Method for efficiently separating mouse spermatogonial stem cells
A spermatogonial stem cell and mouse technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of culturing cells, short doubling time, affecting the culture expansion, etc., and achieve the effects of saving the cost of cell culture, improving the separation purity, and the separation method is simple
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
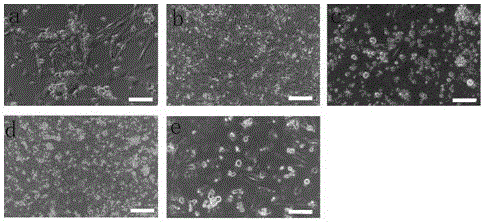
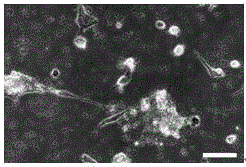
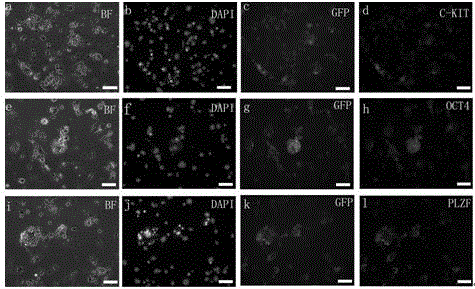
[0053] Establishment and culture of mouse spermatogonial stem cells
[0054] Step 1. Isolation and culture of testicular cells
[0055] (1) Male mice aged 7 days or 8 weeks after birth were killed by cervical dislocation, soaked in 75% alcohol for disinfection, and then the bilateral testes were taken out in an ultra-clean workbench, and the blood stains were washed with DPBS, and the albuginea was removed.
[0056] (2) Cut the tissue with scissors and move it to a 24-well plate containing 440 μl DPBS. Add 50 μl of collagenase IV at a concentration of 1 mg / ml and 10 μl of DNase I at a concentration of 7 mg / ml into the well plate. Digest in an incubator at ℃ for 15 minutes, and blow with a pipette every 3 minutes.
[0057] (3) Transfer the liquid in the orifice plate to a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of DPBS, centrifuge at 600g at 4°C for 7min, and discard the supernatant. Then add 1ml DPBS to resuspend the cells, centrifuge at 600g at 4°C for 7min and wash agai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com