Watermelon sweetness-increasing and high-yield planting method
A planting method and a sweet and high-yield technology, applied in the field of watermelon sweetening and high-yielding planting, can solve the problems of the sweetness not reaching consumers, the low yield of watermelon, affecting the economic benefits of melon farmers, etc. The effect of resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
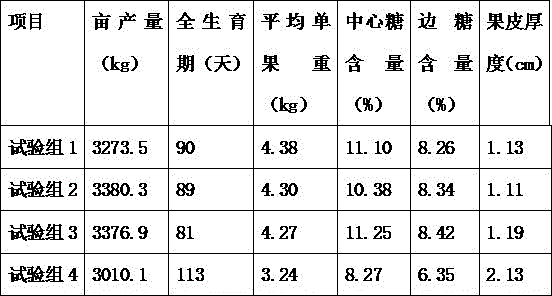
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] A watermelon sweetening and high-yield planting method, comprising the following steps:
[0015] (1) Base fertilizer application: Before transplanting, apply 1300kg of fertilizer A per mu, wherein fertilizer A is made of the following components by weight: 9 parts of sodium erythroconate, 6 parts of mandelic acid, 50 parts of chicken manure, tea 23 parts of seed cake fertilizer, 19 parts of ammonium nitrate, 15 parts of potassium phosphate;
[0016] (2) Seedling fertilization: 18 days after the melon seedlings are transplanted, apply 600kg of fertilizer B per mu, and then put a cotton cloth soaked in nutrient solution on the root of the watermelon seedlings. The size of the cotton cloth is 10*10cm, and the fertilizer B consists of the following parts by weight Made of components: 30 parts of urea, 7 parts of acridinium ester, 6 parts of 2,6-diaminopurine, 5 parts of EDTA calcium salt, 9 parts of organic bentonite;
[0017] (3) Fruit fertilization: After the watermelon ...
Embodiment 2
[0021] A watermelon sweetening and high-yield planting method, comprising the following steps:
[0022] (1) Base fertilizer application: Before transplanting, apply 1400kg of fertilizer A per mu, wherein fertilizer A is made of the following components by weight: 10 parts of sodium erythroconate, 6 parts of mandelic acid, 55 parts of chicken manure, tea 24 parts of seed cake fertilizer, 20 parts of ammonium nitrate, 16 parts of potassium phosphate;
[0023] (2) Seedling fertilization: 19 days after the melon seedlings are transplanted, apply 650kg of fertilizer B per mu, and then put a cotton cloth soaked in nutrient solution on the root of the watermelon seedlings. The size of the cotton cloth is 10*10cm, and the fertilizer B consists of the following parts by weight Made of components: 35 parts of urea, 9 parts of acridinium ester, 8 parts of 2,6-diaminopurine, 6 parts of EDTA calcium salt, 10 parts of organic bentonite;
[0024] (3) Fruit fertilization: After the watermelo...
Embodiment 3
[0028] A watermelon sweetening and high-yield planting method, comprising the following steps:
[0029] (1) Base fertilizer application: Before transplanting, apply 1500kg of fertilizer A per mu, wherein fertilizer A is made of the following components by weight: 11 parts of sodium erythroconate, 7 parts of mandelic acid, 60 parts of chicken manure, tea 25 parts of seed cake fertilizer, 21 parts of ammonium nitrate, 17 parts of potassium phosphate;
[0030] (2) Seedling fertilization: 20 days after the melon seedlings are transplanted, apply 700kg of fertilizer B per mu, and then put a cotton cloth soaked in nutrient solution on the root of the watermelon seedlings. The size of the cotton cloth is 10*10cm, and the fertilizer B consists of the following parts by weight The components are made of: 40 parts of urea, 11 parts of acridinium ester, 9 parts of 2,6-diaminopurine, 7 parts of EDTA calcium salt, and 13 parts of organic bentonite;
[0031] (3) Fruit fertilization: After ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com