Synchronous alignment device and method for short-pulse laser Thomson scattering signal light spots
A short-pulse laser and scattering signal technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, plasma, etc., can solve the problems of different passband wavelengths of interference filters, inability to obtain synchronous monitoring data, unsuitable for accurate comparison of weak signals, etc., and achieve data results Accurate and reliable, contrastive results that increase precision and confidence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
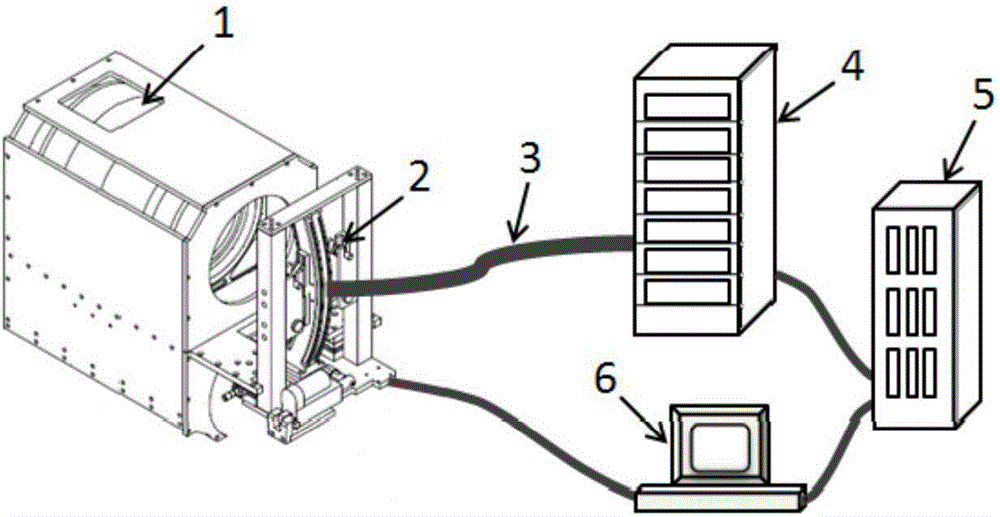
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, a short-pulse laser Thomson scattering signal spot synchronization aligning device includes a lens for collecting short-pulse laser Thomson scattering signals 1, at least two sets of optical fibers 3 with the same structure, and a multi-channel interference filter. Spectrometer 4 and control system 6;
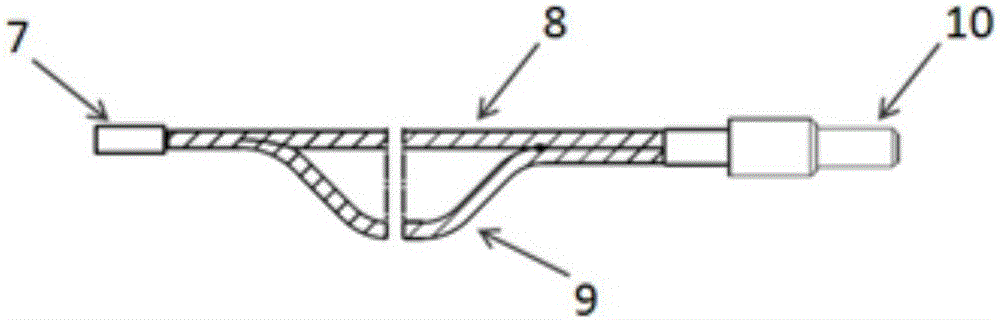
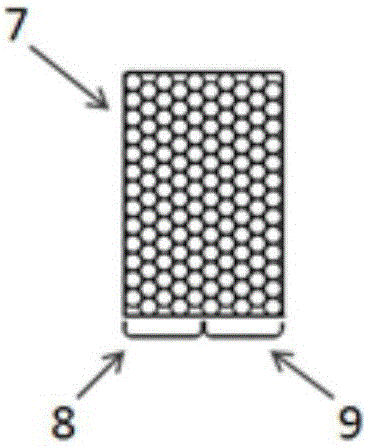
[0027] Such as figure 2 , 3 As shown in 4, each group of optical fibers 3 is composed of two signal transmission fibers 8, 9 of different lengths. The two signal transmission fibers 8, 9 are arranged in the same direction at one end to form a rectangular end face to form a receiving end 7, and the receiving end 7 The end faces of the two signal transmission fibers respectively form the left and right parts of the rectangle. The other ends of the two signal transmission fibers 8 and 9 in the same direction are uniformly mixed into a circular end face to form the output end 10. The receiving end of each group of optical fibers 3 receives the short c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com