Method for controlling generation of iodo-trihalomethanes in drinking water
A technology of trihalomethane iodide and drinking water, which is applied in the field of drinking water treatment, can solve the problems that no one has ever been involved in, and does not have continuous disinfection capabilities, so as to achieve outstanding safety, reduce the risk of carcinogenic by-products, and reduce the amount of production Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
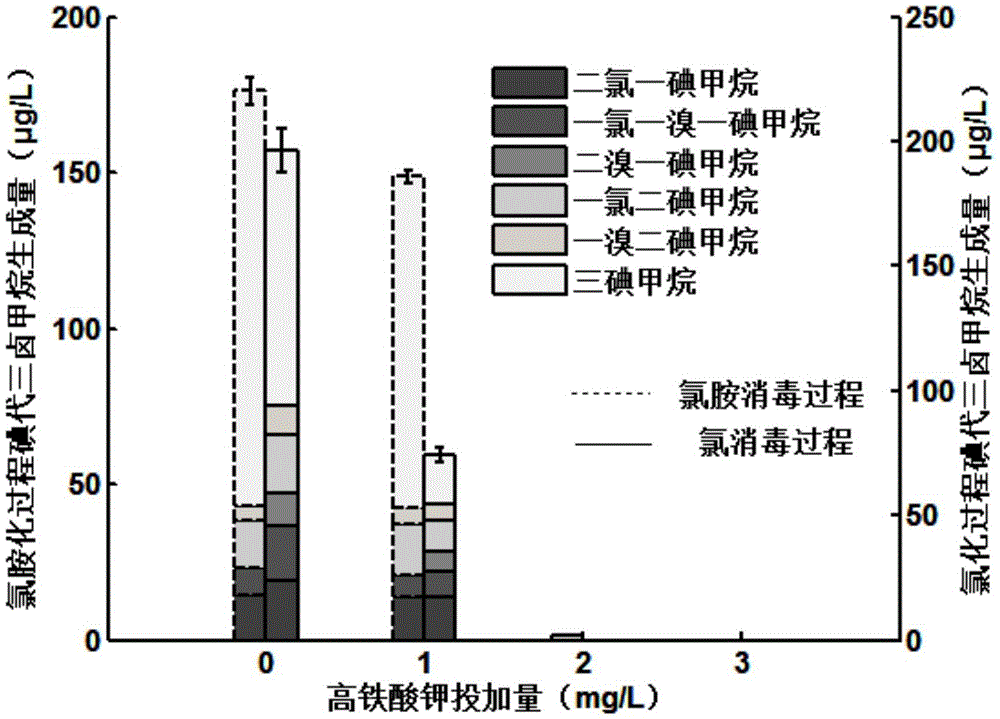
[0028] Add 10 μM iodide ions to the raw water of Huangpu River, control the temperature at 25°C, and pH 7, add potassium ferrate to the reaction solution for pre-oxidation test, and conduct static sedimentation and membrane filtration on the reaction solution after 30 minutes, and filter the water separately Add 3mg / L chlorine and chloramines. Calculated according to the concentration of substances in water, when the dosage of potassium ferrate is 0mg / L, 1mg / L, 2mg / L, and 3mg / L, the formation of I-THMs is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0029] from figure 1 It can be seen that the formation of I-THMs varies greatly under the condition of different dosage of high-speed rail. In the reaction solution without adding potassium ferrate, the amount of I-THMs generated during the chlorination and chloramination processes was close to 200 μg / L. When the dosage of potassium ferrate reached 1 mg / L, the amount of I-THMs generated during the chlorination process The reduction was more th...
Embodiment 2
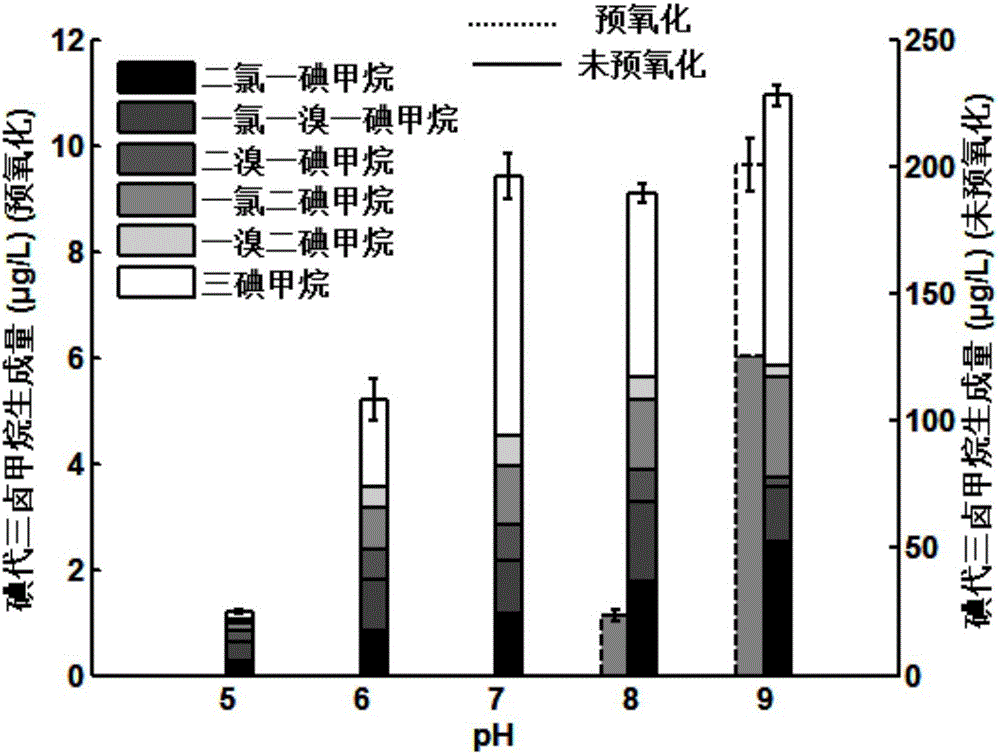
[0031] Add 10 μM iodide ions to the raw water of Huangpu River, control the temperature at 25°C, adjust the pH of the reaction solution, and add potassium ferrate at 2 mg / L. L Chlorine. When the pH is 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 respectively, the formation of I-THMs is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0032] Potassium ferrate is extremely oxidizing under acidic conditions, and can quickly oxidize iodide ions to iodate, and at the same time remove a large amount of natural organic matter. The simultaneous action of the two results in a sharp reduction in the generation of I-THMs.
Embodiment 3
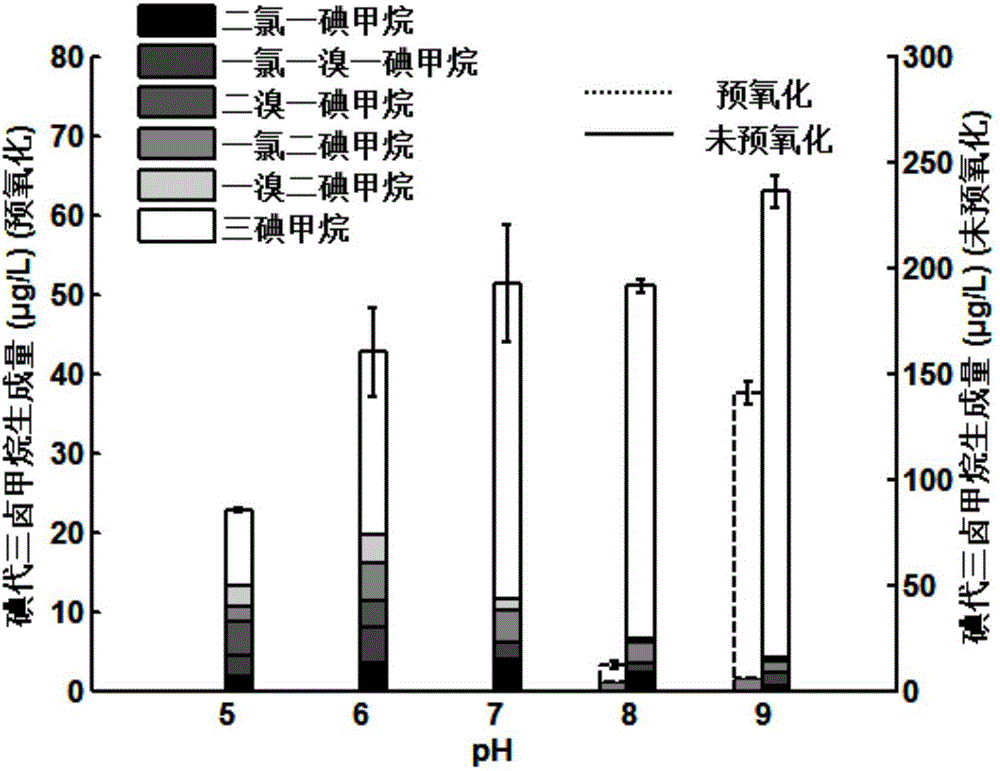
[0034] Add 10 μM iodide ions to the raw water of Huangpu River, control the temperature at 25°C, adjust the pH of the reaction solution, and add potassium ferrate at 2 mg / L. L Chloramine. When the pH is 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 respectively, the formation of I-THMs is as follows image 3 shown.
[0035]Chloramine is less oxidative than free chlorine, and chloramine can only oxidize iodide ions to active iodine species, but cannot further oxidize to iodate. Therefore, the generation of I-THMs in the chloramine disinfection process is much larger than that in the chlorination disinfection process. However, the addition of potassium ferrate under acidic conditions can completely avoid the formation of I-THMs in the process of chloramine disinfection. Although the formation of I-THMs cannot be completely avoided under alkaline conditions, the amount of formation is negligible.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com