A screening method for recombinant vectors and non-transgenic gene editing plants
A recombinant vector and gene editing technology, applied in the field of plant gene editing, can solve the problems of inability to amplify specific bands, side effects, false negatives, etc., and achieve the effect of cheap screening methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] 1. Preparation of BelRNAi gene transcription unit
[0041] The RNA interference used here mainly interferes with Bel transcripts in cells by introducing a 300bp long hairpin (Hairpin) structure.
[0042] Using primers Beli-F1 (gagctcAGCTTAGCCATGGATAACGCCTAC, the lowercase underline is the SacⅠ restriction site) and Beli-R1 (ctgcagAAGGTCACGTCGTGCTCGGTGAAGCACTC, the lowercase underline is the PstⅠ restriction site), and the forward sequence was obtained by PCR amplification.
[0043] On the other hand, primers Beli-F2 (ggtaccAGCTTAGCCATGGATAACGCCTAC, the lowercase underline is the KpnI restriction site) and Beli-R2 (ctcgagAAGGTCACGTCGTGCTCGGTGAAGCACTC, the lowercase underline is the XhoI restriction site) were used. Sequencing was performed after connecting the two sequences to the T vector, and the sequencing result was SEQ ID NO.1.
[0044] After the sequencing is correct, the sequence is loaded into PCAMBIA-1301, assembled with the d35S and NOS terminal on the carrier...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 Using the gene OsLCT1 (Os06g0579200) related to cadmium (Cd) transport as the target gene, screening of plants without transgenic fragments
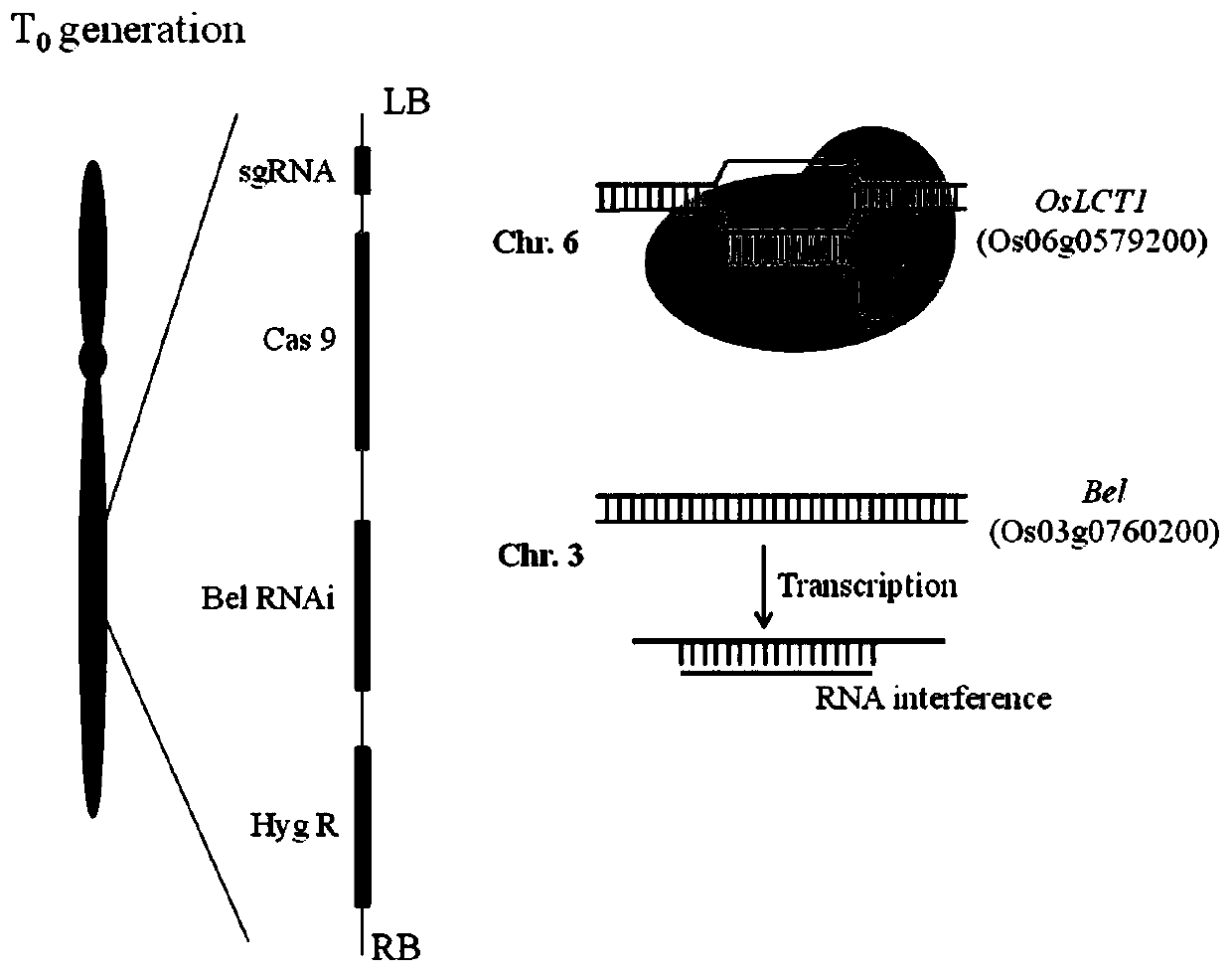
[0050] The cadmium (Cd) transport-related gene OsLCT1 (Os06g0579200) was used as the target gene, and the 20bp fragment 5'-TACTATCCCGCGTGCCAATG-3' was introduced as sgRNA to generate the OsLCT1 mutant.
[0051] Such as figure 2 shown, at T 0 In the generation, on the one hand, the sgRNA will be transcribed under the promoter U3 and matched to the gene OsLCT1; the Cas9 gene is also transcribed and translated into a nuclease in rice cells. The two work together to cleave the target and then introduce mutations during DNA repair in rice cells. On the other hand, the Bel RNAi hairpin structure is transcribed to form RNA, which matches the Bel RNA existing in rice cells, interrupts its fragments, and affects translation.
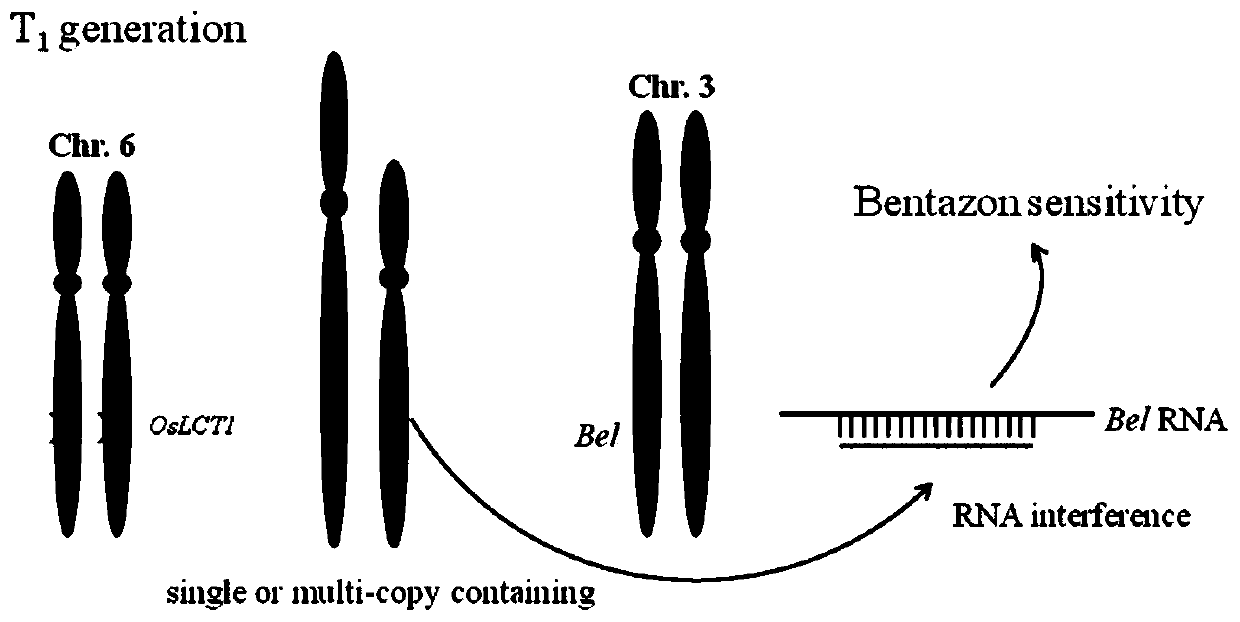
[0052] Through the above steps of Example 1, 58 rice plants were obtained, and the first 30 plants w...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3 Using the gene Betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (OsBADH2) that controls the aroma of rice as the target gene, screening of plants without transgenic fragments
[0071] In order to further verify the applicability of the newly constructed vector pHun4c12-Beli. At the same time, the gene Betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (OsBADH2) was used as the target gene for experiments, and the OsBADH2 mutant plants will show rice aroma and improve rice quality.
[0072] Experimental process and steps are consistent with embodiment 2.
[0073] Select two of the mutant lines, for T 1 Substitute plants were treated with bentazone.
[0074] The result is as Figure 6 As shown, plants showing bendazone sensitivity and resistance in the same line. Among them, the surviving plants are the ideal plants with mutation of gene OsBADH2 and no T-DNA insertion, which can be used for production and rice breeding.
[0075]
[0076]
[0077]
[0078]
[0079]
[0080] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com