Method for nanotube-height-aided control of cytoskeleton change
A highly assisted, cytoskeletal technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc. for materials and surface science, can solve the problem of decreased differentiation speed of osteoblasts or stem cells, unfavorable repair and replacement, and proportional reduction, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below. This embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operating procedures are provided, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following implementation example.
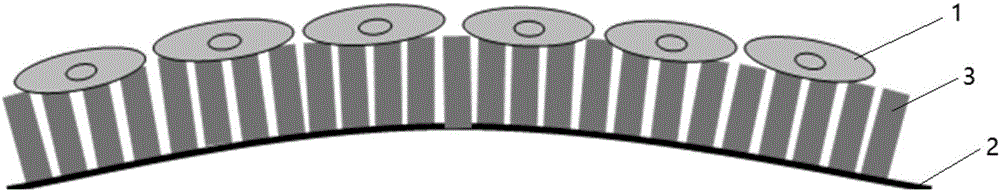
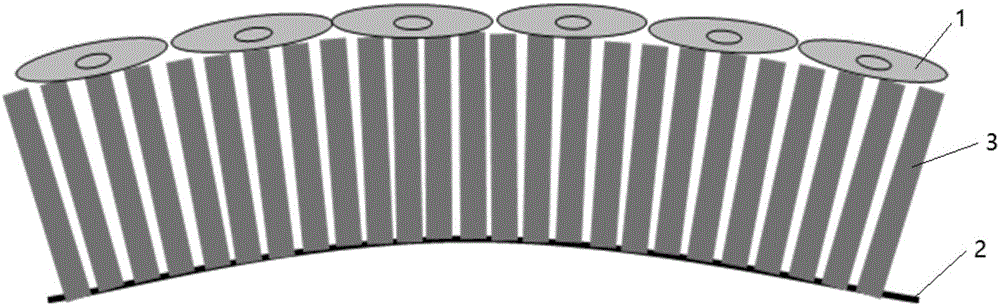
[0029] The present invention provides a method for highly assisted control of cytoskeleton changes using nanotubes, such as figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0030] Anodic oxidation of pure titanium and low-modulus duplex titanium metal test pieces is carried out with organic solution (alcohol-based oxidation medium as electrolyte, such as ethanol solution containing calcium and phosphorus elements), and field emission scanning electron microscope, atomic force microscope, X-ray Diffractometer, Auger spectrometer, X-ray photoelectron spectrometer and other means systematic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com