Primer-type nucleic acid fluorescent probe subjected to two-way strand displacement
A fluorescent probe and two-way chain technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of increasing the overall difficulty of design, and achieve the effects of low design difficulty, high sensitivity real-time fluorescence detection, and high indication sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1 (probe stability verification)
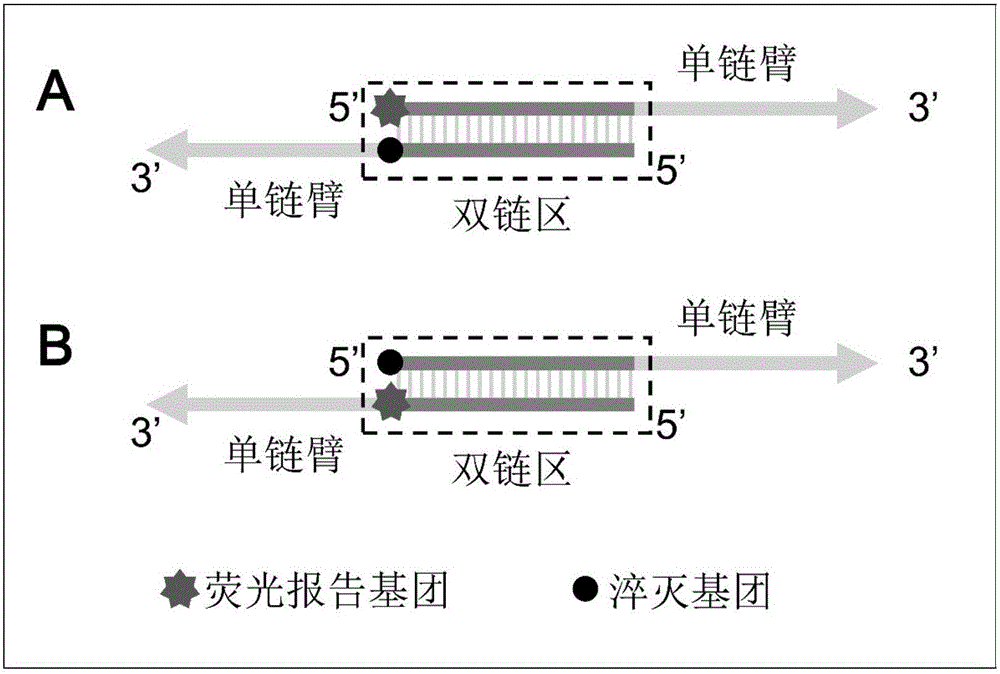
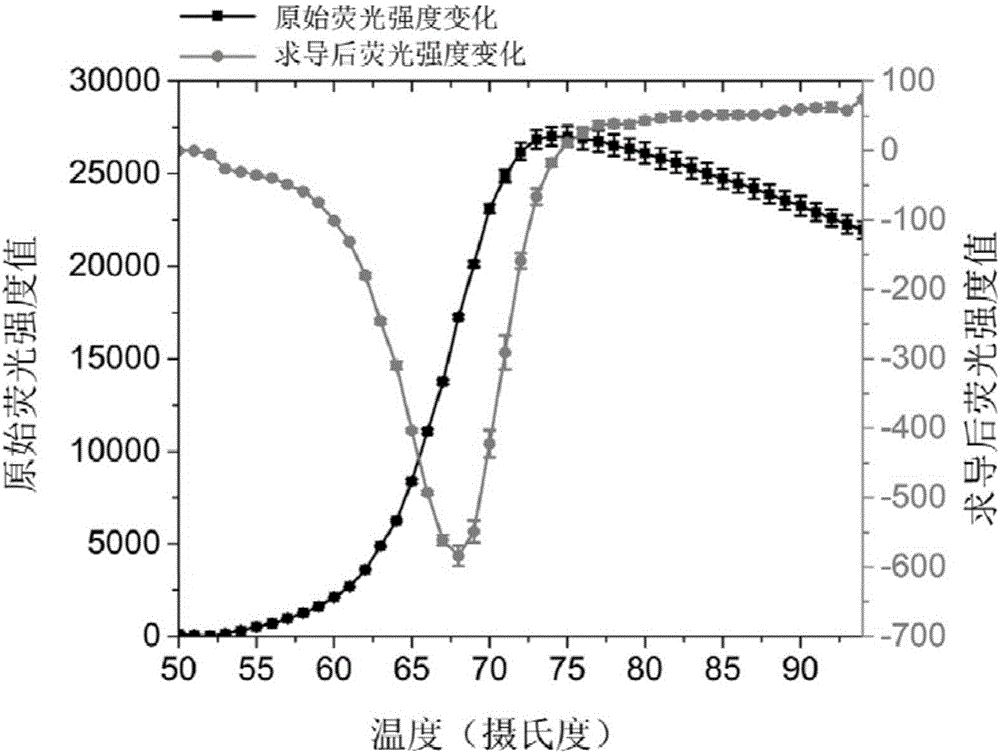
[0040] In this verification example, two primers containing labeling groups (one labeled as FAM fluorescent group and the other labeled as Dabcyl quenching group, respectively denoted as FAM-primer-1 and Dabcyl-primer-1) were melted Curve analysis was used to judge the stability of the probe in the isothermal reaction system at 60-65°C. The structure and composition of this probe can be found in the appendix figure 1 ,Specific steps are as follows:
[0041] Step 1: Take 5 EP tubes and add 21 μL of reaction buffer to each, labeled as A, B, C, D, E;
[0042] Step 2: Add 2.0 μL of FAM-primer-1 to each of the 5 tubes, and the final concentration of the system is 1.6 μM;
[0043] Step 3: Add 2.0 μL Abcyl-primer-1 to each of the 5 tubes, and the final concentration of the system is 1.6 μM;
[0044] Step 4: Mix the 5 tubes of solution thoroughly and incubate at 37°C for 10 minutes. Then, it was placed in an ABI7900HT real-time...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2 (IMSA mediated by the probe of the present invention)
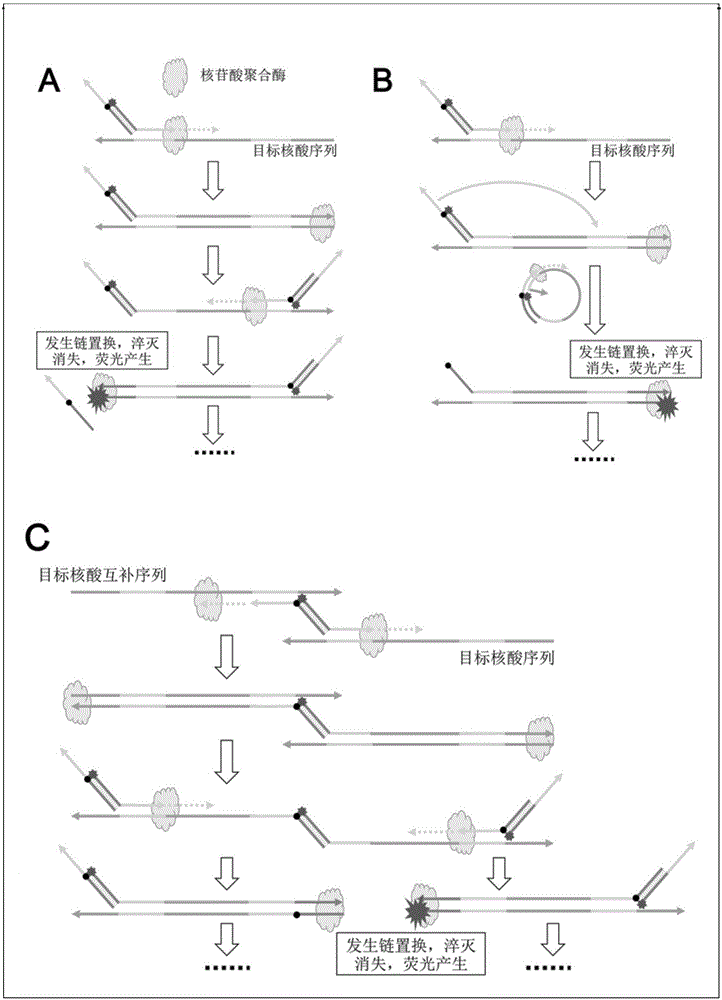
[0056]The purpose of this example is to verify the real-time detection ability of the probe-mediated IMSA of the present invention for the amplification of target nucleic acid sequences and other non-target nucleic acid sequences at different concentrations, that is, its analytical sensitivity and specificity. The composition of the probe structure in this embodiment is shown in the appendix figure 1 , the mechanism of action of the probe is shown in the appendix figure 2 , and the reaction schematic diagram of IMSA is detailed in patent CN104388581A.
[0057] Specific steps are as follows:
[0058] Step 1: Take an EP tube, add 13 μL of FAM-primer-2 (concentration of 20 μM) and 13 μL of Abcyl-primer-2 (concentration of 20 μM), mix well to make a probe solution, and incubate at 37°C in the dark for about 10 minute.
[0059] Step 2: Take 12 EP tubes and add 20.5 μL of the reaction mixture, labeled 1...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Embodiment 3 (probe of the present invention binds to IMSA mediated by HNB)
[0078] The purpose of this example is to verify that the probe of the present invention combined with HNB can establish real-time fluorescence detection of IMSA and dual fluorescence visualization detection of its amplified products. The composition of the probe structure in this embodiment is shown in the appendix figure 1 , the mechanism of action of the probe is shown in the appendix figure 2 , and the reaction schematic diagram of IMSA is detailed in patent CN104388581A. For the mechanism of dual fluorescence establishment, please refer to the summary of the invention.
[0079] Specific steps are as follows:
[0080] Step 1: Take an EP tube, add 9 μL of FAM-primer-2 (concentration of 20 μM) and 9 μL of Abcyl-primer-2 (concentration of 20 μM), mix well to make a probe solution, and incubate at 37°C in the dark for about 10 minute.
[0081] Step 2: Take 8 EP tubes, add 20.5 μL of react...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com