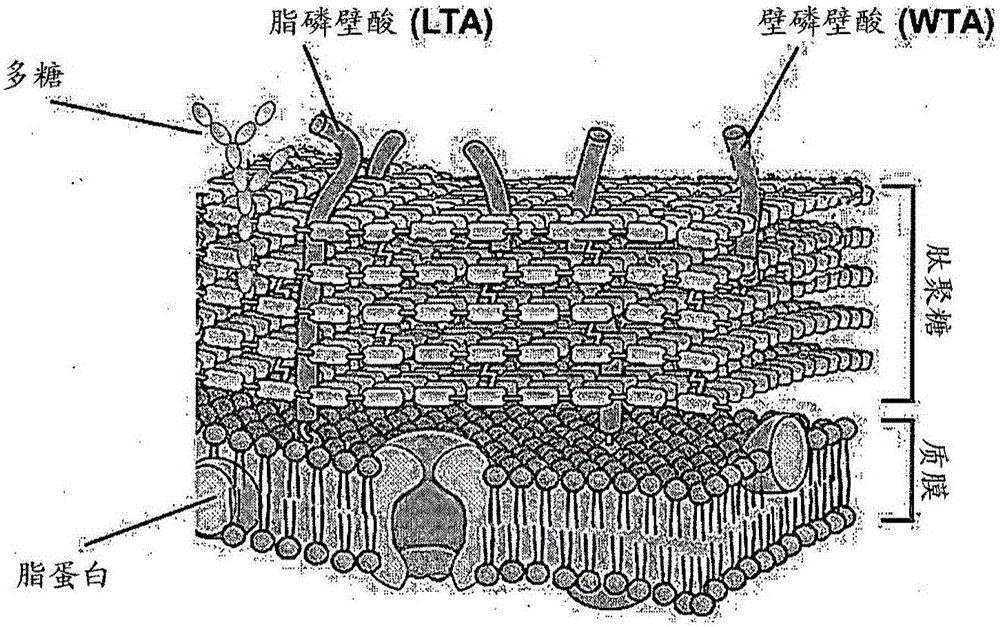
Composition for preventing or treating staphylococcus aureus infection
A staphylococcus, composition technology, applied in the direction of antibacterial drugs, antifungal agents, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve difficult identification, difficulty in prevention and treatment of infectious diseases, separation/purification of difficult materials, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
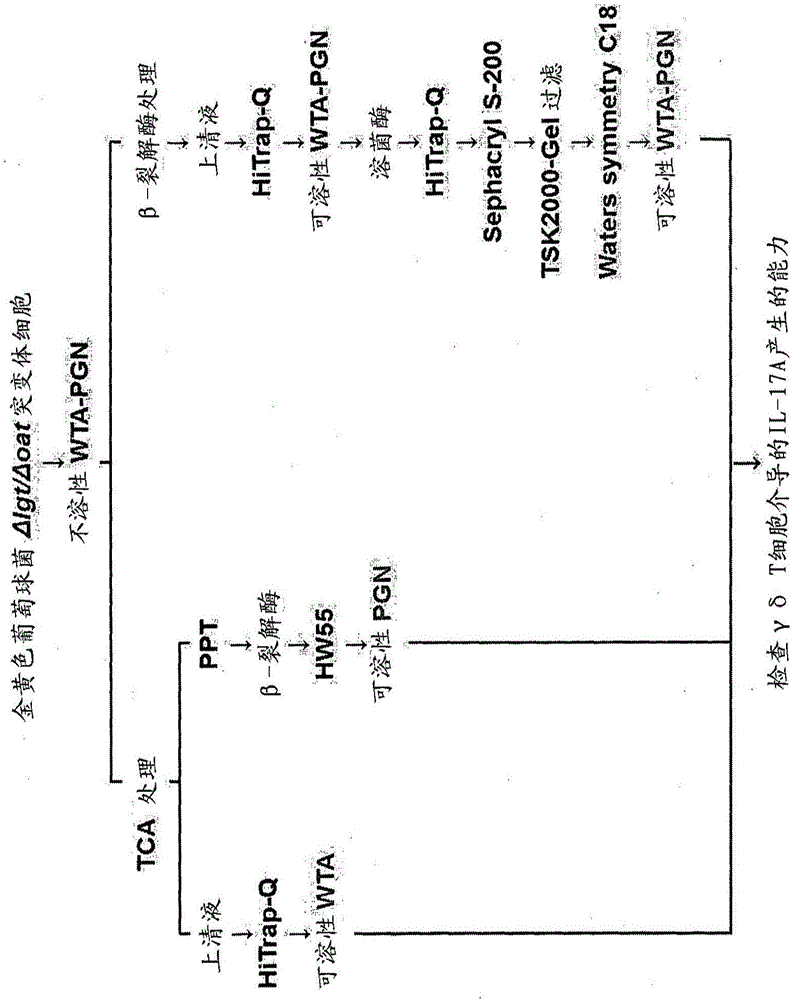
[0125] Embodiment 1: Preparation is used to obtain the bacterial strain of WTA derivative
[0126] For the isolation of WTA-PGN, S. aureus T384 strain (RN4220ΔlgtΔoatA double mutant) was prepared according to the method described in the reference [Kazue Takahashi et al., Plos One 8: e69739, 2013].
[0127] Briefly, bacteriophage 80 was used as a medium by transforming the T363 strain with lipoprotein diacylglycerol transferase (lgt) deletion (Nakayama M et al., Journal of Immunology 189:5903-591, 2012) and with erythromycin resistance. And T0003 strain (Park KH et al., Journal of Biological Chemistry 285, 27167-27175, 2010) with O-acetyltransferase (oatA) gene deletion was used to prepare Staphylococcus aureus T384 strain. Due to the deletion of the lgt gene, this strain can be used to isolate WTA, WTA-PGN and PGN without lipoprotein contamination, and due to the absence of an acetyl group at the oxygen at position 6 of the PGN MurNac residue due to the deletion of the oatA ge...
Embodiment 2
[0128] Example 2: Isolation and purification of soluble WTA-PGN
[0129] Insoluble WTA-PGN was obtained from the Δlgt / ΔoatA mutant strain prepared in Example 1, and soluble WTA was isolated from the insoluble WTA-PGN and purified (see figure 2 ).
[0130] Isolation and purification of insoluble WTA-PGN derivatives
[0131] Insoluble WTA-PGN was isolated and purified by modifying the method described in references [Park KH et al., Journal of Biological Chemistry 285, 27167-27175, 2010; Jung DJ et al., Journal of Immunology 2012, 189: 4951-4959, 2012].
[0132] Specifically, the ΔlgtΔoatA mutant strain of Example 1 was cultured in an incubator, and the obtained bacterial cells were collected. Suspend the recovered bacterial cells (10 mL) in 20 mM citrate buffer (pH 4.5; 30 mL), dilute 50 μL of it 400-fold, and adjust it to OD using a spectrophotometer 600nm is 0.8. Then, in order to remove the 20 mM citrate buffer (pH 4.7), the resultant was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for...
Embodiment 3
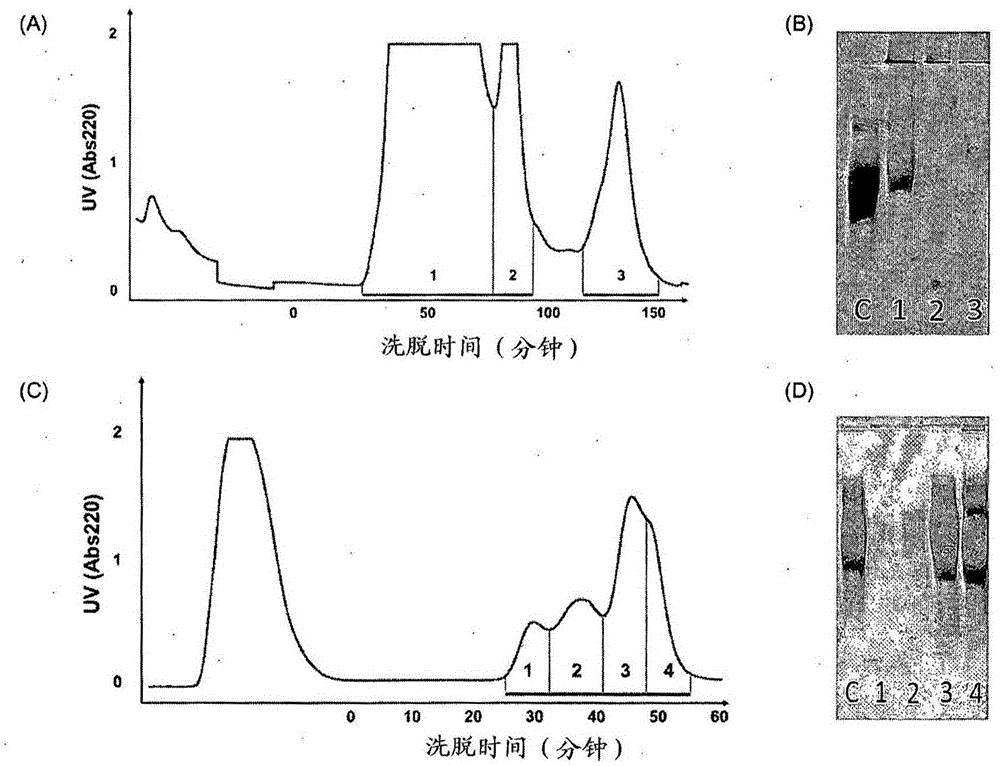
[0151] Example 3: Purification of Soluble WTA
[0152] For purification of WTA, insoluble WTA-PGN (80 mg) was suspended in 20 mM citrate buffer (pH 4.5; 19 mL), and trichloroacetic acid (100 mg / mL; 1 mL) was added to a final concentration of 5 mg / mL. The suspension was reacted in an incubator at 30°C for 12 hours while stirring at 180 rpm, and then centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C. Transfer the supernatant to a 50 mL tube, precipitate with acetone for 1 h, and centrifuge at 15,000 rpm for 25 min at 4 °C. The resulting pellet was transferred to a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube to remove acetone and suspended in 20 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.0; 1 mL).
[0153] Then, the resultant was subjected to HPLC using a Hitrap-Q column. All lines and columns were washed with A buffer which was 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0) and the detector was set to detect and measure absorbance at 220 nm at a sensitivity of 1 and equilibrated. Filter the sample to be loaded with a 0.45 μm filter a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com