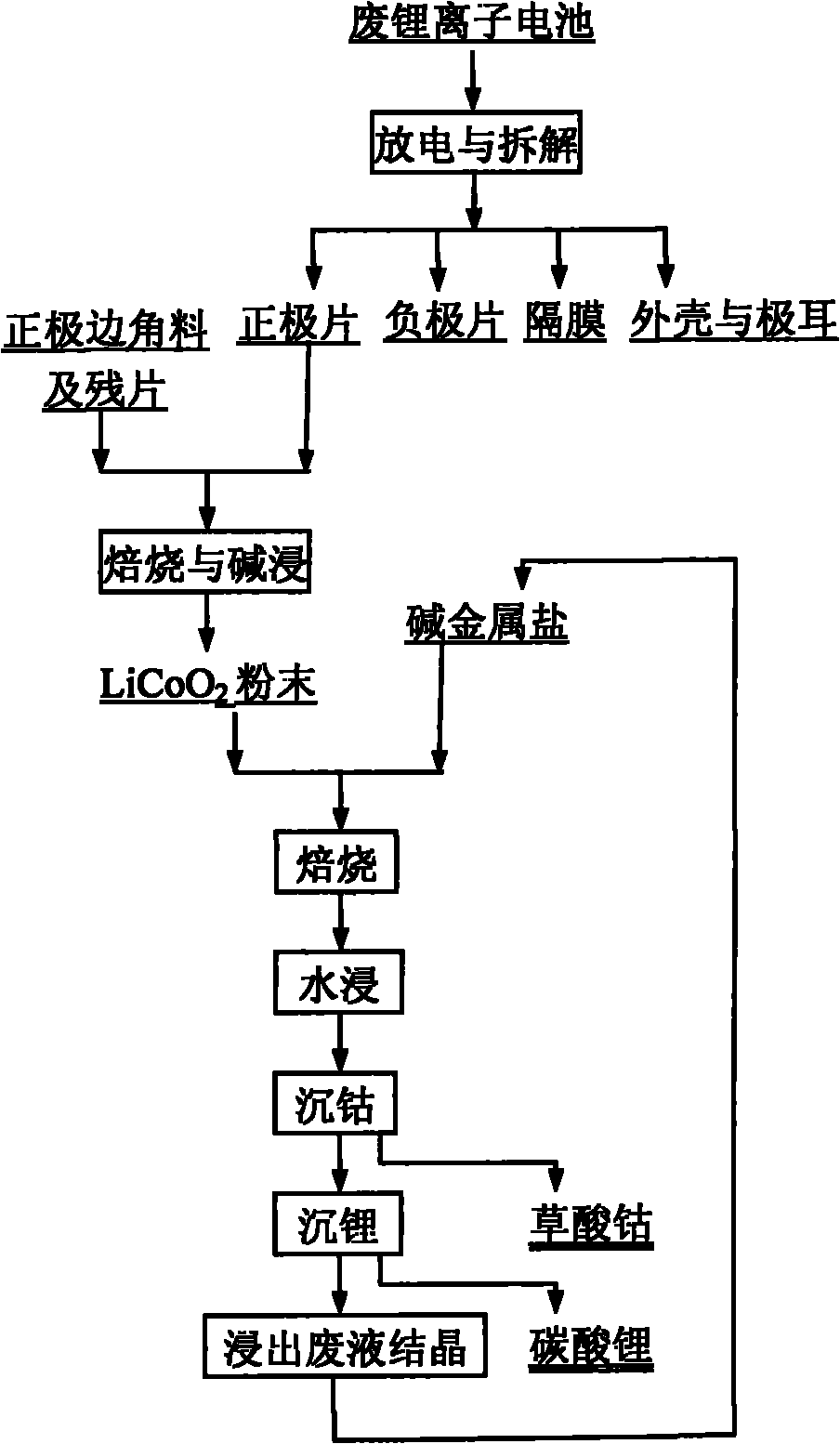
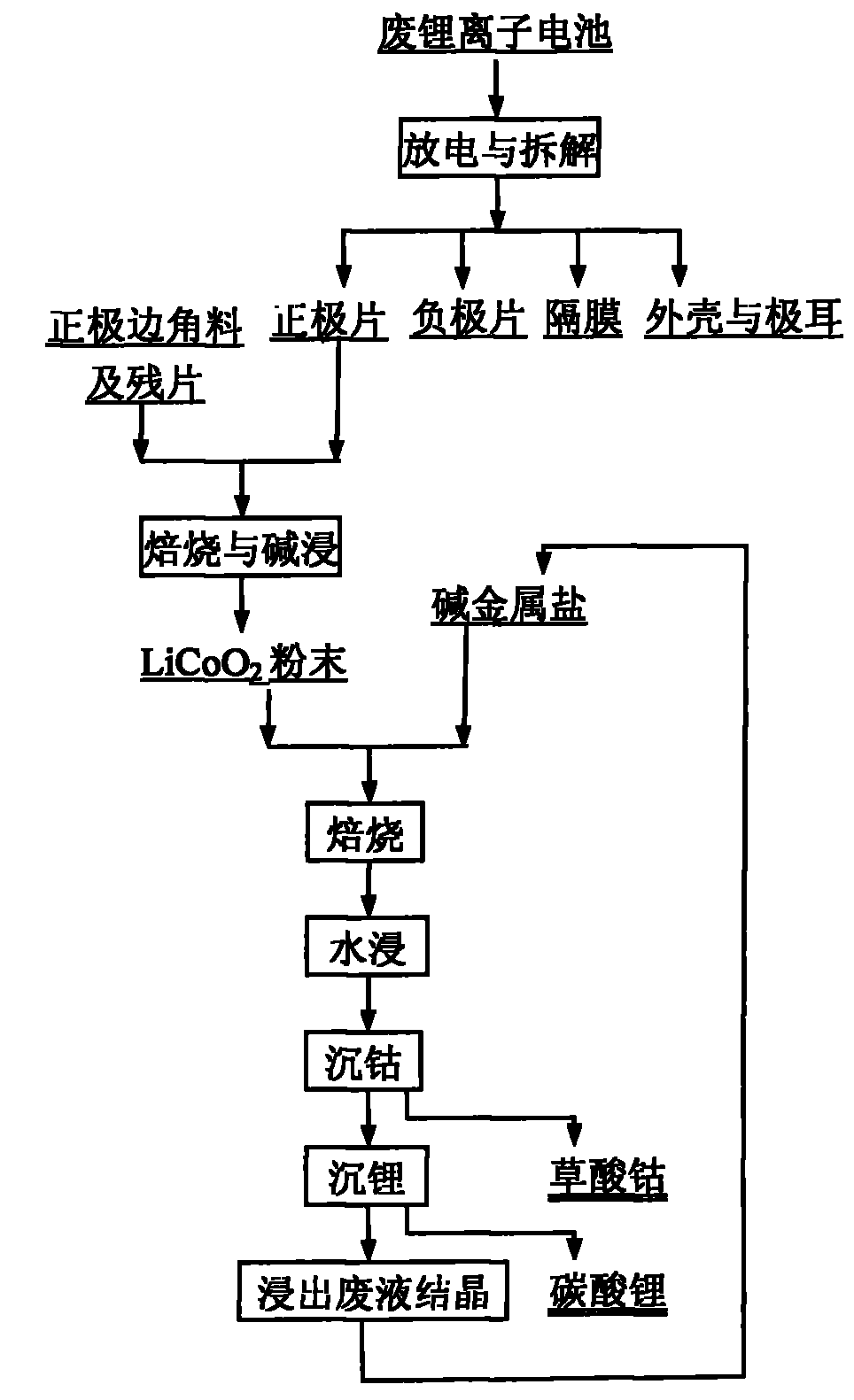
[0027] Weigh the waste LiCoO according to the mass ratio of 1:4.5:4.5 2 Powder, sodium bisulfate, potassium bisulfate mixture 2g, mixed thoroughly, placed in a crucible, roasted at 700°C for 2 hours, leached the contents of the crucible with water at 50°C, the leaching time was 10 minutes. At 50°C, add 0.2mol / l sodium oxalate solution to the leaching solution obtained in the previous step, wash the precipitate, and dry it at 120°C for 2 hours to obtain cobalt oxalate CoC 2 o 4 . At 95°C, 0.5mol / l sodium carbonate solution was added to the leaching solution after cobalt precipitation, and the resulting precipitate was washed and dried at 120°C for 2 hours to obtain lithium carbonate Li 2 CO 3 . The recovery rate of cobalt in the whole process is 99.99%, and the recovery rate of Li is 98.5%.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Weigh the waste LiCoO according to the mass ratio of 1:4.5:4.5 2Powder, sodium bisulfate, potassium bisulfate mixture 2g, mix well, place in a crucible, bake at 700°C for 1 hour, leaching the contents of the crucible with water at 50°C for 10 minutes. At 50°C, add 0.2mol / l sodium oxalate solution to the leaching solution obtained in the previous step, wash the precipitate, and dry it at 120°C for 2 hours to obtain cobalt oxalate CoC 2 o 4 . At 95°C, 0.5mol / l sodium carbonate solution was added to the leaching solution after cobalt precipitation, and the resulting precipitate was washed and dried at 120°C for 2 hours to obtain lithium carbonate Li 2 CO 3 . The recovery rate of cobalt in the whole process is 99.99%, and the recovery rate of Li is 98.5%.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Weigh the waste LiCoO according to the mass ratio of 1:4.5:4.5 2 Powder, sodium bisulfate, potassium hydrogen sulfate mixture 2g, mixed thoroughly, placed in a crucible, baked at 700°C for 0.5 hours, leached the contents of the crucible with water at 50°C, the leaching time was 10 minutes. At 50°C, add 0.2mol / l sodium oxalate solution to the leaching solution obtained in the previous step, wash the precipitate, and dry it at 120°C for 2 hours to obtain CoC 2 o 4 . At 95°C, 0.5mol / l sodium carbonate solution was added to the leaching solution after cobalt precipitation, and the resulting precipitate was washed and dried at 120°C for 2 hours to obtain lithium carbonate Li 2 CO 3 . The recovery rate of cobalt in the whole process is 99.99%, and the recovery rate of Li is 98.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com