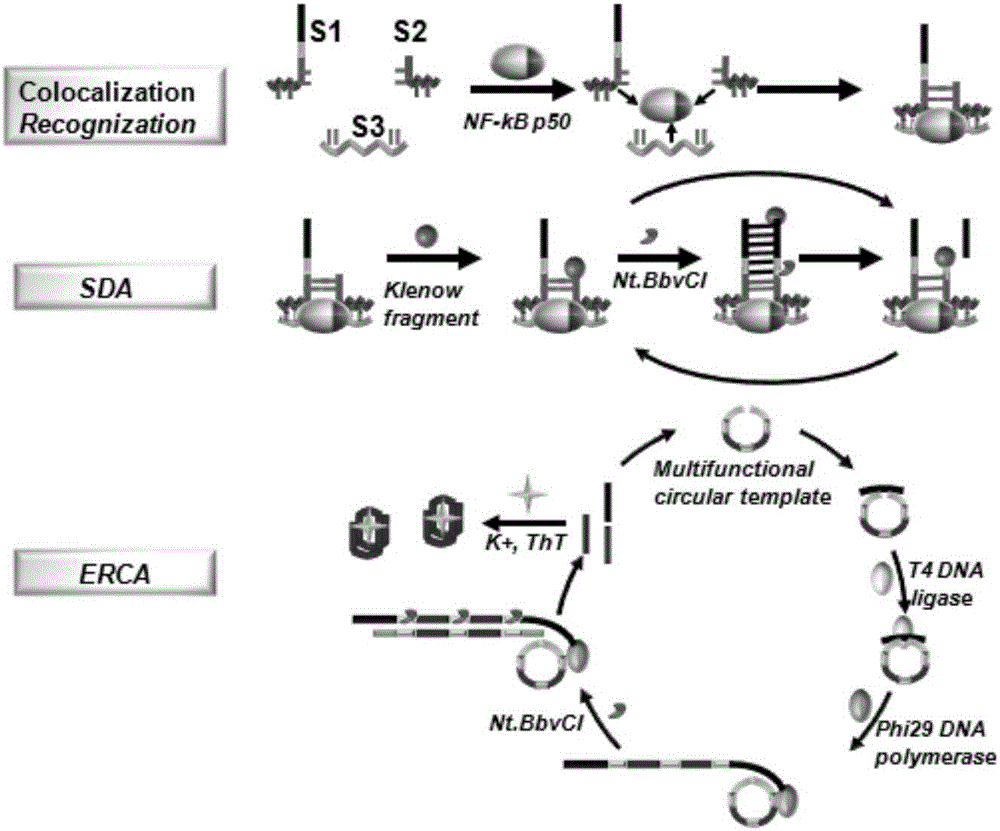
Method for detecting transcription factor through cascade signal amplification strategy on basis of colocalization recognition and activation
A technology for transcription factors and site recognition, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological determination/testing, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve problems such as false positive signals, and achieve the effect of eliminating false positive signals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1: Detection of transcription factors (NF-κB p50) based on a cascade signal amplification strategy based on colocalization recognition activation
[0067] The specific method is as follows:
[0068] (1) Co-regional identification
[0069] 1 μL Cutsmart, 40 nM S1, S2, S3, different concentrations of NF-κB p50 or actual samples were included in a 10 μL reaction system, placed in a 37°C incubator after slight shaking, and reacted for 4 hours.
[0070] (2) Strand Displacement Amplification (SDA)
[0071] In a 20 μL reaction system, 10 μL colocalization recognition product, 2 μL Cutsmart, 1.5mM dNTPs, 1U Klenow fragment, 2U Nt.BbvCI, placed in a 37°C incubator after slight shaking, reacted for 0.5h, and then inactivated at 85°C 0.5h.
[0072] (3) Exponential Rolling Circle Amplification (ERCA)
[0073] ERCA includes ligation and amplification reactions. The ligation reaction was carried out in a 30 μL reaction system, including 20 μL of SDA product, 3 μL of T4 l...
Embodiment 2
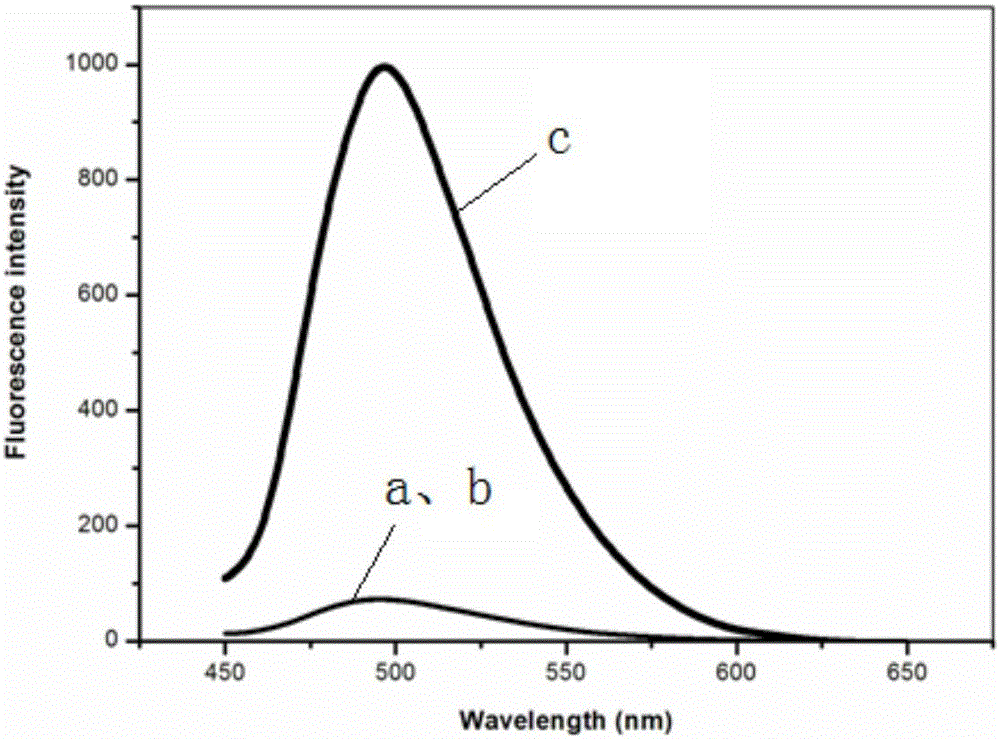
[0077] Embodiment 2: Feasibility study of detection method of the present invention
[0078] In order to verify the feasibility of the detection method of the present invention, the present invention investigates the feasibility of the detection method of the present invention by measuring and comparing the fluorescence intensity under different conditions, such as figure 2shown. It can be seen that both the dyes ThT (a) and negative (b, close to coincide with a) show weak fluorescence, indicating that in the absence of the target NF-κB p50, the three split recognition components cannot self-hybridize into a double-stranded structure, triggering The subsequent cascade signal amplification; when the target NF-κB p50 exists, the fluorescence intensity increases sharply (c), indicating that the affinity induction of the target makes the split recognition components approach each other, and then hybridize into a double-stranded structure, triggering the subsequent cascade signal...
Embodiment 3
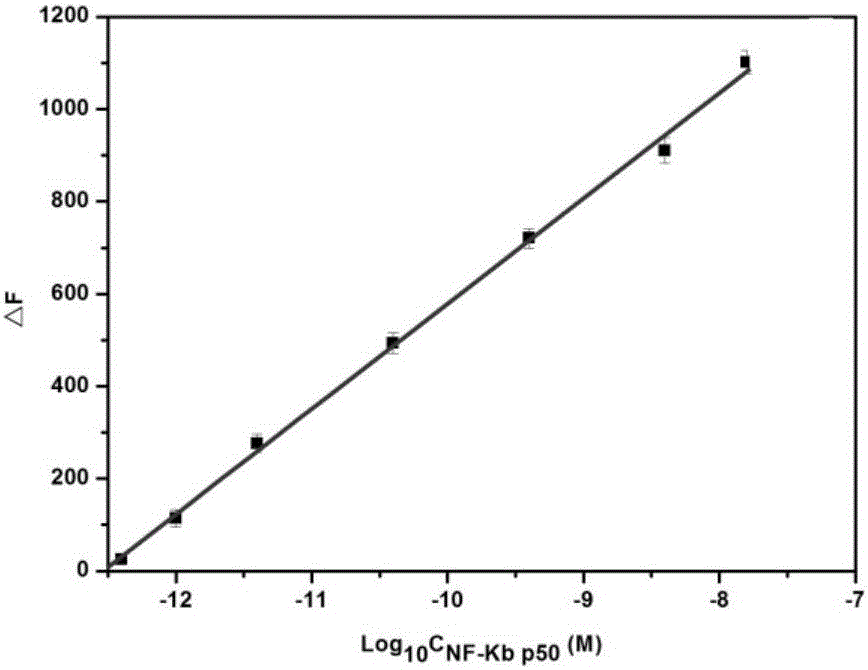
[0079] Embodiment 3: the sensitivity investigation of detection method of the present invention
[0080] The linear range and sensitivity of the method can be determined by measuring the fluorescence intensity corresponding to different concentrations of the target. Such as image 3 shown. It can be seen that the target concentration is 3.8×10 -13 M-1.5×10 -8 In the M range, ΔF has a linear relationship with the logarithm of the target concentration (R 2 =0.994), the estimated LOD of this detection method is 2.5×10 -13 M, better than most reported sensitivities in the literature.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com