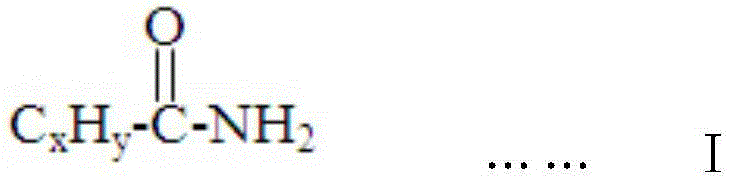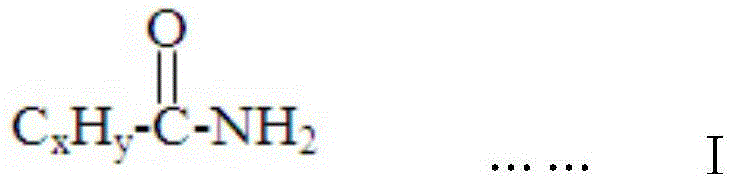Additive for producing melt-blown nonwoven fabrics, and use method thereof
A technology of melt-blown non-woven fabrics and additives, applied in non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking, single-component polyolefin rayon, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable production efficiency, long production process, high cost, and achieve improved production efficiency. The effect of production efficiency, production cost reduction and production time reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Additive A1 was prepared by mixing 2% fatty acid amide and 98% bis-tert-butyl peroxide in a weight ratio.
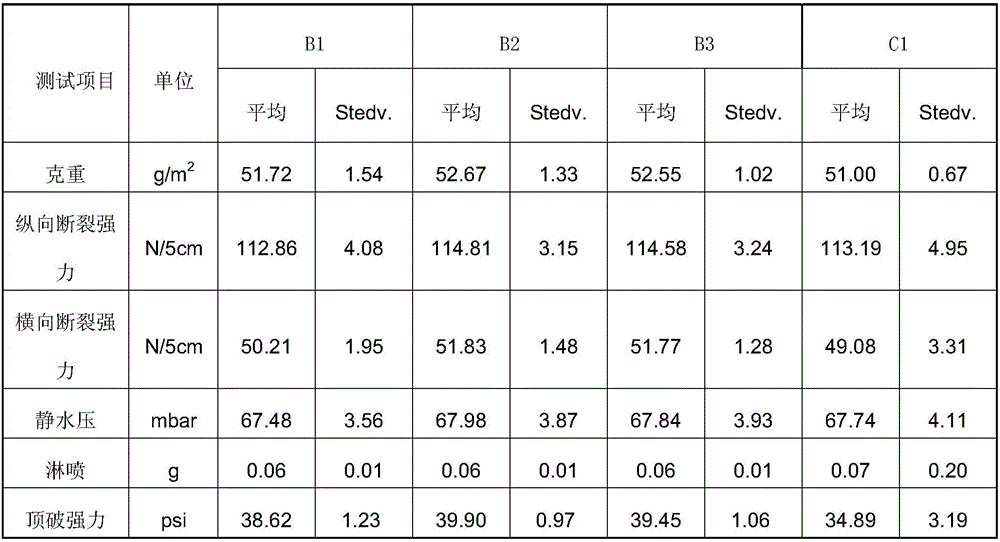
[0054] Add additive A1 to the polypropylene raw material with low melt index, put it into the extruder to heat and melt it, so that the additive A1 reaches 1.8% of the total proportion of the melt, and extrude it from the spinneret hole on the die through the melt distribution flow channel, The hot air flow is super-drawn, and the ultra-fine fibers are cooled and solidified, deposited on the net collection device, and wound into a net to obtain a melt-blown non-woven fabric. Then make 52g / m2 by conventional process method 2 SMMS non-woven fabric B1.
Embodiment 2
[0056] The additive A1 in Example 1 is added to polyolefin for mixing and kneading, and the mixed masterbatch is obtained through the processing processes such as extruder and other equipment metering, mixing, melting, extrusion, pelletizing, etc., and the mixed masterbatch contains 30% The effective component mixture of additive A2 is obtained.
[0057] Add additive A2 to the polypropylene raw material with low melt index, put it into the extruder to heat and melt it, so that the additive A2 reaches 1.8% of the total proportion of the melt, and extrude it from the spinneret hole on the die through the melt distribution flow channel, The hot air flow is super-drawn, and the ultra-fine fibers are cooled and solidified, deposited on the net collection device, and wound into a net to obtain a melt-blown non-woven fabric. Then make 52g / m2 by conventional process method 2 SMMS non-woven fabric B2.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Add fatty acid amide and bis-tert-butyl peroxide into polyolefin for mixing and kneading respectively, and obtain fatty acid amide masterbatch and bis-tert-butyl peroxide through extruder and other equipment metering, mixing, melting, extrusion, pelletizing and other processing processes. Peroxide masterbatch, the fatty acid amide masterbatch contains 30% fatty acid amide, and the bis-tert-butyl peroxide contains 30% bis-tert-butyl peroxide. Additive A3 was prepared by mixing 2% fatty acid amide masterbatch and 98% bis-tert-butyl peroxide masterbatch by weight.
[0060] Add additive A3 to the polypropylene raw material with low melt index, put it into the extruder to heat and melt it, so that the additive A3 reaches 1.8% of the total proportion of the melt, and extrude it from the spinneret hole on the die through the melt distribution channel, The hot air flow is super-drawn, and the ultra-fine fibers are cooled and solidified, deposited on the net collection device, a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melt index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com