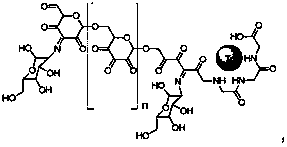
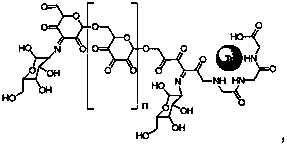
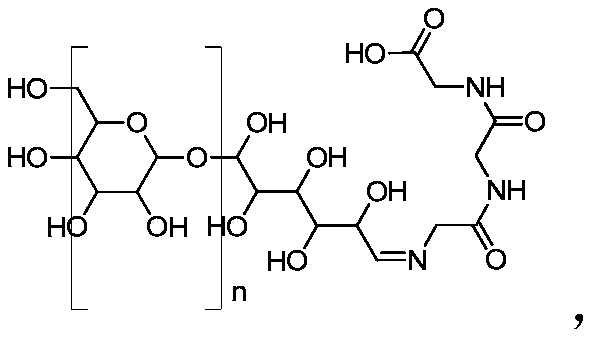
A macromolecular imaging agent for lymph node inspection and preparation method thereof
An imaging agent and macromolecule technology, applied in the field of macromolecular imaging agent for lymph node examination and its preparation, can solve the problems of only one, affecting the stability and effect of the drug, and inhomogeneity, so as to improve the effectiveness, The effect of improving uniformity and increasing retention capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1 macromolecular compound imaging agent 1
[0053] (1) Gly-gly-gly connection:
[0054] In a 100ml round bottom flask add 5g dextran, 0.21g gly-gly-gly and 50ml DMSO. A drop of acetic acid was used as a catalyst and reacted at 80°C for two hours to obtain the first intermediate product. After cooling to room temperature, add 0.084g NaBH 4 and stir overnight. Then add 20ml deionized water and shake well. Finally, the mixed solution was first filtered with a 0.45 μm membrane, and then dialyzed with 10 times of deionized water. The molecular weight cut-off of the semipermeable membrane was 3000. Finally, the dialyzate was concentrated and freeze-dried to obtain the first product.
[0055] (2) Connection of Mannose: The connection of Mannose is divided into two steps.
[0056] The first step is the oxidation of the hydroxyl groups on the dextran backbone. Add 1 g of the gly-gly-gly connected product in the previous step, 7.06 g of Dess-Martin oxidant, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2 macromolecular compound imaging agent 2
[0068] (1) Gly-gly-gly connection:
[0069] In a 100ml round bottom flask add 20g dextran, 1g gly-gly-gly and 50ml DMSO. 4 drops of acetic acid were used as a catalyst, and reacted at 80°C for two hours to obtain the first intermediate product. After cooling to room temperature, add 0.5 g NaBH 4 and stir overnight. Then add 80ml deionized water and shake well. Finally, the mixed solution was first filtered with a 0.45 μm membrane, and then dialyzed with 10 times of deionized water. The molecular weight cut-off of the semipermeable membrane was 3000. Finally, the dialyzate was concentrated and freeze-dried to obtain the first product.
[0070] (2) Connection of Mannose: The connection of Mannose is divided into two steps.
[0071] The first step is the oxidation of the hydroxyl groups on the dextran backbone. Add 1 g of the gly-gly-gly connected product in the previous step, 6.2 g of Dess-Martin oxidant, and 3...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3 macromolecular compound imaging agent 3
[0082] (1) Gly-gly-gly connection:
[0083] In a 100ml round bottom flask add 5g dextran, 0.21g gly-gly-gly and 50ml DMSO. A drop of acetic acid was used as a catalyst and reacted at 80°C for two hours to obtain the first intermediate product. After cooling to room temperature, add 0.084g NaBH 4 and stir overnight. Then add 20ml deionized water and shake well. Finally, the mixed solution was first filtered with a 0.45 μm membrane, and then dialyzed with 10 times of deionized water. The molecular weight cut-off of the semipermeable membrane was 3000. Finally, the dialyzate was concentrated and freeze-dried to obtain the first product.
[0084] (2) Connection of Mannose: The connection of Mannose is divided into two steps.
[0085]The first step is the oxidation of the hydroxyl groups on the dextran backbone. Add 1 g of the gly-gly-gly connected product in the previous step, 7.06 g of Dess-Martin oxidant, and 3...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com