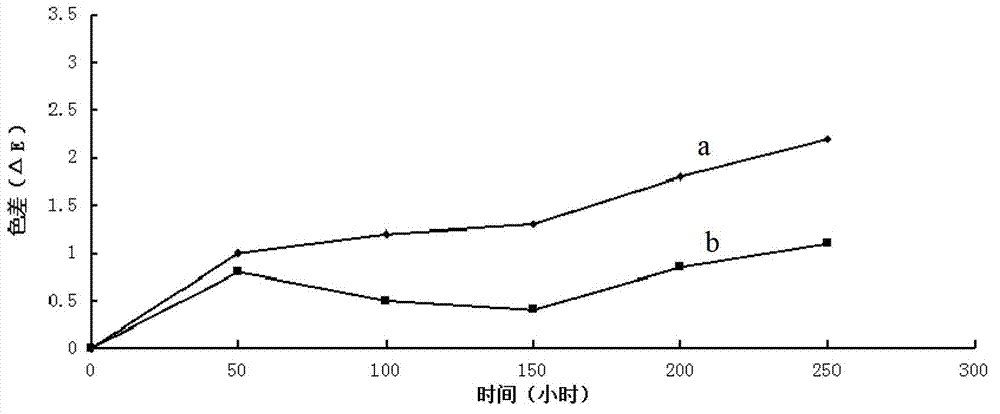
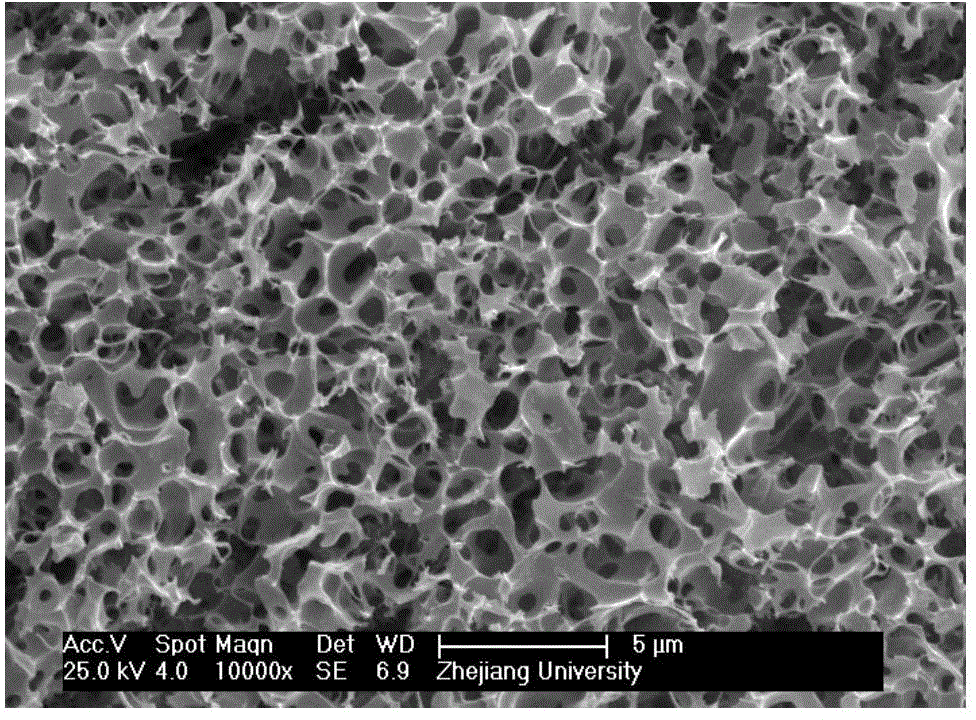
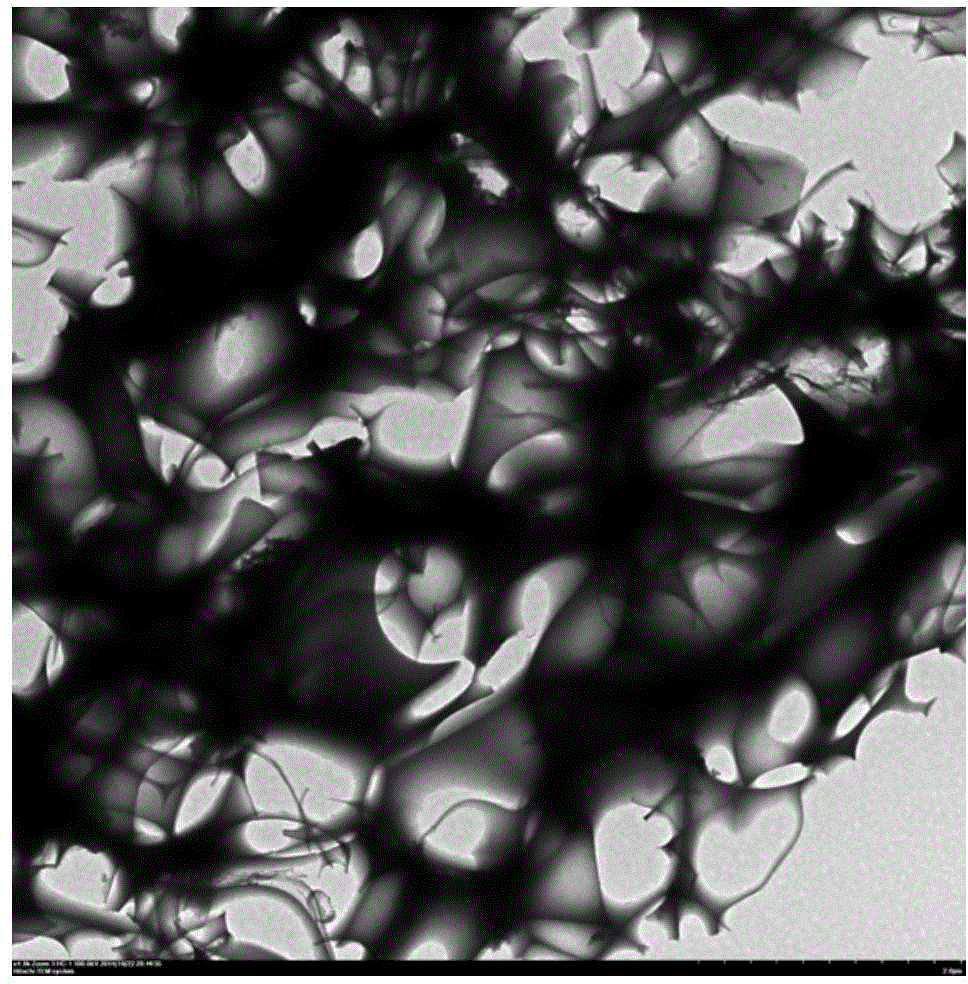
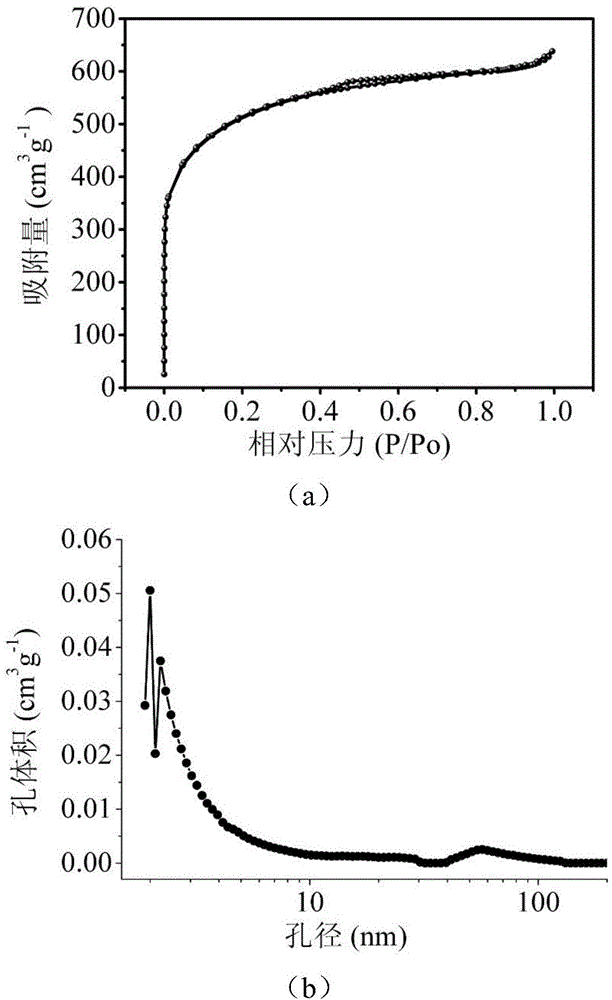
Patents
Literature
535 results about "Sodium oxalate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
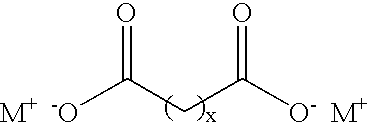
Sodium oxalate, or disodium oxalate, is the sodium salt of oxalic acid with the formula Na₂C₂O₄. It is a white, crystalline, odorless solid, that decomposes above 290 °C. Disodium oxalate can act as a reducing agent, and it may be used as a primary standard for standardizing potassium permanganate (KMnO₄) solutions.
Preparation method of drug and protein sustained-release alginate hybrid gel
InactiveCN103040727AGood biocompatibilityGood slow releasePeptide/protein ingredientsAerosol deliveryBiocompatibility TestingSolvent
The invention provides a preparation method of drug and protein sustained-release alginate hybrid gel. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing calcium alginate hydrogel, then soaking the calcium alginate hydrogel in inorganic salt solutions including trisodium phosphate, diammonium hydrogen phosphate, sodium silicate, sodium carbonate, sodium oxalate and the like at certain concentration to swell for a certain period of time, and soaking the swelled calcium alginate hydrogel into an aqueous solution of drugs and proteins with calcium ions at certain concentration for crosslinking for a period of time, thus obtaining the drug and protein sustained-release alginate hybrid gel. The calcium alginate hydrogel disclosed by the invention can be in the shape of a membrane, a microballoon, a fiber and the like. The method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate and does not adopt any poisonous and harmful solvent; the activity of the immobilized protein is high; the materials are good in biocompatibility; and the drug and protein sustained-release alginate hybrid gel is good in slow release performance, and has good application prospect in the fields of tissue engineering, controlled release, medicine and health, and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method for preparing cubic zirconium phosphate silver-carrying antimicrobial powder
The invention relates to a method for preparing a zirconium phosphate silver-carrying antimicrobial powder, particularly a cubic zirconium phosphate silver containing antimicrobial powder. The cubic zirconium phosphate silver-carrying antimicrobial powder is in the microstructure of a cube, the silver is carried by the cube, and the side of the cube has a length of 400-1,000nm. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a cubic zirconium phosphate carrier, mixing the cubic zirconium phosphate carrier with the aqueous solution of zinc nitrate, stirring to generate a zinc-carrying intermediate; preparing the zinc-carrying intermediate into an aqueous dispersion solution, adding the silver nitrate solution so that the carrier contains 1.5-3.5% of silver ions, stirring, washing, filtering, drying and forging to obtain the final product. The carrier is prepared by adopting the atmospheric-pressure hydrothermal synthesis method, and the hydrofluoric acid used as the template agent in the old process is replaced by the sodium oxalate. The process is simple and convenient to operate, and the equipment has high selectivity. The product and the product producing process are truly safe and nontoxic, the enamel equipment can be used as the production equipment, and the production cost can be saved.
Owner:晋大纳米科技(厦门)有限公司
Preparation method and product of multistage porous carbon material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a multistage porous carbon material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: blending a carbon source with an activator, and performing two-step carbonization and after treatment to obtain the multistage porous carbon material, wherein the two-step carbonization comprises low-temperature carbonization and high-temperature carbonization, the temperature of the low-temperature carbonization is 200-400 DEG C, and the temperature for the high-temperature carbonization is 800-1200 DEG C; the carbon source is a biomass, monosaccharide, disaccharide or polysaccharide of which the cellulose content is more than 20%; and the activator is selected from ammonium oxalate, potassium oxalate, potassium hydrogen oxalate, potassium tetroxalate, sodium oxalate, sodium hydrogen oxalate, sodium tetroxalate, sodium hydrogen carbonate or potassium hydrogen carbonate. The invention provides the preparation method of the multistage porous carbon material rich in macropore, and according to the preparation method, physical expansion and chemical activation are utilized, and a carbon source is used as a raw material to match with a specific activator in order to prepare the multistage porous carbon material rich in macropore; and the raw material is low in price and easy to obtain, the method is simple and strong in sustainability and has a potential for large-scale production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Refining process of biodiesel byproduct crude glycerol
InactiveCN102952000AHigh yieldHigh purityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound separation/purificationBiodieselGlycerol
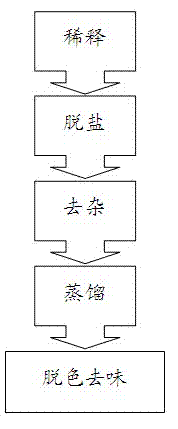
The present invention provides a refining process of biodiesel byproduct crude glycerol, and relates to the technical field of chemical product production. The refining process includes diluting, desalting, removing impurity, distilling, decoloring and deflavouring. The high-quality refined glycerine is produced by employing the technologies of sodium oxalate complexing impurity removal and active carbon decoloring and deflavouring. The refining process is simple, high in glycerin yield, high in finished refined glycerin purity, and good in product quality.
Owner:江苏洁美生物能源有限公司
Preparation methods of 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid and 2,5-furanyl polyester
InactiveCN108997278ALow costLow priceOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionSodium bicarbonatePolyester
The invention provides a preparation method of 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid. The preparation method comprises the following steps: A), with non-grain biomass as a raw material, preparing furfural; B), oxidizing the furfural to obtain furoic acid; C), performing an addition reaction on the furoic acid and carbon dioxide under the action of a catalyst to obtain the 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid, whereinthe catalyst is one or more of potassium carbonate, sodium oxalate, sodium nitrate, potassium nitrate, sodium nitrite, potassium nitrite, potassium acetate, sodium acetate, potassium formate, sodium formate, sodium hydrogen carbonate, potassium hydrogen carbonate, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide. The furfural is prepared from the non-grain biomass as the raw material, so that the raw material cost is low; the furoic acid reacts with the carbon dioxide under the action of the specific catalyst to obtain the 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid; the catalyst is low in price; the used carbon dioxide is environment-friendly; by the preparation method, the yield is high.
Owner:芜湖万隆新材料有限公司
Method for synchronously extracting boron and iron in paigeite
ActiveCN102899434AHigh reactivitySolve the shortcomings of insignificant separation effectChemical industryProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingSodium sulfate
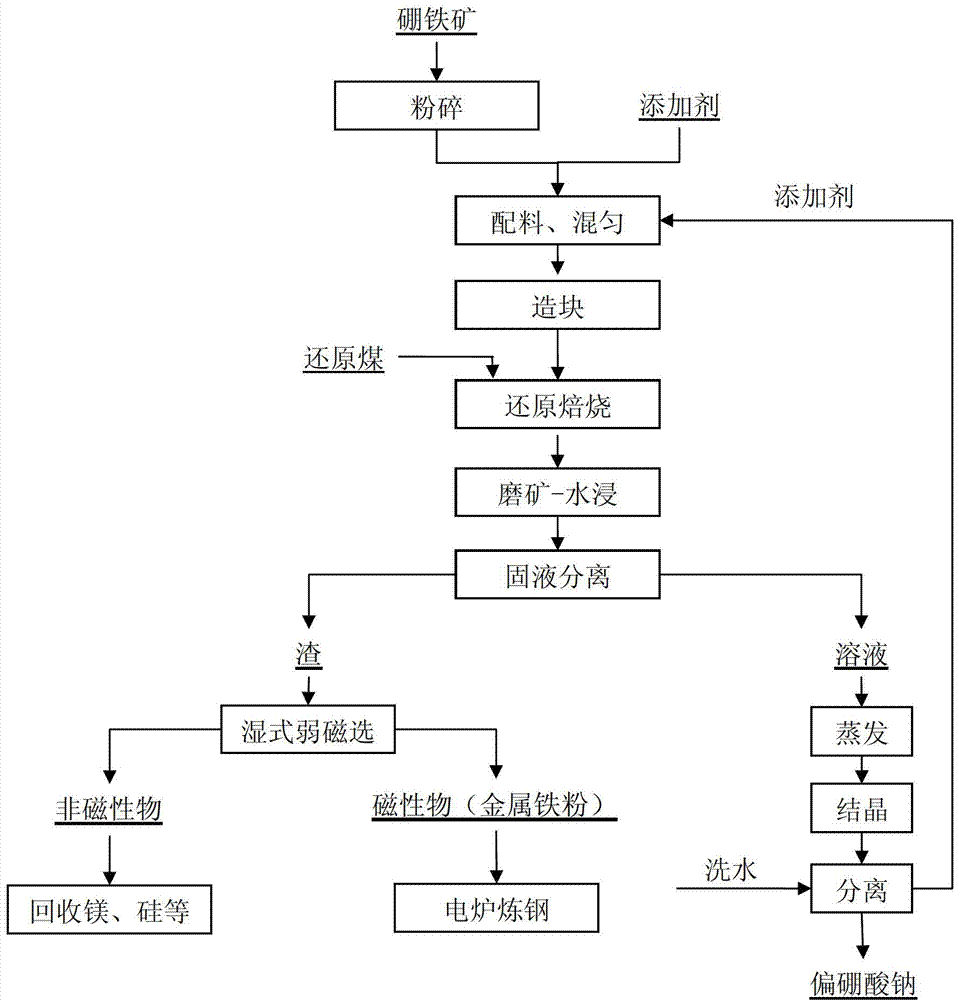
The invention provides a method for synchronously extracting boron and iron in paigeite. The method comprises the following steps: fully mixing a paigeite powder and an additive composed of sodium carbonate, sodium sulfate, natrium humate, sodium fulvate and sodium oxalate by mixing, agglomerating, performing reduction roasting on dried paigeite agglomerates which take coal as a reducing agent, cooling the roasting agglomerates and placing in a bowl mill, synchronously grinding ore and leaching by water, performing solid-liquid separation on a pulp to obtain a filtrate containing sodium metaborate and filter residues containing metallic iron powder, evaporating and crystallizing a filtrate to obtain the sodium metaborate crystals; employ a wet type weak magnetic separation on the filter residue to obtain the directly reduced metallic iron powder with iron grade greater than 90%, wherein the metallic iron powder is a high-quality furnace material used for making steel of an electric furnace; and treating the magnetic separation nonmagnetic products to recover the valuable components such as magnesium and silicon. The method has the advantages of strong raw material adaptability, simple process flow, high production efficiency, less energy consumption, low cost, good comprehensive recovery effect of ferroboron and high product added value. The method provided by the invention can provide technical support for efficiently using the paigeite with abundant reserve volume for our country, and has wide popularization and application prospects.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Combined chemical for fireworks and its prepn process
InactiveCN1810741AReasonable ratio of material selectionImprove thermal stabilityExplosivesSlagFireworks
The present invention is one kind of combined chemical for fireworks and its preparation process, and aims at providing one kind of combined chemical for fireworks possessing high heat stability, high mechanical sensitivity and high safety for compounding, producing, storing and transporting. It is ignited only in burning its fuse. The combined chemical consists of oxidant of barium nitrate and / or potassium nitrate; and inflammable including one or several of sulfur, aluminum powder, Al-Mg alloy powder, charcoal powder, titanium powder, coal powder, alumina slag, iron slag, carbon slag, resin and starch dextrin in the ratio of 100 to 10-120. It may also contain coloring agent of barium nitrate, strontium nitrate, copper carbonate and / or sodium oxalate; and effect chemical comprising sounder and color bead.
Owner:邵兴宾
Method for obtaining large-hole-diameter double-through-hole AAO membrane
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a large-hole-diameter double-through-hole AAO membrane. The method comprises the following steps that 1, aluminum foil is pretreated, and thus aluminum foil with the surface being as smooth and flat as a mirror is obtained; 2, a large-hole-diameter single-through-hole AAO membrane with an aluminum base and a blocking layer is prepared through a secondary anodic oxidation method, wherein an anodic oxidation electrolyte is a mixed solution of phosphoric acid (with the content being 0.05 M-0.2 M) and sodium oxalate (with the content being 0.01 M-0.03 M); and 3, the aluminum base and the blocking layer of the large-hole-diameter single-through-hole AAO membrane are removed through a corrosion stripping method, wherein aluminum base corrosive liquid is a mixed solution of copper chloride (with the content being 0.1 M-0.15 M) and ferric chloride (with the content being 0.15 M-0.18 M). The method has the advantage that the double-through-hole AAO membrane which is large in hole diameter, orderly in hole arrangement, large in area and good in integrality is obtained.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method of purifying organic substance in solution by Bayer method
InactiveCN101058433AAluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide purificationAlkali-metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationSodium aluminateSodium sulfate
The invention discloses a purifying method of sodium aluminate through Baeyer method, which comprises the following steps: evaporating the solution of Baeyer method to condense; adding the crystal additive of one or two composition of sodium carbonate, sodium sulfate, sodium oxalate, calciumaluminate and alumina in the sintering kiln; cooling; crystallizing; evolving organics with additive, sodium carbonate and sodium sulfate; separating the sintering material to obtain the product; combining the evaporating crystal and seed organically; reducing bad influence for organics in the manufacturing course.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
Water flooding oil reservoir fireflood production well selective water controlling and channelling sealing method
ActiveCN107882531ANo pollution in the processWith a clear purposeFluid removalDrilling compositionFatty alcoholSodium sulfate
The invention provides a water flooding oil reservoir fireflood production well selective water controlling and channelling sealing method. The method comprises the steps that a gas channelling preferential migration pathway is sealed and blocked using a channelling sealing agent; and high water-cut preferential migration pathways near an oil well are selectively sealed and blocked. The channelling sealing agent comprises an alkali-resistant surfactant foaming agent and an auxiliary alkaline reducing agent; and the alkali-resistant surfactant foaming agent is selected from one or more of sodium lauryl sulfate, fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate, rosin soap materials, animal and vegetable protein materials, papermaking black liquor and the like, and the auxiliary alkaline reducing agent is sodium oxalate. The water flooding oil reservoir fireflood production well selective water controlling and channelling sealing method is a selective water controlling and channelling sealing integrated technology.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
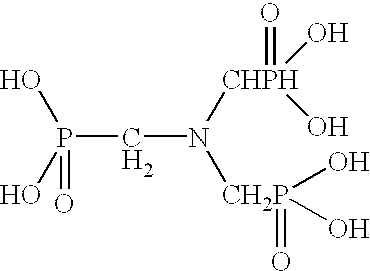
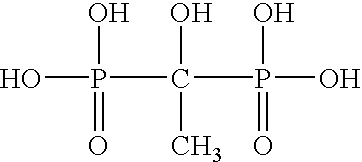
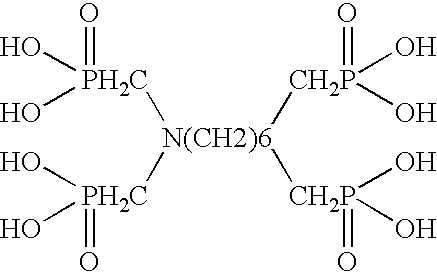
Ammonium polyphosphate solutions containing multi-functional phosphonate corrosion inhibitors
InactiveUS6846437B2Reduce corrosionOther chemical processesLiquid fertilisersSuspending AgentsFerrous Gluconate
A corrosion-inhibited fire retardant composition is provided that comprises at least one ammonium polyphosphate, at least one suspending agent, at least one phosphonate selected from a group consisting of aminotri(methylenephosphonic acid), 1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid, hexamethylenediaminetetra(methylenephosphonic acid), diethylenetriaminepenta(methylenephosphonic acid), salts thereof, and mixtures thereof and a corrosion inhibiting system. The corrosion inhibiting system is comprised of at least one corrosion inhibiting compound selected from a group consisting of azoles, insoluble ferric pyrophosphate, soluble ferric pyrophosphate, ferrous oxalate, ferric citrate, ferrous sulfate, ferric ammonium citrate, insoluble ferric orthophosphate, soluble ferric orthophosphate, ferric ammonium oxalate, ferric ammonium sulfate, ferric bromide, ferric sodium oxalate, ferric stearate, ferric sulfate, ferrous acetate, ferrous ammonium sulfate, ferrous bromide, ferrous gluconate, ferrous iodide, ferric acetate, ferric fluoroborate, ferric hydroxide, ferric oleate, ferrous fumarate, ferrous oxalate, ferrous oxide, ferric lactate, ferric resinate, and any combination thereof. Methods of making and using the same are also described. In addition, agricultural plant nutrients comprising the same are provided.
Owner:PERIMETER SOLUTIONS LP
Fire retardant compositions with reduced aluminum corrosivity
InactiveUS6905639B2Reduced-tendency to corrode various metalBroaden applicationFireproof paintsAntifouling/underwater paintsBiopolymerFerrous Gluconate
Corrosion-inhibited fire retardant compositions and methods of making and using the same are provided. The corrosion-inhibited fire retardant compositions are comprised of at least one fire retardant component, at least one biopolymer having a particle size diameter of less than about 100 microns, and a corrosion inhibiting system. The corrosion inhibiting system is comprised of at least one corrosion inhibiting compound selected from a group of compounds including azoles, insoluble ferric pyrophosphate, soluble ferric pyrophosphate, ferrous oxalate, ferric citrate, ferrous sulfate, ferric ammonium citrate, soluble ferric orthophosphate, insoluble ferric orthophosphate, ferric ammonium oxalate, ferric ammonium sulfate, ferric bromide, ferric sodium oxalate, ferric stearate, ferric sulfate, ferrous acetate, ferrous ammonium sulfate, ferrous bromide, ferrous gluconate, ferrous iodide, ferric acetate, ferric fluoroborate, ferric hydroxide, ferric oleate, ferrous fumarate, ferrous oxide, ferric lactate, ferric resinate and any combination thereof. In a specific embodiment, the corrosion-inhibited fire retardant composition includes a xanthan biopolymer.
Owner:PERIMETER SOLUTIONS LP
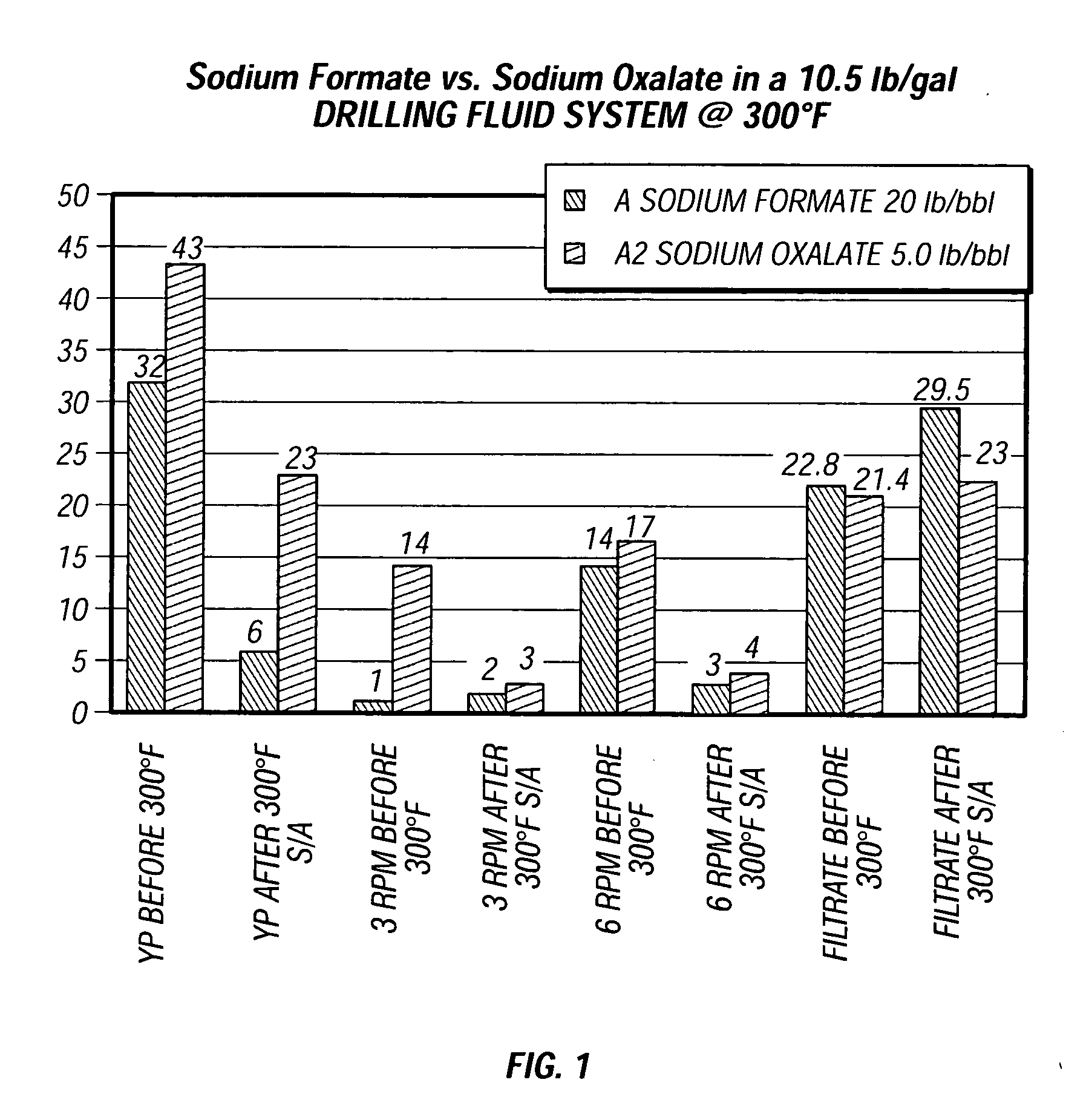
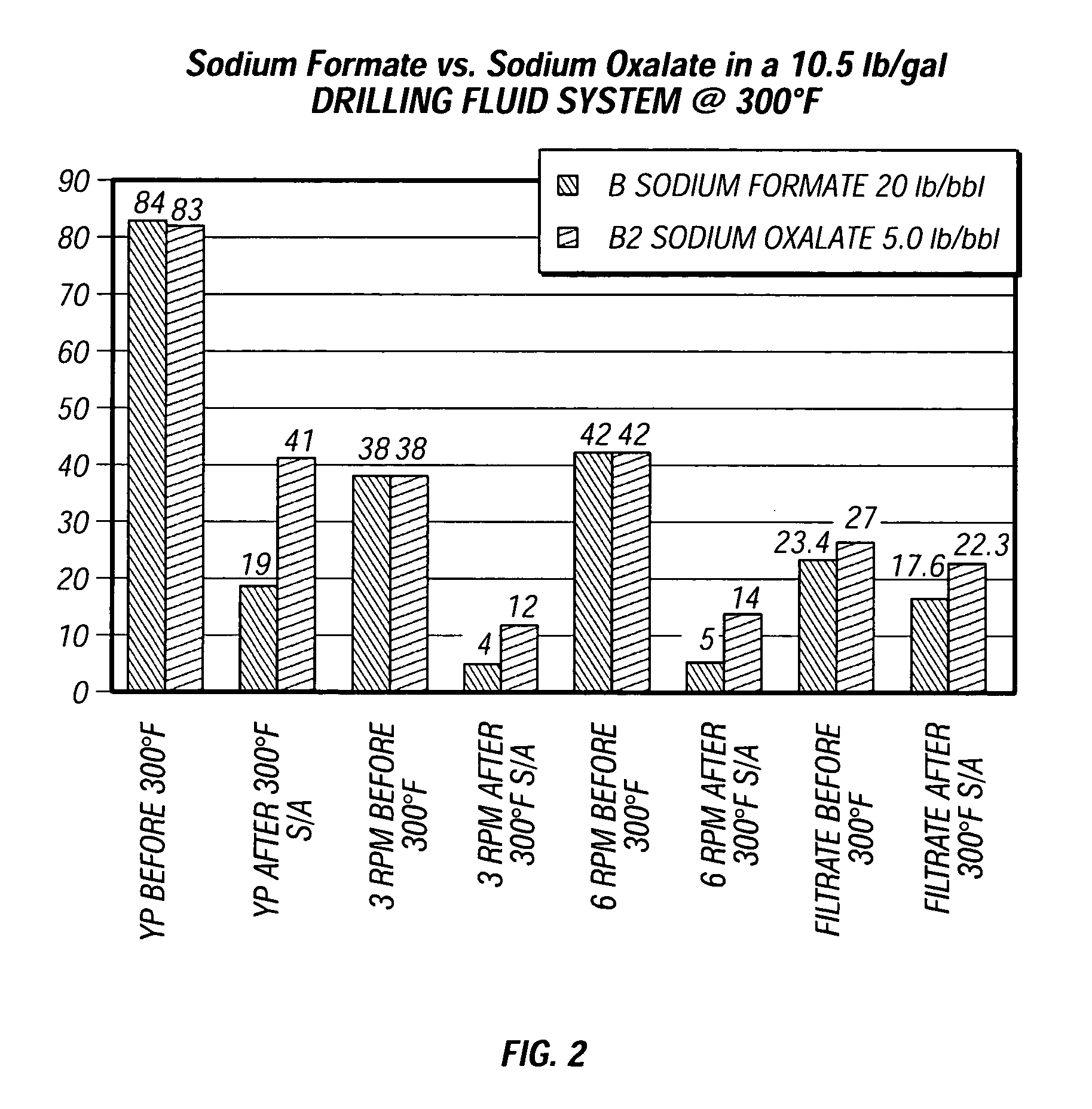
Method and composition for improving performance of aqueous and polymer based fluids at high temperatures
InactiveUS20050148475A1Improve stabilityImprove performanceFlushingDrilling compositionWell drillingThermal stability
The invention provides aqueous based well drilling and servicing fluids containing a polymer viscosifier with enhanced thermal stability provided by a diacid or diacid salt preferably having about two to about eight carbon atoms, such as, for example, sodium oxalate. The invention also provides a method of enhancing the thermal stability of aqueous based well drilling and servicing fluids containing a polymer viscosifer by adding diacid or diacid salt to the fluids.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
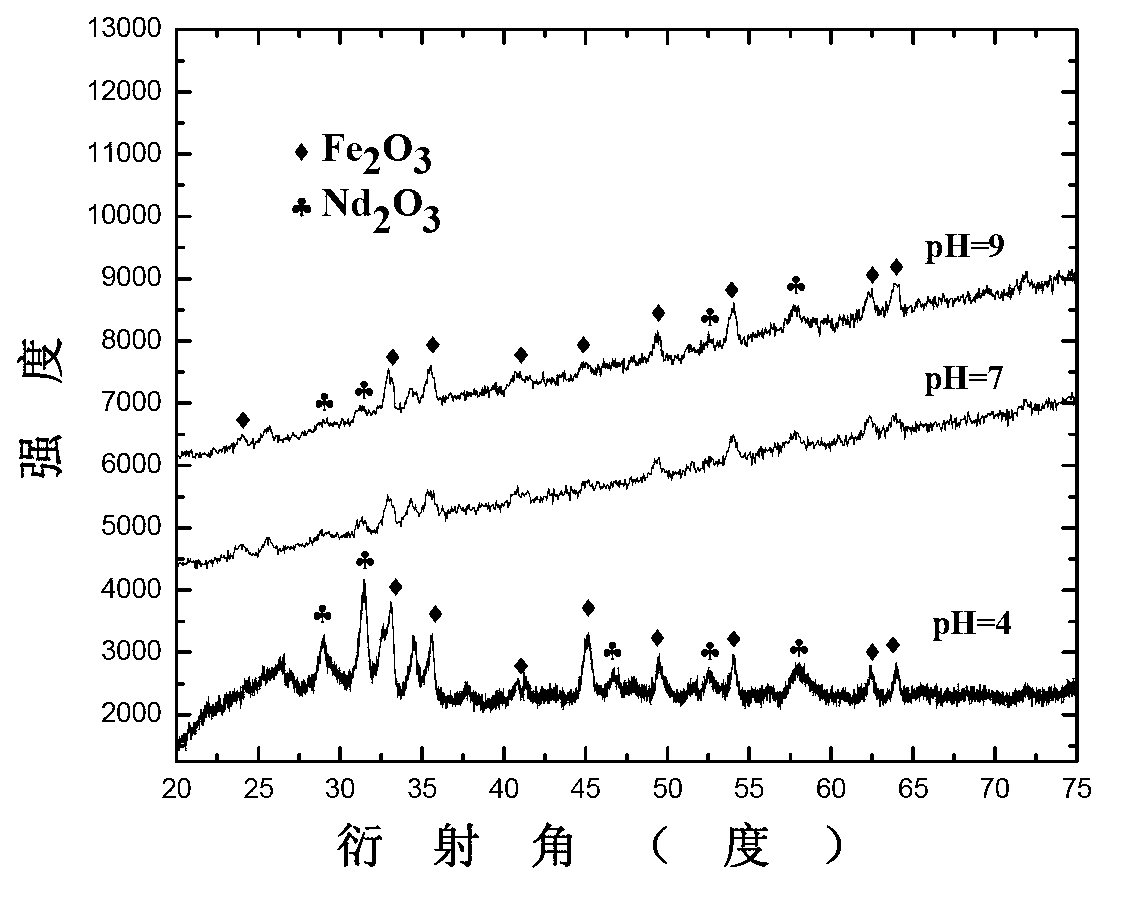
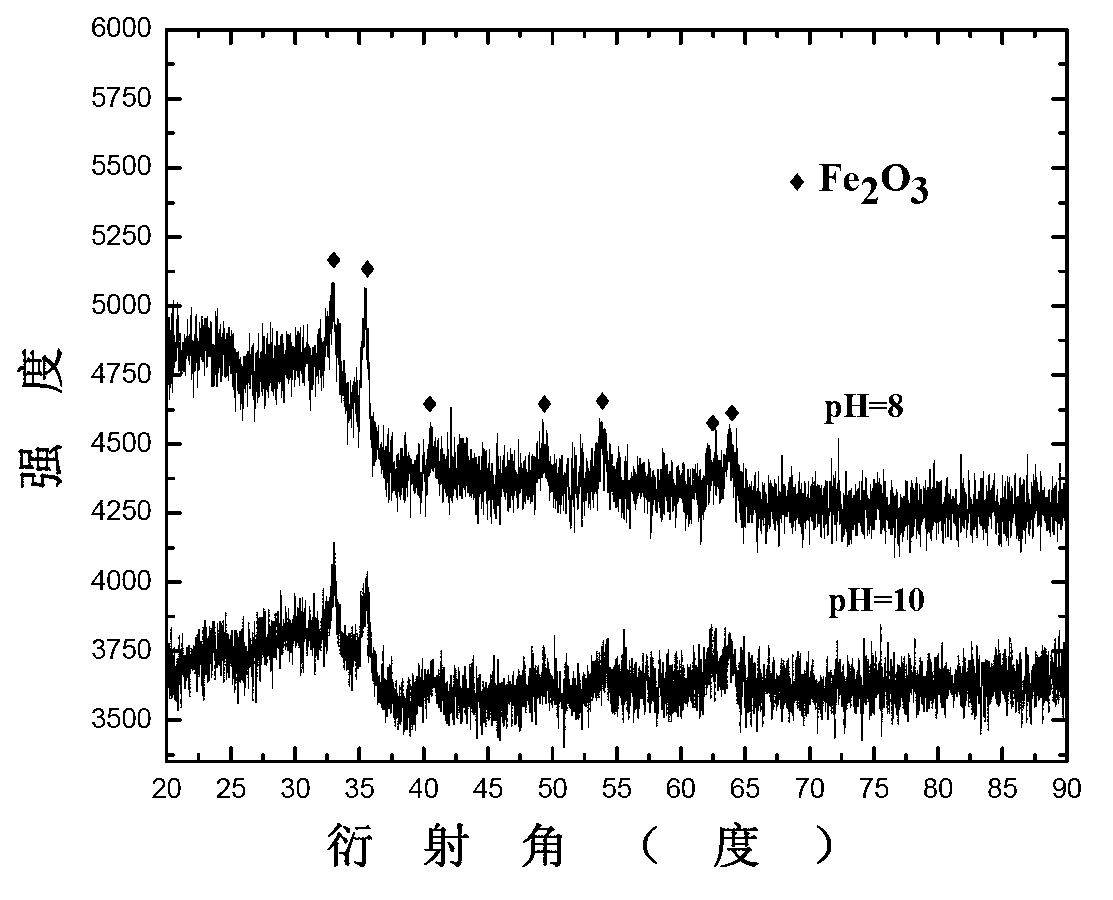
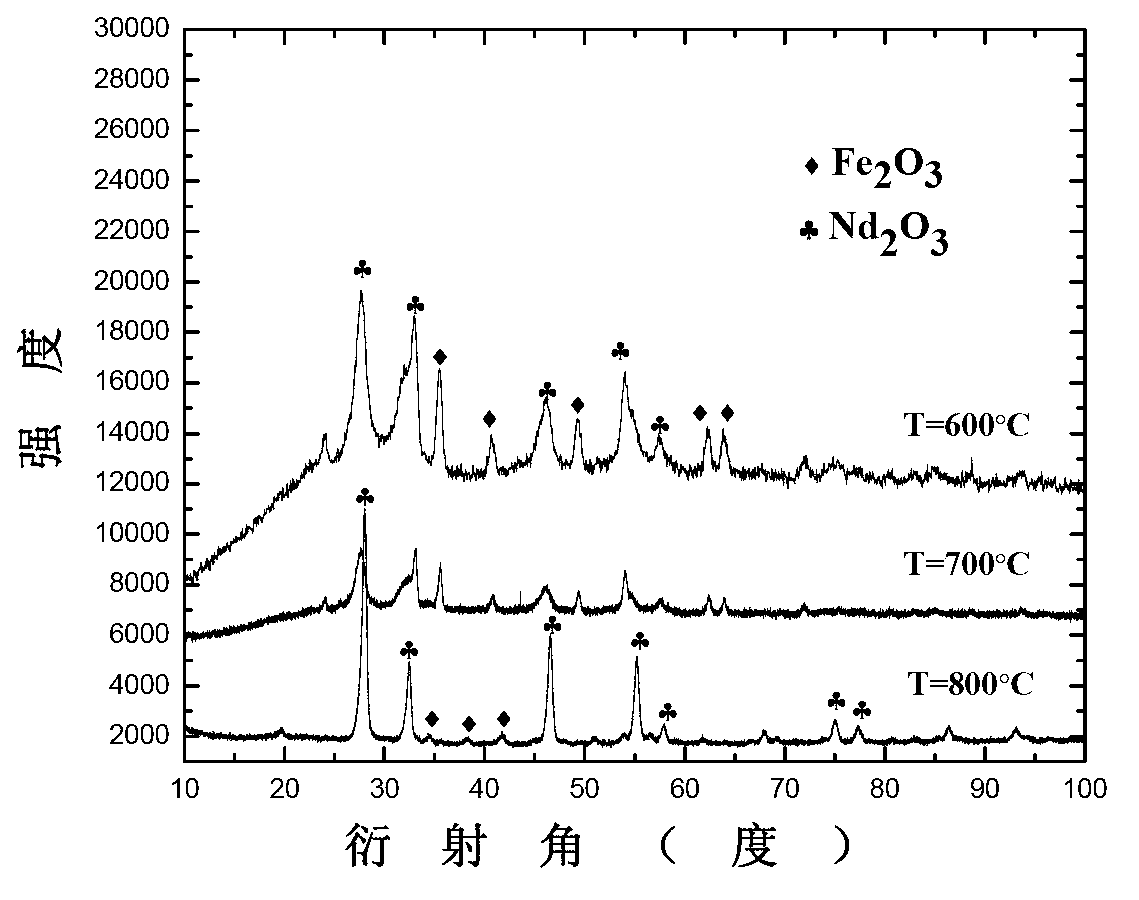
Method for preparing neodymium and iron oxides by using neodymium iron boron oil sludge through regeneration and co-precipitation
ActiveCN103343234AReduce usageShort operation processProcess efficiency improvementOil sludgeAmmonium hydroxide
The invention relates to a method for preparing neodymium and iron oxides by using neodymium iron boron oil sludge through regeneration and co-precipitation, belonging to the field of recycling of neodymium iron boron oil sludge. The method comprises the following steps of: adding hydrogen peroxide to oxidize a pickling liquid of the neodymium iron boron oil sludge, adjusting the PH value, adding a proper amount of sodium hydroxide, ammonium hydroxide or sodium oxalate precipitating agent at one step, preserving the heat of 60-100 DEG C for a period of time, centrifuging a sediment, drying, and roasting at high temperature to obtain a mixture of the neodymium and iron oxides. The method is short in operation process, simple in operation and capable of avoiding using a great deal of reagents.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for repairing organic polluted soil by intensifying Fenton oxidation
ActiveCN104399742AImprove adsorption capacityMaintain a valid formContaminated soil reclamationEthylene diamineNational Ambient Air Quality Standards
The invention relates to the field of polluted soil repair, particularly to a method for repairing organic polluted soil by intensifying Fenton oxidation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting organic pollution soil to be repaired, grinding and crushing, and screening by using a 10-mesh steel screen; (2) adding an enhancer powdery active carbon, sodium oxalate and disodium EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid), uniformly mixing and maintaining soil; (3) adding a catalyst ferrous sulfate, uniformly mixing and maintaining soil; (4) adding diluted industrial hydrogen peroxide, uniformly mixing, and maintaining soil. The method provided by the invention has the benefits that the active carbon powder is added to absorb organic matters so as to enhance the reaction probability of the organic matters and hydrogen peroxide; sodium oxalate is added to provide a continuous hydrogen peroxide source; ferrous sulfate is added to catalyze and enhance the oxidizing ability of hydrogen peroxide, so that the Fenton repair effect is improved; disodium EDTA is added and Fe<2+> form is controlled and maintained by virtue of a chelating effect. By virtue of the above intensifying measures, the polluted soil can be quickly and effectively repaired, so that the content of the organic matters in soil reaches national ambient air quality standard.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNTIME ENVIRONMENTAL REMEDIATION
Alcohol-free fountain solution and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an alcohol-free fountain solution and a preparation method thereof. The alcohol-free fountain solution is prepared by emulsifying a mixture formed by polyethylene glycol, glycerol, potassium oxalate, natural bone glue, oleic acid diethanolamide, coconut oil fatty acid diethanolamide, alkanolamide, sodium benzoate, fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate, polyglycol ether, sodium oxalate and water at the temperature of 30-55 DEG C. By using the alcohol-free fountain solution, the aims of realizing safety and environmental friendliness, saving energy and reducing emission can be fulfilled, and a printing operator can be protected from chronic poisoning of alcohol or isopropanol; the original quality of the alcohol-free fountain solution is kept on the aspect of the quality of printed matters, and meanwhile the using amount can be controlled conveniently by operating personnel.
Owner:陕西天佑成纸业有限责任公司
Nano-superstructure polyporous material of ferrite and method of preparing the same
The invention relates to a ferrite nanometer superstructure porous material and a method for preparing the same, in particular to a method for preparing a nickel ferrite, cobalt ferrite or zinc ferrite nanometer superstructure porous material. The preparation method comprises that: sodium oxalate is used as a precipitator, the soluble nickel, cobalt or zinc salt used as a raw material reacts with the soluble iron salt to prepare a precursor of oxalate, and the precursor is degraded by calcination at certain temperature to obtain the nickel ferrite, cobalt ferrite or zinc ferrite nanometer superstructure porous material. The nickel ferrite, cobalt ferrite or zinc ferrite nanometer superstructure porous material synthesized by the method has the advantages of high purity, uniform size, good dispersibility, mild reaction conditions, simple equipment, easily controlled process conditions and low cost, and meets the need of the actual production.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Modified composite type surface active agent
InactiveCN106693829AImprove performanceWeather resistantTransportation and packagingMixingBetaineAlpha-olefin
The invention discloses a modified composite type surface active agent. The raw materials is prepared from modified organosilicone surface active agent, polyether polyamine organosilicone surface active agent, fluorine silicon surface active agent, triethanolamine, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, sodium oxalate, sodium dodecyl sulfate, cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide, sodium di(2-ethyl-hexyl)sulfosuccinate, Tween 40, polysorbate 40, sodium alpha-olefin sulfonate, dodecyloxy hydroxypropyl betaine, dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid triethanolamine salt, tetraalkyl ammonium chloride and ethyl alcohol. The prepared modified composite type surface active agent has excellent high and low temperature resistance, corrosion resistance and weather resistance, and has excellent chemical stability and waterproof oil repellency at the same time.
Owner:柏青龙
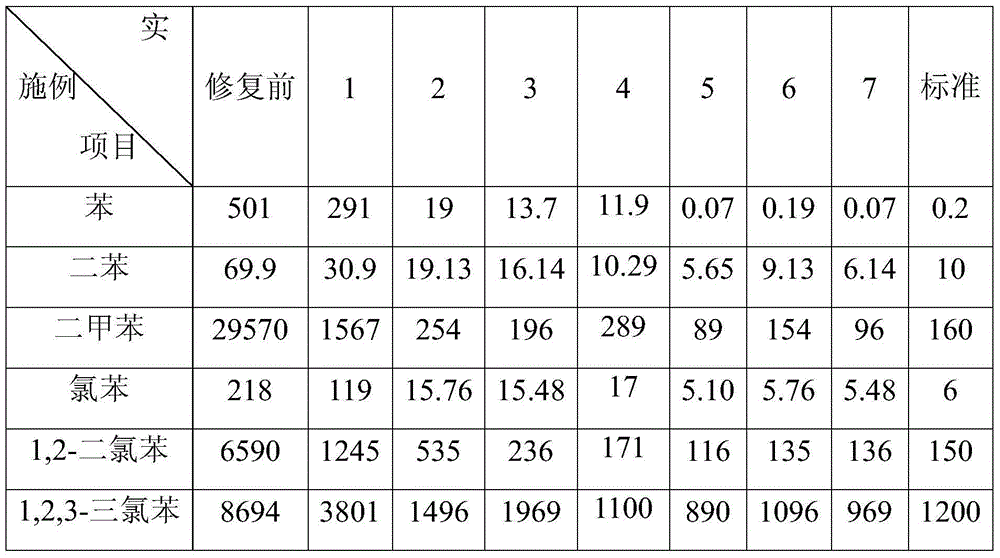
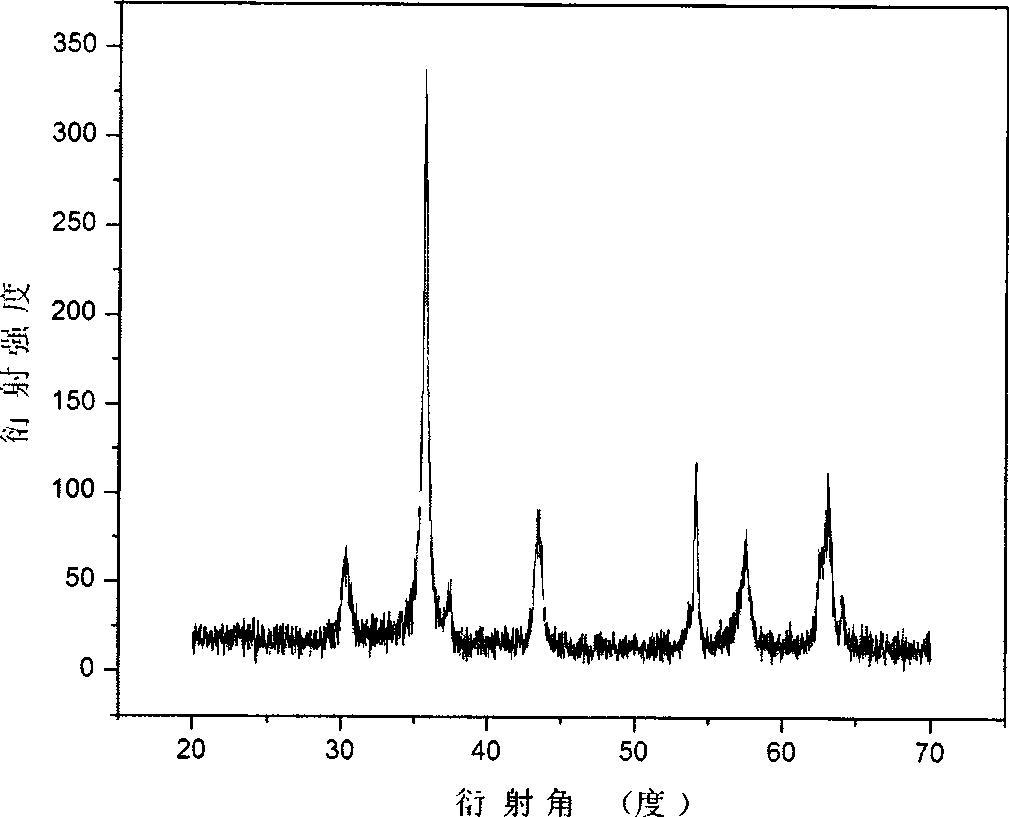
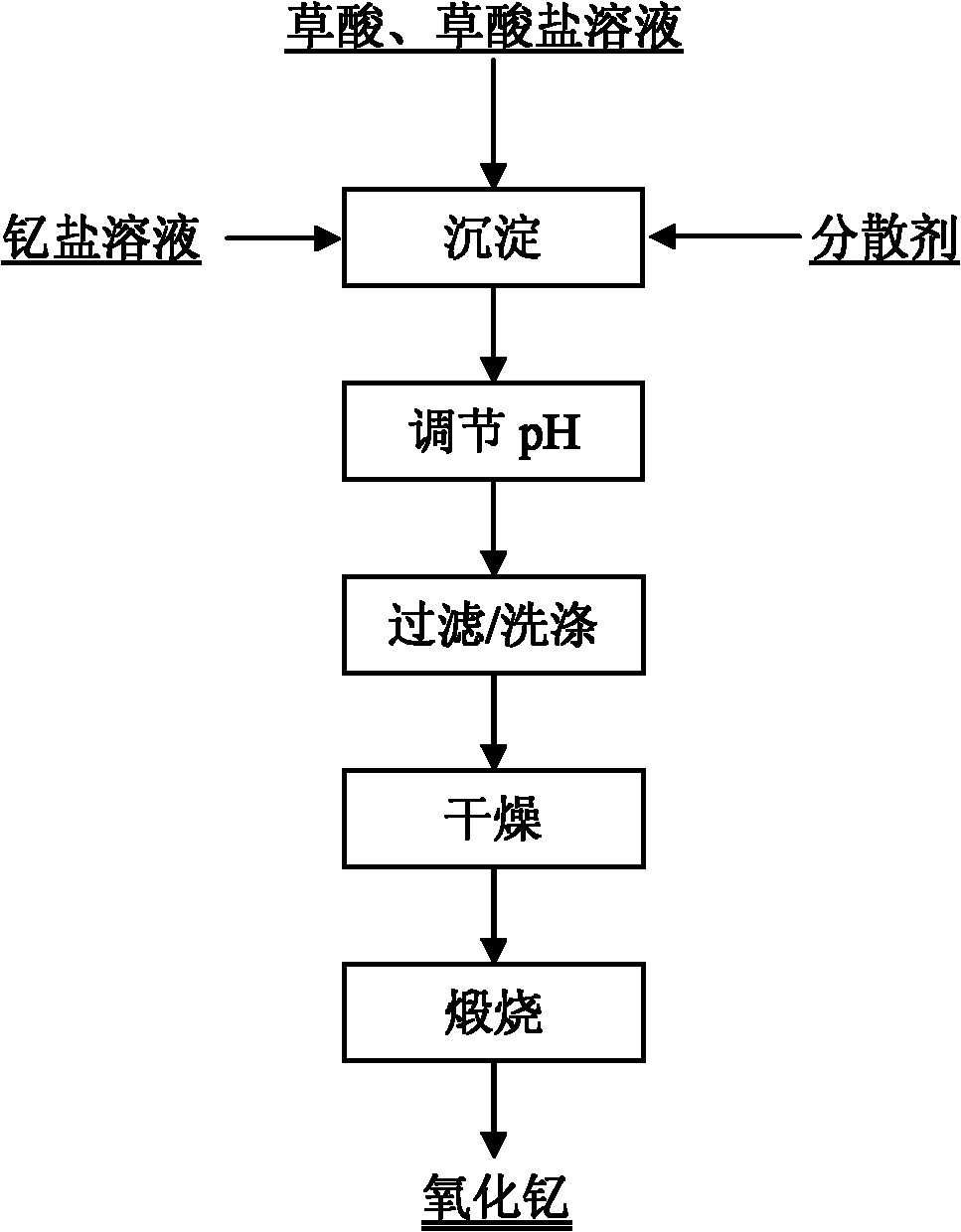
Submicron yttrium oxide and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to submicron yttrium oxide and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: in the presence of a compound precipitator formed by oxalic acid and one oxalate of ammonium oxalate, ammonium hydrogen oxalate, sodium oxalate, sodium hydrogen oxalate, potassium oxalate and potassium hydrogen oxalate, adding a yttrium nitrate and / or yttrium chloride solution into a base solution under certain reaction conditions, regulating the pH value of precipitation size, filtering and washing precipitate for a plurality of times, drying, and calcining to obtain the submicron yttrium oxide. The yttrium oxide has the physical properties that D50 is less than 1.0Mum and more than 0.1Mum, D90 is less than or equal to 1.0Mum, the particle size distribution coefficient Q is less than or equal to 0.20 and the particles are square or spherical in shapes. The invention has the advantages of simple process, operation easiness, low requirement on equipment, low production cost, convenience in production process control, good precipitate dispersibility and filtering property in a technological process, easiness in implementation of industrialized production and stable quality of the prepared product.
Owner:QIANDONG RARE EARTH GRP
Composite zinc removing agent for treating wastewater containing zinc
InactiveCN102464397ASimple processLow running costWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentCompound organicSludge
Owner:CHANGZHOU YAHUAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Method for preparing cubic zirconium phosphate silver-carrying antimicrobial powder
The invention relates to a method for preparing a zirconium phosphate silver-carrying antimicrobial powder, particularly a cubic zirconium phosphate silver containing antimicrobial powder. The cubic zirconium phosphate silver-carrying antimicrobial powder is in the microstructure of a cube, the silver is carried by the cube, and the side of the cube has a length of 400-1,000nm. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a cubic zirconium phosphate carrier, mixing the cubic zirconium phosphate carrier with the aqueous solution of zinc nitrate, stirring to generate a zinc-carrying intermediate; preparing the zinc-carrying intermediate into an aqueous dispersion solution, adding the silver nitrate solution so that the carrier contains 1.5-3.5% of silver ions, stirring, washing, filtering, drying and forging to obtain the final product. The carrier is prepared by adopting the atmospheric-pressure hydrothermal synthesis method, and the hydrofluoric acid used as the template agent in the old process is replaced by the sodium oxalate. The process is simple and convenient to operate, and the equipment has high selectivity. The product and the product producing process are truly safe and nontoxic, the enamel equipment can be used as the production equipment, and the production cost can be saved.
Owner:晋大纳米科技(厦门)有限公司
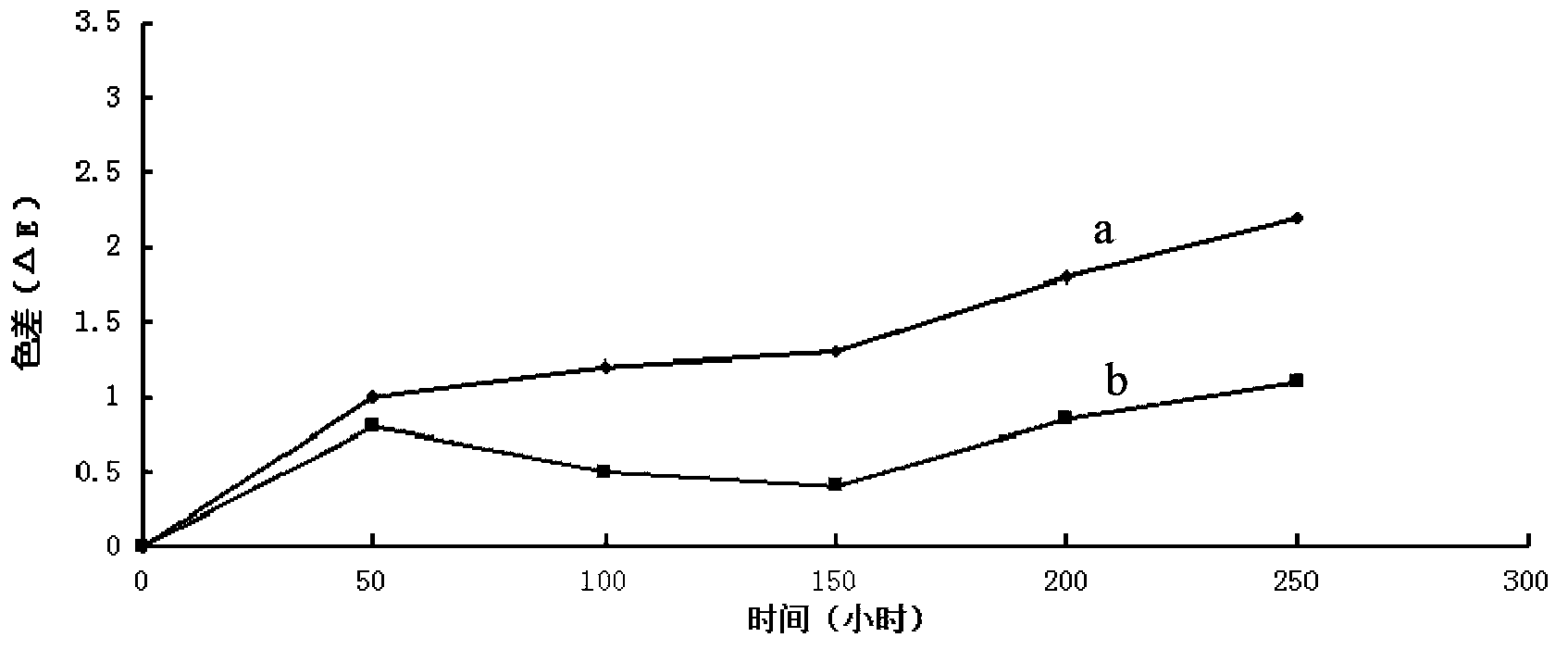
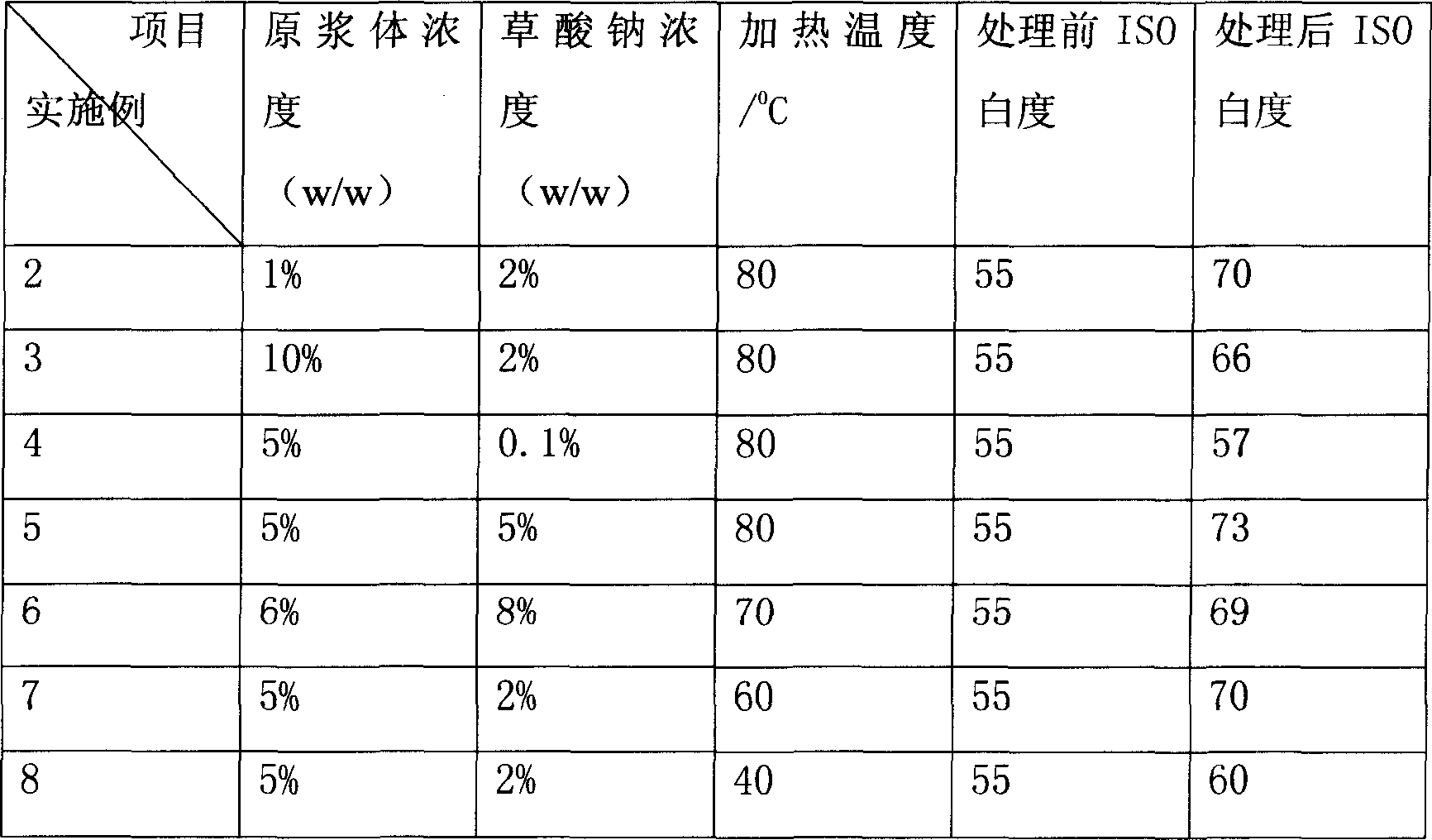
Method for deferrization and whitening of palygorskite by using sodium oxalate and hydrochloric acid
The invention discloses a sodium oxalate and alcaine composite deironing whitening method of paligorskite, which comprises the following steps: dispensing paligorskite and water at 1-10% density rate to prepare slurry; stewing for 1-4 h; sedimenting; draining 60-80 percent upper layer slurry through upper layer discharge method; adding sodium oxalate with 0.1-10% weight rate density in the upper layer slurry; dripping alcaine pH value not more than 3; heating to stir upper layer slurry mechanically at 40-100 deg.c; sucking the slurry at the heating time; washing many times until the filtrate displays neutral; drying; grinding to obtain the product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
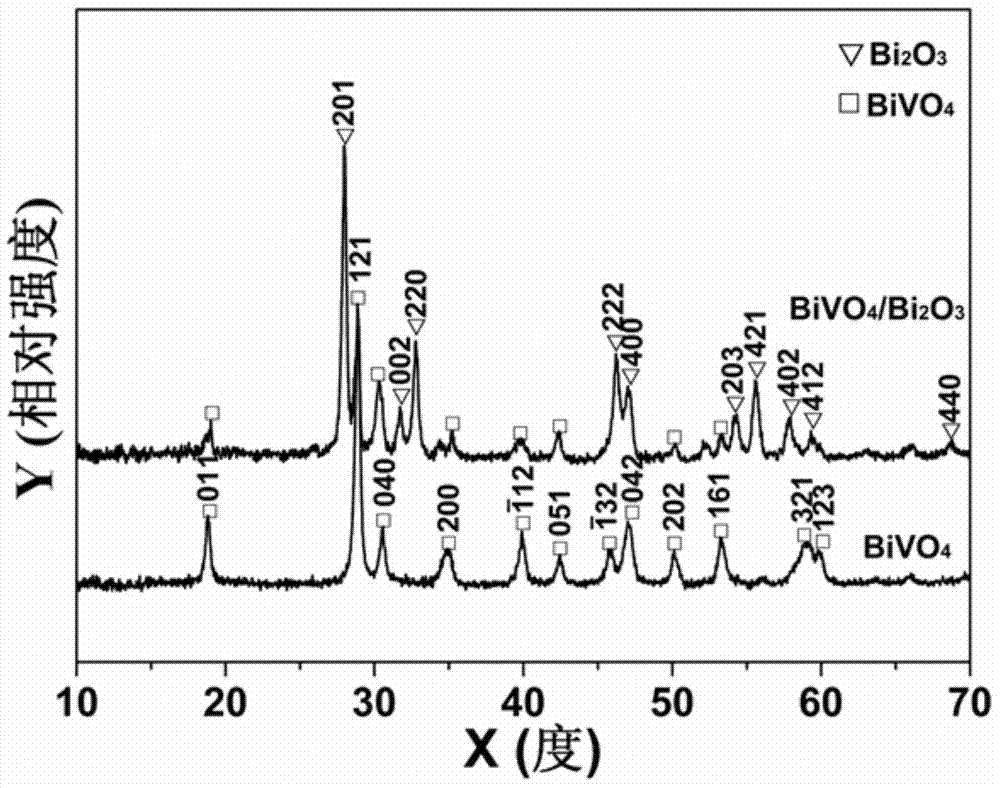
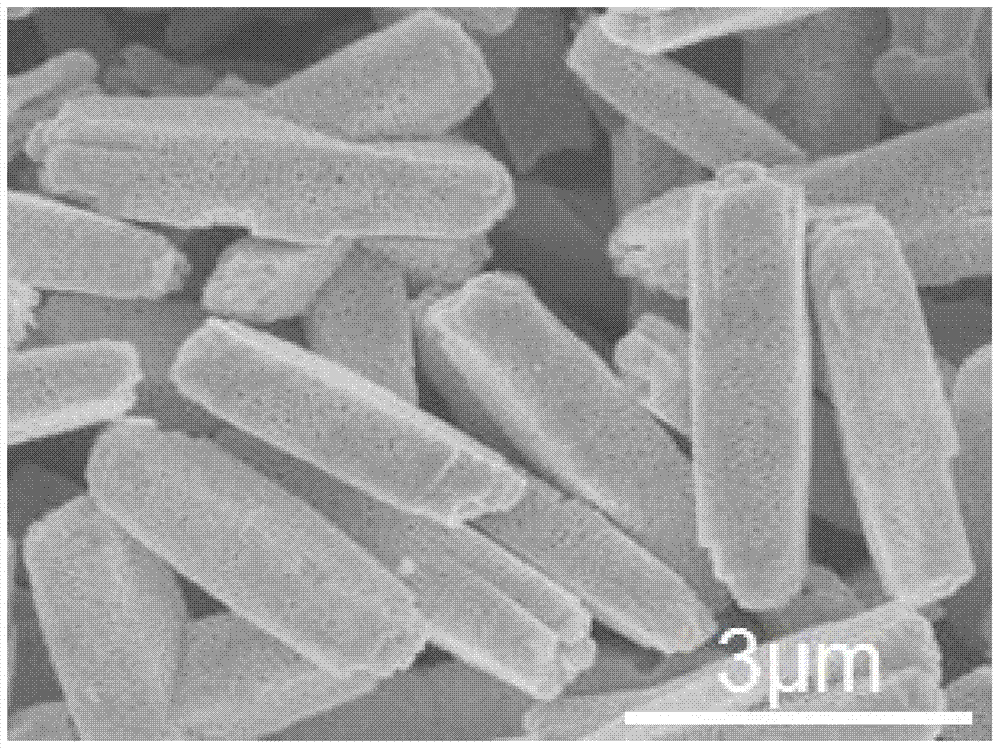
Method for massively preparing mesoporous BiVO4/Bi2O3 composite micro-rod p-n heterojunction photocatalyst
InactiveCN104772134ALow costEasy to controlMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHeterojunctionSurface-active agents
The invention relates to a method for massively preparing a mesoporous BiVO4 / Bi2O3 composite micro-rod p-n heterojunction photocatalyst. The method for massively preparing the mesoporous BiVO4 / Bi2O3 composite micro-rod p-n heterojunction photocatalyst takes metal inorganic salt-bismuth nitrate pentahydrate (Bi (NO3) 3.5H2O) as a reaction precursor, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a surface active agent as well as sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4) and sodium metavanadate (NaVO3) as reactants; the method comprises the steps of feeding the surface active agent into the reaction precursor, carrying out a solvothermal reaction, centrifuging, washing, drying, and carrying out solid-phase reaction calcination on the obtained product at the temperature of 300-400 DEG C to obtain the BiVO4 / Bi2O3 composite micro-rod p-n heterojunction photocatalyst. The prepared mesoporous BiVO4 / Bi2O3 composite micro-rod p-n heterojunction photocatalyst has the length of about 3.5-4.5mu m, the diameter of about 0.7-0.9mu m and the mesoporous average diameter of 30.0nm. The prepared mesoporous BiVO4 / Bi2O3 composite micro-rod p-n heterojunction photocatalyst has the characteristics of being low in cost, easy to control, good in repeatability, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
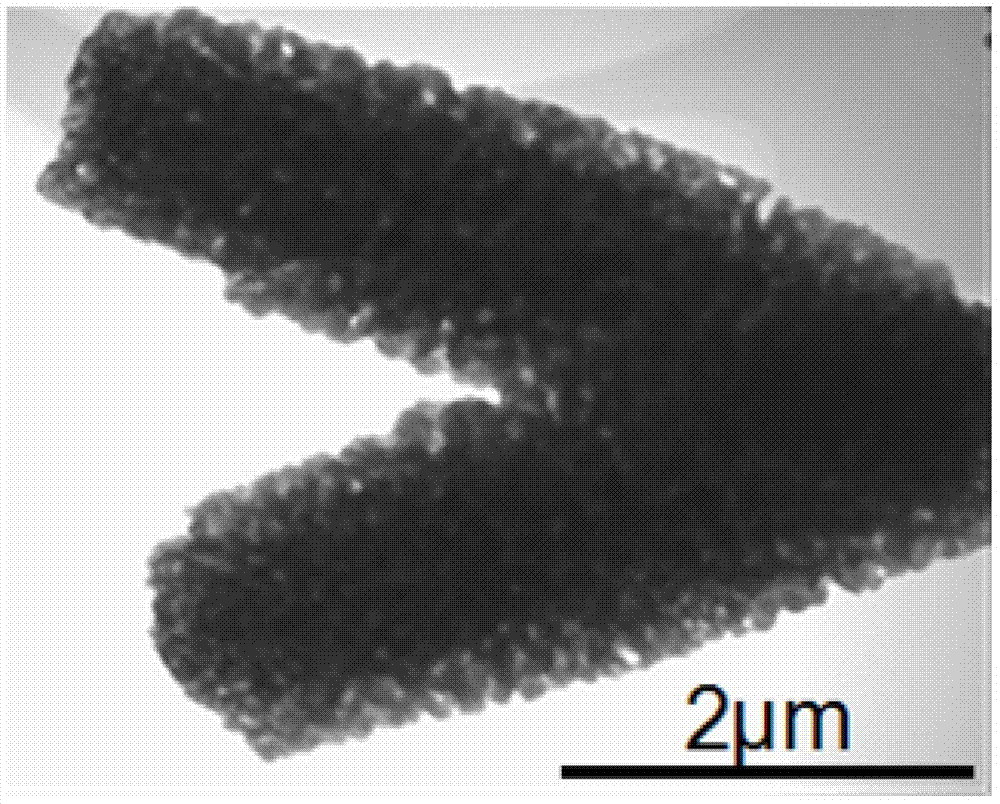
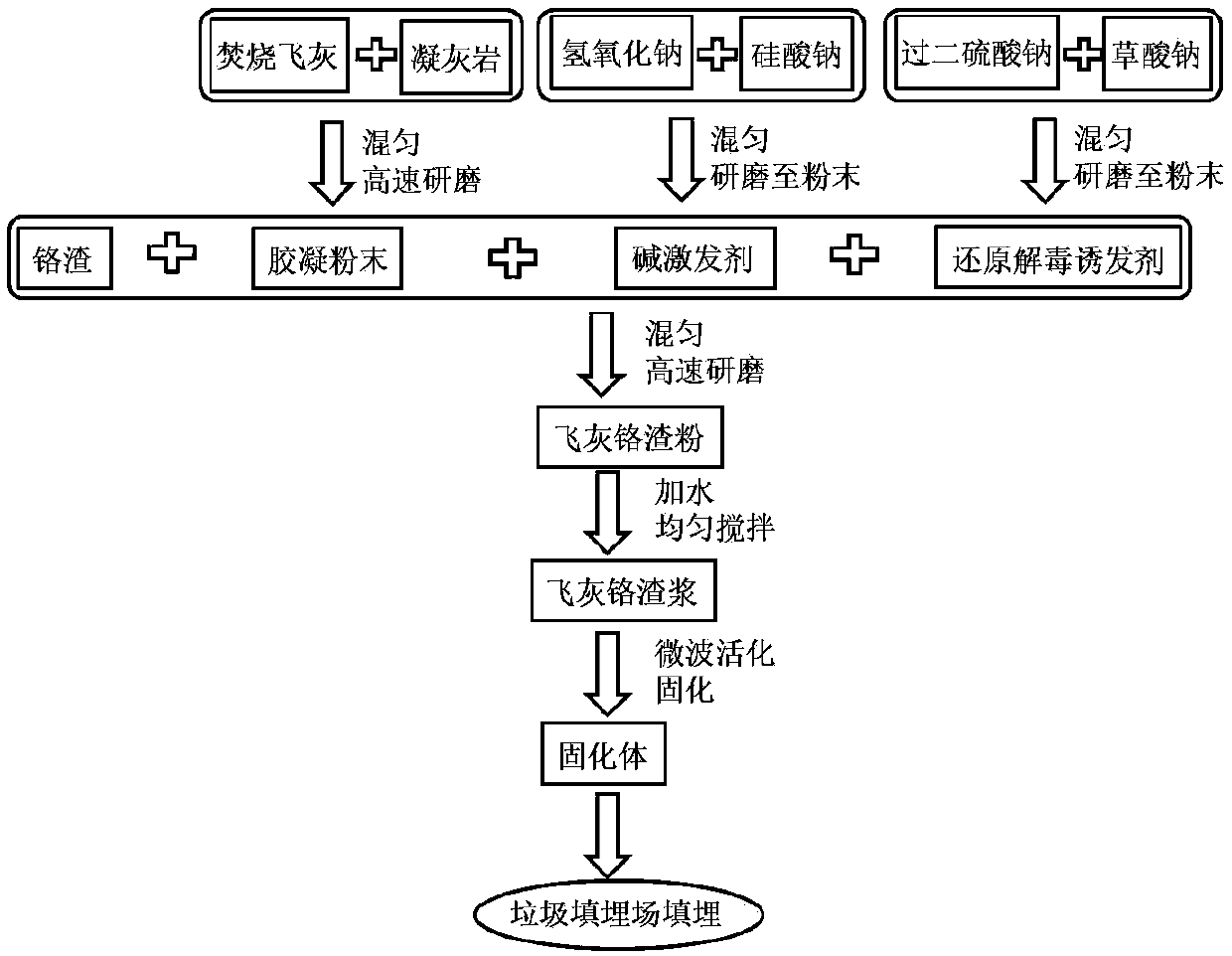
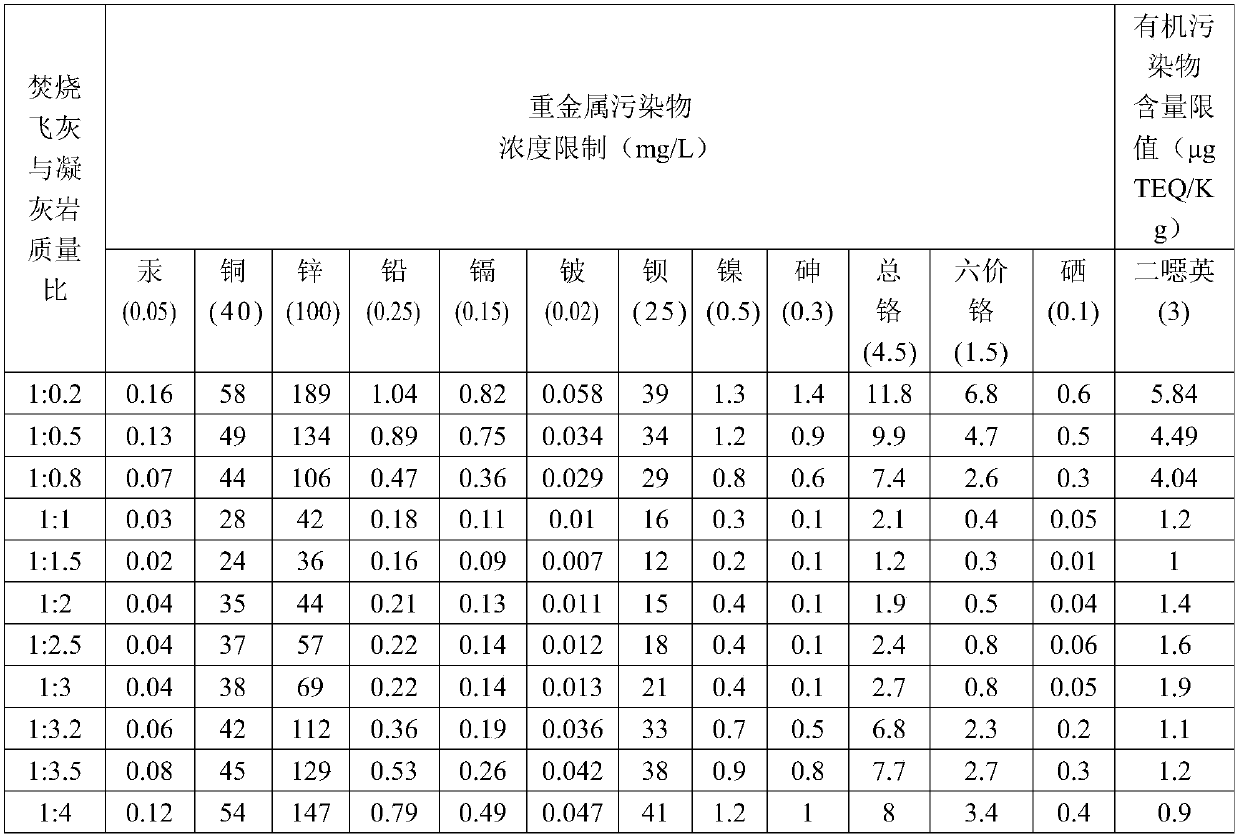
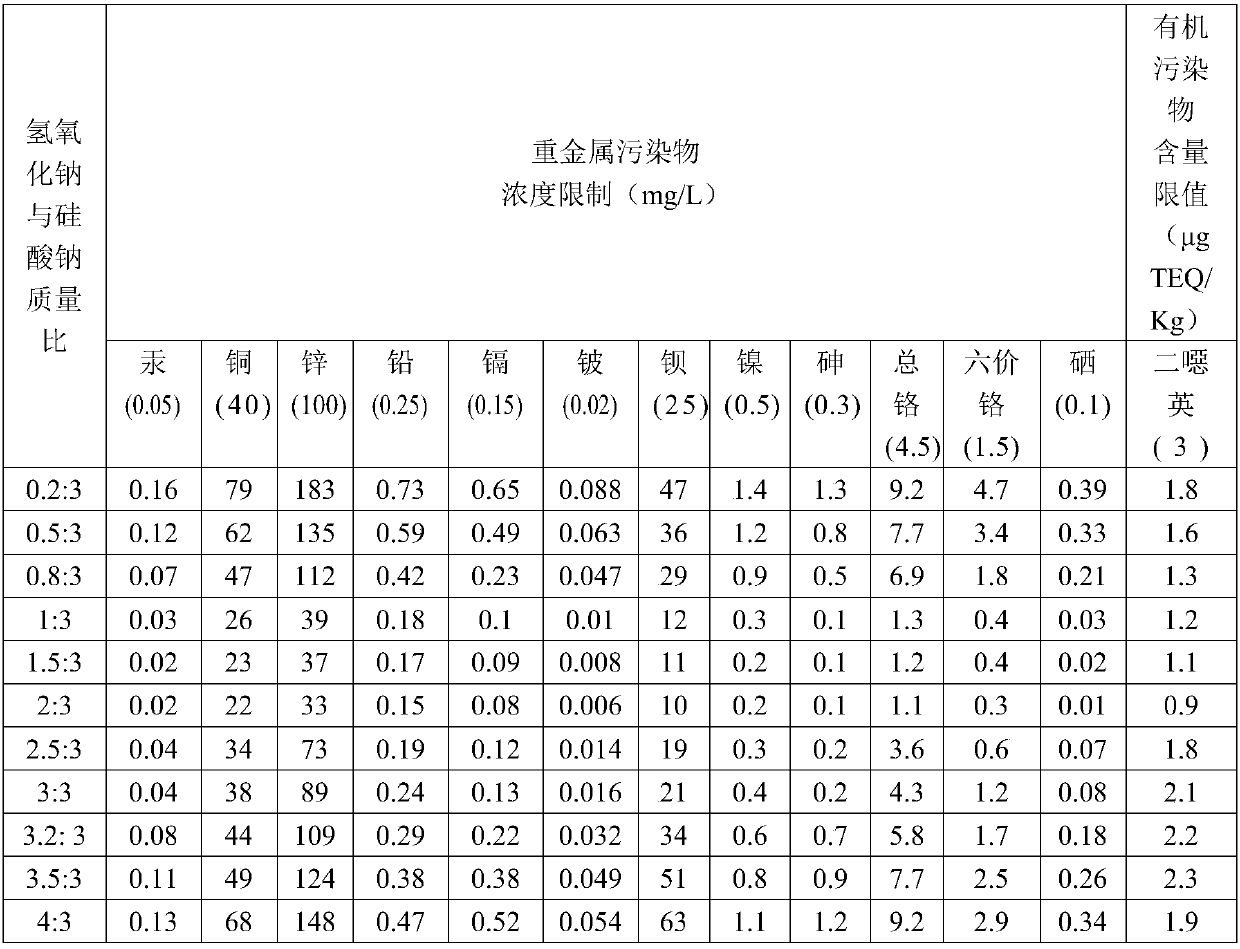
Method for synchronously achieving incineration fly ash detoxification and chromium slag reduction curing
The invention discloses a method for synchronously achieving incineration fly ash detoxification and chromium slag reduction curing. The method includes the following steps that (1), incineration flyash and tuff are weighed, mixed to be uniform and ground, and gelatinized powder is obtained; (2), sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate are weighed, mixed to be uniform and ground, and an alkali activator is obtained; (3), sodium persulfate and sodium oxalate are weighed, mixed to be uniform and ground, and a reductive detoxification inducer is obtained; (4), chromium slag, the gelatinized powder,the alkali activator and the reductive detoxification inducer are weighed, mixed to be uniform and ground, and fly ash and chromium slag powder is obtained; (5), the fly ash and chromium slag powderis weighed and dissolved in water, the materials are mixed to be uniform, and fly ash and chromium slag slurry is obtained; (6), the fly ash and chromium slag slurry is sealed, activated through microwaves, cooled and put in a die to be cured. The leaching concentrations of multiple heavy metals and dioxin in the fly ash and a chromium heavy metal in the chromium slag are all lower than the entrance limiting value of a municipal solid waste landfill. Treated cured bodies have high acid resistance and high constraint capacity for heavy metal inorganic pollutants and organic pollutants.
Owner:浙江中陶环保科技集团有限公司
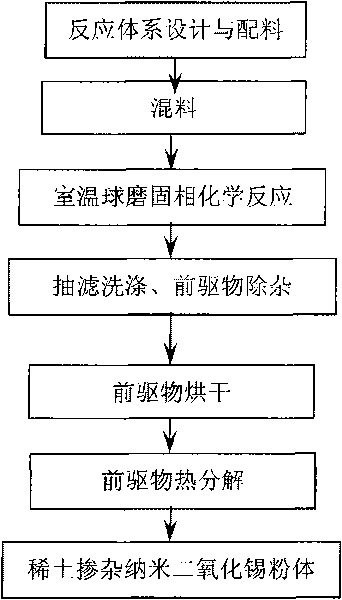
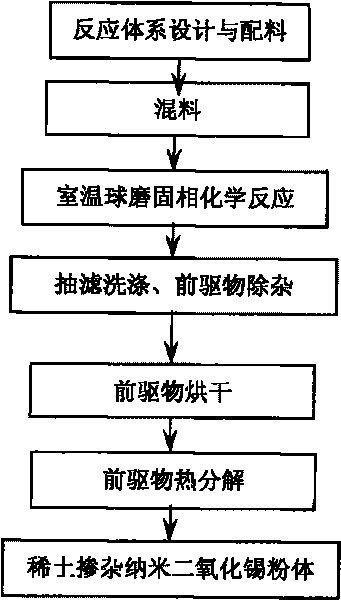
Preparation method of room-temperature ball-milling solid phase chemical reaction of rare earth mixing with nano stannic oxide
InactiveCN101746812ALarge specific surface areaIncrease the speed of diffusionTin oxidesChemical reactionReaction rate
The invention discloses a preparation method of room-temperature ball-milling solid phase chemical reaction of rare earth mixing with nano stannic oxide, relates to a preparation technology of the rare earth mixing with the nano stannic oxide, which can be applied for antistatic coating, plastics, fibre and other fields. Inorganic salts containing stannum and rare earth are taken as reactants, oxalic acid, ammonium carbonate, ammonium bicarbonate, sodium oxalate or sodium carbonate is taken as a ligand, the processing steps are sequentially dosing, mixing and preparing precursors of the room-temperature ball-milling solid phase chemical reaction, and the targeted product can be obtained after impurity removing, drying and thermal decomposition. The preparation method is characterized in that the reaction process does not use water, the stannum ion can be prevented from hydrolysis, uniform mixing can be realized, a solid phase reaction system is broken by utilizing the shearing force and the impact force generated during the ball milling process, the specific surface area of the reactant is increased, the reaction rate is increased, micro-fine and uniform precursors can be prepared, then the processes of cleaning, drying and controlling the thermolysis temperature and time are carried out, and thereby the rare earth mixing with nano stannic oxide powder, the particle size distribution of which is 30 to 80nm and has controllable morphology, can be obtained.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
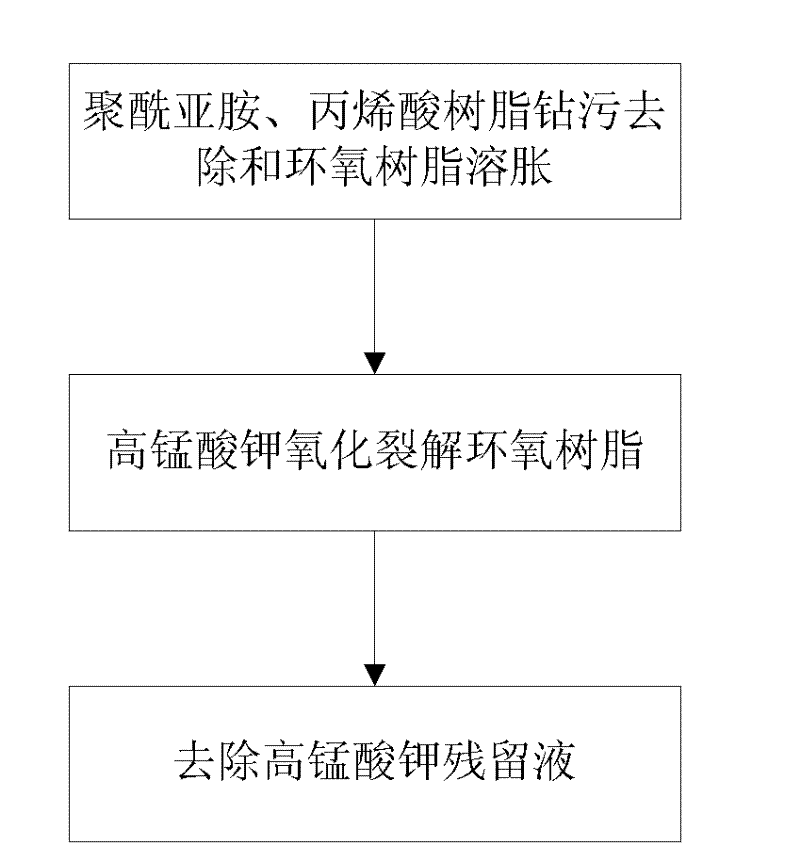
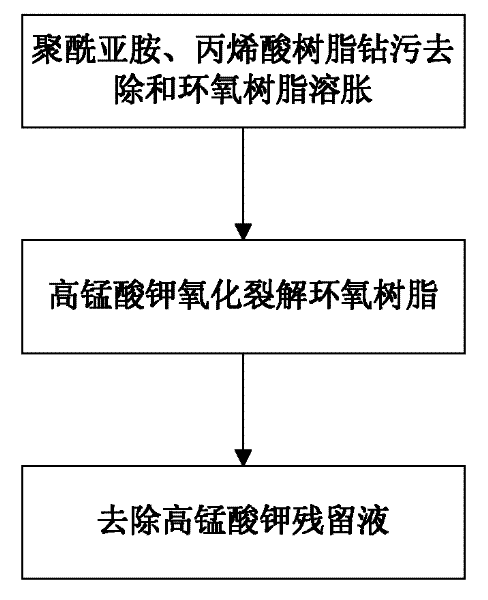
Method for cleaning through hole smears of rigid-flexible printed circuit board
InactiveCN102438405AImprove biteLow costInorganic non-surface-active detergent compositionsConductive pattern polishing/cleaningEpoxyAcrylic resin
The invention relates to a method for cleaning through hole smears of a rigid-flexible printed circuit board, belonging to the field of printed circuit board manufacturing. The cleaning method comprises the following steps: 1) using a novel decontamination liquid to remove polyimide and acrylic resin smears and swell epoxy resin smears; 2) using a potassium permanganate decontamination liquid to oxidize and crack the swollen epoxy resin; and 3) using a sulfuric acid-sodium oxalate system to remove the residual potassium permanganate liquid, thereby realizing the removal of through hole smearsof the rigid-flexible board based on a low-valence chemical method, wherein every liter of decontamination liquid for removing polyimide and acrylic resin smears and swelling epoxy resin contains 20-50g of sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, 10-40g of epoxy resin sweller, 1-5g of solubilizer, 10-60ml of polyimide sweller and the balance of water. The method provided by the invention realizesthe low-cost smear cleaning, and has the characteristics of simple method and high decontamination efficiency. By using the method to clean the through holes of the rigid-flexible printed circuit board, a level hole wall having good hole interlocking capability can be obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
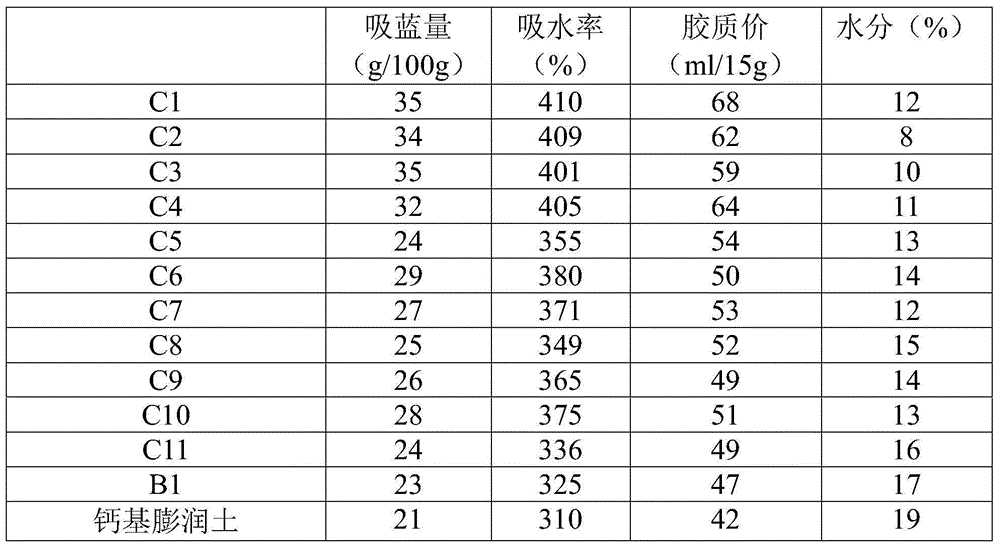
Sodium bentonite and double sodium modifying method for sodium bentonite
ActiveCN104986778ARaise the degree of sodiumImprove sodium effectSilicon compoundsSodium acetateSodium phosphates
The invention discloses sodium bentonite and a double sodium modifying method for the sodium bentonite. The method comprises the steps that 1, calcium bentonite and a sodium salt are mixed and modified in a sodium mode to manufacture first-class sodium bentonite; 2, the first-class sodium bentonite and an addition agent are mixed and inoculated to manufacture second-class sodium bentonite, wherein the addition agent comprises microcrystalline cellulose, silica gel modified by a sodium salt, expanded vermiculite, boric acid, a thickening agent and polyacrylamide; the sodium salt and the sodium salt in the silica gel modified by the sodium salt are independently selected from one or more of sodium carbonate, sodium silicate, sodium fluoride, sodium oxalate, sodium acetate, sodium phosphate, sodium polyacrylate, sodium hydroxide, sodium chloride, sodium thiosulfate and sodium cellulose; the thickening agent is selected from magnesium oxide and / or magnesium hydrate. According to the method, the calcium bentonite is fully modified into the sodium bentonite in the sodium mode, moreover, the sodium bentonite has excellent blue absorption power, a high water absorption rate and large colloid indexes, the steps are simple, and the raw materials are easy to obtain.
Owner:芜湖恒杰膨润土科技有限公司
Method for rapidly measuring permanganate indexes in water by spectrophotometric method
InactiveCN102012362AAvoid titrationReduce usagePreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsInformatizationEthylenediamine
The invention relates to a method for rapidly measuring permanganate indexes in water by a spectrophotometric method. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a colorimeter tube and extracting a water sample; adding a proper amount of sulfuric acid until the water sample is acidic; adding 0.01mu mol / L-0.2mu mol / L of permanganate solution and heating the obtained mixed solution in a heating reactor at 100 DEG C for 15-45 minutes; after the mixed solution is cooled, reducing the remaining permanganate with excessive nitrite, and then adjusting the obtained reaction solution into a constant volume after the reaction; taking out and placing 1ml of the reaction solution with a constant volume in the colorimeter tube of 25ml, adjusting the reaction solution into a constant volume once again, and sequentially adding 0.5ml of sulfanilamide and 0.5ml of ethylenediamine; and standing for 10 minutes, and taking water as a reference and measuring the absorbancy by a cuvette with the optical path length of 10mm at the position with the wavelength of 10mm. In the invention, a rapid quantitative analysis method of the permanganate indexes in the water is established by the mode of indirectly measuring the nitrite; the method is rapid and economical, and the process of titrating sodium oxalate with the permanganate can be avoided; and the method can be widely applied to emergency, online monitoring, flow injection, lab informatization management and the like.
Owner:宁波市环境监测中心
Method for improving brightness of attapulgite
ActiveCN101423673ASimple stepsReduce energy consumptionInorganic pigment treatmentHydrolysisTitanium tetrachloride
The invention discloses a method for improving whiteness of attapulgite. Firstly, natural attapulgite is subjected to dispersion treatment in water phase to prepare an aqueous dispersion solution of the nanometer attapulgite; TiCl4 is used as a raw material to prepare a nanometer titania congeries; secondly, the nanometer titania congeries and the nanometer attapulgite are compounded; an iron element in the attapulgite is dissolved out through utilizing hydrochloric acid produced by the hydrolysis of titanium tetrachloride in the reaction process; and finally, sodium oxalate is used for complexation so as to remove iron. The method is simple and feasible, completes the treatment of the whole process in low temperature, does not need high-temperature heat treatment, does not need to add extra hydrochloric acid, saves cost and reduces environmental pollution; the method utilizes a chemical iron removing method of acid dipping and complexation, is combined with the function of chemical compounding on the surface of titania to whiten synergistically, thereby remarkably improving the whiteness of the attapulgite; and the method can conveniently prepare a titania / attapulgite composite material with different crystal forms through controlling process condition.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
Preparation method of Prussian blue based sodium ion battery positive electrode material
InactiveCN106654263AReduce defectsSlow responseIron cyanidesCell electrodesSingle crystalSodium-ion battery
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Prussian blue based sodium ion battery positive electrode material. The preparation method takes ferrous oxalate and sodium oxalate as raw materials, and makes the raw materials react with sodium ferrocyanide; a reaction speed can be slower and the production speed of a Prussian blue mono-crystal becomes slow, so that the aim of reducing defects in a Prussian blue crystal is realized. A sodium ion battery positive electrode prepared from the Prussian blue crystal can still keep good stability after being subjected to a plurality of times of charge-discharge cycles, and the service life is long. The method is simple in preparation process, easy to implement and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:DONGGUAN JIAQIAN NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com