Enterobacter cloacae, microbial inoculum containing enterobacter cloacae, use of microbial inoculum and method for passivation of mercury
A technology of Enterobacter cloacae and bacteria agent, applied in the field of bioremediation of heavy metal mercury pollution, to achieve the effect of environmental friendliness, easy operation and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0036] The present invention will be described in detail below through examples and comparative examples, but the present invention is not limited thereby.
[0037] The experimental methods in the following examples and comparative examples are conventional methods in the art unless otherwise specified. The experimental materials used in the following examples and comparative examples were purchased from conventional biochemical reagent stores unless otherwise specified.
[0038] Mercury degradation rate = (Hg before treatment 2+ Content - Hg after treatment 2+ content) / Hg before treatment 2+ Content × 100%.
[0039] The cold atomic absorption mercury analyzer was purchased from Beijing Liman Technology Co., Ltd., model Hydra AAAuto.
Embodiment 1
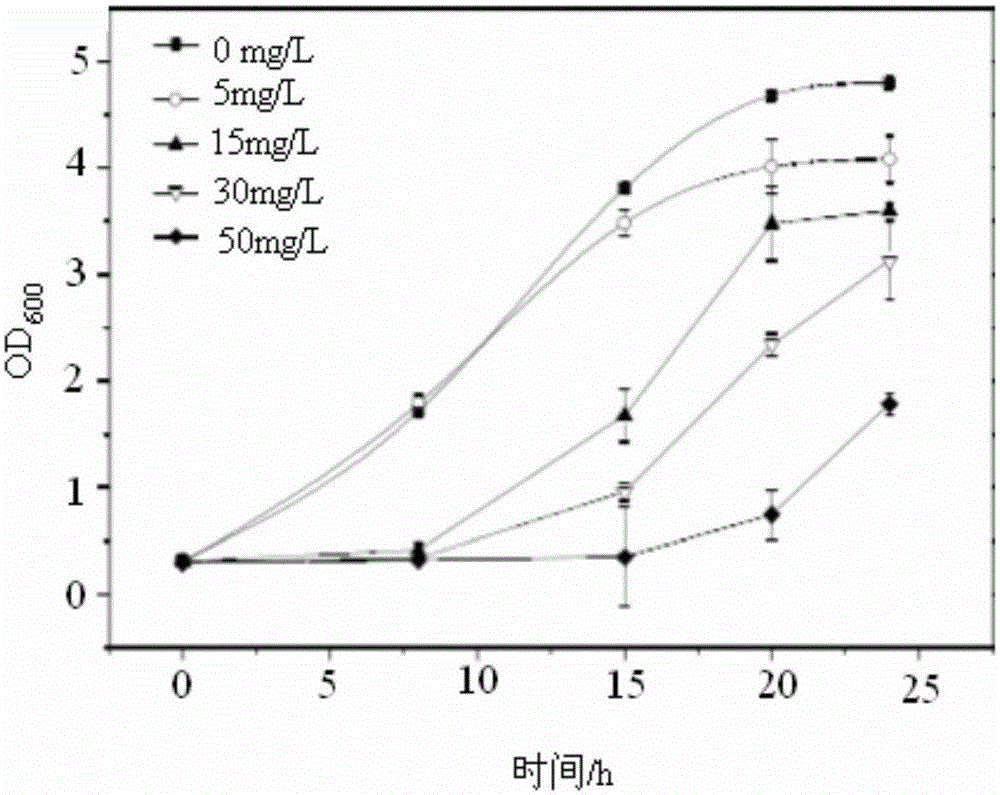
[0043] This example is used to illustrate the tolerance and passivation ability of Enterobacter cloacae with the preservation number of CGMCC NO: 10850 to mercury in the water phase of the present invention
[0044] In 200ml of LB liquid medium, add 1% by volume of the bacterial solution obtained in the preparation example, and add a certain amount of HgCl 2 , so that the final concentrations were 5mg / L, 15mg / L, 30mg / L and 50mg / L respectively. Cultivate in a constant temperature oscillator at 30°C and 170rpm, and take samples at regular intervals to determine the OD of bacteria 600 1. Use a cold atomic absorption mercury analyzer to measure the residual mercury and calculate the mercury degradation rate. Different Hg at 48h 2+ The results of mercury removal rate under the concentration are shown in Table 1, different Hg 2+ The growth status of the strain at the concentration is as follows figure 1 shown. It can be seen from Table 1 that at 48h, Hg 2+ When the concentrati...
Embodiment 2
[0048] This embodiment is used to illustrate that the preservation number of the present invention is the passivation effect of Enterobacter cloacae of CGMCC NO: 10850 on mercury in soil
[0049] Sterilize 100ml of LB liquid medium at 121°C for 15min, then add 1% by volume of the bacterial solution obtained in the preparation example, and incubate at 170rpm, 30±1°C for 12h. The aforementioned bacterial solution was added to 1kg of mercury-contaminated soil (Hg 2+ Content is 25mg / kg), and add sterile deionized water, mix evenly, cultivate for 15 days, and ensure that the water content of the soil is 20% every day. After 15 days, soil samples were taken and dried at 40°C, ground into a uniform powder, and the final residual mercury was determined by a cold atomic absorption mercury analyzer. The results showed that Hg in the soil 2+ From the initial 25mg / kg to 5.47mg / kg, it shows that the strain can be effective on Hg in soil 2+ It produces a strong degradation effect, thereb...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com