Super-resolution microscopy method based on dual-mode competition stimulation and super-resolution microscopy device based on dual-mode competition stimulation
A super-resolution and dual-mode technology, applied in the field of super-resolution, can solve the problems of slow imaging speed, high optical power, complex imaging system, etc., and achieve the effect of simple device, convenient operation, and reduced light-emitting area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
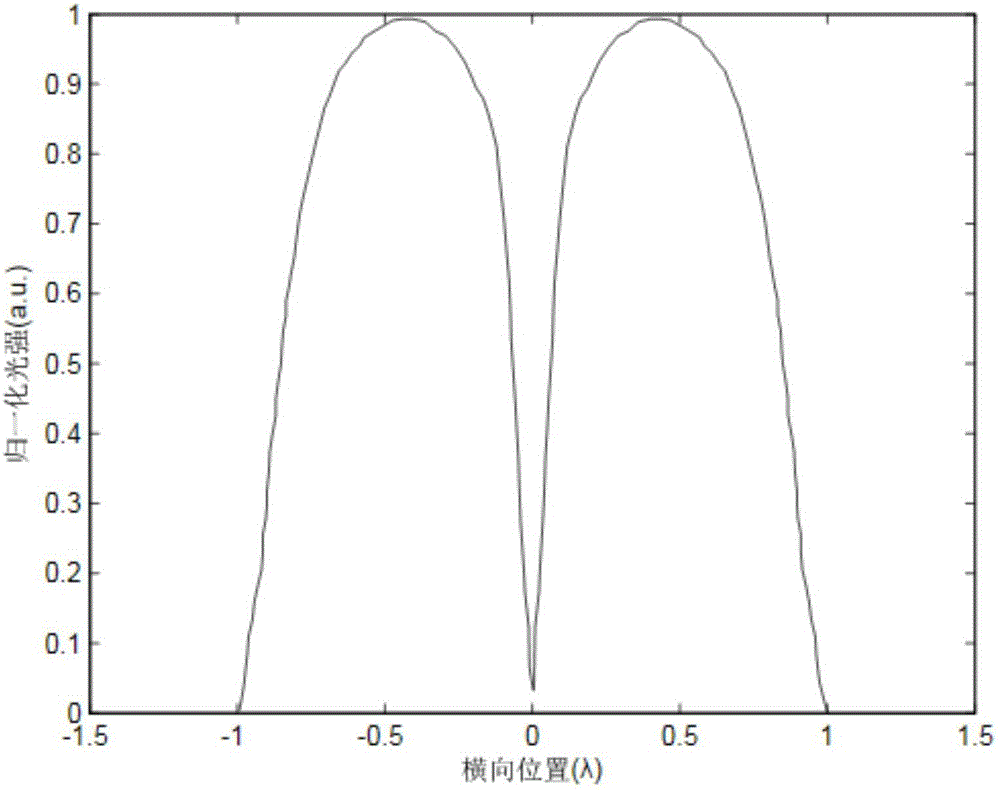
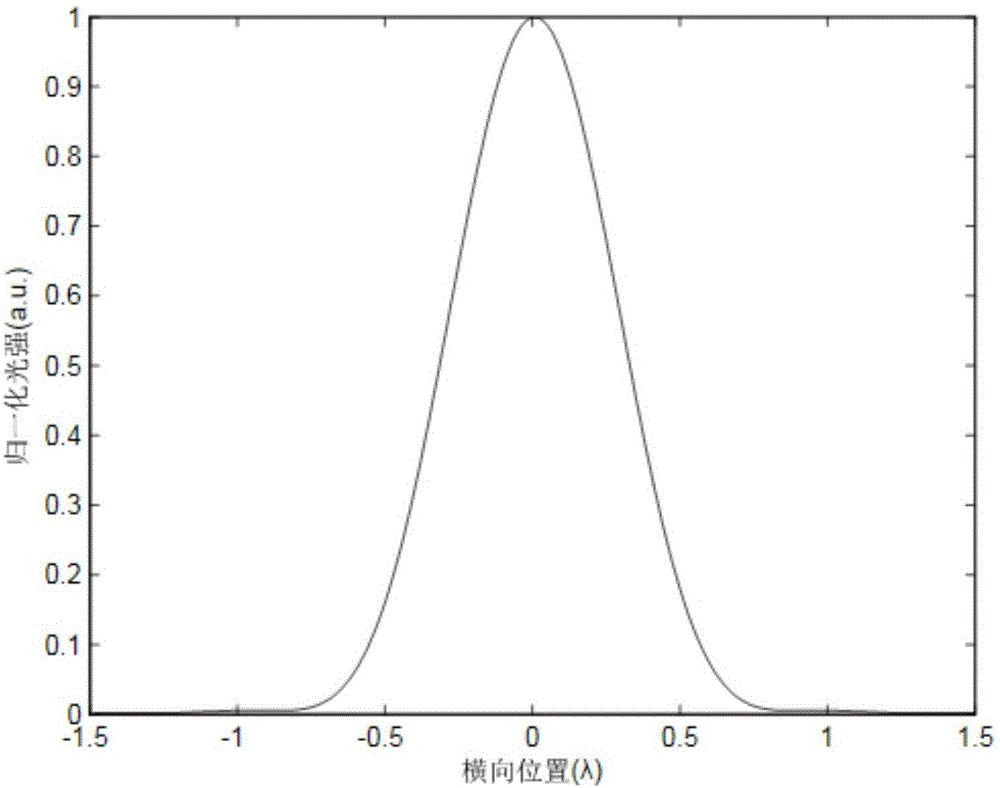
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0059] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the embodiments and accompanying drawings, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
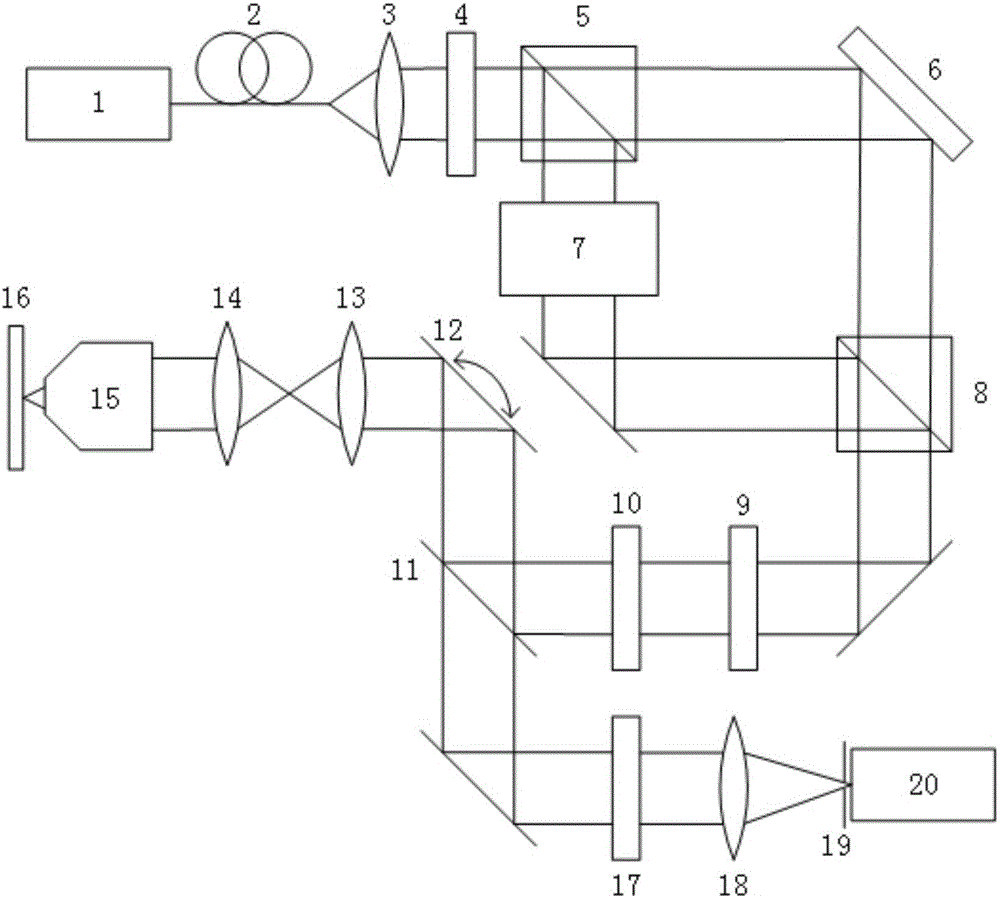
[0060] Such as figure 1 As shown, the super-resolution microscopy device of this embodiment includes: a laser 1, a single-mode fiber 2, a collimator lens 3, a 1 / 2 wave plate 4, a polarization beam splitter 5, a spatial light modulator 6, and an acousto-optic modulation Device 7, polarization beam combiner 8, 1 / 4 wave plate 9, 1 / 4 wave plate 10, dichroic mirror 11, scanning galvanometer 12, scanning lens 13, field lens 14, microscope objective lens 15, sample stage 16, Bandpass filter 17, focusing lens 18, pinhole 19, detector 20.
[0061] Wherein, the single-mode fiber 2, the collimating lens 3, the 1 / 2 wave plate 4, the polarization beam splitter 5, and the spatial light modulator 6 are sequentially located on the optical axis of the laser 1 outgoing beam; the 1 / 2 wave plate 4 The direction of the l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com