Lightweight carbon fiber thermal insulation material surface pore-sealing method
A technology of thermal insulation material and carbon fiber, which is applied in the field of inorganic thermal insulation materials, can solve the problems of high temperature and oxidation resistance, and achieve the effect of small impact and small overall thermal insulation performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
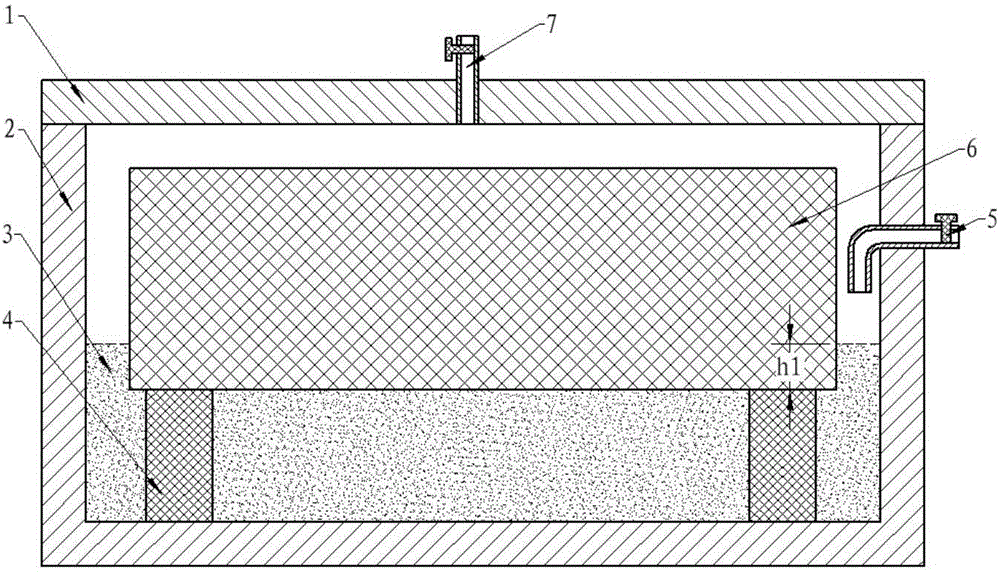
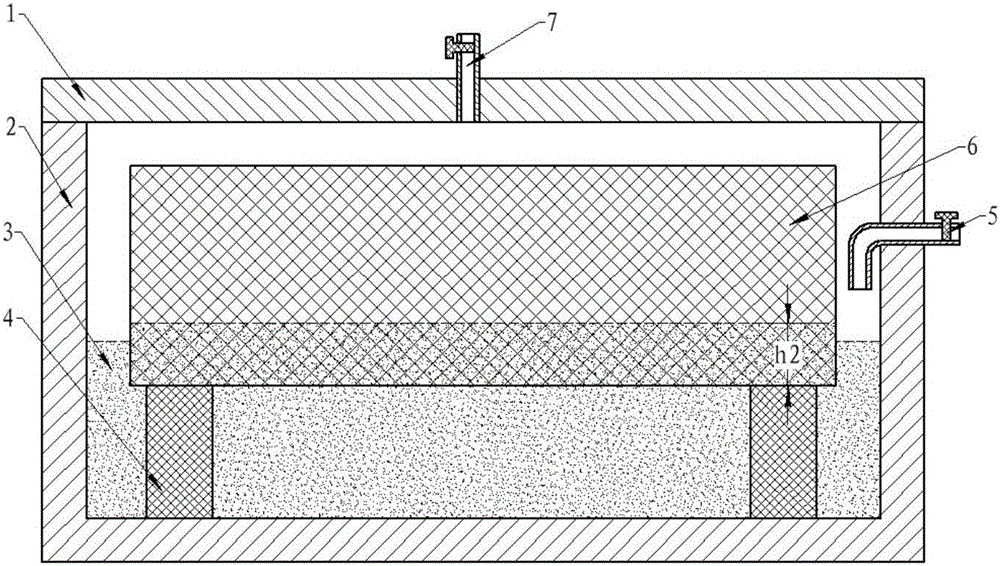
[0037] 1) With a bulk density of 0.5g / cm 3 The lightweight carbon fiber insulation material is used as the research object for surface sealing, and the surface pore size of the material is in the range of 30 μm to 110 μm. Select phenolic resin as the liquid phase carrier, use silicon carbide powder with a particle size of 45 μm as high-temperature resistant ceramic particles, and silicon powder with a particle size of 10 μm as the active component, and mix them according to the volume ratio of 5:1.5:1.5 to form a surface To densify the slurry, add an appropriate amount of ethanol to control its fluidity.
[0038] 2) Place the above-mentioned lightweight carbon fiber heat insulation material with the surface to be sealed facing down on the material pillar in the differential pressure siphon device (to prevent the material from floating, apply a heavy object on the upper surface), and then inject the surface densification slurry to make the material to be sealed. The sealing su...
Embodiment 2
[0042] 1) With a bulk density of 0.4g / cm 3 The lightweight carbon fiber insulation material is used as the research object for surface sealing, and the surface pore size of the material is in the range of 50 μm to 150 μm. Select molten sucrose as the liquid phase carrier, use tantalum silicide powder with a particle size of 80 μm as high-temperature-resistant ceramic particles, and use silicon powder with a particle size of 45 μm as the active component, and mix them according to the volume ratio of 8:1.5:2 to form a surface coating. Densified slurry.
[0043]2) Place the above-mentioned lightweight carbon fiber heat insulation material with the surface to be sealed facing down on the material pillar in the differential pressure siphon device (to prevent the material from floating, apply a heavy object on the upper surface), and then inject the surface densification slurry, so that After the surface is sealed, the slurry is submerged about 6mm. The bottom of the reverse diff...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 1) With a bulk density of 0.6g / cm 3 The lightweight carbon fiber insulation material is used as the research object for surface sealing, and the surface pore size of the material is in the range of 20 μm to 100 μm. Select molten medium-temperature asphalt as the liquid phase carrier, use zirconium boride powder with a particle size of 55 μm as high-temperature resistant ceramic particles, and use silicon powder with a particle size of 15 μm as the active component, and mix according to the volume ratio of 10:2.5:2 A surfaced densified slurry is formed.
[0048] 2) Place the above-mentioned lightweight carbon fiber heat insulation material with the surface to be sealed facing down on the material pillar in the differential pressure siphon device, and then inject surface densification slurry so that the surface to be sealed is submerged in the slurry by about 3mm. To keep the bitumen molten, the bottom of the differential pressure siphon is heated. The surface densifica...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com