Method for preparing phase shift optical fiber bragg grating based on femtosecond laser direct writing
A fiber Bragg and femtosecond laser technology, applied in the field of fiber optics and nonlinear optics, can solve the problems of inability to precisely control the size of the phase shift, time-consuming, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing precision requirements, simple operation, and high processing accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] This embodiment takes processing a high-temperature F-P temperature sensor as an example, as follows:
[0033] Original material: Fiber Bragg Grating
[0034] The preparation steps of FBG with phase shift structure are described in detail as follows:
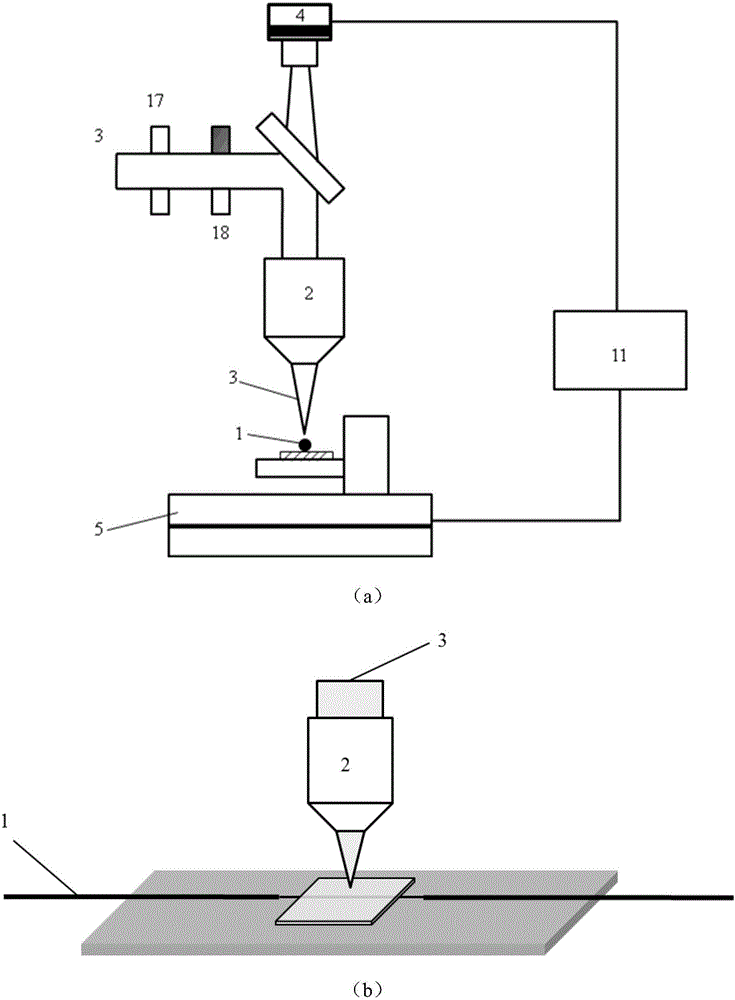
[0035] (1) Fix the fiber Bragg grating 1 on a glass slide, and add a refractive index matching solution to the grating area, and then cover it with a cover glass, such as figure 1 shown;
[0036] (2) Place the fixed fiber Bragg grating 1 on the three-dimensional electric translation platform 5, such as figure 1 shown. The repetition frequency of the femtosecond laser 3 is 1000 Hz, the pulse width is 50 fs, and the power is set at 0.7 mW. A microscopic objective lens 2 with 20× and a numerical aperture of 0.45 is selected to focus the femtosecond laser 3 near the core of the fiber Bragg grating 1 through the microscopic objective lens 2 . The scan rate of the three-dimensional electric translation stage 5 is 20 μm / s. ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Original material: Fiber Bragg Grating.
[0042] (1) Fixing of the fiber Bragg grating 1 Refer to the corresponding process of the first embodiment.
[0043] (2) The process of femtosecond laser 3 scanning the optical fiber refers to the corresponding process of embodiment 1. The parameters are: the repetition frequency of femtosecond laser 3 is 1000 Hz, the pulse width is 50 fs, and the power is set to 2 mW; select 20 ×, numerical aperture 0.45 The microscope objective lens 2; the scanning rate of the three-dimensional electric translation stage 5 is 20 μm / s.
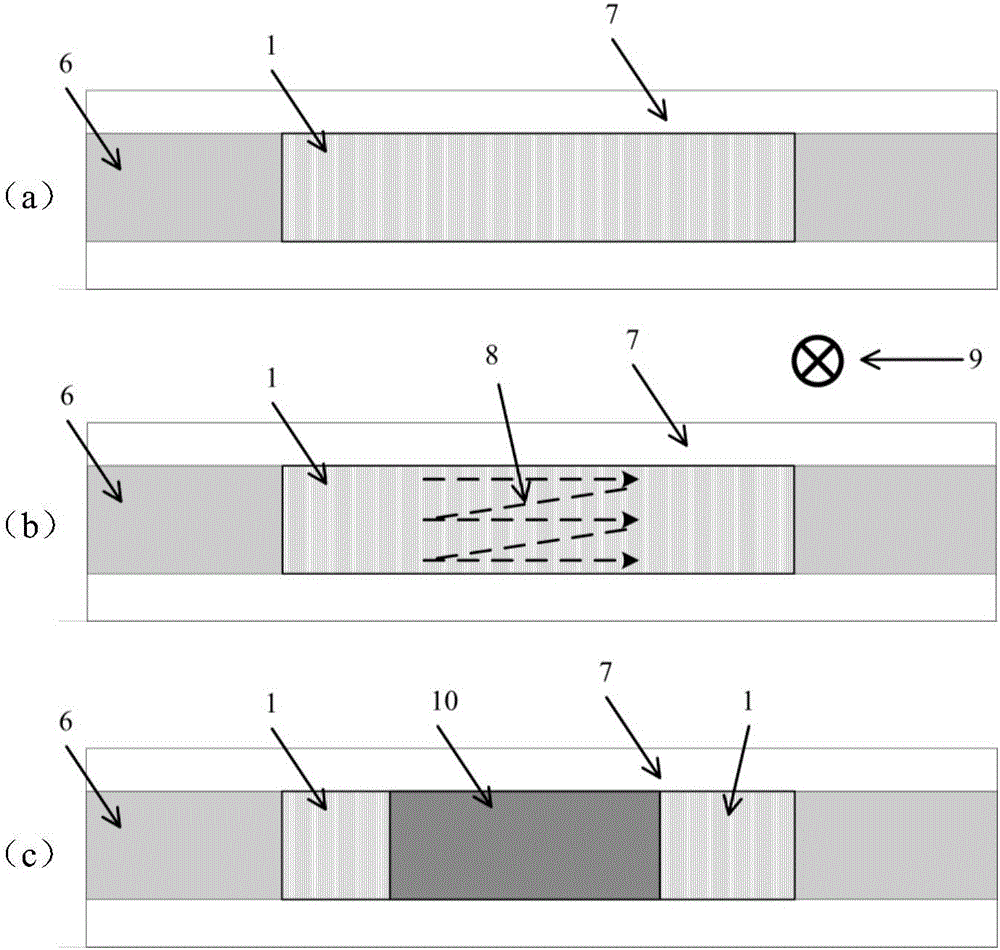
[0044] (3) Refer to Case 1 for the scanning method of the femtosecond laser. The scanning length is 1000 μm. After scanning the first straight line, move 0.8 μm vertically to scan the second line. A total of 14 lines are scanned to cover the entire fiber core area.
[0045] (4) Cleaning of the optical fiber after scanning by the femtosecond laser 3 refers to the corresponding process of Example 1.
[0046] F...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Original material: Fiber Bragg Grating.
[0049] (1) Fixing of the fiber Bragg grating 1 Refer to the corresponding process of the first embodiment.
[0050] (2) The process of femtosecond laser 3 scanning the optical fiber refers to the corresponding process of embodiment 1. The parameters are: the repetition frequency of femtosecond laser 3 is 1000Hz, the pulse width is 50fs, and the power is set to 8mW; select 5×, numerical aperture 0.15 The microscope objective lens 2; the scanning rate of the three-dimensional electric translation stage 5 is 195 μm / s.
[0051] (3) Refer to Case 1 for the scanning method of the femtosecond laser. The scanning length is 1500 μm. After scanning the first straight line, move 0.9 μm vertically to scan the second line. A total of 12 lines are scanned to cover the entire fiber core area.
[0052] (4) Cleaning of the optical fiber after scanning by the femtosecond laser 3 refers to the corresponding process of Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com