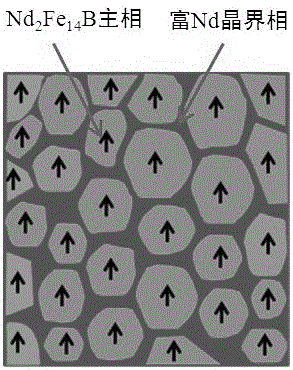
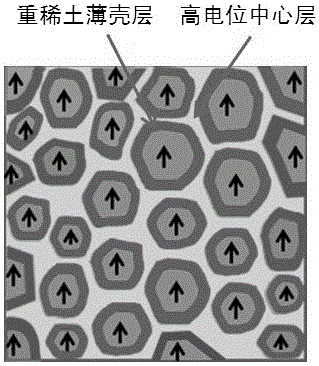
Preparation method of high-performance sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet with multi-layer grain boundary structure and prepared product
A multi-layer structure, high-performance technology, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, inductor/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problems of single grain boundary strengthening effect, failure to realize grain boundary structure, waste of heavy rare earth resources, etc., to achieve The effect of reducing the driving force of electrochemical corrosion, reducing the amount of heavy rare earths, and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] (1) Preparation of NdFeB main phase powder with low rare earth content
[0043] First prepare Nd-Fe-B main phase powder with low rare earth content, the composition is Nd 12.3 Fe bal B 6.1 . NdFeB quick-setting flakes are prepared by smelting and flake rapid cooling. Subsequently, the main phase powder with an average particle size of about 3.8 μm was obtained through hydrogen explosion and jet milling processes.
[0044] (2) Preparation of grain boundary reconstruction alloy
[0045] According to the phase diagram of the alloy and the mixing enthalpy between elements, the alloy composition is designed to reconstruct the grain boundary of heavy rare earth elements with low melting point. It is required that the alloy contains more heavy rare earth elements and has a low melting point, which can be melted and evenly distributed in the main phase grains during heat treatment. around.
[0046] The inventor chooses Dy-Fe binary eutectic point composition Dy 71.5 Fe ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] (1) Preparation of Nd-Fe-B main phase powder with low rare earth content
[0052] First prepare Nd-Fe-B main phase powder with low rare earth content, the composition is Nd 12.3 Fe bal B 6.1 . NdFeB quick-setting flakes are prepared by smelting and flake rapid cooling. Subsequently, the main phase powder with an average particle size of about 3.8 μm was obtained through hydrogen explosion and jet milling processes.
[0053] (2) Preparation of grain boundary reconstruction alloy
[0054] According to the phase diagram of the alloy and the mixing enthalpy between elements, the alloy composition is designed to reconstruct the grain boundary of heavy rare earth elements with low melting point. It is required that the alloy contains more heavy rare earth elements and has a low melting point, which can be melted and evenly distributed in the main phase grains during heat treatment. around.
[0055] The inventor chooses Dy-Fe binary eutectic point composition Tb 71.5 Fe...
Embodiment 3
[0060] (1) Preparation of NdFeB main phase powder with low rare earth content
[0061] First prepare Nd-Fe-B main phase powder with low rare earth content, the composition is Nd 12.3 Fe bal B 6.1 . NdFeB quick-setting flakes are prepared by smelting and flake rapid cooling. Subsequently, the main phase powder with an average particle size of about 3.8 μm was obtained by means of hydrogen explosion and jet milling.
[0062] (2) Preparation of grain boundary reconstruction alloy
[0063] According to the alloy phase diagram and inter-element mixing enthalpy, design the low-melting point heavy rare earth grain boundary to reconstruct the alloy composition. It is required that the alloy contains more heavy rare earth elements and has a low melting point, which can be melted and evenly distributed in the main phase grains during heat treatment. around.
[0064] We chose the Dy-Fe binary eutectic point composition Dy 71.5 Fe 28.5(Atomic percent) As a heavy rare earth grain b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com