Method and system for determining nucleic acid sequence
A nucleic acid sequence and sequence technology, used in sequence analysis, biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of low total cellular RNA content, easy degradation, and difficult RNA.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] Example 1 Construction of a sequencing library and acquisition of sequencing data.
[0082] (1) Sample preparation
[0083] 1. Take 5-10mL of peripheral blood from the host, store it in EDTA anticoagulant tubes, and separate the peripheral blood within 4-6 hours;
[0084] 2. According to the instructions of the QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit extraction reagent, plasma free DNA was extracted, and Qubit (Invitrogen, the Quant-iT TM dsDNA HS Assay Kit) was used to quantify the extracted DNA, with a total amount of about 5-50 ng. Plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) was obtained.
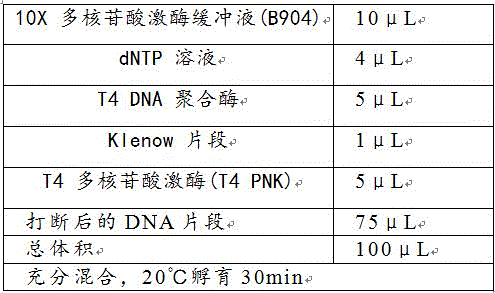
[0085] 3. Use an ultrasonic breaker to break the synthesized second-strand nucleic acid sample into fragments of about 200-300 bp in size. The breaking procedure is 15 s of breaking, 15 s of resting, and a total of 10 minutes of breaking. The product synthesized by the reaction was purified with a QIAquick PCR purification kit, and finally dissolved in 78 μL of ultrapure water.
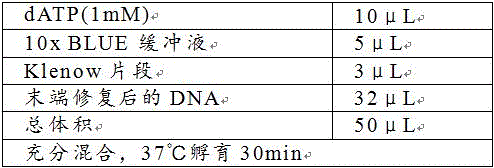
[0086] (2) Libra...
Embodiment 2
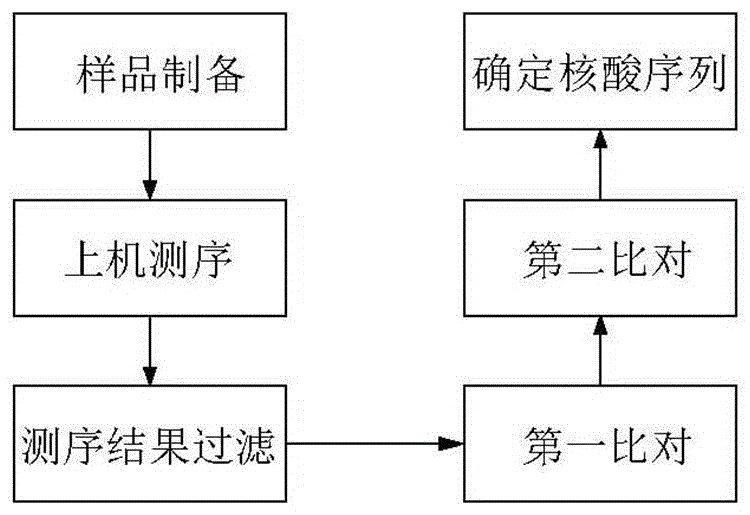
[0101] Example 2 Determining the nucleic acid sequence, the specific process is detailed in figure 1 .
[0102]1. Obtain sequencing data according to the method of Example 1.
[0103] 2. Filter the sequencing data. Remove reads with an uncertain base ratio greater than 1% and / or reads with a base quality value not greater than 5 and a ratio of not less than 50% of the reads to obtain the filtered sequencing results.
[0104] 3. The first comparison. Use the BWA comparison software to compare the filtered sequencing results with the host gene database as the first database, such as the human genome (hg19). After comparison, remove the matching sequencing sequences, that is, exclude the host gene sequence, and obtain non-matching sequence.
[0105] 4. The second comparison. Using the BWA comparison software, the obtained unmatched sequencing sequences are compared with the second database to obtain a second comparison result. The second database is a bacteria database or a...
Embodiment 3
[0108] Example 3 Construction of Nucleic Acid Sequence Expression Abundance Map
[0109] 1. Obtain the abundance of bacterial or viral species. According to the method of embodiment two, bacteria or virus comparison results are obtained, and the abundance of bacteria or virus species is calculated according to formula 1, and said formula 1 is:
[0110] 1
[0111] i is the species in the second database; N is the length of the entire sequence compared to the second database; Ni is the length of the sequence compared to the species; Li is the genome length of species i; bi is the abundance.
[0112] Formula 1 is the abundance of double normalization: for the abundance of a certain bacterial or viral species in a sample, it is the amount of data (bp) per thousand (bp) length from a certain species in the amount of data per million, In this way, the influence of species genome length and sample data volume is eliminated.
[0113] 2. Obtain the relative abundance of bacterial ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com